Question 1
Expand `32/((x+2)^3)` in ascending power of `x`, up to and including the term in`x^3`.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Expand `1/sqrt(4-2x)` in ascending power of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Evaluate `int_0^(1/2pi)x^2sin x dx`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Expand `sqrt(frac{1+2x}{1-x})` in ascending power of`x`, up to and including the term in `x^3`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Show that `int_0^1(x+2)e^(-2x)dx=5/4-7/(4e^2)`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
(a) Expand `1/sqrt(1-4x)` in ascending power of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`, simplifying the coefficients.
(b) Hence find the coefficient of `x^2` in the expansion of`( 1+2x)/sqrt(4-16x)`.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
When `(1+ax)^-2`, where `a` is a positive constant, is expanded in ascending powers of `x`, the coefficients of`x` and `x^3` are equal.
(a) Find the exact value of `a`.
(b) When `a` has this value, obtain the expansion up to and including the term in `x^2`, simplifying the coefficients.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
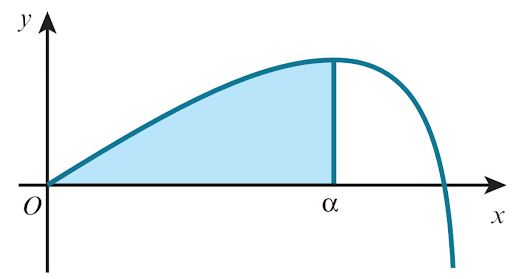
The diagram shows the curve `y=8sinfrac{1}{2}x -tanfrac{1}{2}x` for `0≤x≤π`. The x-coordinate of the maximum point is and the shaded region is enclosed by the curve and the lines`x=α` and `y=0`.
(a) Show that `α=2/3 pi`.
(b) Find the exact value of the area of the shaded region.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Show that `int_0^5 frac{5-3x}{(x+1)(3x+1)}dx=4ln frac{4}{3}` .
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Let `I=int_0^(1/2)frac{4x^2}(sqrt(1-x^2))dx`.
(a) Using the substitution`x=sin theta`, show that `I=int_0^(pi/2)4 theta dθ`.
(b) Hence show that `I=pi/3-sqrt3/2`.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
It is given that `int_1^a xln x dx=30`, where `a>1`. Show that `a=sqrt(frac{119}{2ln a -1})`.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
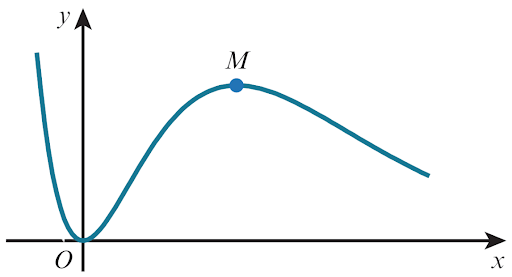
The diagram shows the curve
`y=x^2e^(2-x)` and its maximum point `M`.
(a) Show that the x-coordinate of `M` is `2`.
(b) Find the exact value of `int_0^2x^2e^(2-x)dx`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
Let `f(x)=frac{12+8x-x^2}{(2-x)(4+x^2)}`.
(a) Express `f(x)` in the form `A/(2-x)+(Bx+C)/(4+x^2)`.
(b) Show that `int_0^1f(x)dx=ln frac{25}{2}`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
It is given that `int_1^aln (2x) dx=1`, where `a>1`. Show that `a=1/2`exp `(1+(ln 2)/ a)` to where exp `x` denotes `e^x`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 15
(a) Express `frac{4+12x+x^2}{(3-x)(1+2x)^2}` in partial fraction.
(b) Hence obtain the expansion of `frac{4+12x+x^2}{(3-x)(1+2x)^2}` in ascending powers of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 16
Let `f(x)=frac{x^2-8x+9}{(1-x)(2-x)^2}`.
(a) Express `f(x)` in partial fractions.
(b) Hence obtain the expansion of`f(x)` in ascending powers of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 17
(a) Given that `frac{x^3-2}{x^2(2x-1)}=A+B/x+C/(x^2)+D/(2x-1)`, find the values of the constant A, B, C and D.
(b) Hence show that `int_1^2frac{x^3-2}{x^2(2x-1)}dx=3/2-2ln frac{9}{4} +1/4ln 3`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 18
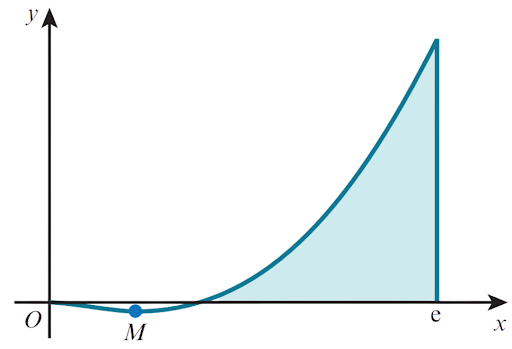
The diagram shows the curve `y=x^2ln x` and its minimum point `M`.
(a) Find the exact values of the coordinates of `M`.
(b) Find the exact value of the area of the shaded region bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line `x=e`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 19
(a) Show that `int_2^4 4xln x dx=56ln 2 -12`.
(b) Use the substitution `u=sin 4x` to find the exact value of `int_0^(1/24 pi)4x dx`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 20
(a) Express `4cos theta +3sin theta` in the form `Rcos (θ-α)`, where `R>0` and `0<α<1/2 pi`. Give the value of correct to `4` decimal places.
(b) Hence solve the equation `4cos theta +3sin theta =2` for `0<θ<2π`.
(c) Hence find `int frac{50}{(4cos theta +3sin theta)^2}dθ`.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Expand `32/((x+2)^3)` in ascending power of `x`, up to and including the term in`x^3`.
`32(x+2)^-3`
`=32(2^-3)(1+x/2)^-3`
`=4{1+(-3)(x/2)+frac{(-3)(-4)}{2!}((x^2)/2)+frac{(-3)(-4)(-5)}{3!}(x/2)^3+…}`
`=4-6x+6x^2-5x^3+…`
Question 2
Expand `1/sqrt(4-2x)` in ascending power of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`.
`(4-2x)^(-1/2)`
`=4^(-1/2)(1-x/2)^(-1/2)`
`=1/2{1+(-1/2)(-x/2)+frac{(-1/2)(-3/2)}{2!}(-x/2)^2+…}`
`=1/2+1/8x+3/64x^2+…`
Question 3
Evaluate `int_0^(1/2pi)x^2sin x dx`.
Using integration by parts:
`int_0^(1/2pi)x^2sin x dx`
`=[x^2(-cos x )]_0^(pi/2)-int_0^(pi/2)-2xcos x dx`
`=0-0+2int_0^(pi/2)xcos x dx`
`=2[xsin x]_ 0^(pi/2)-2int_0^(pi/2)sin x dx`
`=2(pi/2-0)-2[-cos x]_0^(pi/2)`
`=π+2(0-1)`
`=π-2`
Question 4
Expand `sqrt(frac{1+2x}{1-x})` in ascending power of`x`, up to and including the term in `x^3`.
`sqrt(frac{1+2x}{1-x})=(1+2x)^(1/2)(1-x)^(-1/2)`
`(1+2x)^(1/2)`
`=1+(1/2)(2x)+frac{(1/2)(-1/2)}{2!}(2x)^2+frac{(1/2)(-1/2)(-3/2)}{3!}(2x)^3+…`
`=1+x-1/2x^2+1/2x^3-…`
`(1-x)^(-1/2)`
`=1+(-1/2)(-x)+frac{(-1/2)(-3/2)}{2!}(-x)^2+frac{(-1/2)(-3/2)(-5/2)}{3!}(-x)^3+…`
`=1+1/2x+3/8x^2+5/16x^3+…`
`(1+2x)^(1/2)(1-x)^(-1/2)=(1+x-1/2x^2+1/2x^3-…)(1+1/2x+3/8x^2+5/16x^3+… )`
`=1+(1/2+1)x+(3/8-1/2+1/2)x^2+(5/16+1/2+3/8-1/4)x^3+…`
`=1+3/2x+3/8x^2+15/16x^3+…`
Question 5
Show that `int_0^1(x+2)e^(-2x)dx=5/4-7/(4e^2)`.
Using integration by parts:
`int_0^1(x+2)e^(-2x)dx`
`=[-1/2(x+2)e^(-2x)]_0^1-int_0^1-1/2e^(-2x)dx`
`=-3/2e^-2+1+1/2int_0^1e^(-2x)dx`
`=1-3/(2e^2)+1/2[-1/2e^(-2x)]_0^1`
`=1-3/(2e^2)-1/4(e^-2-1)`
`=5/4-7/(4e^2)`
Question 6
(a) Expand `1/sqrt(1-4x)` in ascending power of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`, simplifying the coefficients.
(b) Hence find the coefficient of `x^2` in the expansion of`( 1+2x)/sqrt(4-16x)`.
(a)
`(1-4x)^(-1/2)`
`=1+(-1/2)(-4x)+frac{(-1/2)(-3/2)}{2!}(-4x)^2+…`
`=1+2x+6x^2+…`
(b)
`frac{1+2x}sqrt{4-16x }`
`=frac{1+2x}{sqrt(4)sqrt(1-4x) }`
`=1/2(1+2x)(1-4x)^(-1/2)`
`=1/2(1+2x)(1+2x+6x^2+… )`
Coefficient of `x^2`
`=1/2(6+4)=5`
Question 7
When `(1+ax)^-2`, where `a` is a positive constant, is expanded in ascending powers of `x`, the coefficients of`x` and `x^3` are equal.
(a) Find the exact value of `a`.
(b) When `a` has this value, obtain the expansion up to and including the term in `x^2`, simplifying the coefficients.
(a)
`(1+ax)^-2`
`=1+(-2)(ax)+frac{(-2)(-3)}{2!}(ax)^2+frac{(-2)(-3)(-4)}{3!}(ax^3)+…`
`=1-2ax+3a^2x^2-4a^3x^3+…`
Using the fact that the coefficient of `x` and `x^3` are equal:
`-2a=-4a^3`
`2a(2a^2-1)=0`
`a>0`
`2a^2-1=0`
`a^2=1/2`
`a=sqrt2/2`
(b)
`(1+ax)^-2=1-2ax+3a^2x^2-4a^3x^3+…`
`(1+(sqrt(2x))/2)^-2`
`=1-2(sqrt(2)/2)x+3(sqrt(2)/2)^2x^2-…`
`=1-sqrt2x+3/2x^2-…`
Question 8

The diagram shows the curve `y=8sinfrac{1}{2}x -tanfrac{1}{2}x` for `0≤x≤π`. The x-coordinate of the maximum point is and the shaded region is enclosed by the curve and the lines`x=α` and `y=0`.
(a) Show that `α=2/3 pi`.
(b) Find the exact value of the area of the shaded region.
(a)
`y=8sinfrac{1}{2}x -tanfrac{1}{2}x`
`(dy)/dx=4cosfrac{1}{2}x -1/2 1/2x`
At the maximum point,`x=alpha` and `(dy)/dx=0`:
`4cosfrac{1}{2}alpha -1/2 1/2 alpha =0`
`8cos frac{1}{2} alpha =1/2 alpha`
`8cosfrac{1}{2} alpha =1/(1/2 alpha)`
`1/2 alpha =1/8`
`cos frac{1}{2} alpha =1/2`
`1/2α=pi/3`
`α=(2π)/3`
(b)
`int_0^alpha(8 sinfrac{1}(2}x -tanfrac{1}{2}x) dx`
`=[-16cosfrac{1}{2}x +2ln| cosfrac{1}{2}x|]_ 0^alpha`
`=-16cosfrac{alpha}{2} +2ln| cos frac{1}{2}| +16-2ln 1`
`=-16cos frac{pi}{3} +2ln cos frac{pi}{3} +16`
`=-8+2ln frac{1}{2} +16`
`=8+2ln frac{1}{2}`
Question 9
Show that `int_0^5 frac{5-3x}{(x+1)(3x+1)}dx=4ln frac{4}{3}` .
`frac{5-3x}{(x+1)(3x+1)}=A/(x+1)+B/(3x+1)`
`5-3x=A(3x+1)+B(x+1)`
Letting `x=-1` and `x=-1/3`:
`A=-4` and `B=9`
`frac{5-3x}{(x+1)(3x+1)}=-4/(x+1)+9/(3x+1 )`
`int_0^5frac{5-3x}{(x+1)(3x+1)}dx=int_0^5 (-4/(x+1)+9/(3x+1)) dx`
`=[-4ln |x+1| +3ln| 3x+1|] _0^5`
`=-4ln 6 +3ln 16 +4ln 1 -3ln 1`
`=3ln 16 -4ln 6`
`=3ln 2^4 -4ln 6`
`=4ln 2^3 -4ln 6`
`=4lnfrac{ 8}{6}`
`=4ln frac{4}{3}`
Question 10
Let `I=int_0^(1/2)frac{4x^2}(sqrt(1-x^2))dx`.
(a) Using the substitution`x=sin theta`, show that `I=int_0^(pi/2)4 theta dθ`.
(b) Hence show that `I=pi/3-sqrt3/2`.
(a)
`x=sin theta`
`(dx)/(dθ)=cos theta`
`dx=cos theta dθ`
`x=0→θ=0`
`x=1/2 -> sin theta =1/2→θ= pi/6`
`I= int_0^(pi/6) frac{4 theta}{sqrt( 1- theta)} cos theta dθ`
`I=int_0^(pi/6) frac{4theta}{sqrttheta} cos theta dθ`
`I=int_0^(pi/6)4 theta dθ`
(b)
`I=int_0^(pi/6) 4theta dθ`
`I=int_0^(pi/6)4(1/2-1/2cos 2θ) dθ`
`I=int_0^(pi/6)(2-2cos 2θ) dθ`
`I=[2θ-sin 2θ] _0^(pi/6)`
`I=pi/3-sinfrac{pi}{ 3} -0+0`
`I=pi/3-sqrt3/2`
Question 11
It is given that `int_1^a xln x dx=30`, where `a>1`. Show that `a=sqrt(frac{119}{2ln a -1})`.
`int_1^axln x dx=30`
Using integration by parts:
`[1/2x^2ln x]_ 1^aint_-1^a((1/2x^2)(1/x))dx=30`
`1/2a^2ln a -0int_-1^a1/2xdx=30`
`1/2a^2ln a -[1/4x^2]_1^a=30`
`1/2a^2ln a -1/4a^2=30-1/4`
`2a^2ln a -a^2=120-1`
`a^2(2ln a -1)=119`
`a^2=frac{119}{2ln a -1}`
`a>1`
`a=sqrt(frac{119}{2ln a -1})`
Question 12

The diagram shows the curve
`y=x^2e^(2-x)` and its maximum point `M`.
(a) Show that the x-coordinate of `M` is `2`.
(b) Find the exact value of `int_0^2x^2e^(2-x)dx`.
(a)
`y=x^2e^(2-x)`
Using the product rule:
`(dy)/dx=2xe^(2-x)-x^2e^(2-x)`
`=e^(2-x)(2x-x^2)`
At `M`, `(dy)/dx=0`
`2x-x^2=0`
`x=0`or `x=2`
`x>0`
`x=2`
(b)
Using integration by parts twice:
`int_0^2x^2e^(2-x)dx`
`=[-x^2e^(2-x)]_0^2-int_0^2-2xe^(2-x)dx`
`=-4+0+2int_0^2xe^(2-x)dx`
`=-4+2[-xe^(2-x)]_0^2-2int_0^2-e^(2-x)dx`
`=-4-4+0+2[-e^(2-x)]_0^2`
`=-8+2(-1+e^2)`
`=2e^2-10`
Question 13
Let `f(x)=frac{12+8x-x^2}{(2-x)(4+x^2)}`.
(a) Express `f(x)` in the form `A/(2-x)+(Bx+C)/(4+x^2)`.
(b) Show that `int_0^1f(x)dx=ln frac{25}{2}`.
(a)
`f(x)=frac{12+8x-x^2}{(2-x)(4+x^2)}=A/(2-x)+(Bx+C)/(4+x^2)`
`12+8x-x^2=A(4+x^2)+(Bx+C)(2-x)`
Letting `x=2`and `x=0`
`A=3`and `C=0`
Equating coefficients of `x^2`:
`-1=A-B`
`B=4`
`f(x)=frac{12+8x-x^2}{(2-x)(4+x^2)}=3/(2-x)+(4x)/(4+x^2)`
(b)
`int_0^1f(x)dx=int_0^1(3/(2-x)+(4x)/(4+x^2))dx`
`=[-3ln |2-x| +2ln| 4+x^2|]_ 0^1`
`=-3ln 1 +2ln 5 +3ln 2 -2ln 4`
`=ln frac{(25)(8)}{16}`
`=lnfrac{ 25}{2}`
Question 14
It is given that `int_1^aln (2x) dx=1`, where `a>1`. Show that `a=1/2`exp `(1+(ln 2)/ a)` to where exp `x` denotes `e^x`.
`int_1^a(1)ln (2x) dx=1`
Using integration by parts:
`[xln (2x)]_1^a-int_1^a(x)(1/x)dx=1`
`aln 2a -ln 2 -int_1^a1dx=1`
`aln 2a -ln 2 -a+1=1`
`aln 2a =ln 2 +a`
`ln 2a =1+(ln 2)/ a`
`2a=exp( 1+(ln 2)/ a )`
`a=1/2exp (1+(ln 2)/ a)`
Note: exp `(x)`means `e^x`.
Question 15
(a) Express `frac{4+12x+x^2}{(3-x)(1+2x)^2}` in partial fraction.
(b) Hence obtain the expansion of `frac{4+12x+x^2}{(3-x)(1+2x)^2}` in ascending powers of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`.
(a)
`frac{4+12x+x^2}{(3-x)(1+2x)^2}=A/(3-x)+B/(1+2x)+C/((1+2x)^2)`
`4+12x+x^2=A(1+2x)^2+B(3-x)(1+2x)+C(3-x)`
Letting `x=3`, `x=-1/2`, `x=0`
`A=1, C=-1/2, B=3/2`
`frac{4+12x+x^2}{(3-x)(1+2x)^2}=1/(3-x)+3/(2(1+2x))-1/(2(1+2x)^2)`
(b)
`1/(3-x)+3/(2(1+2x))-1/(2(1+2x)^2)=(3-x)^-1+3/2(1+2x)^-1-1/2(1+2x)^-2 (3-x)^-1`
`=3^-1(1-x/3)^-1`
`=1/3{1+(-1)(-x/3)+frac{(-1)(-2)}{2!}(-x/3)^2+… }`
`=1/3+1/9x+1/27x^2+…`
`3/2(1+2x)^-1`
`=3/2{1+(-1)(2x)+frac{(-1)(-2)}{2!}(2x)^2+… }`
`=3/2-3x+6x^2+…`
`1/2(1+2x)^-2`
`=1/2{1+(-2)(2x)+frac{(-2)(-3)}{2!}(2x)^2+… }`
`=1/2-2x+6x^2-…`
`(3-x)^-1+3/2(1+2x)^-1-1/2(1+2x)^-2`
`=(1/3+1/9x+1/27x^2+… )+(3/2-3x+6x^2+…)-(1/2-2x+6x^2-… )`
`=(1/3+3/2-1/2)+(1/9-3+2)x+(1/27+6-6)x^2+…`
`=4/3-8/9x+1/27x^2+…`
Question 16
Let `f(x)=frac{x^2-8x+9}{(1-x)(2-x)^2}`.
(a) Express `f(x)` in partial fractions.
(b) Hence obtain the expansion of`f(x)` in ascending powers of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`.
(a)
`f(x)=frac{x^2-8x+9}{(1-x)(2-x)^2}=A/(1-x)+B/(2-x)+C/((2-x)^2 )`
`x^2-8x+9=A(2-x)^2+B(1-x)(2-x)+C(1-x)`
Letting `x=1, x=2, x=0`
`A=2, C=3, B=-1`
`f(x)=frac{x^2-8x+9}{(1-x)(2-x)^2}=2/(1-x)-1/(2-x)+3/((2-x)^2 )`
(b)
`f(x)=frac{x^2-8x+9}{(1-x)(2-x)^2}=2/(1-x)-1/(2-x)+3/((2-x)^2 )`
`f(x)=2(1-x)^-1-(2-x)^-1+3(2-x)^-2`
`2(1-x)^-1`
`=2{1+(-1)(-x)+frac{(-1)(-2)}{2!}(-x)^2+… }`
`=2+2x+2x^2+…`
`(2-x)^-1`
`=2^-1(1-x/2)^-1`
`=1/2{1+(-1)(x/2)+frac{(-1)(-2)}{2!}(x/2)^2+… }`
`=1/2+1/4x+1/8x^2+…`
`3(2-x)^-2`
`=3(2)^-2(1-x/2)^-2`
`=3/4{1+(-2)(-x/2)+frac{(-2)(-3)}{2!}(-x/2)^2+… }`
`=3/4+3/4x+9/16x^2+…`
`2(1-x)^-1-(2-x)^-1+3(2-x)^-2`
`=(2+2x+2x^2+… )-(1/2+1/4x+1/8x^2+… )+(3/4+3/4x+9/16x^2+…)` `=(2-1/2+3/4)+(2-1/4+3/4)x+(2-1/8+9/16)x^2+…`
`=9/4+5/2x+39/16x^2+…`
Question 17
(a) Given that `frac{x^3-2}{x^2(2x-1)}=A+B/x+C/(x^2)+D/(2x-1)`, find the values of the constant A, B, C and D.
(b) Hence show that `int_1^2frac{x^3-2}{x^2(2x-1)}dx=3/2-2ln frac{9}{4} +1/4ln 3`.
(a)
`frac{x^3-2}{x^2(2x-1)}=frac{x^3-2}{2x^3-x^2}=A+B/x+C/(x^2)+D/(2x-1)`
`x^3-2=Ax^2(2x-1)+Bx(2x-1)+C(2x-1)+Dx^2`
Letting `x=1/2`and `x=0`
`D=-15/2` and`C=2`
Equating coefficients of `x`:
`0=-B+2C`
`B=4`
Letting `x=1`:
`-1=A+B+C+D`
`A=1/2`
(b)
`frac{x^3-2}{x^2(2x-1)}=1/2+4/x+2/(x^2)-15/(2(2x-1))`
`int_1^2frac{x^3-2}{x^2(2x-1)}dx=int_1^2(1/2+4/x+2/(x^2)-15/(2(2x-1)))dx`
`=int_1^2(1/2+4/x+2x^-2-15/(2(2x-1)))dx`
`=[1/2x+4ln |x| -2x^-1-15/4ln |2x-1|]_1^2`
`=1+4ln 2 -1-15/4ln 3 -1/2-4ln 1 +2+15/4ln 1`
`=3/2+4ln 2 -16/4ln 31 +1/4ln 3`
`=3/2+2lnfrac{ 4}{9} +1/4ln 3`
`=3/2-2ln frac{9}{4} +1/4ln 3`
Question 18

The diagram shows the curve `y=x^2ln x` and its minimum point `M`.
(a) Find the exact values of the coordinates of `M`.
(b) Find the exact value of the area of the shaded region bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line `x=e`.
(a)
`y=x^2ln x`
Using the product rule:
`(dy)/dx=2xln x +x`
At `M`, `(dy)/dx=0`
`x(2ln x +1)=0`
`x>0`at `M`
`x=e^(-1/2)=1/sqrte`
`y=(e^(-1/2))^2ln e^(-1/2) =-1/(2e)`
The coordinate of `M` are `(1/sqrte, -1/(2e))`
(b)
Lower bound of region when `y=0`
`x^2ln x =0`
`x=0` or `x=e`
Using integration by parts for the shaded region:
`int_0^e x^2ln x dx`
`=[1/3x^3ln x]_ 1^e-int_1^e1/3x^2dx`
`=1/3e^3-[1/9x^3]_1^e`
`=1/3e^3-1/9e^3+1/9`
`=2/9e^3+1/9`
Question 19
(a) Show that `int_2^4 4xln x dx=56ln 2 -12`.
(b) Use the substitution `u=sin 4x` to find the exact value of `int_0^(1/24 pi)4x dx`.
(a)
`int_2^4 4xln x dx=[2x^2ln x]_ 2^4-int_2^4 2xdx`
`=32ln 4 -8ln 2 -[x^2]_2^4`
`=64ln 2 -8ln 2 -(16-4)`
`=56ln 2 -12`
(b)
`u=sin 4x`
`(du)/(dx)=4cos 4x dx`
`1-u^2=1-4x =4x`
`1/4(1-u^2)du=4x dx`
`x=0→u=0` and `x=pi/24→u=1/2`
`int_0^(1/24 pi)4x dx`
`=int_0^(1/2)1/4( 1-u^2)du`
`=[1/4u-1/12u^3]_0^(1/2)`
`=11/96`
Question 20
(a) Express `4cos theta +3sin theta` in the form `Rcos (θ-α)`, where `R>0` and `0<α<1/2 pi`. Give the value of correct to `4` decimal places.
(b) Hence solve the equation `4cos theta +3sin theta =2` for `0<θ<2π`.
(c) Hence find `int frac{50}{(4cos theta +3sin theta)^2}dθ`.
(a)
`4cos theta +3sin theta =Rcos theta cos alpha +Rsin theta sin alpha`
`Rsin alpha =3`
`Rcos alpha =4`
`R^2=3^2+4^2=25→R=5`
`tan alpha =3/4→α=0.6435`
`4cos theta +3sin theta =5cos (θ-0.6435)`
(b)
Using the result from part a:
`5cos (θ-0.6435) =2`
`cos (θ-0.6435) =2/5`
`θ-0.6435=1.1592…`or `θ-0.6435=5.1239…`
`θ=1.80`or `θ=5.77`
(c)
Using the result from part a:
`int frac{50}{(4cos theta +3sin theta )^2}dθ`
`=int frac{50}{25(θ-0.6435)} dθ`
`=int 2(θ-0.6435) dθ`
`=2tan (θ-0.6435) +C`
Question 1
Expand `32/((x+2)^3)` in ascending power of `x`, up to and including the term in`x^3`.
Question 2
Expand `1/sqrt(4-2x)` in ascending power of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`.
Question 3
Evaluate `int_0^(1/2pi)x^2sin x dx`.
Question 4
Expand `sqrt(frac{1+2x}{1-x})` in ascending power of`x`, up to and including the term in `x^3`.
Question 5
Show that `int_0^1(x+2)e^(-2x)dx=5/4-7/(4e^2)`.
Question 6
(a) Expand `1/sqrt(1-4x)` in ascending power of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`, simplifying the coefficients.
(b) Hence find the coefficient of `x^2` in the expansion of`( 1+2x)/sqrt(4-16x)`.
Question 7
When `(1+ax)^-2`, where `a` is a positive constant, is expanded in ascending powers of `x`, the coefficients of`x` and `x^3` are equal.
(a) Find the exact value of `a`.
(b) When `a` has this value, obtain the expansion up to and including the term in `x^2`, simplifying the coefficients.
Question 8

The diagram shows the curve `y=8sinfrac{1}{2}x -tanfrac{1}{2}x` for `0≤x≤π`. The x-coordinate of the maximum point is and the shaded region is enclosed by the curve and the lines`x=α` and `y=0`.
(a) Show that `α=2/3 pi`.
(b) Find the exact value of the area of the shaded region.
Question 9
Show that `int_0^5 frac{5-3x}{(x+1)(3x+1)}dx=4ln frac{4}{3}` .
Question 10
Let `I=int_0^(1/2)frac{4x^2}(sqrt(1-x^2))dx`.
(a) Using the substitution`x=sin theta`, show that `I=int_0^(pi/2)4 theta dθ`.
(b) Hence show that `I=pi/3-sqrt3/2`.
Question 11
It is given that `int_1^a xln x dx=30`, where `a>1`. Show that `a=sqrt(frac{119}{2ln a -1})`.
Question 12

The diagram shows the curve
`y=x^2e^(2-x)` and its maximum point `M`.
(a) Show that the x-coordinate of `M` is `2`.
(b) Find the exact value of `int_0^2x^2e^(2-x)dx`.
Question 13
Let `f(x)=frac{12+8x-x^2}{(2-x)(4+x^2)}`.
(a) Express `f(x)` in the form `A/(2-x)+(Bx+C)/(4+x^2)`.
(b) Show that `int_0^1f(x)dx=ln frac{25}{2}`.
Question 14
It is given that `int_1^aln (2x) dx=1`, where `a>1`. Show that `a=1/2`exp `(1+(ln 2)/ a)` to where exp `x` denotes `e^x`.
Question 15
(a) Express `frac{4+12x+x^2}{(3-x)(1+2x)^2}` in partial fraction.
(b) Hence obtain the expansion of `frac{4+12x+x^2}{(3-x)(1+2x)^2}` in ascending powers of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`.
Question 16
Let `f(x)=frac{x^2-8x+9}{(1-x)(2-x)^2}`.
(a) Express `f(x)` in partial fractions.
(b) Hence obtain the expansion of`f(x)` in ascending powers of `x`, up to and including the term in `x^2`.
Question 17
(a) Given that `frac{x^3-2}{x^2(2x-1)}=A+B/x+C/(x^2)+D/(2x-1)`, find the values of the constant A, B, C and D.
(b) Hence show that `int_1^2frac{x^3-2}{x^2(2x-1)}dx=3/2-2ln frac{9}{4} +1/4ln 3`.
Question 18

The diagram shows the curve `y=x^2ln x` and its minimum point `M`.
(a) Find the exact values of the coordinates of `M`.
(b) Find the exact value of the area of the shaded region bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line `x=e`.
Question 19
(a) Show that `int_2^4 4xln x dx=56ln 2 -12`.
(b) Use the substitution `u=sin 4x` to find the exact value of `int_0^(1/24 pi)4x dx`.
Question 20
(a) Express `4cos theta +3sin theta` in the form `Rcos (θ-α)`, where `R>0` and `0<α<1/2 pi`. Give the value of correct to `4` decimal places.
(b) Hence solve the equation `4cos theta +3sin theta =2` for `0<θ<2π`.
(c) Hence find `int frac{50}{(4cos theta +3sin theta)^2}dθ`.