Question 1
A mass m1 travelling with speed u1 collides with a mass m2 travelling with speed u2 in the same direction. After the collision, mass m1 has speed v1 and mass m2 has speed v2 in the same direction. The collision is perfectly elastic. 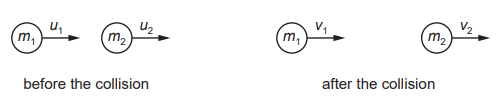
Which equation is not correct
A. `m_1u_1^2-m_1v_1^2=m_2v_2^2-m_2u_2^2`.
B. `v_2+u_2=v_1+u_1`.
C. `m_1(u_1-v_1)=m_2(u_2-v_2)`.
D. `m_1(u_1-v_1)^2=m_2(u_2-v_2)^2`.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Two frictionless trolleys are moving towards each other along the same horizontal straight line. Their masses and velocities are shown.
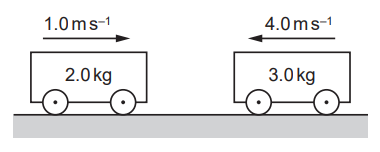
The trolleys collide and stick together. What is the velocity of the trolleys after the collision?
A. 2.0 m.s–1 to the left.
B. 2.0 m.s–1 to the right.
C. 2.8 m.s–1 to the left.
D. 2.8 m.s–1 to the right.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
A glider of mass 0.2 kg is moving at 3.6 m.s-1 on an air track towards a second glider of mass 0.25 kg, which is moving at 2 m.s-1 in the opposite direction. When the two gliders collide they stick together.
a. Calculate their joint velocity after the collision.
b. Show that the collision is inelastic.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Two balls, each of mass 0.50 kg, collide as shown in figure. Show that their total momentum before the collision is equal to their total momentum after the collision.
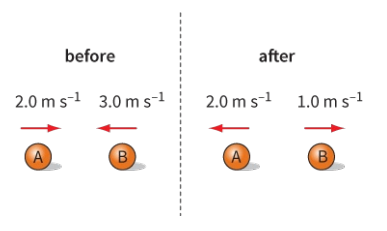
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
A trolley of mass 1 kg is moving at 2 m.s-1. It collides with a stationary trolley of mass 2 kg. This second trolley moves off at 1.2 m.s-1.
a. Draw ‘before’ and ‘after’ diagrams to show the situation.
b. Use the principle of conservation of momentum to calculate the speed of the first trolley after the collision. In what direction does it move?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
State the principle of conservation of momentum.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
A ball of mass 0.20 kg, travelling in the x-direction at a speed of 0.50 m.s–1, collides with a ball of mass 0.30 kg travelling in the y-direction at a speed of 0.40 m.s–1. The two balls stick together after the collision, travelling at an angle θ to the x-direction.
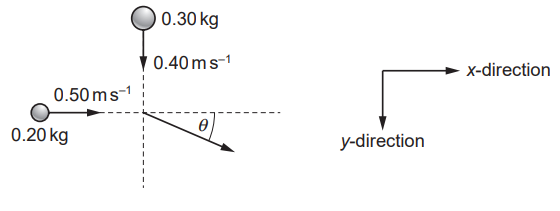
What is the value of θ?
A. 39°.
B. 40°.
C. 50°.
D. 51°.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which quantities are conserved in an inelastic collision?
| Kinetic energy | Total energy | Linear momentum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | conserved | not conserved | conserved |
| B | conserved | not conserved | not conserved |
| C | not conserved | conserved | conserved |
| D | not conserved | conserved | not conserved |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
A marble of mass 100 g is moving at a speed of 0.40 m.s-1 in the x-direction.
a. Calculate the marble’s momentum.
The marble strikes a second, identical marble. Each moves off at an angle of 45° to the x-direction.
b. Use the principle of conservation of momentum to determine the speed of each marble after the collision.
c. Show that kinetic energy is conserved in this collision.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
A stationary firework explodes into three pieces. The masses and the velocities of the three pieces immediately after the explosion are shown.
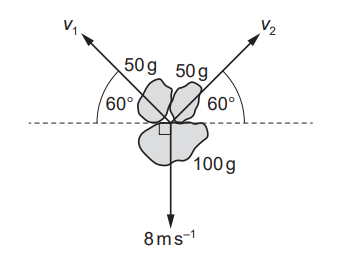
What are speed `v_1` and speed `v_2`?
| `v_1"/"" m"."s"^-1` | `v_2"/"" m"."s"^-1` | |
|---|---|---|
| A | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| B | 9.2 | 9.2 |
| C | 14 | 14 |
| D | 16 | 16 |
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
A mass m1 travelling with speed u1 collides with a mass m2 travelling with speed u2 in the same direction. After the collision, mass m1 has speed v1 and mass m2 has speed v2 in the same direction. The collision is perfectly elastic. 
Which equation is not correct
A. `m_1u_1^2-m_1v_1^2=m_2v_2^2-m_2u_2^2`.
B. `v_2+u_2=v_1+u_1`.
C. `m_1(u_1-v_1)=m_2(u_2-v_2)`.
D. `m_1(u_1-v_1)^2=m_2(u_2-v_2)^2`.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: The equation correctly represents the conservation of kinetic energy in an elastic collision, as the difference in kinetic energy before and after the collision must be zero.
B. Incorrect: The equation is valid under the assumption of conservation of momentum for a perfectly elastic collision, where the velocities of the two masses are related.
C. Incorrect: The equation expresses the conservation of momentum in a different form. It is derived from the law of conservation of momentum for elastic collisions.
D. Correct: The equation does not represent the conservation of kinetic energy or momentum.
Question 2
Two frictionless trolleys are moving towards each other along the same horizontal straight line. Their masses and velocities are shown.

The trolleys collide and stick together. What is the velocity of the trolleys after the collision?
A. 2.0 m.s–1 to the left.
B. 2.0 m.s–1 to the right.
C. 2.8 m.s–1 to the left.
D. 2.8 m.s–1 to the right.
Answer: A
The total momentum before the collision must equal the total momentum after the collision. Since the trolleys stick together after the collision, they will have a combined velocity `v`.
`m_1u_1+m_2u_2=(m_1+m_2)v`.
`2xx1+3xx(-4)=(2+3)v`.
`v=-2" m"."s"^-1`.
The negative sign indicates that the velocity is in the direction of the first trolley, which is to the left.
Question 3
A glider of mass 0.2 kg is moving at 3.6 m.s-1 on an air track towards a second glider of mass 0.25 kg, which is moving at 2 m.s-1 in the opposite direction. When the two gliders collide they stick together.
a. Calculate their joint velocity after the collision.
b. Show that the collision is inelastic.
a.
`"Momentum before the collision"=(0.2xx3.6)+(0.25xx(-2))=0.22" kg"."m"."s"^-1`.
`"Momentum after the collision"=(0.2+0.25)v=0.45v`.
Where `v` is the velocity of the two gliders after the collision.a
`v=0.49 " m"."s"^-1`.
b.
`"Kinetic energy before the collision"=(1/2xx0.2xx3.6^2)+(1/2xx0.25xx2^2)="1.8 J"`
`"Kinetic energy after the collision"=1/2xx0.45xx0.49^2="0.054 J"`.
The kinetic energy after the collision is less than the kinetic energy before the collision, therefore the collision is inelastic.
Question 4
Two balls, each of mass 0.50 kg, collide as shown in figure. Show that their total momentum before the collision is equal to their total momentum after the collision.

Momentum before the collision:
`m_Au_A+m_Bu_B=(0.5xx2)+(0.5xx(-3))=-0.5 " kg"."m"."s"^-1`
Momentum after the collision:
`m_Av_A+m_Bv_B=(0.5xx(-2))+(0.5xx1)=-0.5 " kg"."m"."s"^-1`
Question 5
A trolley of mass 1 kg is moving at 2 m.s-1. It collides with a stationary trolley of mass 2 kg. This second trolley moves off at 1.2 m.s-1.
a. Draw ‘before’ and ‘after’ diagrams to show the situation.
b. Use the principle of conservation of momentum to calculate the speed of the first trolley after the collision. In what direction does it move?
a.
 b.
b.
Conservation of momentum:
`"Momentum before the collision "=" momentum after the collision".`
`m_Au_A+m_Bu_B=m_Av_A+m_Bv_B`.
`v_A=(m_Au_A+m_Bu_B-m_Bv_B)/m_A=((1xx2)+(2xx0)-(2xx1.2))/1=-0.4" m"."s"^-1`
The minus sign indicates that the first trolley reverses direction.
Question 6
State the principle of conservation of momentum.
In an isolated system, where no external forces are acting, the total momentum before a collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision.
Question 7
A ball of mass 0.20 kg, travelling in the x-direction at a speed of 0.50 m.s–1, collides with a ball of mass 0.30 kg travelling in the y-direction at a speed of 0.40 m.s–1. The two balls stick together after the collision, travelling at an angle θ to the x-direction.

What is the value of θ?
A. 39°.
B. 40°.
C. 50°.
D. 51°.
Answer: C
Momentum is conserved in both the x and y directions.
In the x-direction:
`m_1u_1+m_2u_2=(m_1+m_2)v_x`.
`v_x=(0.2xx0.5+0xx0.3)/(0.2+0.3)=0.2 " m"."s"^-1`.
In the y-direction:
`m_1u_1+m_2u_2=(m_1+m_2)v_y`.
`v_y=(0.3xx0.4)/(0.2+0.3)=0.24" m"."s"^-1`.
The magnitude of the resultant velocity:
`v=sqrt(v_x^2+v_y^2)=sqrt(0.2^2+0.24^2)=0.312" m"."s"^-1`.
`tantheta=v_y/v_x=0.24/0.2=1.2`.
`theta=tan^-1(1.2)~~50^o`.
Question 8
Which quantities are conserved in an inelastic collision?
| Kinetic energy | Total energy | Linear momentum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | conserved | not conserved | conserved |
| B | conserved | not conserved | not conserved |
| C | not conserved | conserved | conserved |
| D | not conserved | conserved | not conserved |
Answer: C
In an inelastic collision:
Kinetic energy is not conserved because some of the kinetic energy is converted into other forms of energy like heat or sound.
Total energy is conserved because energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Linear momentum is conserved in an inelastic collision, assuming no external forces act on the system (momentum is always conserved in isolated systems).
Question 9
A marble of mass 100 g is moving at a speed of 0.40 m.s-1 in the x-direction.
a. Calculate the marble’s momentum.
The marble strikes a second, identical marble. Each moves off at an angle of 45° to the x-direction.
b. Use the principle of conservation of momentum to determine the speed of each marble after the collision.
c. Show that kinetic energy is conserved in this collision.
a. `"Momentum"=0.1xx0.4=0.04 " " kg.m.s^-1`.
b. For each marble, component of momentum in x-direction = half of original momentum = 0.02 kg.m.s-1.
So, `"momentum of one marble"=(0.02/cos45^o) =0.0283" kg"."m"."s"^-1`.
And `"velocity"=0.0283/10=0.283 " m"."s"^-1`.
c. `"KE before the collision"=1/2xx0.1xx0.4^2="0.008 J"`.
`"KE after the collision (both marbles)"=2xx1/2xxmxxv^2=0.1xx0.283^2="0.008 J"`
Hence, kinetic energy is conserved in this collision.
Question 10
A stationary firework explodes into three pieces. The masses and the velocities of the three pieces immediately after the explosion are shown.

What are speed `v_1` and speed `v_2`?
| `v_1"/"" m"."s"^-1` | `v_2"/"" m"."s"^-1` | |
|---|---|---|
| A | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| B | 9.2 | 9.2 |
| C | 14 | 14 |
| D | 16 | 16 |
Answer: B
In the x-direction:
`0.05xxv_2cos60^o-0.05xxv_1cos60^o=0`.
`v_1=v_2`.
In the y-direction:
`0.05xxv_1sin(60^o)+0.05xxv_2sin(60^o)-8xx0.1=0`.
`0.05xxv_1sin(60^o)+0.05xxv_1sin(60^o)-8xx0.1=0`.
`v_1=9.2" m"."s"^-1`.
Question 1
A mass m1 travelling with speed u1 collides with a mass m2 travelling with speed u2 in the same direction. After the collision, mass m1 has speed v1 and mass m2 has speed v2 in the same direction. The collision is perfectly elastic. 
Which equation is not correct
A. `m_1u_1^2-m_1v_1^2=m_2v_2^2-m_2u_2^2`.
B. `v_2+u_2=v_1+u_1`.
C. `m_1(u_1-v_1)=m_2(u_2-v_2)`.
D. `m_1(u_1-v_1)^2=m_2(u_2-v_2)^2`.
Question 2
Two frictionless trolleys are moving towards each other along the same horizontal straight line. Their masses and velocities are shown.

The trolleys collide and stick together. What is the velocity of the trolleys after the collision?
A. 2.0 m.s–1 to the left.
B. 2.0 m.s–1 to the right.
C. 2.8 m.s–1 to the left.
D. 2.8 m.s–1 to the right.
Question 3
A glider of mass 0.2 kg is moving at 3.6 m.s-1 on an air track towards a second glider of mass 0.25 kg, which is moving at 2 m.s-1 in the opposite direction. When the two gliders collide they stick together.
a. Calculate their joint velocity after the collision.
b. Show that the collision is inelastic.
Question 4
Two balls, each of mass 0.50 kg, collide as shown in figure. Show that their total momentum before the collision is equal to their total momentum after the collision.

Question 5
A trolley of mass 1 kg is moving at 2 m.s-1. It collides with a stationary trolley of mass 2 kg. This second trolley moves off at 1.2 m.s-1.
a. Draw ‘before’ and ‘after’ diagrams to show the situation.
b. Use the principle of conservation of momentum to calculate the speed of the first trolley after the collision. In what direction does it move?
Question 6
State the principle of conservation of momentum.
Question 7
A ball of mass 0.20 kg, travelling in the x-direction at a speed of 0.50 m.s–1, collides with a ball of mass 0.30 kg travelling in the y-direction at a speed of 0.40 m.s–1. The two balls stick together after the collision, travelling at an angle θ to the x-direction.

What is the value of θ?
A. 39°.
B. 40°.
C. 50°.
D. 51°.
Question 8
Which quantities are conserved in an inelastic collision?
| Kinetic energy | Total energy | Linear momentum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | conserved | not conserved | conserved |
| B | conserved | not conserved | not conserved |
| C | not conserved | conserved | conserved |
| D | not conserved | conserved | not conserved |
Question 9
A marble of mass 100 g is moving at a speed of 0.40 m.s-1 in the x-direction.
a. Calculate the marble’s momentum.
The marble strikes a second, identical marble. Each moves off at an angle of 45° to the x-direction.
b. Use the principle of conservation of momentum to determine the speed of each marble after the collision.
c. Show that kinetic energy is conserved in this collision.
Question 10
A stationary firework explodes into three pieces. The masses and the velocities of the three pieces immediately after the explosion are shown.

What are speed `v_1` and speed `v_2`?
| `v_1"/"" m"."s"^-1` | `v_2"/"" m"."s"^-1` | |
|---|---|---|
| A | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| B | 9.2 | 9.2 |
| C | 14 | 14 |
| D | 16 | 16 |