Question 1
A beaker has mass of 48 g. When 120 cm3 of copper sulfate solution are poured into the beaker it is found to have a total mass of 174 g. Calculate the density of the copper sulfate solution.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
A U-shaped glass tube contains liquid of density 2000 kg.m–3, as shown.
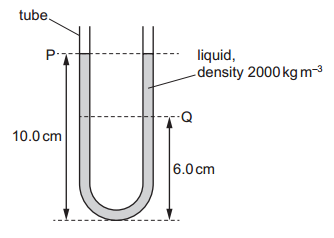
What is the difference in pressure due to the liquid between levels P and Q?
A. 780 Pa.
B. 1200 Pa.
C. 1600 Pa.
D. 2000 Pa.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which expression for pressure is correct?
A. Force per unit area.
B. Force per unit volume.
C. Mass per unit area.
D. Mass per unit volume.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
A piece of wax is attached to a newton-meter. In air, the reading on the newton meter is 0.27 N and when submerged in water of density 1000 kg.m-3 the reading is 0.16 N. Calculate:
a. The upthrust on the wax when in water.
b. The volume of the wax.
c. The reading on the newton-meter when the wax is submerged in a liquid of density 800 kg.m-3.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
A cube of side 0.20 m floats in water with 0.15 m below the surface of the water. The density of water is 1000 kg.m-3. Calculate the pressure due to the water that acts upwards on the bottom surface of the cube and the force upwards on the cube caused by this pressure. (This force is the upthrust on the cube.)
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A volume of 1.5 m3 of water is mixed with 0.50 m3 of alcohol. The density of water is 1000 kg.m–3 and the density of alcohol is 800 kg.m–3. The volume of the mixture is 2.0 m3.
What is the density of the mixture?
A. 850 kg.m–3.
B. 900 kg.m–3.
C. 940 kg.m–3.
D. 950 kg.m–3.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
An object is falling at a constant speed through a viscous liquid. FU is the upthrust on the object due to the liquid. WL is the weight of the liquid displaced by the object. WO is the weight of the object. Which equation must be correct?
A. FU = WL.
B. FU = WO – WL.
C. FU = WO.
D. FU = WO + WL.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
A rectangular block of mass 150 kg has sides of 60 cm, 90 cm and 12 cm (figure). What is the minimum pressure that the block exerts on the ground when it is resting on one of its sides?
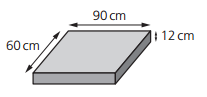
A. 0.27 kPa.
B. 0.28 kPa.
C. 1.4 kPa.
D. 2.7 kPa.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
A solid sphere of diameter 30.0 cm is fully immersed near the surface of the sea. The sphere is released from rest and moves vertically downwards through the seawater. The weight of the sphere is 1100 N. An upthrust U acts on the sphere. The upthrust remains constant as the sphere moves downwards. The density of the seawater is 1030 kg.m–3.
a. Calculate the density of the material of the sphere.
b. Briefly explain the origin of the upthrust acting on the sphere.
c. Show that the upthrust U is 140 N.
d. Calculate the initial acceleration of the sphere.
e. The viscous (drag) force D acting on the sphere is given by `D = 1/2 C rho pi r^2 v^2`
Where r is the radius of the sphere and v is its speed. ρ is the density of the seawater. The constant C has no units and is equal to 0.50.
Determine the constant (terminal) speed reached by the sphere.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
A boy stands on a platform of area 0.050 m2 and a manometer measures the pressure created in a flexible plastic container by the weight W of the boy, as shown.
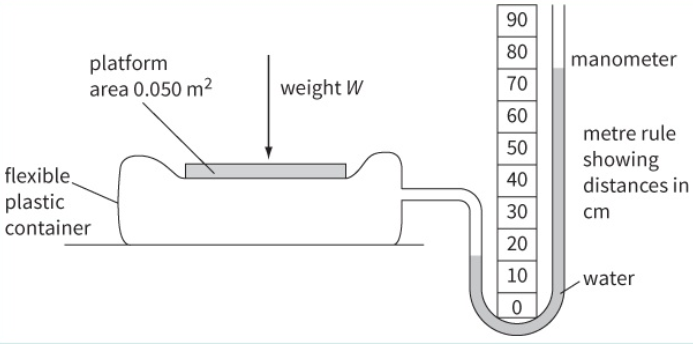
The density of water is 1000 kg.m-3. Determine:
a. The pressure difference between the inside of the plastic container and the atmosphere outside.
b. The weight W of the boy.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
A beaker has mass of 48 g. When 120 cm3 of copper sulfate solution are poured into the beaker it is found to have a total mass of 174 g. Calculate the density of the copper sulfate solution.
`"Mass of copper sulfate solution" = 174 - 48 = "126 g"`
`rho = m / v = 126 / 120 = 1.05 " g"."cm"^-3`
Question 2
A U-shaped glass tube contains liquid of density 2000 kg.m–3, as shown.

What is the difference in pressure due to the liquid between levels P and Q?
A. 780 Pa.
B. 1200 Pa.
C. 1600 Pa.
D. 2000 Pa.
Answer: A
`Delta P = rhoxx g xx Delta h = 2000 xx 9.8 xx (0.1-0.06) ~~ "780 Pa"`
In formula: `P = rho g h`.
is the depth below the liquid surface. It is not measured from the bottom of the container.
Question 3
Which expression for pressure is correct?
A. Force per unit area.
B. Force per unit volume.
C. Mass per unit area.
D. Mass per unit volume.
Answer: A
This is the definition of pressure:
`"Pressure" = "Force" / "Area" " " ("Unit": " N"."m"^-2 or "Pascal")`
It tells us how much force is acting perpendicular to a surface, per unit area.
Question 4
A piece of wax is attached to a newton-meter. In air, the reading on the newton meter is 0.27 N and when submerged in water of density 1000 kg.m-3 the reading is 0.16 N. Calculate:
a. The upthrust on the wax when in water.
b. The volume of the wax.
c. The reading on the newton-meter when the wax is submerged in a liquid of density 800 kg.m-3.
a. The upthrust is the difference in the reading in air and in water:
`U = W_(air) - W_("in water") = "0.27 N" - "0.16 N" = "0.11 N"`
b.
Use Archimedes' principle:
`U = "weight of water displaced" = m_("water") xx g => m_("water") = U / g = 0.11 / 9.81 ~~ "0.0112 kg"`
The volume: `V = m_("water")/ rho_(water) = 0.0112 / 1000 = 1.12 xx 10^-5 " m"^3`
c.
The upthrust in the new liquid:
`U = rho_(liquid) xx g xx V = 800 xx 9.81 xx 1.12 xx 10^-5 ~~ "0.088 N"`
The new reading: `W_(air) - U = 0.27 - 0.088 = "0.18 N"`
Question 5
A cube of side 0.20 m floats in water with 0.15 m below the surface of the water. The density of water is 1000 kg.m-3. Calculate the pressure due to the water that acts upwards on the bottom surface of the cube and the force upwards on the cube caused by this pressure. (This force is the upthrust on the cube.)
Pressure due to water: `p = rho xx g xx h = 1000 xx 9.81 xx 0.15 = "1470 Pa"`
`"Area of base of cube" = 0.2 xx 0.2 = 0.04 " m"^2`
`"Force caused by the pressure" = pressure xx area = 1470 xx 0.04 = "58.8 N"`
Question 6
A volume of 1.5 m3 of water is mixed with 0.50 m3 of alcohol. The density of water is 1000 kg.m–3 and the density of alcohol is 800 kg.m–3. The volume of the mixture is 2.0 m3.
What is the density of the mixture?
A. 850 kg.m–3.
B. 900 kg.m–3.
C. 940 kg.m–3.
D. 950 kg.m–3.
Answer: D
`"Mass of water" = rho xx V = 1000 xx 1.5 = 1500 " " kg`
`"Mass of alcohol" = 800 xx 0.5 = 400 " " kg`
`"Total mass" = 1500 + 400 = 1900 " " kg`
`"Density of mixture" = "Total mass" / "Total volume" = 1900 / 2.0 = 950 " " kg.m^3`
Question 7
An object is falling at a constant speed through a viscous liquid. FU is the upthrust on the object due to the liquid. WL is the weight of the liquid displaced by the object. WO is the weight of the object. Which equation must be correct?
A. FU = WL.
B. FU = WO – WL.
C. FU = WO.
D. FU = WO + WL.
Answer: A
A. Correct: This is directly based on Archimedes’ Principle, which states: The upthrust (buoyant force) FU on an object submerged in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object, WL.
Question 8
A rectangular block of mass 150 kg has sides of 60 cm, 90 cm and 12 cm (figure). What is the minimum pressure that the block exerts on the ground when it is resting on one of its sides?

A. 0.27 kPa.
B. 0.28 kPa.
C. 1.4 kPa.
D. 2.7 kPa.
Answer: D
Largest face area (to minimize pressure):
`A = "90 cm" xx "60 cm" = 5400 " " cm^2 = 0.54 " m"^2`
The weight (force):
`F = m g = 150 xx 9.8 = "1470 N"`
Minimum pressure:
`P = 1470 / 0.54 ~~ "2722 Pa" = "2.7 kPa"`
Question 9
A solid sphere of diameter 30.0 cm is fully immersed near the surface of the sea. The sphere is released from rest and moves vertically downwards through the seawater. The weight of the sphere is 1100 N. An upthrust U acts on the sphere. The upthrust remains constant as the sphere moves downwards. The density of the seawater is 1030 kg.m–3.
a. Calculate the density of the material of the sphere.
b. Briefly explain the origin of the upthrust acting on the sphere.
c. Show that the upthrust U is 140 N.
d. Calculate the initial acceleration of the sphere.
e. The viscous (drag) force D acting on the sphere is given by `D = 1/2 C rho pi r^2 v^2`
Where r is the radius of the sphere and v is its speed. ρ is the density of the seawater. The constant C has no units and is equal to 0.50.
Determine the constant (terminal) speed reached by the sphere.
a. Mass: `m = W / g = 1100 / 9.8 ~~ "112.24 kg"`
Volume of sphere: `V = (4/3) pi r^3 = (4/3) pi (0.15)^3 ~~ 0.01414 " m"^3`
Density of sphere: `rho = m / V ~~ 112.24 / 0.01414 ~~ 7939.7 " kg"."m"^3`
b. The upthrust (buoyant force) arises due to the pressure difference in the fluid between the top and bottom of the submerged sphere. The fluid exerts a greater pressure on the bottom than on the top, resulting in a net upward force.
c. `U = rho_(fluid) xx g xx V = 1030 xx 9.8 xx 0.01414 ~~ "140 N"`
d. Net force: `F_"net" = W - U = 1100 - 140 = "960 N"`
Acceleration: `a = F_("net")/m = 960 / 112.24 ~~ 8.55 " m"."s"^2`
e. At terminal speed, drag force = weight `-` upthrust = 960 N
`v = sqrt((2D) / (C rho pi r^2)) = sqrt(960 / (0.5 xx 1030 xx pi xx (0.15)^2)) ~~ 7.26 " m"."s"^-1`
Question 10
A boy stands on a platform of area 0.050 m2 and a manometer measures the pressure created in a flexible plastic container by the weight W of the boy, as shown.

The density of water is 1000 kg.m-3. Determine:
a. The pressure difference between the inside of the plastic container and the atmosphere outside.
b. The weight W of the boy.
a.
From the manometer, we observe:
`"Height difference" " " "h" = "70 cm" - "10 cm" = "60 cm" = "0.6 m"`
Pressure difference is:
`Delta P = rho xxgxx h= 1000 xx 9.81 xx 0.60 = "5886 Pa"`
b.
`"Pressure" = "Force" / "Area" => "Force" = "Pressure" xx "Area"`
The weight of the boy: `W = 5886 xx 0.050 = "294.3 N"`
Question 1
A beaker has mass of 48 g. When 120 cm3 of copper sulfate solution are poured into the beaker it is found to have a total mass of 174 g. Calculate the density of the copper sulfate solution.
Question 2
A U-shaped glass tube contains liquid of density 2000 kg.m–3, as shown.

What is the difference in pressure due to the liquid between levels P and Q?
A. 780 Pa.
B. 1200 Pa.
C. 1600 Pa.
D. 2000 Pa.
Question 3
Which expression for pressure is correct?
A. Force per unit area.
B. Force per unit volume.
C. Mass per unit area.
D. Mass per unit volume.
Question 4
A piece of wax is attached to a newton-meter. In air, the reading on the newton meter is 0.27 N and when submerged in water of density 1000 kg.m-3 the reading is 0.16 N. Calculate:
a. The upthrust on the wax when in water.
b. The volume of the wax.
c. The reading on the newton-meter when the wax is submerged in a liquid of density 800 kg.m-3.
Question 5
A cube of side 0.20 m floats in water with 0.15 m below the surface of the water. The density of water is 1000 kg.m-3. Calculate the pressure due to the water that acts upwards on the bottom surface of the cube and the force upwards on the cube caused by this pressure. (This force is the upthrust on the cube.)
Question 6
A volume of 1.5 m3 of water is mixed with 0.50 m3 of alcohol. The density of water is 1000 kg.m–3 and the density of alcohol is 800 kg.m–3. The volume of the mixture is 2.0 m3.
What is the density of the mixture?
A. 850 kg.m–3.
B. 900 kg.m–3.
C. 940 kg.m–3.
D. 950 kg.m–3.
Question 7
An object is falling at a constant speed through a viscous liquid. FU is the upthrust on the object due to the liquid. WL is the weight of the liquid displaced by the object. WO is the weight of the object. Which equation must be correct?
A. FU = WL.
B. FU = WO – WL.
C. FU = WO.
D. FU = WO + WL.
Question 8
A rectangular block of mass 150 kg has sides of 60 cm, 90 cm and 12 cm (figure). What is the minimum pressure that the block exerts on the ground when it is resting on one of its sides?

A. 0.27 kPa.
B. 0.28 kPa.
C. 1.4 kPa.
D. 2.7 kPa.
Question 9
A solid sphere of diameter 30.0 cm is fully immersed near the surface of the sea. The sphere is released from rest and moves vertically downwards through the seawater. The weight of the sphere is 1100 N. An upthrust U acts on the sphere. The upthrust remains constant as the sphere moves downwards. The density of the seawater is 1030 kg.m–3.
a. Calculate the density of the material of the sphere.
b. Briefly explain the origin of the upthrust acting on the sphere.
c. Show that the upthrust U is 140 N.
d. Calculate the initial acceleration of the sphere.
e. The viscous (drag) force D acting on the sphere is given by `D = 1/2 C rho pi r^2 v^2`
Where r is the radius of the sphere and v is its speed. ρ is the density of the seawater. The constant C has no units and is equal to 0.50.
Determine the constant (terminal) speed reached by the sphere.
Question 10
A boy stands on a platform of area 0.050 m2 and a manometer measures the pressure created in a flexible plastic container by the weight W of the boy, as shown.

The density of water is 1000 kg.m-3. Determine:
a. The pressure difference between the inside of the plastic container and the atmosphere outside.
b. The weight W of the boy.