Question 1
A weight-lifter raises weights with a mass of 200 kg from the ground to a height of 1.5 m. Calculate how much work he does. By how much does the GPE of the weights increase?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
A climber of mass 100 kg (including the equipment she is carrying) ascends from sea level to the top of a mountain 5500 m high. Calculate the change in her gravitational potential energy.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Calculate the change in kinetic energy of a ball of mass 200 g when it bounces. Assume that it hits the ground with a speed of 15.8 m.s-1 and leaves it at 12.2 m.s-1.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
An object falls at terminal velocity in air. What overall conversion of energy is occurring?
A. Gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy.
B. Gravitational potential energy to thermal energy.
C. Kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy.
D. Kinetic energy to thermal energy.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
An object of mass 0.40 kg is projected into the air and follows a curved path above horizontal ground.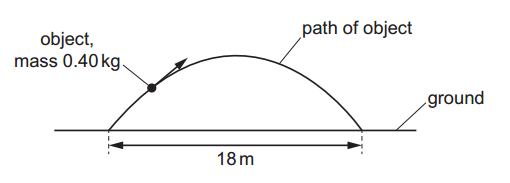 The object takes a time of 1.5 s to move along its path. The object lands a horizontal distance of 18 m from its initial position. Air resistance is negligible. What is the kinetic energy of the object at its maximum height?
The object takes a time of 1.5 s to move along its path. The object lands a horizontal distance of 18 m from its initial position. Air resistance is negligible. What is the kinetic energy of the object at its maximum height?
A. 0 J.
B. 2.4 J.
C. 11 J.
D. 29 J.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A pendulum consists of a brass sphere of mass 5.0 kg hanging from a long string.
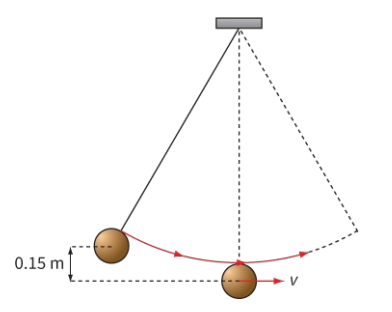
The sphere is pulled to the side so that it is 0.15 m above its lowest position. It is then released. How fast will it be moving when it passes through the lowest point along its path?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
a. A steel ball of mass 20.0 g is placed on a smooth, curved track as shown:
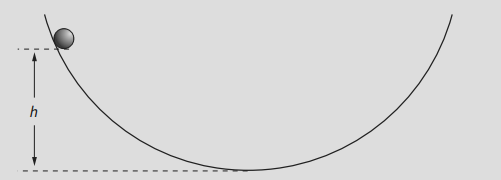
When released, the ball rolls back and forth along the track. At its lowest point, its speed is 0.47 m.s-1. Calculate its KE at this point.
b. Deduce the height h above the bottom of the track from which it was released.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
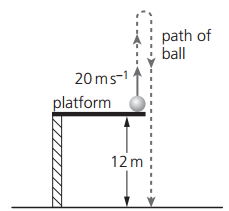
A ball of mass 0.50 kg is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m.s–1. It is thrown from a platform 12m above the ground reaches a maximum height before the ball falls to the ground, as shown in figure. What is the kinetic energy of the ball just as it hits the ground? Assume air resistance is negligible.
A. 59 J.
B. 100 J.
C. 160 J.
D. 260 J.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
A child holds a thin metal wire that is attached to a kite. The graph shows how the extension of the wire varies with its tension.
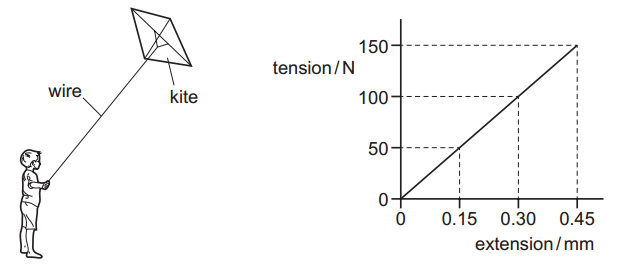
A gust of wind increases the tension from 100 N to 150 N. What is the change in the elastic potential energy of the wire caused by the gust of wind?
A. 3.8 mJ.
B. 19 mJ.
C. 34 mJ.
D. 38 mJ.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
a. Distinguish between gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy.
b. A ball of mass 65 g is thrown vertically upwards from ground level with a speed of 16 m.s-1. Air resistance is negligible.
i. Calculate, for the ball:
1. The initial kinetic energy.
2. the maximum height reached.
ii. The ball takes time t to reach maximum height. For time t/2 after the ball has been thrown.
Calculate the ratio `"potential energy of ball"/"kinetic energy of ball"`.
iii. State and explain the effect of air resistance on the time taken for the ball to reach maximum height.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
A weight-lifter raises weights with a mass of 200 kg from the ground to a height of 1.5 m. Calculate how much work he does. By how much does the GPE of the weights increase?
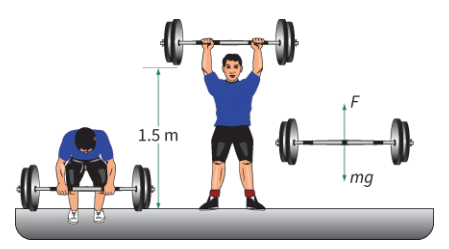
As shown in figure, the downward force on the weights is their weight. An equal, upward force F is required to lift them.
`W = F = m xxg = 200 xx 9.81 = "1962 N"`.
`"Work done" = "force" xx "distance moved" = 1962 xx 1.5 ~~ "2940 J"`.
Note that the distance moved is in the same direction as the force. So the work done on the weights is about 2940 J. This is also the value of the increase in their GPE.
Question 2
A climber of mass 100 kg (including the equipment she is carrying) ascends from sea level to the top of a mountain 5500 m high. Calculate the change in her gravitational potential energy.
Change in gravitational potential energy:
`E_p = mxx gxx h = 100 xx 9.81 xx 5500 = "5400000 J" = "5400 kJ "`
Question 3
Calculate the change in kinetic energy of a ball of mass 200 g when it bounces. Assume that it hits the ground with a speed of 15.8 m.s-1 and leaves it at 12.2 m.s-1.
`"Change in kinetic energy "= 1/2 xx 0.200 xx (15.8)^2 - (1/2) xx 0.200 xx (12.2)^2 = 25 - 15 = "10 J"`
Question 4
An object falls at terminal velocity in air. What overall conversion of energy is occurring?
A. Gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy.
B. Gravitational potential energy to thermal energy.
C. Kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy.
D. Kinetic energy to thermal energy.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: because at terminal velocity, kinetic energy does not increase — it stays constant.
B. Correct:
At terminal velocity, an object falls at constant speed. This means:
Kinetic energy stays constant (no gain or loss).
Gravitational potential energy (GPE) continues to decrease as the object falls.
Since kinetic energy is not increasing, the energy lost from GPE must be transferred to another form.
That form is thermal energy due to air resistance (drag) — it heats the air and the object slightly.
C. Incorrect: because the object is falling, not rising — GPE is decreasing, not increasing.
D. Incorrect: because KE is constant at terminal velocity — it's not being converted to anything.
Question 5
An object of mass 0.40 kg is projected into the air and follows a curved path above horizontal ground. The object takes a time of 1.5 s to move along its path. The object lands a horizontal distance of 18 m from its initial position. Air resistance is negligible. What is the kinetic energy of the object at its maximum height?
The object takes a time of 1.5 s to move along its path. The object lands a horizontal distance of 18 m from its initial position. Air resistance is negligible. What is the kinetic energy of the object at its maximum height?
A. 0 J.
B. 2.4 J.
C. 11 J.
D. 29 J.
Answer: D
At maximum height, vertical velocity = 0, but horizontal velocity remains constant.
`v_x = 18 / 1.5 = 12 " m"."s"^-1`.
`KE = 1/2 xx 0.40 xx 12^2 = "28.8 J" ~~ "29 J"`.
Question 6
A pendulum consists of a brass sphere of mass 5.0 kg hanging from a long string.

The sphere is pulled to the side so that it is 0.15 m above its lowest position. It is then released. How fast will it be moving when it passes through the lowest point along its path?
Calculate the loss in GPE as the sphere falls from its highest position:
`E_p = mxx gxx h = 5.0 xx 9.81 xx 0.15 = "7.36 J"`
The gain in the sphere’s KE is 7.36 J. We can use this to calculate the sphere’s speed. First, calculate v2, then v:
`1/2 m v^2 = 7.36`
`1/2 xx 5.0 xx v^2 = 7.36`
`v^2 = 2 xx (7.36 / 5.0)`
`v = sqrt(2.944) ~~ 1.72 " " m.s^-1 ~~ 1.7 " " m.s^-1`
`"Change in GPE" " = " "change in KE"`
`mxx xxg h = 1/2xx mxx v^2`
`gxx h = v^2 / 2`
`v^2 = 2xx gxx h`
`v = sqrt(2 xxg xxh)`
Question 7
a. A steel ball of mass 20.0 g is placed on a smooth, curved track as shown:

When released, the ball rolls back and forth along the track. At its lowest point, its speed is 0.47 m.s-1. Calculate its KE at this point.
b. Deduce the height h above the bottom of the track from which it was released.
a. `KE = 1/2xx mxx v^2=1/2 xx 0.020 xx 0.47^2 = "0.0022 J"`
b.
As the ball moves downward:
The ball loses gravitational potential energy.
That energy is converted into kinetic energy as the ball speeds up.
At the bottom of the curve:
The ball has minimum gravitational potential energy (approaches 0).
It has maximum kinetic energy (moving fastest).
All the GPE has been converted into KE:
`1/2xxmxxv^2= mxx gxx h = "0.0022 J"`
`h = "0.011 m"`
Question 8
A ball of mass 0.50 kg is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m.s–1. It is thrown from a platform 12m above the ground reaches a maximum height before the ball falls to the ground, as shown in figure. What is the kinetic energy of the ball just as it hits the ground? Assume air resistance is negligible.

A. 59 J.
B. 100 J.
C. 160 J.
D. 260 J.
Answer: C
At the moment just before hitting the ground, the ball has converted all its initial kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy into kinetic energy.
Initial kinetic energy:
`KE = 1/2 xx 0.50 xx 20^2 = "100 J"`
Initial potential energy (from 12 m above ground):
`PE = 0.50 xx 9.8 xx 12 = "58.8 J"`
Total mechanical energy at start:
`E_"total" = 100 + 58.8 = "158.8 J"`
Since air resistance is negligible, mechanical energy is conserved.
This means that the total mechanical energy (KE + PE) at the beginning will be equal to the kinetic energy at the moment it hits the ground.
As the ball falls, it loses height, so its potential energy decreases.
At the same time, it gains speed, so its kinetic energy increases.
Just before it hits the ground, all of the energy has been converted into kinetic energy.
The kinetic energy just before hitting the ground is equal to the total mechanical energy the ball had at the beginning, which is 158.8 J.
Question 9
A child holds a thin metal wire that is attached to a kite. The graph shows how the extension of the wire varies with its tension.

A gust of wind increases the tension from 100 N to 150 N. What is the change in the elastic potential energy of the wire caused by the gust of wind?
A. 3.8 mJ.
B. 19 mJ.
C. 34 mJ.
D. 38 mJ.
EPE at 0.45 mm: `EPE_(150) = 1/2xx150xx0.00045 = "0.03375 J"`
EPE at 0.3 mm: `EPE_(100) = 1/2xx100xx0.00030 = "0.015 J"`
Change in elastic potential energy:
`Delta EPE = 0.03375 - 0.015 = "0.01875 J" = "18.75 mJ"`
Question 10
a. Distinguish between gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy.
b. A ball of mass 65 g is thrown vertically upwards from ground level with a speed of 16 m.s-1. Air resistance is negligible.
i. Calculate, for the ball:
1. The initial kinetic energy.
2. the maximum height reached.
ii. The ball takes time t to reach maximum height. For time t/2 after the ball has been thrown.
Calculate the ratio `"potential energy of ball"/"kinetic energy of ball"`.
iii. State and explain the effect of air resistance on the time taken for the ball to reach maximum height.
a.
Gravitational potential energy is the energy of an object due to its position in a gravitational field.
Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in a moving-object.
b.
i.1. `KE = 1/2 xx 0.065 xx 16^2 = "8.32 J"`
i.2. `h = v^2 / (2 xx 9.81) = 256 / 19.62 = "13.05 m"`
ii.
At ground level, KE = 8.32 J, GPE = 0. Hence, total energy is 8.32 J.
At t/2:
Speed = 8 m.s-1
`"KE at t/2" = 1/2 xx 0.065 xx 8^2 = "2.08 J`
So, potential energy = 8.32 − 2.08 = 6.24 J
`(PE) / (KE) = 6.24 / 2.08 = 3`
iii. The time is less because the average acceleration is greater due to air resistance acting downward in addition to gravity.
Question 1
A weight-lifter raises weights with a mass of 200 kg from the ground to a height of 1.5 m. Calculate how much work he does. By how much does the GPE of the weights increase?
Question 2
A climber of mass 100 kg (including the equipment she is carrying) ascends from sea level to the top of a mountain 5500 m high. Calculate the change in her gravitational potential energy.
Question 3
Calculate the change in kinetic energy of a ball of mass 200 g when it bounces. Assume that it hits the ground with a speed of 15.8 m.s-1 and leaves it at 12.2 m.s-1.
Question 4
An object falls at terminal velocity in air. What overall conversion of energy is occurring?
A. Gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy.
B. Gravitational potential energy to thermal energy.
C. Kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy.
D. Kinetic energy to thermal energy.
Question 5
An object of mass 0.40 kg is projected into the air and follows a curved path above horizontal ground. The object takes a time of 1.5 s to move along its path. The object lands a horizontal distance of 18 m from its initial position. Air resistance is negligible. What is the kinetic energy of the object at its maximum height?
The object takes a time of 1.5 s to move along its path. The object lands a horizontal distance of 18 m from its initial position. Air resistance is negligible. What is the kinetic energy of the object at its maximum height?
A. 0 J.
B. 2.4 J.
C. 11 J.
D. 29 J.
Question 6
A pendulum consists of a brass sphere of mass 5.0 kg hanging from a long string.

The sphere is pulled to the side so that it is 0.15 m above its lowest position. It is then released. How fast will it be moving when it passes through the lowest point along its path?
Question 7
a. A steel ball of mass 20.0 g is placed on a smooth, curved track as shown:

When released, the ball rolls back and forth along the track. At its lowest point, its speed is 0.47 m.s-1. Calculate its KE at this point.
b. Deduce the height h above the bottom of the track from which it was released.
Question 8
A ball of mass 0.50 kg is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m.s–1. It is thrown from a platform 12m above the ground reaches a maximum height before the ball falls to the ground, as shown in figure. What is the kinetic energy of the ball just as it hits the ground? Assume air resistance is negligible.

A. 59 J.
B. 100 J.
C. 160 J.
D. 260 J.
Question 9
A child holds a thin metal wire that is attached to a kite. The graph shows how the extension of the wire varies with its tension.

A gust of wind increases the tension from 100 N to 150 N. What is the change in the elastic potential energy of the wire caused by the gust of wind?
A. 3.8 mJ.
B. 19 mJ.
C. 34 mJ.
D. 38 mJ.
Question 10
a. Distinguish between gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy.
b. A ball of mass 65 g is thrown vertically upwards from ground level with a speed of 16 m.s-1. Air resistance is negligible.
i. Calculate, for the ball:
1. The initial kinetic energy.
2. the maximum height reached.
ii. The ball takes time t to reach maximum height. For time t/2 after the ball has been thrown.
Calculate the ratio `"potential energy of ball"/"kinetic energy of ball"`.
iii. State and explain the effect of air resistance on the time taken for the ball to reach maximum height.