Question 1
Figure shows the force–extension graphs for four springs, A, B, C and D.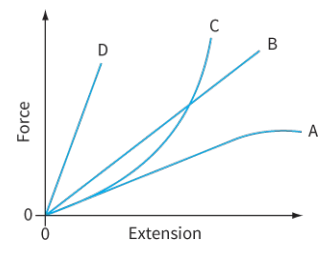 a. State which spring has the greatest value of force constant.
a. State which spring has the greatest value of force constant.
b. State which is the least stiff.
c. State which of the four springs does not obey Hooke’s law.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
For each of the materials whose stress–strain graphs are shown in figure, deduce the values of the Young modulus.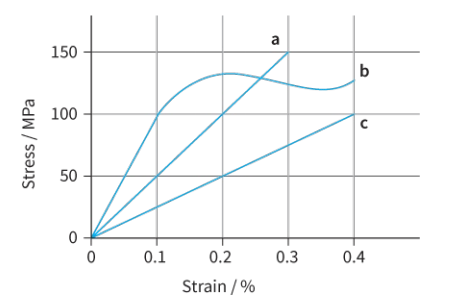
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Two guitar strings are stretched by tensile forces.
String X is stretched by a tensile force F that causes an extension x.
String Y is stretched by a tensile force 2F that causes an extension 2x.
The strings obey Hooke’s law.
What is the ratio `"strain energy in stretched string X"/"strain energy in stretched string Y"`
A. 4
B. 2
C. `1/2`
D. `1/4`
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
A block of plastic foam is placed on firm ground. It is in the shape of a cube with sides of length 20.0 cm. A heavy weight is placed on top of the block, compressing it to a thickness of 17.4 cm.
a. Calculate the strain produced by the load.
b. The heavy weight consists of six masses, each of 5 kg. Determine the stress in the block. Give your answer in kPa.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
A wire is being stretched by a tensile force.
Which statement about the elastic limit must be correct?
A. The deformation is plastic after the elastic limit has been reached.
B. The deformation is plastic until the elastic limit is reached.
C. The extension is proportional to the tensile force after the elastic limit has been reached.
D. The extension is proportional to the tensile force until the elastic limit is reached.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A sample of fishing line is 1.0 m long and is of circular cross-section of radius 0.25 mm. When a weight is hung on the line, the extension is 50 mm and the stress is 2.0 × 108 Pa. Calculate:
a. The cross-sectional area of the line.
b. The weight added.
c. The strain in the line.
d. The Young modulus.
e. The percentage and absolute uncertainties in the Young modulus if the uncertainty in the extension is ±1 mm.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
A copper wire of diameter 1.78 mm and length 1.40 m is suspended from a fixed point and a mass of weight 32.0 N is suspended from its free end. The Young modulus of the material of the wire is 1.10 × 1011 Pa. Assuming that the limit of proportionality of the wire is not exceeded, calculate:
a. The applied stress.
b. The strain.
c. The extension of the wire.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
A metal wire obeys Hooke’s law and has a Young modulus of 2.0 × 1011 Pa. The wire has an original length of 1.6 m and a diameter of 0.48 × 10−3 m. What is the spring constant of the wire?
A. 7.2 × 103 N.m−1.
B. 2.3 × 104 N.m−1.
C. 2.9 × 104 N.m−1.
D. 9.0 × 104 N.m−1.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
A lamp is suspended in equilibrium from a fixed support by three long identical wires. The weight of the lamp causes each wire to extend by 0.40 cm. The height h of the lamp above the floor is measured.
The weight of the lamp causes each wire to extend by 0.40 cm. The height h of the lamp above the floor is measured.
The middle wire suddenly breaks, and the lamp falls a small distance as the extensions of the remaining two wires increase. The wires obey Hooke’s law.
When the lamp is again in equilibrium, the new height hh of the lamp above the floor is measured.
What is the difference between the two values of ?
A. 0.2 cm.
B. 0.27 cm.
C. 0.4 cm.
D. 0.26 cm.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
An elastic cord of unstretched total length 16.0 cm and cross-sectional area 2.0 x 10⁻⁶ m² is held horizontally by two smooth pins a distance 8.0 cm apart.
The cord obeys Hooke’s law. A load of mass 0.40 kg is suspended centrally on the cord. The angle between the two sides of the cord supporting the load is 60°.
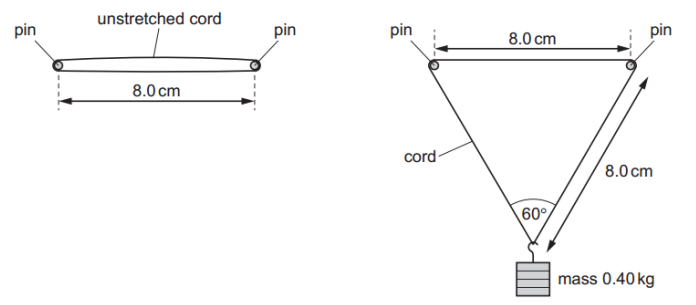 What is the Young modulus of the cord material?
What is the Young modulus of the cord material?
A. 5.7 x 10⁵ Pa.
B. 1.1 x 10⁶ Pa.
C. 2.5 x 10⁶ Pa.
D. 3.9 x 10⁶ Pa.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Figure shows the force–extension graphs for four springs, A, B, C and D. a. State which spring has the greatest value of force constant.
a. State which spring has the greatest value of force constant.
b. State which is the least stiff.
c. State which of the four springs does not obey Hooke’s law.
a. Spring D has the greatest value of force constant (the graph has the steepest gradient).
b. Spring A is the least stiff (it extends the most for each unit of force applied).
c. Spring C does not obey Hooke’s law: there is no section of the graph that forms a straight line.
Question 2
For each of the materials whose stress–strain graphs are shown in figure, deduce the values of the Young modulus.
a. `"Young modulus" = "stress" / ("strain") = (150 xx 10^6) / 0.003 = "50 GPa"`
b. `"Young modulus" = "stress" / "strain" = (100 xx 10^6) / 0.001 = "100 GPa"`
c. `"Young modulus" = "stress" / "strain" = (100 xx 10^6) / 0.004 = "25 GPa"`
Question 3
Two guitar strings are stretched by tensile forces.
String X is stretched by a tensile force F that causes an extension x.
String Y is stretched by a tensile force 2F that causes an extension 2x.
The strings obey Hooke’s law.
What is the ratio `"strain energy in stretched string X"/"strain energy in stretched string Y"`
A. 4
B. 2
C. `1/2`
D. `1/4`
Answer: D
String X: `E_X = 1/2 F x`
String Y: `E_Y = 1/2(2F)(2x) = 2F x`
`(E_X)/(E_Y) = ((1/2) F x)/(2 F x) = 1/4`
Question 4
A block of plastic foam is placed on firm ground. It is in the shape of a cube with sides of length 20.0 cm. A heavy weight is placed on top of the block, compressing it to a thickness of 17.4 cm.
a. Calculate the strain produced by the load.
b. The heavy weight consists of six masses, each of 5 kg. Determine the stress in the block. Give your answer in kPa.
a. `"Strain" = (DeltaL)/L= (0.026) / (0.20) = 0.13`
b. Weight: `F = 30 xx 9.81 = "294 N"`
Stress: `"Stress" = F/A= 294 / (0.20^2) = "7350 Pa" = "7.35 kPa"`
Question 5
A wire is being stretched by a tensile force.
Which statement about the elastic limit must be correct?
A. The deformation is plastic after the elastic limit has been reached.
B. The deformation is plastic until the elastic limit is reached.
C. The extension is proportional to the tensile force after the elastic limit has been reached.
D. The extension is proportional to the tensile force until the elastic limit is reached.
Answer: A
A. Correct: Once a material exceeds the elastic limit, it no longer returns to its original shape after the force is removed.
This is called plastic deformation, which is permanent.
B. Incorrect: Before reaching the elastic limit, the deformation is elastic, meaning the material will return to its original shape. Plastic deformation only occurs after the elastic limit is exceeded.
C. Incorrect: According to Hooke’s Law, extension is proportional to force only within the elastic region. After the elastic limit, this relationship breaks down, and the extension increases non-linearly.
D. Incorrect: The limit of proportionality is where extension and force stop being strictly proportional, and this can happen before the elastic limit. So the material may still behave elastically (i.e., return to its shape), but not follow Hooke’s Law anymore.
Question 6
A sample of fishing line is 1.0 m long and is of circular cross-section of radius 0.25 mm. When a weight is hung on the line, the extension is 50 mm and the stress is 2.0 × 108 Pa. Calculate:
a. The cross-sectional area of the line.
b. The weight added.
c. The strain in the line.
d. The Young modulus.
e. The percentage and absolute uncertainties in the Young modulus if the uncertainty in the extension is ±1 mm.
a. `"Cross-sectional area" = pixx r^2 = 1.96 xx 10^-7 " m"^2 approx 2.0 xx 10^-7 " m"^2`
b. `"Weight" = "stress" xx "area" = 2.0 xx 10^8 xx 1.96 xx 10^-7 = 39.3 " N" approx 39 " N"`
c. `"Strain" = "extension" / "length" = 0.050 / 1.0 = 0.050 = "5%"`
d. `"Young modulus" = "stress" / "strain" = (2.0 xx 10^8) / 0.050 = 4.0 xx 10^9 " Pa"`
e. `"Percentage uncertainty in E" = "uncertainty in extension" = +-2% "absolute uncertainty"`
`= 0.02 xx 4.0 xx 10^9 = +-8.0 xx 10^7 " Pa"`
Question 7
A copper wire of diameter 1.78 mm and length 1.40 m is suspended from a fixed point and a mass of weight 32.0 N is suspended from its free end. The Young modulus of the material of the wire is 1.10 × 1011 Pa. Assuming that the limit of proportionality of the wire is not exceeded, calculate:
a. The applied stress.
b. The strain.
c. The extension of the wire.
a. `A = pi ((1.78 xx 10^-3) / 2)^2 = 2.49 xx 10^-6 " m"^2`
`"Stress" = 32.0 / (2.49 xx 10^-6) = 1.29 xx 10^7 " Pa"`
b. `"Strain" = (1.29 xx 10^7) / (1.10 xx 10^11) = 1.17 xx 10^-4`
c. `DeltaL = "strain" xx L = 1.17 xx 10^-4 xx 1.40 = 1.64 xx 10^-4 " m" = 0.16 " mm"`
Question 8
A metal wire obeys Hooke’s law and has a Young modulus of 2.0 × 1011 Pa. The wire has an original length of 1.6 m and a diameter of 0.48 × 10−3 m. What is the spring constant of the wire?
A. 7.2 × 103 N.m−1.
B. 2.3 × 104 N.m−1.
C. 2.9 × 104 N.m−1.
D. 9.0 × 104 N.m−1.
Answer: B
Prove the formula:
`E = "stress"/"strain"= (F/A)/(x/L) = (F L)/(A x)`
`F = (E A x)/L`
`kx=(EAx)/L`
`k=(EA)/L`
Calculate the cross-sectional area:
`A = pi (0.24 xx 10^-3)^2 approx 1.81 xx 10^-7 " m"^2`
`k = (2.0 xx 10^11 xx 1.81 xx 10^-7) / 1.6 approx 2.26 xx 10^4 " N"."m"^-1`
Question 9
A lamp is suspended in equilibrium from a fixed support by three long identical wires. The weight of the lamp causes each wire to extend by 0.40 cm. The height h of the lamp above the floor is measured.
The weight of the lamp causes each wire to extend by 0.40 cm. The height h of the lamp above the floor is measured.
The middle wire suddenly breaks, and the lamp falls a small distance as the extensions of the remaining two wires increase. The wires obey Hooke’s law.
When the lamp is again in equilibrium, the new height hh of the lamp above the floor is measured.
What is the difference between the two values of ?
A. 0.2 cm.
B. 0.27 cm.
C. 0.4 cm.
D. 0.26 cm.
Answer: A
After the middle wire breaks, only 2 wires share the same total force, so each wire must support more force. Since the wires are identical and obey Hooke’s Law:
New extension in each wire: `x' = 2 xx 0.40 = "0.80 cm"`
Initially, extension was 0.40 cm.
After the break, extension is 0.80 cm.
So the lamp falls by: `Delta h= 0.8 -0.4="0.4 cm"`
But this 0.40 cm is the new extension of each of the two wires.
Because the middle wire is gone, the actual position of the lamp lowers only half of the extra extension, since two wires stretch symmetrically
So: `Delta h = (0.40) / 2 = "0.20 cm"`
Question 10
An elastic cord of unstretched total length 16.0 cm and cross-sectional area 2.0 x 10⁻⁶ m² is held horizontally by two smooth pins a distance 8.0 cm apart.
The cord obeys Hooke’s law. A load of mass 0.40 kg is suspended centrally on the cord. The angle between the two sides of the cord supporting the load is 60°.
 What is the Young modulus of the cord material?
What is the Young modulus of the cord material?
A. 5.7 x 10⁵ Pa.
B. 1.1 x 10⁶ Pa.
C. 2.5 x 10⁶ Pa.
D. 3.9 x 10⁶ Pa.
Answer: C
At equilibrium, the vertical component of the tensions balances the weight: `2T_y=mg`
`T_y=Txxcos30^o`
`2T_y=mg`
`2xx(Txxcos30^o)=0.4xx9.81`
`T="2.26 N"=F`
Young modulus: `(Fxxl_o)/(Axxx)=(2.26xx0.16)/(2xx10^-6xx0.08)~~2.3xx10^6 " Pa"`
Question 1
Figure shows the force–extension graphs for four springs, A, B, C and D. a. State which spring has the greatest value of force constant.
a. State which spring has the greatest value of force constant.
b. State which is the least stiff.
c. State which of the four springs does not obey Hooke’s law.
Question 2
For each of the materials whose stress–strain graphs are shown in figure, deduce the values of the Young modulus.
Question 3
Two guitar strings are stretched by tensile forces.
String X is stretched by a tensile force F that causes an extension x.
String Y is stretched by a tensile force 2F that causes an extension 2x.
The strings obey Hooke’s law.
What is the ratio `"strain energy in stretched string X"/"strain energy in stretched string Y"`
A. 4
B. 2
C. `1/2`
D. `1/4`
Question 4
A block of plastic foam is placed on firm ground. It is in the shape of a cube with sides of length 20.0 cm. A heavy weight is placed on top of the block, compressing it to a thickness of 17.4 cm.
a. Calculate the strain produced by the load.
b. The heavy weight consists of six masses, each of 5 kg. Determine the stress in the block. Give your answer in kPa.
Question 5
A wire is being stretched by a tensile force.
Which statement about the elastic limit must be correct?
A. The deformation is plastic after the elastic limit has been reached.
B. The deformation is plastic until the elastic limit is reached.
C. The extension is proportional to the tensile force after the elastic limit has been reached.
D. The extension is proportional to the tensile force until the elastic limit is reached.
Question 6
A sample of fishing line is 1.0 m long and is of circular cross-section of radius 0.25 mm. When a weight is hung on the line, the extension is 50 mm and the stress is 2.0 × 108 Pa. Calculate:
a. The cross-sectional area of the line.
b. The weight added.
c. The strain in the line.
d. The Young modulus.
e. The percentage and absolute uncertainties in the Young modulus if the uncertainty in the extension is ±1 mm.
Question 7
A copper wire of diameter 1.78 mm and length 1.40 m is suspended from a fixed point and a mass of weight 32.0 N is suspended from its free end. The Young modulus of the material of the wire is 1.10 × 1011 Pa. Assuming that the limit of proportionality of the wire is not exceeded, calculate:
a. The applied stress.
b. The strain.
c. The extension of the wire.
Question 8
A metal wire obeys Hooke’s law and has a Young modulus of 2.0 × 1011 Pa. The wire has an original length of 1.6 m and a diameter of 0.48 × 10−3 m. What is the spring constant of the wire?
A. 7.2 × 103 N.m−1.
B. 2.3 × 104 N.m−1.
C. 2.9 × 104 N.m−1.
D. 9.0 × 104 N.m−1.
Question 9
A lamp is suspended in equilibrium from a fixed support by three long identical wires. The weight of the lamp causes each wire to extend by 0.40 cm. The height h of the lamp above the floor is measured.
The weight of the lamp causes each wire to extend by 0.40 cm. The height h of the lamp above the floor is measured.
The middle wire suddenly breaks, and the lamp falls a small distance as the extensions of the remaining two wires increase. The wires obey Hooke’s law.
When the lamp is again in equilibrium, the new height hh of the lamp above the floor is measured.
What is the difference between the two values of ?
A. 0.2 cm.
B. 0.27 cm.
C. 0.4 cm.
D. 0.26 cm.
Question 10
An elastic cord of unstretched total length 16.0 cm and cross-sectional area 2.0 x 10⁻⁶ m² is held horizontally by two smooth pins a distance 8.0 cm apart.
The cord obeys Hooke’s law. A load of mass 0.40 kg is suspended centrally on the cord. The angle between the two sides of the cord supporting the load is 60°.
 What is the Young modulus of the cord material?
What is the Young modulus of the cord material?
A. 5.7 x 10⁵ Pa.
B. 1.1 x 10⁶ Pa.
C. 2.5 x 10⁶ Pa.
D. 3.9 x 10⁶ Pa.