Question 1
Which pair contains one transverse and one longitudinal wave?
A. Water wave, visible light.
B. X-ray, ultrasound.
C. Primary (P) wave, sound wave.
D. Infrared wave, vibration on a guitar string.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Distinguish between longitudinal and transverse waves.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Figure shows a longitudinal wave.
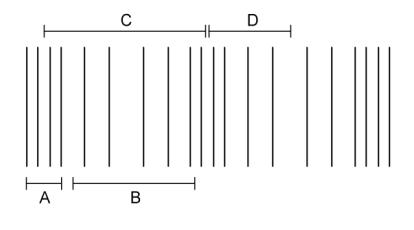
Which label correctly shows the wavelength of a longitudinal wave?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The figure below shows two ways in which a wave can travel along a slinky spring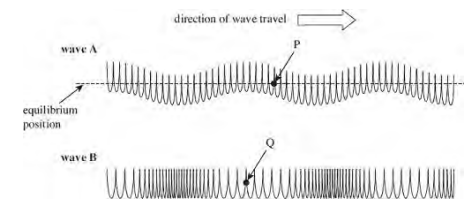 State and explain which wave is longitudinal.
State and explain which wave is longitudinal.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
The graph shows how the displacement of a particle in a wave varies with time. 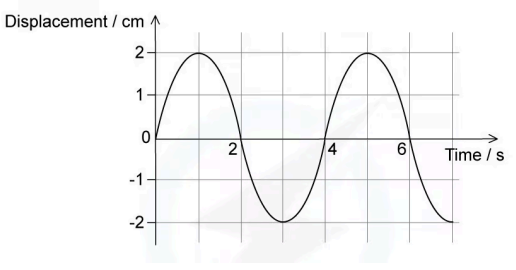 Which statementis correct?
Which statementis correct?
A. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and could be eithertransverse or longitudinal.
B. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and a period of 6 s.
C. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and a period of 4 s.
D. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and must be transverse.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A transverse wave and a longitudinal wave both travel in the same direction down a long stretched spring.
Which statement is not correct for these two forms of wave?
A. The displacement measurements for the particles of the two waves are made at right angles to each other.
B. The energy transferred by the two waves is in the same direction.
C. The velocities of the two waves are in the same direction.
D. The wavelength measurements for the two waves are made at right angles to each other.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
The variation with distance x of the displacement y of a transverse wave on a rope is shown at time t = 0.
The wave has a frequency of 0.5 Hz.
A point P on the rope is marked. The diagram shows the original position of P and four new positions: A, B, C, and D.
What is the position of P at time t = 1 s?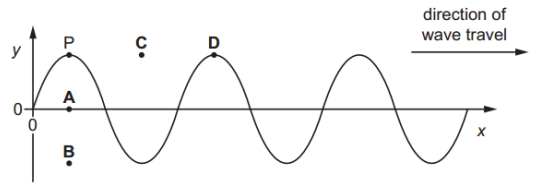
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
a. Explain briefly how transmission of energy by a longitudinal wave differs from transmission of energy by a transverse wave. Give one example of a transverse wave.
b. With the aid of a clearly labelled diagram explain how a sound wave in air transmits energy away from its source.
c. Short pulses of sound are reflected from a wall 30 m from the sound source. The reflected pulses return to the source after 0.18 s. Calculate the speed of sound.
d. Figure represents the sound wave from part c.
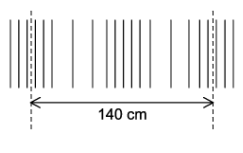 Calculate the frequency of the sound wave.
Calculate the frequency of the sound wave.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Sound travels with a speed of 330 ms in air. The variation with time of the displacement of an air particle due to a sound wave is shown below.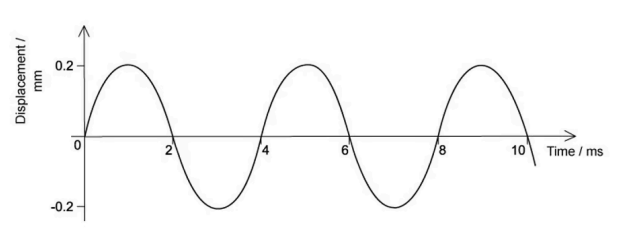 Which of the following statements about the wave is correct?
Which of the following statements about the wave is correct?
A. The wavelength of the sound wave is 1.32 m.
B. The graph shows that the sound is a transverse wave.
C. The frequency of the wave is 500 Hz.
D. The intensity of the wave will be doubled if its amplitude is increased to 0.4 mm.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Two particles in a progressive wave are a distance 10 cm apart. The two graphs show the variation with time t of the displacement d of the two particles.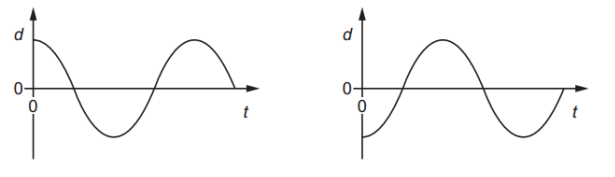 What could be represented by the two graphs?
What could be represented by the two graphs?
A. Particles in a longitudinal wave with a compression and the nearest rarefaction separated by 10 cm.
B. Particles in a longitudinal wave with a compression and the nearest rarefaction separated by 20 cm.
C. Particles in a transverse wave with a peak and the nearest trough separated by 20 cm.
D. Particles in a transverse wave with two adjacent peaks separated by 10 cm.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Which pair contains one transverse and one longitudinal wave?
A. Water wave, visible light.
B. X-ray, ultrasound.
C. Primary (P) wave, sound wave.
D. Infrared wave, vibration on a guitar string.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: Water waves and visible light are both transverse waves.
B. Correct: An X-ray is a transverse wave as it is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. An ultrasound wave is a longitudinal wave as it is a high frequency sound wave.
C. Incorrect: Primary (P) waves and sound waves are both longitudinal waves.
D. Incorrect: Infrared waves and vibrations on guitar strings are both transverse waves.
Question 2
Distinguish between longitudinal and transverse waves.
In longitudinal waves, the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of the wave velocity.
In transverse waves, the particles of the medium vibrate at right angles to the direction of the wave velocity.
Question 3
Figure shows a longitudinal wave.

Which label correctly shows the wavelength of a longitudinal wave?
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: The label highlights one compression.
B. Incorrect: The label highlights one refraction.
C. Correct: The label goes from the middle of one compression to another. This is the wavelength.
D. Incorrect:
The label goes from the middle of a compression to a middle of a refraction.
This is half a wavelength.
For a longitudinal wave, a wavelength can also be measured from one rarefaction to another.
Question 4
The figure below shows two ways in which a wave can travel along a slinky spring State and explain which wave is longitudinal.
State and explain which wave is longitudinal.
Wave B is the longitudinal wave because the parts of the spring oscillate back and forth in the direction of or parallel to the direction of wave travel. Additionally, it shows compressions and rarefactions, which are characteristic features of longitudinal waves.
Question 5
The graph shows how the displacement of a particle in a wave varies with time.  Which statementis correct?
Which statementis correct?
A. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and could be eithertransverse or longitudinal.
B. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and a period of 6 s.
C. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and a period of 4 s.
D. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and must be transverse.
Answer: A
Each peak and trough is 2 cm away from the equilibrium position on the graph.
So,the amplitude is 2 cm.
4 seconds pass before the wave repeats its pattern again, so the period is 4 s.
The x-axis of this graph is time, so all that can be inferred is that the particle is displaced periodically.
This occurs if a transverse wave or a longitudinal wave is causing its oscillations, as it is not mentioned how it is oscillating relative to the direction of wave travel.
Therefore the wave could be either transverse or longitudinal.
Question 6
A transverse wave and a longitudinal wave both travel in the same direction down a long stretched spring.
Which statement is not correct for these two forms of wave?
A. The displacement measurements for the particles of the two waves are made at right angles to each other.
B. The energy transferred by the two waves is in the same direction.
C. The velocities of the two waves are in the same direction.
D. The wavelength measurements for the two waves are made at right angles to each other.
Answer: D
A. True
In transverse waves, particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of wave travel.
In longitudinal waves, particles vibrate parallel to the direction of wave travel.
⟶ So yes, the displacement measurements (i.e., particle motion directions) are at right angles to each other.
B. True
Both transverse and longitudinal waves in this case are moving in the same direction down the spring, so their energy is transferred in that same direction.
C. True
Since both waves are said to be traveling in the same direction, their wave velocities (the direction of wave propagation) are the same.
D. False
Wavelength is always measured along the direction of wave travel, not based on the direction of displacement.
For both transverse and longitudinal waves, we measure wavelength as the distance between two corresponding points along the wave propagation
The direction of displacement may differ, but wavelength measurement direction is the same for both.
Question 7
The variation with distance x of the displacement y of a transverse wave on a rope is shown at time t = 0.
The wave has a frequency of 0.5 Hz.
A point P on the rope is marked. The diagram shows the original position of P and four new positions: A, B, C, and D.
What is the position of P at time t = 1 s?
Answer: B
Period: `T = 1 / 0.5 = "2 s"`
This means the wave completes one full cycle every 2 seconds.
So after t = 1 s, the wave will have moved through half a cycle.
After half a period, a crest becomes a trough.
So, P will now be at the bottom, same vertical distance but opposite direction.
Question 8
a. Explain briefly how transmission of energy by a longitudinal wave differs from transmission of energy by a transverse wave. Give one example of a transverse wave.
b. With the aid of a clearly labelled diagram explain how a sound wave in air transmits energy away from its source.
c. Short pulses of sound are reflected from a wall 30 m from the sound source. The reflected pulses return to the source after 0.18 s. Calculate the speed of sound.
d. Figure represents the sound wave from part c.
 Calculate the frequency of the sound wave.
Calculate the frequency of the sound wave.
a. Explain:
The disturbances/oscillations/vibrations are parallel for longitudinal and perpendicular for transverse.
To the direction of transmission of energy/wave/propagation/direction.
Example: waves on a string, ripples on the surface of water.
b.
 Explain:
Explain:
Energy is transferred to (air) molecules.
Energy is transferred by collisions between molecules.
Oscillations/waves are longitudinal/energy transfer is parallel to vibrations.
c.
The total distance is equal to the distance to and from the wall.
Distance travelled = 2 × 30 = 60 m.
`"Speed" = "distance" / "time"=60 / 0.18 = 333.3 " m"."s"^-1`
d. From figure: 140 cm = 2λ
λ = 70 cm
`"Frequency" = v / lambda=333 / 0.70 = "476 Hz"`
Question 9
Sound travels with a speed of 330 ms in air. The variation with time of the displacement of an air particle due to a sound wave is shown below. Which of the following statements about the wave is correct?
Which of the following statements about the wave is correct?
A. The wavelength of the sound wave is 1.32 m.
B. The graph shows that the sound is a transverse wave.
C. The frequency of the wave is 500 Hz.
D. The intensity of the wave will be doubled if its amplitude is increased to 0.4 mm.
Answer: A
The diagram shows a displacement time graph of a sound wave which is a longitudinal wave.
Two wavelengths have a period of 2T = 8 ms, so T = 4 ms.
`F=1/T=1/(4xx10^-3)="250 Hz"`
`lambda=330/250="1.32 m"`
B. Incorrect: The the graph shows a sine wave or sinusoid wave, this is a graphical depiction of the wave that describes a periodic oscillation this will be seen for both transverse and longitudinal waves.
C. Incorrect: When the frequency is calculated from the graph it is 250 Hz, not 500 Hz.
D. Incorrect: The intensity of the wave depends on the square of the amplitude. Doubling of the amplitude multiplies the intensity by a factor of 4.
Question 10
Two particles in a progressive wave are a distance 10 cm apart. The two graphs show the variation with time t of the displacement d of the two particles. What could be represented by the two graphs?
What could be represented by the two graphs?
A. Particles in a longitudinal wave with a compression and the nearest rarefaction separated by 10 cm.
B. Particles in a longitudinal wave with a compression and the nearest rarefaction separated by 20 cm.
C. Particles in a transverse wave with a peak and the nearest trough separated by 20 cm.
D. Particles in a transverse wave with two adjacent peaks separated by 10 cm.
Answer: A
A. Correct:
A longitudinal wave is made up of compressions and rarefactions.
In a compression, particles are close together, while in a rarefaction, they are spread out.
The displacement - time graphs of two particles half a wavelength apart (i.e., from a compression to the nearest rarefaction) will show this exact 180° phase difference.
Since the particles are 10 cm apart and this corresponds to half a wavelength, the wavelength is 20 cm, which fits this description.
B. Incorrect: B says 20 cm between compression and rarefaction, implying wavelength = 40 cm, but here 10 cm = `1/2`λ, so wavelength is 20 cm.
C. Incorrect: refers to a transverse wave with peak and nearest trough separated by 20 cm - that would be half a wavelength, but the separation given is 10 cm, not 20 cm.
D. Incorrect: D refers to two adjacent peaks separated by 10 cm → that would be one full wavelength, and they would be in phase, not out of phase as shown in the graphs.
Question 1
Which pair contains one transverse and one longitudinal wave?
A. Water wave, visible light.
B. X-ray, ultrasound.
C. Primary (P) wave, sound wave.
D. Infrared wave, vibration on a guitar string.
Question 2
Distinguish between longitudinal and transverse waves.
Question 3
Figure shows a longitudinal wave.

Which label correctly shows the wavelength of a longitudinal wave?
Question 4
The figure below shows two ways in which a wave can travel along a slinky spring State and explain which wave is longitudinal.
State and explain which wave is longitudinal.
Question 5
The graph shows how the displacement of a particle in a wave varies with time.  Which statementis correct?
Which statementis correct?
A. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and could be eithertransverse or longitudinal.
B. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and a period of 6 s.
C. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and a period of 4 s.
D. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and must be transverse.
Question 6
A transverse wave and a longitudinal wave both travel in the same direction down a long stretched spring.
Which statement is not correct for these two forms of wave?
A. The displacement measurements for the particles of the two waves are made at right angles to each other.
B. The energy transferred by the two waves is in the same direction.
C. The velocities of the two waves are in the same direction.
D. The wavelength measurements for the two waves are made at right angles to each other.
Question 7
The variation with distance x of the displacement y of a transverse wave on a rope is shown at time t = 0.
The wave has a frequency of 0.5 Hz.
A point P on the rope is marked. The diagram shows the original position of P and four new positions: A, B, C, and D.
What is the position of P at time t = 1 s?
Question 8
a. Explain briefly how transmission of energy by a longitudinal wave differs from transmission of energy by a transverse wave. Give one example of a transverse wave.
b. With the aid of a clearly labelled diagram explain how a sound wave in air transmits energy away from its source.
c. Short pulses of sound are reflected from a wall 30 m from the sound source. The reflected pulses return to the source after 0.18 s. Calculate the speed of sound.
d. Figure represents the sound wave from part c.
 Calculate the frequency of the sound wave.
Calculate the frequency of the sound wave.
Question 9
Sound travels with a speed of 330 ms in air. The variation with time of the displacement of an air particle due to a sound wave is shown below. Which of the following statements about the wave is correct?
Which of the following statements about the wave is correct?
A. The wavelength of the sound wave is 1.32 m.
B. The graph shows that the sound is a transverse wave.
C. The frequency of the wave is 500 Hz.
D. The intensity of the wave will be doubled if its amplitude is increased to 0.4 mm.
Question 10
Two particles in a progressive wave are a distance 10 cm apart. The two graphs show the variation with time t of the displacement d of the two particles. What could be represented by the two graphs?
What could be represented by the two graphs?
A. Particles in a longitudinal wave with a compression and the nearest rarefaction separated by 10 cm.
B. Particles in a longitudinal wave with a compression and the nearest rarefaction separated by 20 cm.
C. Particles in a transverse wave with a peak and the nearest trough separated by 20 cm.
D. Particles in a transverse wave with two adjacent peaks separated by 10 cm.