Question 1
What property of water leads to aquatic environments having low fluctuations of temperature throughout the year?
A. High specific heat capacity because covalent bonding restricts molecular motion
B. Low specific heat capacity because covalent bonding restricts molecular motion
C. Low specific heat capacity because hydrogen bonding restricts molecular motion
D. High specific heat capacity because hydrogen bonding restricts molecular motion
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Water shows strong cohesive properties. Which of the following can occur because of the cohesive properties of water?
A. Water can be pulled up a plant through the xylem.
B. Enzymes can react with their substrates in cells.
C. Sweating cools the body on a hot day.
D. Salt can dissolve in seawater.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which property of water allows the insect to walk on water?

A. Adhesion.
B. Capillarity.
C. Surface tension.
D. Transparency.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
What describes bonding within a water molecule?
A. Hydrogen bonding due to transfer of electrons.
B. Double bonds due to equal sharing of electrons.
C. Non-polar covalent bonding due to equal sharing of electrons.
D. Polar covalent bonding due to unequal sharing of electrons.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Which symbol indicates the polarity of the oxygen atom in the water molecule?
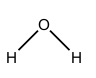
A. `δ⁻`
B. `δ⁺`
C. `+`
D. `–`
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Which characteristic of water vapour classifies it as a greenhouse gas?
A. It absorbs and then re-emits some of the long-wave radiation emitted by the Earth’s surface.
B. It prevents short-wave radiation from reaching the Earth’s surface
C. It absorbs UV radiation but does not re-emit it.
D. It absorbs infra-red radiation but does not re-emit it.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Which planet in the table falls within the “Goldilocks zone” and may be capable of sustaining extraterrestrial life?
| Planet | Temperature/°C | Atmosphere | Gravity / g | |
| A. | Kepler-22b | -11 to 16 | unknown | 2.4 |
| B. | WASP-39b | 750 | hydrogen, helium and other elements | 25.0 |
| C. | Gliese 876d | 50 to 80 | high levels of toxic gases | 20.0 |
| D. | Kepler-16b | -100 | unknown | 0.9 |
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What characteristic(s) of water allow(s) effective transport of nutrients around the body by blood?
I. Solvent properties
II. Thermal capacity
III. Transparency
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II, and III
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Describe four properties of water that are due to hydrogen bonding and polarity. [4]
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Outline how the properties of water make it an ideal transport medium in plants. [4]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
What property of water leads to aquatic environments having low fluctuations of temperature throughout the year?
A. High specific heat capacity because covalent bonding restricts molecular motion
B. Low specific heat capacity because covalent bonding restricts molecular motion
C. Low specific heat capacity because hydrogen bonding restricts molecular motion
D. High specific heat capacity because hydrogen bonding restricts molecular motion
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. Although water has a high specific heat capacity, the main mechanism is due to hydrogen bonds (which occur between water molecules), not covalent bonds (which occur within a single water molecule).
B, C. Incorrect. Water has a relatively high specific heat capacity, not a low one. The high specific heat capacity is the reason why the temperature of aquatic environments remains stable.
Question 2
Water shows strong cohesive properties. Which of the following can occur because of the cohesive properties of water?
A. Water can be pulled up a plant through the xylem.
B. Enzymes can react with their substrates in cells.
C. Sweating cools the body on a hot day.
D. Salt can dissolve in seawater.
Answer: A
A. Correct. Cohesion is the attraction between water molecules. This property creates a continuous column of water in the plant’s xylem, allowing water to be pulled upward from the roots to the leaves through transpiration pull.
B. Incorrect. Enzymatic reactions are mainly related to the solvent properties of water, which provides a liquid medium for dissolved substances to interact.
C. Incorrect. Cooling occurs due to water’s high latent heat of vaporization, a thermal property of water, although it is caused by hydrogen bonding.
D. Incorrect. Dissolution (solvation) results from water’s polarity, which makes it an effective solvent.
Question 3
Which property of water allows the insect to walk on water?

A. Adhesion.
B. Capillarity.
C. Surface tension.
D. Transparency.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Adhesion is the attraction between water and other solid surfaces.
B. Incorrect. Capillarity (capillary action) is the tendency of water to move upward in narrow tubes.
C. Correct. The strong cohesive forces between water molecules at the surface create very high surface tension, higher than any other liquid except mercury. This surface tension acts like an elastic membrane, strong enough to support the weight of small organisms (such as pond skaters) and prevent them from breaking through the water’s surface.
D. Incorrect. This optical property is unrelated to the ability to move across the water’s surface.
Question 4
What describes bonding within a water molecule?
A. Hydrogen bonding due to transfer of electrons.
B. Double bonds due to equal sharing of electrons.
C. Non-polar covalent bonding due to equal sharing of electrons.
D. Polar covalent bonding due to unequal sharing of electrons.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. A hydrogen bond is an intermolecular bond (between molecules), not an intramolecular one.
B. Incorrect. The bonds are single, and the sharing is unequal (polar).
C. Incorrect. The sharing is unequal (polar).
D. Correct. The intramolecular bond within a water molecule is a polar covalent bond because oxygen attracts electrons more strongly than hydrogen, leading to unequal sharing.
Question 5
Which symbol indicates the polarity of the oxygen atom in the water molecule?

A. `δ⁻`
B. `δ⁺`
C. `+`
D. `–`
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. This symbol represents a slight positive charge, which belongs to the hydrogen atoms.
B. Correct. The water molecule is polar. The oxygen nucleus attracts the electrons (which carry a negative charge) from the hydrogen nuclei. This causes the oxygen atom to have a slight negative charge (`δ−`).
C, D. Incorrect. These symbols represent full charges (ions), not partial charges in a polar molecule.
Question 6
Which characteristic of water vapour classifies it as a greenhouse gas?
A. It absorbs and then re-emits some of the long-wave radiation emitted by the Earth’s surface.
B. It prevents short-wave radiation from reaching the Earth’s surface
C. It absorbs UV radiation but does not re-emit it.
D. It absorbs infra-red radiation but does not re-emit it.
Answer: A
A. Correct: Water vapor is one of the most important greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases are substances that absorb and emit infrared radiation. The greenhouse effect works as follows: shortwave radiation (from the Sun) mostly passes through the atmosphere and warms the Earth’s surface. When the Earth’s surface warms, it emits longwave (infrared) radiation back toward space. Greenhouse gases, including water vapor, absorb this longwave radiation, become heated, and then re-emit infrared radiation (i.e., heat) in all directions, warming the atmosphere and trapping heat on Earth.
B. Incorrect. The greenhouse effect depends on the fact that shortwave radiation (mainly visible light, along with ultraviolet (UV) and shorter-wavelength infrared) passes through most of the atmosphere to warm the land and oceans.
C. Incorrect. Although UV radiation is harmful to living tissues, it is mainly absorbed by the ozone layer, not by water vapor (a greenhouse gas). Furthermore, greenhouse gases must both absorb and re-emit infrared radiation to contribute to the greenhouse effect.
D. Incorrect. Greenhouse gases absorb longwave (infrared) radiation. However, to produce the greenhouse effect and warm the atmosphere, they must re-emit the absorbed thermal energy. Without re-emission, heat trapping as described in the greenhouse effect would not occur.
Question 7
Which planet in the table falls within the “Goldilocks zone” and may be capable of sustaining extraterrestrial life?
| Planet | Temperature/°C | Atmosphere | Gravity / g | |
| A. | Kepler-22b | -11 to 16 | unknown | 2.4 |
| B. | WASP-39b | 750 | hydrogen, helium and other elements | 25.0 |
| C. | Gliese 876d | 50 to 80 | high levels of toxic gases | 20.0 |
| D. | Kepler-16b | -100 | unknown | 0.9 |
Answer: A
A. Correct. This temperature range (`−11°C` to `16°C`) includes temperatures at which water can exist in a liquid state. Although the minimum temperature is `−11°C` (below the freezing point), the maximum temperature of `16°C` lies comfortably within the range that allows liquid water to exist. This planet is located in the “Goldilocks zone” and is capable of sustaining liquid water.
B. Incorrect. A temperature of `750°C` is far too hot. Water would completely boil and evaporate at this temperature, even under high pressure.
C. Incorrect. Although this range falls within the limits where liquid water could exist (`0 –100°C`), this planet is reported to have high levels of toxic gases, which would seriously hinder its ability to support life. Such a toxic atmosphere would exceed the tolerance limits of biological systems.
D. Incorrect. A temperature of `−100°C` is far too cold. Water would freeze completely at this temperature and could not exist in liquid form.
Question 8
What characteristic(s) of water allow(s) effective transport of nutrients around the body by blood?
I. Solvent properties
II. Thermal capacity
III. Transparency
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II, and III
Answer: A
I. Solvent properties: Water is a powerful solvent for polar (hydrophilic) substances such as ions and sugars (e.g., glucose). These substances dissolve in blood (an aqueous solution) and are transported throughout the body
II.Thermal capacity: Water has a high specific heat capacity. The large amount of water in blood allows it to carry heat from heat-producing areas (such as contracting muscles) to areas that need to release heat, helping to regulate body temperature.
III. Transparency: This property is unrelated to the transport of nutrients or heat.
Therefore, A. I only is correct.
Question 9
Describe four properties of water that are due to hydrogen bonding and polarity. [4]
Descriptions of properties expected not lists of properties.
Hydrogen bonding: (any two of the following):
a. High specific heat capacity requiring large amounts of energy to break the H-bonds/to raise the temperature;
b. Boiling point is high/`100 °C` as H-bonds must be broken to change from liquid to gas; cooling effect of evaporation due to H-bonds taking energy from liquid water to break / high latent heat of evaporation;
c. water molecules on the surface are resistant to forces because of surface tension;
d. water is most dense at`4 °C` due to more regular hydrogen bonding;
Polarity:
e. Water molecules stick together through cohesion; (full idea required)
f. Water molecules stick to other polar molecules through adhesion; good solvent for polar organic molecules (full idea required)
Sample answer:
- Water has a relatively high specific heat capacity. This means a large amount of energy is required to raise its temperature. The supplied energy must be used to break the numerous hydrogen bonds that hold the water molecules together and restrict their movement [1]. This property helps maintain a more stable temperature in aquatic environments compared to terrestrial ones.
- Water has a high latent heat of evaporation [1]. For water to change from liquid to vapor (evaporation), its molecules must break the hydrogen bonds with neighboring water molecules. This process absorbs a large amount of heat energy from the remaining liquid or the surrounding surface, producing a strong cooling effect.
- Water molecules stick tightly to each other due to cohesive forces [1]. This occurs because of the strong hydrogen bonds formed between polar water molecules. The cohesive force allows a column of water to resist tension, enabling it to be pulled upward through the xylem vessels of plants to replace water lost through transpiration (the transpiration pull).
- Water is an excellent solvent for polar substances and ionic compounds. Because of its polarity, the oxygen end (`δ⁻`) of the water molecule is attracted to positive ions (cations), while the hydrogen end (`δ⁺`) is attracted to negative ions (anions). Water forms a hydration shell around these solute particles, keeping them dispersed and preventing them from clumping together. This allows water to efficiently transport many essential substances (such as glucose and mineral salts) within living organisms [1].
Question 10
Outline how the properties of water make it an ideal transport medium in plants. [4]
Any four of the following:
a. polarity of water;
b.hydrogen bonds between water molecules;
c. cohesion between water molecules/water molecules stick together;
d. cohesion allows tensions/low pressures/transpiration pull/movement upward/against gravity;
e. adhesion to cellulose/cell walls generates tensions/pull (in xylem)
OR
adhesion to xylem walls/vessel walls causes capillary rise/upward movement;
f. solvent for many substances / many substances dissolve;
g. liquid at most temperatures experienced by plants / liquid so can flow;
Sample answer:
- Polarity of water: The water molecule is a polar molecule, with the oxygen atom carrying a partial negative charge (`δ−`) and the hydrogen atoms carrying partial positive charges (`δ+`) [1]
- Hydrogen bonding: This polarity creates attractive forces between the partially positive hydrogen atom of one molecule and the partially negative oxygen atom of a neighboring water molecule, forming hydrogen bonds [1]
- Cohesion: Due to hydrogen bonding, water molecules exhibit strong mutual attraction, causing them to “stick together.” This property is known as cohesion [1]
- Cohesion-driven water transport: This strong cohesive force allows the column of water in the xylem to withstand high tension (or low pressure) without breaking. Cohesion is the basis for the transpiration pull, which enables water to be drawn upward against gravity from the roots to the leaves [1]
Question 1
What property of water leads to aquatic environments having low fluctuations of temperature throughout the year?
A. High specific heat capacity because covalent bonding restricts molecular motion
B. Low specific heat capacity because covalent bonding restricts molecular motion
C. Low specific heat capacity because hydrogen bonding restricts molecular motion
D. High specific heat capacity because hydrogen bonding restricts molecular motion
Question 2
Water shows strong cohesive properties. Which of the following can occur because of the cohesive properties of water?
A. Water can be pulled up a plant through the xylem.
B. Enzymes can react with their substrates in cells.
C. Sweating cools the body on a hot day.
D. Salt can dissolve in seawater.
Question 3
Which property of water allows the insect to walk on water?

A. Adhesion.
B. Capillarity.
C. Surface tension.
D. Transparency.
Question 4
What describes bonding within a water molecule?
A. Hydrogen bonding due to transfer of electrons.
B. Double bonds due to equal sharing of electrons.
C. Non-polar covalent bonding due to equal sharing of electrons.
D. Polar covalent bonding due to unequal sharing of electrons.
Question 5
Which symbol indicates the polarity of the oxygen atom in the water molecule?

A. `δ⁻`
B. `δ⁺`
C. `+`
D. `–`
Question 6
Which characteristic of water vapour classifies it as a greenhouse gas?
A. It absorbs and then re-emits some of the long-wave radiation emitted by the Earth’s surface.
B. It prevents short-wave radiation from reaching the Earth’s surface
C. It absorbs UV radiation but does not re-emit it.
D. It absorbs infra-red radiation but does not re-emit it.
Question 7
Which planet in the table falls within the “Goldilocks zone” and may be capable of sustaining extraterrestrial life?
| Planet | Temperature/°C | Atmosphere | Gravity / g | |
| A. | Kepler-22b | -11 to 16 | unknown | 2.4 |
| B. | WASP-39b | 750 | hydrogen, helium and other elements | 25.0 |
| C. | Gliese 876d | 50 to 80 | high levels of toxic gases | 20.0 |
| D. | Kepler-16b | -100 | unknown | 0.9 |
Question 8
What characteristic(s) of water allow(s) effective transport of nutrients around the body by blood?
I. Solvent properties
II. Thermal capacity
III. Transparency
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II, and III
Question 9
Describe four properties of water that are due to hydrogen bonding and polarity. [4]
Question 10
Outline how the properties of water make it an ideal transport medium in plants. [4]