Question 1
What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses?
A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation.
B. Viruses have no RNA.
C. Viruses have no metabolism.
D. Viruses have a protein shell that protects them.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Which sequence shows increasing relative size?
| Smallest `->`Largest | |||
| A. | membrane thickness | virus | bacterium |
| B. | molecule | virus | membrane thickness |
| C. | bacterium | virus | eukaryotic cell |
| D. | bacterium | organelle | virus |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
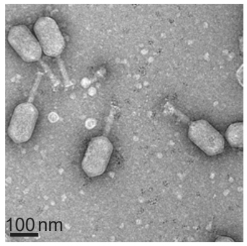
The image shows an electron micrograph of virus particles known to infect the bacterium Vibrio parahaemolyticus, which is associated with gastroenteritis, wound infections and septicemia in humans and animals.
What does a virus have in common with living cells?
A. 70S ribosomes
B. Genetic material
C. Reproduction by binary fission
D. Anaerobic respiration
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
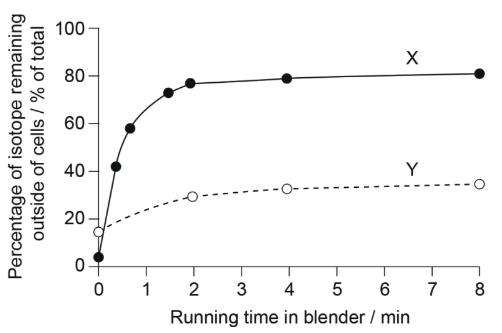
The graph shows results of an experiment by Hershey and Chase in 1952 in which bacteria were infected with a mixture of virus particles labelled with either 32P or 35S. A suspension of the infected bacteria was agitated with a blender, and samples collected from the suspension were centrifuged to record the percentage of isotope remaining on the outside of the cells.
What do curves X and Y represent?
| Curve X | Curve Y | |
| A. | 32P in sediment | 35S in supernatant |
| B. | 35S in supernatant | 32P in supernatant |
| C. | 32P in supernatant | 35S in sediment |
| D. | 35S in sediment | 32P in sediment |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
What is a difference between the lytic and the lysogenic cycle of the bacteriophage lambda?
A. Only in the lytic cycle is lambda DNA inserted into the host DNA.
B. Only in the lysogenic cycle is the host metabolism used to replicate.
C. Only in the lytic cycle is the host metabolism used to replicate.
D. Only in the lysogenic cycle is lambda DNA inserted into the host DNA.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
What is a reason for the ineffectiveness of antibiotics against viruses?
A. Viruses have genes for antibiotic resistance.
B. Viruses do not have cell membranes.
C. Antibiotics are only effective against archaea.
D. Antibiotics target metabolic processes.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
List two structural features that vary among viruses. [2]
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
State a virus that produces reverse transcriptase.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
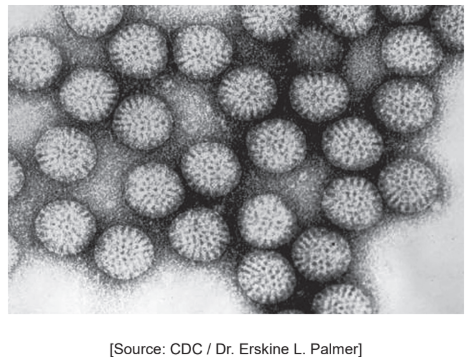
The figure shows a transmission electron micrograph of rotavirus particles. Each rotavirus is
about 70 nanometers in diameter. [3]
(a) State a reason for using an electron microscope to view this virus rather than a light microscope. [1]
(b) Rotavirus causes diarrhea and vomiting. Explain why viral diseases cannot be treated using antibiotics. [2]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
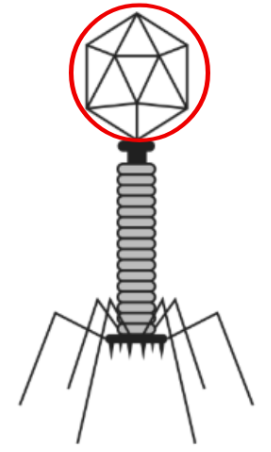
The diagram shows the structure of a bacteriophage lambda virus. [5]
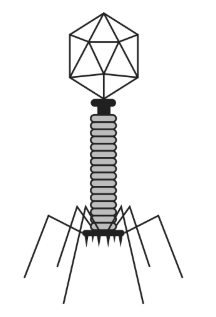
(a) On the image, label the capsid. [1]
(b) Describe one reason that viruses are not considered to be living.[1]
(c) Explain how the bacteriophage lambda reproduces in the lysogenic cycle.[3]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses?
A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation.
B. Viruses have no RNA.
C. Viruses have no metabolism.
D. Viruses have a protein shell that protects them.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: Indeed, viruses do have a high rate of mutation, however, this only affects the effectiveness of antiviral medications and vaccines. The question asked about the mechanism actions of antibiotics; therefore, this answer is irrelevant.
B. Incorrect: Many viruses have RNA as their genetic material, such as Coronaviruses, Hepatitis C virus and Orthomyxoviridae.
C. Correct: Antibiotics work by disrupting specific structures or metabolic processes such as cell wall synthesis and protein production. Viruses do not have these machinery or structures; they rely on the host cells to reproduce. Therefore, antibiotics are ineffective against viruses.
D. Incorrect: Viruses do have capsids that enclose their genetic material. However, capsids are not the target of antibiotics.
Question 2
Which sequence shows increasing relative size?
| Smallest `->`Largest | |||
| A. | membrane thickness | virus | bacterium |
| B. | molecule | virus | membrane thickness |
| C. | bacterium | virus | eukaryotic cell |
| D. | bacterium | organelle | virus |
Answer: A
A. Correct. The size of the membrane is 7-10nm, viruses are 50-200nm and bacteria are 1000-5000nm.
B. Incorrect. The size of molecules are about 1nm, the size of the membrane is 7-10nm, and viruses are 50-200nm. Meaning molecule < membrane < virus.
C. Incorrect. The size of bacteria are 1-5μm, viruses are 50-200nm (0.05-0.2μm) and eukaryote cells are 10-100μm. Meaning virus < bacteria < eukaryote cell.
D. Incorrect. The size of bacteria are 1-5μm, organelles are 0.1-10μm depending on the organelles, and viruses are 0.05-0.2μm. Meaning virus < organelle ~ bacterium (depend on the organelles).
Question 3
The image shows an electron micrograph of virus particles known to infect the bacterium Vibrio parahaemolyticus, which is associated with gastroenteritis, wound infections and septicemia in humans and animals.

What does a virus have in common with living cells?
A. 70S ribosomes
B. Genetic material
C. Reproduction by binary fission
D. Anaerobic respiration
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. 70S ribosomes are found in prokaryotic cells, not viruses. Viruses cannot synthesize proteins and require host cells for protein production.
B. Correct. Both viruses and living cells need genetic material (DNA/RNA) to carry information for reproduction and function.
C. Incorrect. Binary fission is how bacteria reproduce. Viruses use host cell machinery to make copies of themselves.
D. Incorrect. Viruses do not have metabolic pathways, and do not use anaerobic respiration to produce energy.
Question 4
The graph shows results of an experiment by Hershey and Chase in 1952 in which bacteria were infected with a mixture of virus particles labelled with either 32P or 35S. A suspension of the infected bacteria was agitated with a blender, and samples collected from the suspension were centrifuged to record the percentage of isotope remaining on the outside of the cells.

What do curves X and Y represent?
| Curve X | Curve Y | |
| A. | 32P in sediment | 35S in supernatant |
| B. | 35S in supernatant | 32P in supernatant |
| C. | 32P in supernatant | 35S in sediment |
| D. | 35S in sediment | 32P in sediment |
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. The sample is collected from outside of the cell, meaning, in the supernatant. Therefore, curve X cannot represent 32P in the sediment.
B. Correct. 32P is used to label DNA and 35S is used to label protein. The viral protein stayed outside of the cell, meaning, higher percentage of 35S in the supernatant. The viral DNA is delivered inside the cell, meaning a lower percentage of 32P in the supernatant.
C. Incorrect. The sample is collected from outside of the cell, meaning, in the supernatant. Therefore, curve Y cannot represent 35S in the sediment.
D. Incorrect. The sample is collected from outside of the cell, meaning, in the supernatant. Therefore, curve X cannot represent 35S in the sediment and curve Y cannot represent 32P in the sediment.
Question 5
What is a difference between the lytic and the lysogenic cycle of the bacteriophage lambda?
A. Only in the lytic cycle is lambda DNA inserted into the host DNA.
B. Only in the lysogenic cycle is the host metabolism used to replicate.
C. Only in the lytic cycle is the host metabolism used to replicate.
D. Only in the lysogenic cycle is lambda DNA inserted into the host DNA.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. In the lytic cycle, viral DNA is not inserted into the host DNA but remains separated and uses the host machinery to reproduce, until the cell lyses.
B. Incorrect. Both lytic and lysogenic cycles use the host metabolism to replicate.
C. Incorrect. Both lytic and lysogenic cycles use the host metabolism to replicate.
D.Correct. In the lysogenic cycle, viral DNA is inserted into the host DNA, becoming a prophage and remains dormant until switching to the lytic cycle.
Question 6
What is a reason for the ineffectiveness of antibiotics against viruses?
A. Viruses have genes for antibiotic resistance.
B. Viruses do not have cell membranes.
C. Antibiotics are only effective against archaea.
D. Antibiotics target metabolic processes.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. Viruses do not have genes for antibiotic resistance, they are found in bacteria.
B. Incorrect. Some viruses have cell membranes, some do not. However, antibiotics attack metabolic pathways, which viruses lack.
C. Incorrect. Antibiotics are effective against bacteria, not archaea.
D. Correct. Antibiotics only target metabolic pathways found in bacteria such as DNA synthesis, protein synthesis and cell wall synthesis. Bacteria do not have those, therefore, antibiotics are ineffective against viruses.
Question 7
List two structural features that vary among viruses. [2]
Any two of the following:
a. Capsid / naked or enveloped capsid;
b. Nucleic acid / DNA or RNA;
c. Number of strands on nucleic acid / single or double strands;
Sample answer:
Structures vary among viruses:
- Genetic material: Viruses can use both DNA and RNA as their genetic material.
- The nucleic acid can be both single strand or double strands.
Question 8
State a virus that produces reverse transcriptase.
Any one of the following:
Retrovirus/HIV/RNA virus/Hepatitis B virus/any other example
Sample answer:
Retrovirus
Question 9
The figure shows a transmission electron micrograph of rotavirus particles. Each rotavirus is
about 70 nanometers in diameter. [3]

(a) State a reason for using an electron microscope to view this virus rather than a light microscope. [1]
(b) Rotavirus causes diarrhea and vomiting. Explain why viral diseases cannot be treated using antibiotics. [2]
(a) Any one of the following:
Electron microscopes electron microscope has greater resolution/ magnification/
70nm is too small/ viruses are too small to be viewed by a light microscope.
Sample answer:
We use electron microscopes to see the rotavirus particle, which is 70nm in diameter because electron microscopes have better resolution and see smaller structure [1]. Light microscopes with lower resolution can only view structures more than 200nm in size.
(b) Any two of the following:
a. viruses are not living
b. viruses lack metabolism/lack enzymes for metabolism/lack cell walls
c. antibiotics target metabolic «pathways»/cell wall production
Sample answer:
We can not use antibiotics for viral infections because viruses are not living things, they require host cells for reproduction [1]. Antibiotics work by targeting structure and metabolic processes found in bacteria, such as DNA synthesis, protein synthesis or cell wall synthesis [1]. Viruses lack these pathways, therefore, antibiotics are ineffective against viruses [1].
Question 10
The diagram shows the structure of a bacteriophage lambda virus. [5]

(a) On the image, label the capsid. [1]
(b) Describe one reason that viruses are not considered to be living.[1]
(c) Explain how the bacteriophage lambda reproduces in the lysogenic cycle.[3]
(a)
(b) Any one of the following:
a. (Viruses) do not have a metabolism of their own (rely on a host cell for chemical processes) / cannot carry out transcription/protein synthesis / cannot perform ATP synthesis.
b. They are not made of cells (but consist only of a nucleic acid core and protein coat/capsid).
c. They do not carry out all reproduction but only multiply inside other living cells.
Sample answer:
Viruses are not considered living because they cannot reproduce on their own, they need to infect host cells, to hijack their machinery for reproduction [1].
(c) Any three of the following:
a. The virus attaches to maltoporin/protein in the host/bacterium membrane.
b. The viral DNA/genome is integrated into a host/bacterium.
c. When the host DNA replicates/does mitosis, viral DNA is also replicated.
d. All daughter cells contain viral DNA/genetic material.
e. The inserted DNA is known as a prophage.
f. Bacteriophage/prophage remains in dormant state in host/bacterium or later prophage may exit to initiate lytic cycle.
Sample answer:
In the lysogenic cycle, the lambda bacteriophage reproduces by attaching itself to the bacterium membrane and delivers its DNA inside the host cell [1]. The viral DNA is integrated into the host DNA, called prophage. When the host replicates, the virus also replicates and all of its DNA is present inside the daughter cells. [1]. The prophage remains dormant inside the host and can later initiate lytic cycle [1].
Question 1
What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses?
A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation.
B. Viruses have no RNA.
C. Viruses have no metabolism.
D. Viruses have a protein shell that protects them.
Question 2
Which sequence shows increasing relative size?
| Smallest `->`Largest | |||
| A. | membrane thickness | virus | bacterium |
| B. | molecule | virus | membrane thickness |
| C. | bacterium | virus | eukaryotic cell |
| D. | bacterium | organelle | virus |
Question 3
The image shows an electron micrograph of virus particles known to infect the bacterium Vibrio parahaemolyticus, which is associated with gastroenteritis, wound infections and septicemia in humans and animals.

What does a virus have in common with living cells?
A. 70S ribosomes
B. Genetic material
C. Reproduction by binary fission
D. Anaerobic respiration
Question 4
The graph shows results of an experiment by Hershey and Chase in 1952 in which bacteria were infected with a mixture of virus particles labelled with either 32P or 35S. A suspension of the infected bacteria was agitated with a blender, and samples collected from the suspension were centrifuged to record the percentage of isotope remaining on the outside of the cells.

What do curves X and Y represent?
| Curve X | Curve Y | |
| A. | 32P in sediment | 35S in supernatant |
| B. | 35S in supernatant | 32P in supernatant |
| C. | 32P in supernatant | 35S in sediment |
| D. | 35S in sediment | 32P in sediment |
Question 5
What is a difference between the lytic and the lysogenic cycle of the bacteriophage lambda?
A. Only in the lytic cycle is lambda DNA inserted into the host DNA.
B. Only in the lysogenic cycle is the host metabolism used to replicate.
C. Only in the lytic cycle is the host metabolism used to replicate.
D. Only in the lysogenic cycle is lambda DNA inserted into the host DNA.
Question 6
What is a reason for the ineffectiveness of antibiotics against viruses?
A. Viruses have genes for antibiotic resistance.
B. Viruses do not have cell membranes.
C. Antibiotics are only effective against archaea.
D. Antibiotics target metabolic processes.
Question 7
List two structural features that vary among viruses. [2]
Question 8
State a virus that produces reverse transcriptase.
Question 9
The figure shows a transmission electron micrograph of rotavirus particles. Each rotavirus is
about 70 nanometers in diameter. [3]

(a) State a reason for using an electron microscope to view this virus rather than a light microscope. [1]
(b) Rotavirus causes diarrhea and vomiting. Explain why viral diseases cannot be treated using antibiotics. [2]
Question 10
The diagram shows the structure of a bacteriophage lambda virus. [5]

(a) On the image, label the capsid. [1]
(b) Describe one reason that viruses are not considered to be living.[1]
(c) Explain how the bacteriophage lambda reproduces in the lysogenic cycle.[3]