Question 1
The diploid number of chromosomes in humans (Homo sapiens) is 46 and the diploid number of chromosomes in rice (Oryza sativa) is 24. What does this indicate about diploid chromosome numbers?
A. Plant species have a lower diploid number of chromosomes than animals.
B. Members of a species have the same diploid number of chromosomes.
C. The evolutionary progress of species is determined by the diploid number of chromosomes.
D. The complexity of the organisms is correlated to the diploid number of chromosomes.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Which is a source of chromosomes for pre-natal diagnosis of abnormalities by karyotyping?
A. Sperm.
B. Ovaries.
C. Erythrocytes.
D. Chorionic villi.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
A collection of four animal specimens is observed and a dichotomous key is applied. Which specimen is an arthropod?
1. Non-segmented body .................................go to 2
Segmented body .........................................go to 3
2. Body is not symmetrical ............................... specimen A
Body is symmetrical ………………………...specimen B
3. Jointed appendages present ............................. specimen C
Jointed appendages absent ............................. specimen D
A. Specimen A.
B. Specimen B.
C. Specimen C.
D. Specimen D.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
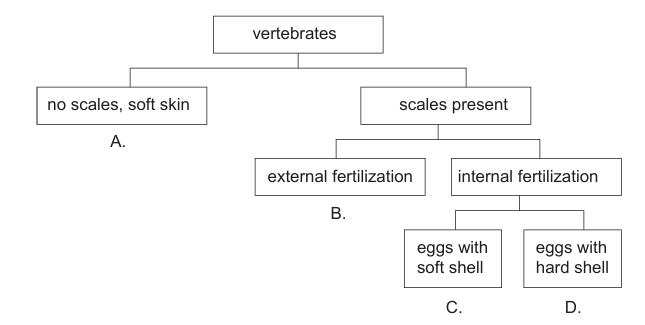
The dichotomous key shows general features of four vertebrate classes. Which letter identifies most fish?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
What determines the genomic size of a species?
A. The total amount of DNA
B. The total number of genes
C. The total number of alleles
D. The total number of chromosomes
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
A pregnant woman had fetal cells removed by chorionic villus sampling and tested. The following karyogram was produced?
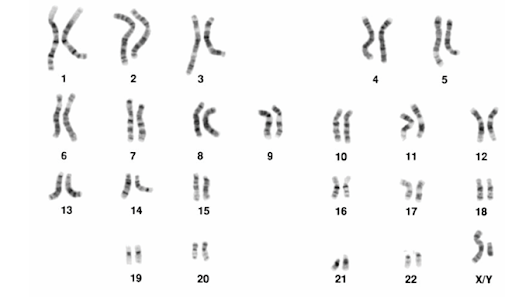
[Source: Mediscan / Alamy Stock Photo]
What does this show?
A. The child is female with Down syndrome.
B. The child is female without Down syndrome.
C. The child is male with Down syndrome.
D. The child is male without Down syndrome.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
The salamander genus Ensatina from California, USA, has evolved several different forms, depending on location. Two such forms are shown.

What determines if these forms are members of the same species?
A. Have similar appearance
B. Populations mix freely
C. Produce fertile offspring
D. Can interbreed
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What is one application of DNA barcoding?
A. Selective breeding
B. Preserving an endangered species
C. Analysing environmental DNA
D. Sequencing a genome
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Genes such as the one coding for CTP1 can be located by searching for open reading frames. Outline how open reading frames are identified. [3]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Explain how online databases can be used to investigate the functions of a newly discovered protein. [6]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
The diploid number of chromosomes in humans (Homo sapiens) is 46 and the diploid number of chromosomes in rice (Oryza sativa) is 24. What does this indicate about diploid chromosome numbers?
A. Plant species have a lower diploid number of chromosomes than animals.
B. Members of a species have the same diploid number of chromosomes.
C. The evolutionary progress of species is determined by the diploid number of chromosomes.
D. The complexity of the organisms is correlated to the diploid number of chromosomes.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Chromosome number varies widely and does not distinguish plants from animals. Some plants have very high chromosome numbers due to polyploidy.
B. Correct. Each species has a characteristic and stable chromosome number. Humans always have 46; rice always has 24. Chromosome number is consistent within a species, but can vary between species.
C. Incorrect. Chromosome number does not reflect evolutionary advancement. Less complex organisms can have more chromosomes.
D. Incorrect. Chromosome number does not correlate with complexity; e.g., some ferns have hundreds of chromosomes.
Question 2
Which is a source of chromosomes for pre-natal diagnosis of abnormalities by karyotyping?
A. Sperm.
B. Ovaries.
C. Erythrocytes.
D. Chorionic villi.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. Sperm are haploid and not suitable for karyotyping, which requires diploid chromosomes to observe homologous pairs.
B. Incorrect. Ovarian tissue is not sampled for prenatal chromosome analysis.
C. Incorrect. Mammalian erythrocytes lack a nucleus, so they contain no chromosomes and cannot be karyotyped..
D. Correct. Chorionic villi contain diploid fetal cells, which allow construction of a karyogram.
Question 3
A collection of four animal specimens is observed and a dichotomous key is applied. Which specimen is an arthropod?
1. Non-segmented body .................................go to 2
Segmented body .........................................go to 3
2. Body is not symmetrical ............................... specimen A
Body is symmetrical ………………………...specimen B
3. Jointed appendages present ............................. specimen C
Jointed appendages absent ............................. specimen D
A. Specimen A.
B. Specimen B.
C. Specimen C.
D. Specimen D.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. This specimen is identified as: Non-segmented body → go to 2.
Then, body not symmetrical → specimen A.
Because arthropods have segmented bodies and bilateral symmetry
B. Incorrect. This specimen is identified as: Non-segmented body → go to 2.
Then, symmetrical body → specimen B. Since arthropods must have segmented bodies.
C. Correct. This specimen is identified as: Segmented body → go to 3.
Then, jointed appendages present → specimen C.
These are defining characteristics of arthropods.
D. Incorrect. This specimen is identified as: Segmented body → go to 3.
Then, jointed appendages absent → specimen D.
Although the body is segmented, the lack of jointed appendages rules out arthropods (since they must have jointed limbs).
Question 4
The dichotomous key shows general features of four vertebrate classes. Which letter identifies most fish?

Answer: B
Therefore, the path that identifies most fish is: Vertebrates → Scales present → External fertilization.
Question 5
What determines the genomic size of a species?
A. The total amount of DNA
B. The total number of genes
C. The total number of alleles
D. The total number of chromosomes
Answer: A
A. Correct. Genome size is defined as the total amount of DNA in one complete genome.
B. Incorrect. Gene count does not determine genome size; much of the genome is non-coding DNA.
C. Incorrect. Alleles reflect variation in a population, not the physical size of the genome.
D. Incorrect. Chromosome number is about DNA packaging and does not correlate with total DNA amount.
Question 6
A pregnant woman had fetal cells removed by chorionic villus sampling and tested. The following karyogram was produced?

[Source: Mediscan / Alamy Stock Photo]
What does this show?
A. The child is female with Down syndrome.
B. The child is female without Down syndrome.
C. The child is male with Down syndrome.
D. The child is male without Down syndrome.
Answer: D
Analyze the karyogram:
Question 7
The salamander genus Ensatina from California, USA, has evolved several different forms, depending on location. Two such forms are shown.

What determines if these forms are members of the same species?
A. Have similar appearance
B. Populations mix freely
C. Produce fertile offspring
D. Can interbreed
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. This criterion (also known as the Morphological Species Concept) is often subjective and not a primary biological criterion, because large differences in appearance can still occur within the same species (for example: sexual dimorphism or other morphological variations such as in Poodles and Chihuahuas, which are both Canis familiaris, or color variations in the jaguar Panthera onca).
B. Incorrect. Free mixing only describes gene flow, but it is the ability to produce fertile offspring that determines whether such mixing is genetically successful in maintaining the integrity of a species.
C. Correct. This is the key component of the biological species concept. The definition of a biological species is a group of organisms that can naturally interbreed and produce viable, fertile offspring. The "fertile" part is crucial; it means the offspring can also reproduce and continue the lineage.
D. Incorrect. The ability to interbreed is necessary but not sufficient. If individuals of two different species mate (hybridization) and produce sterile offspring, they are still considered separate species.
Question 8
What is one application of DNA barcoding?
A. Selective breeding
B. Preserving an endangered species
C. Analysing environmental DNA
D. Sequencing a genome
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. This is a process in which humans intentionally alter a population. Although DNA techniques (such as DNA profiling) can be used to track lineage, DNA barcoding mainly focuses on identifying species for classification and surveying, which is not the goal of selective breeding.
B. Incorrect. DNA barcoding is a supporting tool in conservation because it helps identify species that are difficult to distinguish. However, analyzing eDNA is a direct technical application of barcoding, whereas “preservation” is a broader ecological goal.
C. Correct. eDNA is DNA collected from non-living environmental materials such as water, soil, or any other part of the abiotic environment. By using DNA barcoding to analyze eDNA, scientists can quickly identify species that have interacted with the sampled environment. This allows rapid assessment of biodiversity within a habitat.
D. Incorrect. DNA barcoding involves sequencing only a short region from a specific gene (e.g., the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase I gene in most animals). It does not involve determining the full base sequence of an entire genome (genome sequencing).
Question 9
Genes such as the one coding for CTP1 can be located by searching for open reading frames. Outline how open reading frames are identified. [3]
Any three of the following:
a. a DNA sequence with a promoter, a start and a stop codon;
b. start codon is ATG;
c. stop codon is TAA/TAG/TGA;
d. nucleotide sequence with a considerable length;
e. named bioinformatics software OR ORF finder;
Sample answer:
Open reading frames (ORFs) are identified by analyzing a DNA sequence that contains a promoter, a start codon, and a stop codon. The start codon is typically ATG [1], which signals the beginning of translation, while stop codons such as TAA, TAG, or TGA [1] indicate the end of the coding sequence. To locate ORFs efficiently, bioinformatic tools such as ORF Finder can be used to scan the nucleotide sequence for stretches of DNA with a considerable length between start and stop codons, helping to predict potential genes like CTP1 [1].
Question 10
Explain how online databases can be used to investigate the functions of a newly discovered protein. [6]
Any six of the following:
a. sequence of amino acids determined for new protein;
b. (large amount of) information easily accessed in databases;
c. search database to see if sequence exists in another organism;
d. BLASTp search used for amino acid/protein sequences;
e. using sequence alignment software;
f. (new) sequences compared to those with known function;
g. finding a model organism narrows the search;
h. model organisms have similar protein with similar genetic basis/code;
i. coding nucleotide sequence can be established;
j. target nucleotide sequence compared to different organisms using BLASTn;
Sample answer:
Once the sequence of amino acids is determined for a new protein [1], researchers can use the large amount of information easily accessed in online databases [1] to investigate its function. They can search the database to see if the sequence exists in another organism [1] and perform a BLASTp search for amino acid/protein sequences [1]. By using sequence alignment software [1], the new sequence can be compared to those with known function [1] to identify similarities. Finding a model organism narrows the search [1] , since model organisms have similar proteins with similar genetic basis/code [1], allowing scientists to infer the likely function of the newly discovered protein.
Question 1
The diploid number of chromosomes in humans (Homo sapiens) is 46 and the diploid number of chromosomes in rice (Oryza sativa) is 24. What does this indicate about diploid chromosome numbers?
A. Plant species have a lower diploid number of chromosomes than animals.
B. Members of a species have the same diploid number of chromosomes.
C. The evolutionary progress of species is determined by the diploid number of chromosomes.
D. The complexity of the organisms is correlated to the diploid number of chromosomes.
Question 2
Which is a source of chromosomes for pre-natal diagnosis of abnormalities by karyotyping?
A. Sperm.
B. Ovaries.
C. Erythrocytes.
D. Chorionic villi.
Question 3
A collection of four animal specimens is observed and a dichotomous key is applied. Which specimen is an arthropod?
1. Non-segmented body .................................go to 2
Segmented body .........................................go to 3
2. Body is not symmetrical ............................... specimen A
Body is symmetrical ………………………...specimen B
3. Jointed appendages present ............................. specimen C
Jointed appendages absent ............................. specimen D
A. Specimen A.
B. Specimen B.
C. Specimen C.
D. Specimen D.
Question 4
The dichotomous key shows general features of four vertebrate classes. Which letter identifies most fish?

Question 5
What determines the genomic size of a species?
A. The total amount of DNA
B. The total number of genes
C. The total number of alleles
D. The total number of chromosomes
Question 6
A pregnant woman had fetal cells removed by chorionic villus sampling and tested. The following karyogram was produced?

[Source: Mediscan / Alamy Stock Photo]
What does this show?
A. The child is female with Down syndrome.
B. The child is female without Down syndrome.
C. The child is male with Down syndrome.
D. The child is male without Down syndrome.
Question 7
The salamander genus Ensatina from California, USA, has evolved several different forms, depending on location. Two such forms are shown.

What determines if these forms are members of the same species?
A. Have similar appearance
B. Populations mix freely
C. Produce fertile offspring
D. Can interbreed
Question 8
What is one application of DNA barcoding?
A. Selective breeding
B. Preserving an endangered species
C. Analysing environmental DNA
D. Sequencing a genome
Question 9
Genes such as the one coding for CTP1 can be located by searching for open reading frames. Outline how open reading frames are identified. [3]
Question 10
Explain how online databases can be used to investigate the functions of a newly discovered protein. [6]