Question 1
The foxglove, Digitalis purpurea, was once classified in the figwort family. The figwort family has been reclassified and is now much smaller.

Why were species such as the foxglove moved into other families?
A. The appearance was too dissimilar.
B. The plants are found in different locations.
C. The genera were different.
D. The DNA sequences indicated different ancestry.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The image shows an organism belonging to the Kingdom Animalia.

[Source: Titan beetle male. Locality: “RK4,5 route Cacao”, French Guiana © 2011, Didier Descouens https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/]
What feature does this organism have in common with all members of the phylum chordata?
A. Legs and wings
B. Mouth but no anus
C. Bilateral symmetry
D. Chitinous exoskeleton
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which is the hierarchy of taxa in order of decreasing numbers of species?
A. domain, phylum, order, family
B. phylum, order, family, class
C. domain, phylum, order, class
D. phylum, class, family, order
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which phyla have bilateral symmetry?
A. annelida, arthropoda, platyhelmintha
B. porifera, arthropoda, platyhelmintha
C. cnidaria, porifera, mollusca
D. porifera, annelida, mollusca
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
The cladogram shows some of the groups in the three domains.
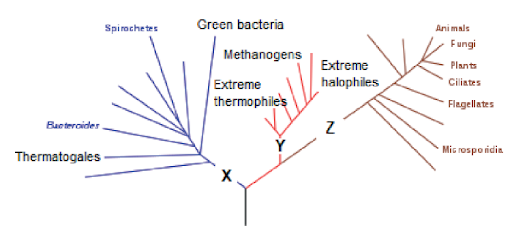
What domains do X, Y and Z represent?
| Domains | |||
| X | Y | Z | |
| A | prokaryote | archaea | eukaryote |
| B | archaea | eubacteria | prokaryote |
| C | eubacteria | archaea | eukaryote |
| D | eubacteria | prokaryote | eukaryote |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
The table compares ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequences of two organisms from each of the three domains by showing an association coefficient. The more similar the rRNA sequences of the organisms, the larger the coefficient.
| S. cerevisiae | L. minor | E. Coli | B. firmus | M. ruminantium | M. barkeri | |
| S. cerevisiae | - | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.08 |
| L. minor | - | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.07 | |
| E. Coli | - | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.12 | ||
| B. firmus | - | 0.13 | 0.12 | |||
| M. ruminantium | - | 0.24 | ||||
| M. barkeri | - |
What can be concluded from the data?
A. L. minor and E. coli are both eubacteria.
B. S. cerevisiae and M. barkeri are in the same domain.
C. M. ruminantium is an archaean, therefore so is B. firmus.
D. E. coli and B. firmus are in the same domain.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
The DNA base sequences in a gene coding for a particular protein in four different species are shown. Locations where mutations have occurred resulting in changes to the base sequences are outlined in boxes.
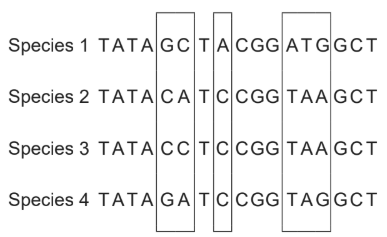
[Source: © International Baccalaureate Organization 2019]
Which cladogram shows the most likely phylogenetic relationship between the four species, based on the data provided?
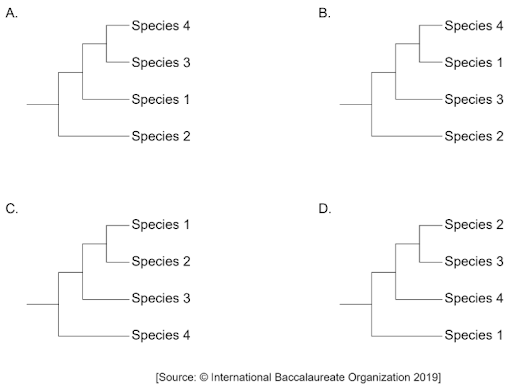
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
State the domain into which ticks are classified. [1]
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Explain how cladistics can be used to investigate evolutionary relationships. [2]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Explain how a newly discovered plant species would be classified and named. [7]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
The foxglove, Digitalis purpurea, was once classified in the figwort family. The figwort family has been reclassified and is now much smaller.

Why were species such as the foxglove moved into other families?
A. The appearance was too dissimilar.
B. The plants are found in different locations.
C. The genera were different.
D. The DNA sequences indicated different ancestry.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. Traditional classification was based on morphology to differentiate species; however, modern taxonomy uses genetic material classified species. Some species that look different can be closely related; therefore, appearance alone cannot be the reason for the reclassification.
B. Incorrect. Location alone cannot be used to determine the evolutionary relationship between species. Some species in the same area can be unrelated.
C. Incorrect. This answer does not explain the reclassification. Scientists need to use genetic evidence to determine the relationship between species, then classify them into different genera.
D. Correct. Modern taxonomy uses genetic evidence such as DNA sequencing to determine the evolutionary relation between species.
Question 2
The image shows an organism belonging to the Kingdom Animalia.

[Source: Titan beetle male. Locality: “RK4,5 route Cacao”, French Guiana © 2011, Didier Descouens https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/]
What feature does this organism have in common with all members of the phylum chordata?
A. Legs and wings
B. Mouth but no anus
C. Bilateral symmetry
D. Chitinous exoskeleton
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Phylum chordata is the phylum that includes all vertebrates and some invertebrates such as tunicates and lancelets. Many animals do not have wings or legs, such as fish. Therefore, this is not the shared feature among all members of phylum chordata.
B. Incorrect. Phylum chordata is the phylum that includes all vertebrates and some invertebrates such as tunicates and lancelets. All animals from this phylum have a complete digestive system, meaning a mouth and an anus. Therefore, this is not the shared feature among all members of phylum chordata.
C. Correct. Phylum chordata is the phylum that includes all vertebrates and some invertebrates such as tunicates and lancelets. Bilateral symmetry is a shared feature among phylum chordata. All animals from this phylum have bodies that can be divided into mirror-image left and right halves.
D. Incorrect. This feature is found in arthropods, not in chordates. Animals from phylum chordata have endoskeleton and not made from chitin.
Question 3
Which is the hierarchy of taxa in order of decreasing numbers of species?
A. domain, phylum, order, family
B. phylum, order, family, class
C. domain, phylum, order, class
D. phylum, class, family, order
Answer: A
A. Correct. The hierarchy of taxa from largest to smallest is: Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species.
B. Incorrect. The hierarchy of taxa from largest to smallest is: Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species. Wrong because class should come before order and family.
C. Incorrect. The hierarchy of taxa from largest to smallest is: Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species. Wrong because class should come before order.
D. Incorrect. The hierarchy of taxa from largest to smallest is: Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species. Wrong because family should comes after order.
Question 4
Which phyla have bilateral symmetry?
A. annelida, arthropoda, platyhelmintha
B. porifera, arthropoda, platyhelmintha
C. cnidaria, porifera, mollusca
D. porifera, annelida, mollusca
Answer: A
A. Correct. Bilateral symmetry means the body can be divided into left and right mirror images. Phyla with bilateral symmetry includes: Platyhelmintha (flatworms), Annelida (segmented worms), Mollusca (snails, clams), Arthropoda (insects, crustaceans), Chordata (vertebrates).
B. Incorrect. Bilateral symmetry means the body can be divided into left and right mirror images. Phyla with bilateral symmetry includes: Platyhelmintha (flatworms), Annelida (segmented worms), Mollusca (snails, clams), Arthropoda (insects, crustaceans), Chordata (vertebrates). Porifera (sponges) are asymmetrical.
C. Incorrect. Bilateral symmetry means the body can be divided into left and right mirror images. Phyla with bilateral symmetry includes: Platyhelmintha (flatworms), Annelida (segmented worms), Mollusca (snails, clams), Arthropoda (insects, crustaceans), Chordata (vertebrates). Cnidaria (jellyfish, corals) are radially symmetrical, and Porifera are asymmetrical.
D. Incorrect. Bilateral symmetry means the body can be divided into left and right mirror images. Phyla with bilateral symmetry includes: Platyhelmintha (flatworms), Annelida (segmented worms), Mollusca (snails, clams), Arthropoda (insects, crustaceans), Chordata (vertebrates). Porifera (sponges) are asymmetrical.
Question 5
The cladogram shows some of the groups in the three domains.

What domains do X, Y and Z represent?
| Domains | |||
| X | Y | Z | |
| A | prokaryote | archaea | eukaryote |
| B | archaea | eubacteria | prokaryote |
| C | eubacteria | archaea | eukaryote |
| D | eubacteria | prokaryote | eukaryote |
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Three domain systems include: Eubacteria, Archaea and Eukaryote. Both eubacteria and archaea are prokaryote cells, however, eubacteria diverge first from common ancestors, and archaea are closer to eukaryote. X must be eubacteria.
B. Incorrect. Three domain systems include: Eubacteria, Archaea and Eukaryote. Both eubacteria and archaea are prokaryote cells, however, eubacteria diverge first from common ancestors, and archaea are closer to eukaryote. X must be eubacteria, Y must be archaea and Z must be eukaryote.
C. Correct. Three domain systems include: Eubacteria, Archaea and Eukaryote. Both eubacteria and archaea are prokaryote cells, however, eubacteria diverge first from common ancestors, and archaea are closer to eukaryote.
D. Incorrect. Three domain systems include: Eubacteria, Archaea and Eukaryote. Both eubacteria and archaea are prokaryote cells, however, eubacteria diverge first from common ancestors, and archaea are closer to eukaryote. Y must be archaea.
Question 6
The table compares ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequences of two organisms from each of the three domains by showing an association coefficient. The more similar the rRNA sequences of the organisms, the larger the coefficient.
| S. cerevisiae | L. minor | E. Coli | B. firmus | M. ruminantium | M. barkeri | |
| S. cerevisiae | - | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.08 |
| L. minor | - | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.07 | |
| E. Coli | - | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.12 | ||
| B. firmus | - | 0.13 | 0.12 | |||
| M. ruminantium | - | 0.24 | ||||
| M. barkeri | - |
What can be concluded from the data?
A. L. minor and E. coli are both eubacteria.
B. S. cerevisiae and M. barkeri are in the same domain.
C. M. ruminantium is an archaean, therefore so is B. firmus.
D. E. coli and B. firmus are in the same domain.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. L. minor vs E. coli `= 0.10` 🡪 Low score, meaning they cannot be both eubacteria.
B. Incorrect. S. cerevisiae vs M. barkeri `= 0.08` 🡪 Low score, meaning they cannot be in the same domain.
C. Incorrect. M. ruminatium vs B. firmus `= 0.13` -🡪 Low score, meaning if M. ruminatium is archaea, B. firmus cannot be archaea.
D. Correct. E. coli vs B. firmus`= 0.25` 🡪 High score, meaning they are in the same domain.
Question 7
The DNA base sequences in a gene coding for a particular protein in four different species are shown. Locations where mutations have occurred resulting in changes to the base sequences are outlined in boxes.

[Source: © International Baccalaureate Organization 2019]
Which cladogram shows the most likely phylogenetic relationship between the four species, based on the data provided?

Answer: D
A. Incorrect. Comparing the mutation region, species 2 and species 3 only one mutation: A (sequence 2) 🡪 C (sequence 3), meaning 2 and 3 are sister taxa. Sequence 4 has 2 mutations compared to sequence 2: C (sequence 2) 🡪 G (sequence 4) and A (sequence 2) 🡪 G (sequence 4), meaning they are closely related. Sequence 1 has mutations in all three regions, meaning it is the most distant one. This answer is incorrect because sequence 2 and sequence 3 are more closely related than sequence 3 and 4.
B. Incorrect. Comparing the mutation region, species 2 and species 3 only one mutation: A (sequence 2) 🡪 C (sequence 3), meaning 2 and 3 are sister taxa. Sequence 4 has 2 mutations compared to sequence 2: C (sequence 2) 🡪 G (sequence 4) and A (sequence 2) 🡪 G (sequence 4), meaning they are closely related. Sequence 1 has mutations in all three regions, meaning it is the most distant one. This answer is incorrect because sequence 4 and sequence 3 are more closely related than sequence 1 and 4.
C. Incorrect. Comparing the mutation region, species 2 and species 3 only one mutation: A (sequence 2) 🡪 C (sequence 3), meaning 2 and 3 are sister taxa. Sequence 4 has 2 mutations compared to sequence 2: C (sequence 2) 🡪 G (sequence 4) and A (sequence 2) 🡪 G (sequence 4), meaning they are closely related. Sequence 1 has mutations in all three regions, meaning it is the most distant one. This answer is incorrect because sequence 2 and sequence 3 are more closely related than sequence 1 and 2.
D. Correct. Comparing the mutation region, species 2 and species 3 only one mutation: A (sequence 2) 🡪 C (sequence 3), meaning 2 and 3 are sister taxa. Sequence 4 has 2 mutations compared to sequence 2: C (sequence 2) 🡪 G (sequence 4) and A (sequence 2) 🡪 G (sequence 4), meaning they are closely related. Sequence 1 has mutations in all three regions, meaning it is the most distant one.
Question 8
State the domain into which ticks are classified. [1]
Answer: Eukaryote
Question 9
Explain how cladistics can be used to investigate evolutionary relationships. [2]
Any two of the following:
a. Shows evolutionary relationships through a common ancestor
b. Cladistics uses DNA/ protein/ derived/ shared anatomical characteristics/ traits
c. Time of divergence is related to the number of differences in DNA (base sequence) /protein (sequence of amino acids)
d. Homologous (versus analogous) traits are used to place an organism in a clade
e. More shared characteristics mean a more recent common ancestor
Sample answer:
Cladistics show evolutionary relationships between organisms by identifying those that share a common ancestor [1]. They use DNA, protein sequences, or derived anatomical traits to determine relatedness among species [1]. The time of divergence between species is estimated by the number of differences in their DNA base sequences or amino acid sequences [1]. Only homologous traits are used to place organisms into cables, rather than analogous traits that evolved independently [1]. The more characteristics two species share, the more recent their common ancestor is inferred to be [1].
Question 10
Explain how a newly discovered plant species would be classified and named. [7]
Any seven of the following, with three from the naming and four from the classification:
Naming:
a. binomial nomenclature/ given a binomial/double name
b. first name is the genus and second name is the species/genus initial uppercase and species lower case
c. names (of plant species) are international/are universally understood/are published in journals
Classification:
d. study the characteristics/ structure/ reproduction/ chemical properties/ DNA (of the plant)
e. put/classify (the plant) in a group/genus with other similar species
f. natural classification corresponds with evolution/natural classification is based on many feature
g. analogous features/features due to convergent evolution should not be used
h. hierarchy of groups/taxa (in traditional classification/3 or more taxa in correct sequence (kingdom-phylum-class)
i. two or more of bryophyta, filicinophyta, coniferophyta and angiospermophyta named
j. a clade is a group of organisms evolved from a common ancestor
k. base sequences/amino acid sequences used to group organisms into clades/deduce evolutionary relationships
l. cladograms show the relationships between clades/likely evolutionary divergence of clades
m. each branch point/node represents where species are formed via divergent evolution
n. species are now classified into a sequence of clades (rather than a rigid hierarchy of taxa)
Sample answer:
The newly discovered plant species is studied for its structural, chemical, and genetic features, and compared with known species [1]. It would be placed into a genus with species showing similar features [1] and organized into a hierarchical system of taxa [1]. Techniques such as DNA sequencing or amino acid sequencing can be used to determine its evolutionary ancestry and assign it to the correct clade [1]. The species would then be named using the binomial system [1], where the first name is the genus and is capitalized and the second name is the species and is in lowercase [1]. These names are Latin and internationally recognized, ensuring that scientists around the world can identify the plant consistently [1].
Question 1
The foxglove, Digitalis purpurea, was once classified in the figwort family. The figwort family has been reclassified and is now much smaller.

Why were species such as the foxglove moved into other families?
A. The appearance was too dissimilar.
B. The plants are found in different locations.
C. The genera were different.
D. The DNA sequences indicated different ancestry.
Question 2
The image shows an organism belonging to the Kingdom Animalia.

[Source: Titan beetle male. Locality: “RK4,5 route Cacao”, French Guiana © 2011, Didier Descouens https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/]
What feature does this organism have in common with all members of the phylum chordata?
A. Legs and wings
B. Mouth but no anus
C. Bilateral symmetry
D. Chitinous exoskeleton
Question 3
Which is the hierarchy of taxa in order of decreasing numbers of species?
A. domain, phylum, order, family
B. phylum, order, family, class
C. domain, phylum, order, class
D. phylum, class, family, order
Question 4
Which phyla have bilateral symmetry?
A. annelida, arthropoda, platyhelmintha
B. porifera, arthropoda, platyhelmintha
C. cnidaria, porifera, mollusca
D. porifera, annelida, mollusca
Question 5
The cladogram shows some of the groups in the three domains.

What domains do X, Y and Z represent?
| Domains | |||
| X | Y | Z | |
| A | prokaryote | archaea | eukaryote |
| B | archaea | eubacteria | prokaryote |
| C | eubacteria | archaea | eukaryote |
| D | eubacteria | prokaryote | eukaryote |
Question 6
The table compares ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequences of two organisms from each of the three domains by showing an association coefficient. The more similar the rRNA sequences of the organisms, the larger the coefficient.
| S. cerevisiae | L. minor | E. Coli | B. firmus | M. ruminantium | M. barkeri | |
| S. cerevisiae | - | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.08 |
| L. minor | - | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.07 | |
| E. Coli | - | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.12 | ||
| B. firmus | - | 0.13 | 0.12 | |||
| M. ruminantium | - | 0.24 | ||||
| M. barkeri | - |
What can be concluded from the data?
A. L. minor and E. coli are both eubacteria.
B. S. cerevisiae and M. barkeri are in the same domain.
C. M. ruminantium is an archaean, therefore so is B. firmus.
D. E. coli and B. firmus are in the same domain.
Question 7
The DNA base sequences in a gene coding for a particular protein in four different species are shown. Locations where mutations have occurred resulting in changes to the base sequences are outlined in boxes.

[Source: © International Baccalaureate Organization 2019]
Which cladogram shows the most likely phylogenetic relationship between the four species, based on the data provided?

Question 8
State the domain into which ticks are classified. [1]
Question 9
Explain how cladistics can be used to investigate evolutionary relationships. [2]
Question 10
Explain how a newly discovered plant species would be classified and named. [7]