Question 1
Which of the following are used as evidence for evolution?
I. Homologous structures
II. Selective breeding of domesticated animals
III. Overproduction of offspring
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
What is essential for natural selection to occur?
A. Variation between members of a species.
B. Large population size.
C. High mortality rate.
D. Environmental catastrophe.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which evidence for evolution do the common features in the bone structure of vertebrate limbs provide?
A. Adaptive radiation
B. Divergent radiation
C. Convergent evolution
D. Discontinuous variation
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Darwin described evolution as “descent with modification”. What would make evolution less probable?
A. Stable environment.
B. Migration.
C. Variation in offspring.
D. Random mutation.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Modified hairs (quills) cover the bodies of hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) and short-beaked echidnas (Tachyglossus aculeatus). However, these structures do not have the same evolutionary origin
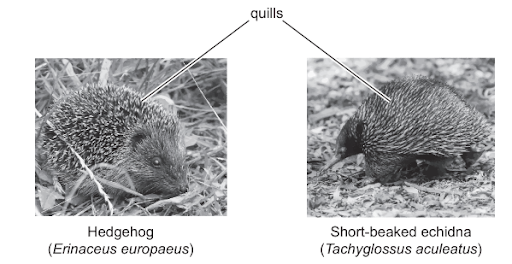
What is a possible explanation for the presence of quills in both species?
A. Both species diverged gradually, but quills were conserved for successful survival.
B. Quills developed in response to similar environmental pressures.
C. Quills are homologous structures that result from adaptation to a similar predator.
D. They developed by adaptive radiation to survive in slightly different habitats.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Which evolutionary pathway is most likely to result in the evolution of analogous structures in Species W and Z?
| A. |
|
| B. |
|
| C. |
|
| D. |
|
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
What is evolution?
A. Change in the heritable characteristics of a species
B. Change in the phenotype of a species
C. Speciation due to geographical separation
D. Survival of the fittest
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What is accepted by scientists as evidence for evolution?
I. Similarities in bone structure between the wings of a bat and the fins of a porpoise
II. Changes in dog breeds caused by artificial selection
III. Extinction of dinosaurs
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Outline how adaptive radiation provides evidence for evolution. [3]
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Using the mammalian pentadactyl limb as an example, outline the process of adaptive radiation. [2]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Which of the following are used as evidence for evolution?
I. Homologous structures
II. Selective breeding of domesticated animals
III. Overproduction of offspring
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Answer: A
I. Homologous structures (e.g., pentadactyl limb in vertebrates) provide evidence for evolution because they share the same basic structural origin but have been modified for different functions, indicating a common ancestor.
II. Artificial selection is a process in which humans intentionally breed individuals with desired traits. Significant changes in domesticated species (e.g., dogs or crops) over relatively short periods provide strong evidence that selection can drive evolution.
III. Overproduction and competition for resources are factors that drive natural selection, but they are not direct evidence that evolution has occurred. They create high mortality rates and favor survival of the fittest, but do not themselves prove evolution.
Therefore, the statements I and II are correct.
B, C, and D. Incorrect.
Question 2
What is essential for natural selection to occur?
A. Variation between members of a species.
B. Large population size.
C. High mortality rate.
D. Environmental catastrophe.
Answer: A
A. Correct. Natural selection can only act if there is variation among individuals in a population. Variation allows some individuals to be better adapted to the environment and have higher survival and reproduction. Mutations are the original source of all genetic variation.
B. Incorrect. While large populations help maintain gene frequency equilibrium (Hardy-Weinberg), natural selection can occur in any population with variation. Small populations may experience genetic drift more strongly.
C. Incorrect. High mortality is a consequence of overproduction and competition. It can drive selection, but without variation, mortality does not change allele frequencies adaptively.
D. Incorrect. Catastrophes can act as strong selection pressures, but evolution can occur in stable environments through biotic selection pressures (e.g., predation or competition).
Question 3
Which evidence for evolution do the common features in the bone structure of vertebrate limbs provide?
A. Adaptive radiation
B. Divergent radiation
C. Convergent evolution
D. Discontinuous variation
Answer: A
A. Correct. The pentadactyl limb in vertebrates shows a single ancestral structure that has diverged into multiple forms adapted to different ecological niches (e.g., swimming in whales, flying in bats, grasping in primates). This is an example of adaptive radiation, where one ancestor gives rise to many species specialized for different environments.
B. Incorrect. Divergent evolution is the broader process of species becoming different from a common ancestor, but it does not specifically describe the branching into multiple specialized forms.
C. Incorrect. Convergent evolution occurs when unrelated species independently evolve similar structures due to similar selection pressures (e.g., wings of bats and insects). Vertebrate limbs share a common ancestor, so this is not convergent.
D. Incorrect. Discontinuous variation refers to traits controlled by a few genes that result in distinct categories (e.g., blood groups). Limb structure similarity is not an example of this.
Question 4
Darwin described evolution as “descent with modification”. What would make evolution less probable?
A. Stable environment.
B. Migration.
C. Variation in offspring.
D. Random mutation.
Answer: A
A. Correct. Evolution is the cumulative change of genetic traits in a population. Natural selection acts most strongly when the environment changes. In a stable environment, selection pressures are low, and allele frequencies change little, making evolution less likely..
B. Incorrect. Migration introduces gene flow between populations, changing the gene pool and potentially promoting evolution
C. Incorrect. Variation is essential for natural selection. Without variation, populations cannot adapt, leading to stagnation or extinction.
D. Incorrect. Random mutation is the source of all new genetic variation. Without mutation, no new variation arises, slowing evolution. Mutations promote, not hinder, evolution.
Question 5
Modified hairs (quills) cover the bodies of hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) and short-beaked echidnas (Tachyglossus aculeatus). However, these structures do not have the same evolutionary origin

What is a possible explanation for the presence of quills in both species?
A. Both species diverged gradually, but quills were conserved for successful survival.
B. Quills developed in response to similar environmental pressures.
C. Quills are homologous structures that result from adaptation to a similar predator.
D. They developed by adaptive radiation to survive in slightly different habitats.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. This describes divergent evolution, where structures are inherited from a common ancestor. This contradicts the information in the question stating that the structures “do not share a common evolutionary origin.”
B. Correct. This is the definition of convergent evolution: similar selection pressures (e.g., presence of predators) lead to similar evolutionary solutions in unrelated species.
C. Incorrect. Homologous structures share a common ancestral origin. Homologous structures are evidence of divergent evolution, not convergent evolution.
D. Incorrect. Adaptive radiation occurs when one ancestral species diversifies into multiple new species, each adapted to a different ecological niche. This is a form of divergent evolution, which does not apply to the scenario described.
Question 6
Which evolutionary pathway is most likely to result in the evolution of analogous structures in Species W and Z?
| A. |
|
| B. |
|
| C. |
|
| D. |
|
Answer: C
A. and D. Incorrect. These diagrams show a single, linear lineage (anagenesis). In both cases, Species W is a direct ancestor of Species Z. Any similar structures would be inherited and modified, making them homologous, not analogous.
B. Incorrect. This diagram shows that Species W and Species Z are closely related, as they both evolved from a recent common ancestor, Species Y. Similar structures between them would most likely be homologous, inherited from Species Y.
C. Correct. This diagram shows two completely separate and parallel evolutionary lineages. Species W evolved from Species V, while Species Z evolved from Species Y. Because they do not share a recent common ancestor, any similar structures they possess must have evolved independently (likely due to adapting to similar environmental pressures). This is the definition of convergent evolution, which results in analogous structures.
Question 7
What is evolution?
A. Change in the heritable characteristics of a species
B. Change in the phenotype of a species
C. Speciation due to geographical separation
D. Survival of the fittest
Answer: A
A. Correct. According to the modern definition, evolution is the cumulative change in heritable characteristics of a population over many generations. This distinguishes Darwinian evolution from Lamarckism, as only changes with a genetic basis are considered evolution. Although evolution is usually defined at the population level, the key aspect is the change in heritable traits.
B. Incorrect. Phenotype refers to observable traits of an organism. It can occur during an individual’s life due to environmental influences (acquired characteristics), e.g., a tennis player develops stronger muscles in one arm, or a tree grows asymmetrically due to wind. Acquired traits are not inherited, so phenotypic change in an individual does not constitute evolution.
C. Incorrect. Speciation is the process by which an ancestral species splits into two or more new species. It is a result of evolution, not a definition of it. Geographic separation can lead to reproductive isolation, which facilitates speciation, but it does not define evolution.
D. Incorrect. Survival of the fittest summarizes how natural selection operates. It is a mechanism explaining how evolution occurs, based on differences in adaptation, survival, and reproduction among individuals. Therefore, it describes a process driving evolution, not the definition of evolution itself.
Question 8
What is accepted by scientists as evidence for evolution?
I. Similarities in bone structure between the wings of a bat and the fins of a porpoise
II. Changes in dog breeds caused by artificial selection
III. Extinction of dinosaurs
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
Answer: B
I. These structures are examples of homologous structures, meaning they share a common ancestral origin but have evolved to perform different functions over time (e.g., the pentadactyl limb). The structural similarity indicates that these vertebrates diverged from a common ancestor through a process called adaptive radiation.
II. Artificial selection, where humans intentionally select traits in breeding, demonstrates that selection can cause cumulative changes in heritable characteristics in a population over generations. The significant and rapid changes in dog breeds from ancestral wolves provide strong evidence that selection can drive evolution.
III. Although the fossil record shows that life has changed over time and many species have gone extinct, extinction itself is merely a historical event - a disappearance. It does not directly provide evidence for the mechanism of evolution (natural selection acting on genetic variation) in the way homologous structures or artificial selection do
A, C, and D. Incorrect. They are incorrect because they either omit important evidence (A lacks II) or include a factor that is not direct evidence of evolutionary mechanisms (C and D include III).
Question 9
Outline how adaptive radiation provides evidence for evolution. [3]
Any three of the following:
a. diversification/ different species produced from a common/shared ancestor;
b. homologous features have similarities of structure
c. despite different functions;
d. (different) adaptation to different environments/different selective pressures;
e. pentadactyl limbs/Darwin’s finches/other example of adaptive radiation
described correctly;
Sample answer:
Adaptive radiation provides evidence for evolution because it shows how multiple different species can diversify from a shared common ancestor [1] as they spread into new environments. These species often possess homologous structures that share a similar underlying anatomy [1], even though they may perform different functions [1] depending on the ecological niche they occupy. For example, the pentadactyl limb occurs in bats, whales, and humans, and its shared structure (modified for flying, swimming, or grasping) demonstrates how natural selection shapes organisms differently while preserving evidence of common ancestry.
Question 10
Using the mammalian pentadactyl limb as an example, outline the process of adaptive radiation. [2]
Any two of the following
a. limb bone pattern of mammals shows the same basic arrangement;
b. derived from common ancestor/homologous structures;
c. common ancestral pattern adapted to different environment conditions;
suitable example (eg wing of bat adapted for flight and limbs of mole for
digging);
Sample answer:
Adaptive radiation is demonstrated in the mammalian pentadactyl limb because all mammals share the same basic limb-bone arrangement [1], even though their limbs now serve very different functions. This structural similarity shows that the limbs were derived from a common ancestor [1], and over time the ancestral pattern was modified as different mammal groups adapted to different environmental conditions. For example, the pentadactyl limb became a wing in bats for flight and a powerful digging limb in moles [1], illustrating how one ancestral structure diversified into specialized forms through natural selection.
Question 1
Which of the following are used as evidence for evolution?
I. Homologous structures
II. Selective breeding of domesticated animals
III. Overproduction of offspring
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Question 2
What is essential for natural selection to occur?
A. Variation between members of a species.
B. Large population size.
C. High mortality rate.
D. Environmental catastrophe.
Question 3
Which evidence for evolution do the common features in the bone structure of vertebrate limbs provide?
A. Adaptive radiation
B. Divergent radiation
C. Convergent evolution
D. Discontinuous variation
Question 4
Darwin described evolution as “descent with modification”. What would make evolution less probable?
A. Stable environment.
B. Migration.
C. Variation in offspring.
D. Random mutation.
Question 5
Modified hairs (quills) cover the bodies of hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) and short-beaked echidnas (Tachyglossus aculeatus). However, these structures do not have the same evolutionary origin

What is a possible explanation for the presence of quills in both species?
A. Both species diverged gradually, but quills were conserved for successful survival.
B. Quills developed in response to similar environmental pressures.
C. Quills are homologous structures that result from adaptation to a similar predator.
D. They developed by adaptive radiation to survive in slightly different habitats.
Question 6
Which evolutionary pathway is most likely to result in the evolution of analogous structures in Species W and Z?
| A. |
|
| B. |
|
| C. |
|
| D. |
|
Question 7
What is evolution?
A. Change in the heritable characteristics of a species
B. Change in the phenotype of a species
C. Speciation due to geographical separation
D. Survival of the fittest
Question 8
What is accepted by scientists as evidence for evolution?
I. Similarities in bone structure between the wings of a bat and the fins of a porpoise
II. Changes in dog breeds caused by artificial selection
III. Extinction of dinosaurs
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
Question 9
Outline how adaptive radiation provides evidence for evolution. [3]
Question 10
Using the mammalian pentadactyl limb as an example, outline the process of adaptive radiation. [2]