Question 1
The diagram is a three-dimensional molecular model of a protein.
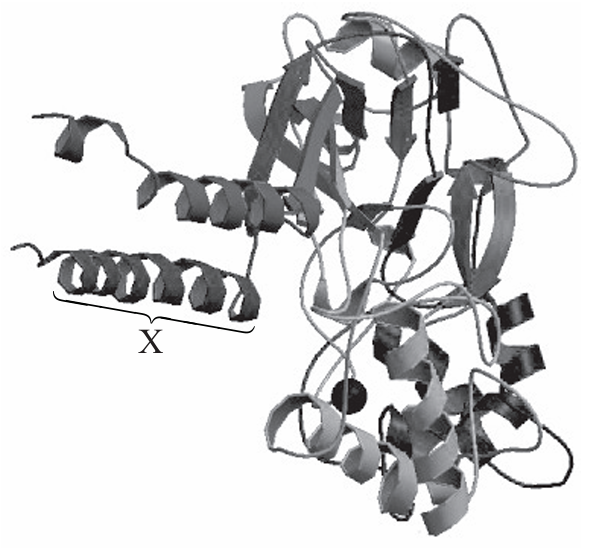
[Source: Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature, Toshimitsu Kawate, Jennifer Carlisle Michel, William T. Birdsong & Eric Gouaux, ‘Crystal structure of the ATP-gated P2X4 ion channel in the closed state’, 460, pp 592–598, © 2009. www.nature.com.]
Which bonds stabilize the shape of the area labelled X?
A. Covalent bonds between adjacent amino acids
B. Hydrogen bonds between N–H and C=O groups of amino acids
C. Hydrophobic interactions between R groups of amino acid
D. Disulphide bridges between cysteine molecules
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Which element is most common in proteins?
A. Sodium
B. Nitrogen
C. Phosphorus
D. Iron
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
The image shows the structure of the protein hemoglobin?
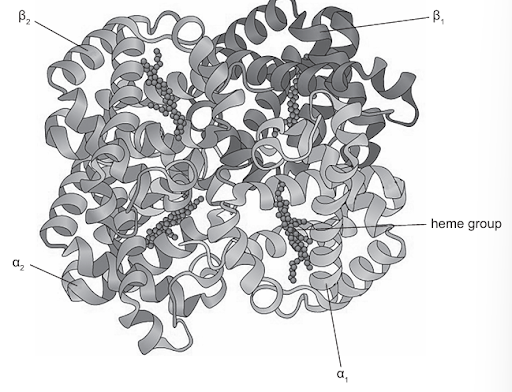
What level of protein structure bonds the α and β chains together?
A. Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D.Quaternary
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which is an effect of protein denaturation?
A. The order of amino acids is changed when the protein overheats.
B. The bonds between amino acids are broken by condensation.
C. Parts of the protein become linked together by hydrolysis.
D. The three-dimensional structure of the protein is altered.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Which row correctly matches the level of structure of a protein molecule with the bonds that stabilize it?
| Level of structure | Bonds | |
| A. | primary | peptide and hydrogen bonds between amine and carboxyl groups |
| B. | secondary | hydrogen bonds between R-groups of amino acids |
| C. | tertiary | disulfide, hydrogen and ionic bonds between R-groups of amino acids |
| D. | quaternary | covalent bonds between hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions on the polypeptide subunits |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Which protein has the highest tensile strength (ability to resist breaking when stretched)?
A. Cellulose
B. Actin
C. Spider silk
D. Albumin
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Myoglobin is a globular protein in which nearly all the non-polar R-groups point towards the inside of the molecule. The outside surface contains all the polar R-groups. What can be deduced from this?
A. Disulfide bonds occur on the inside.
B. Hydrogen bonds form with water on the outside.
C. Ionic bonds form with water on the outside.
D. Covalent bonds occur on the inside.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Diagrams of three different proteins, X, Y and Z, are shown

Which row describes the structure of each protein shown?
| X | Y | Z | |
| A. | quaternary | globular | secondary |
| B. | conjugated | fibrous | globular |
| C. | tertiary | quaternary | primary |
| D. | globular | secondary | fibrous |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Outline the process of protein denaturation. [4]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Describe how the diversity of amino acids gives proteins a broad range of forms. [2]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
The diagram is a three-dimensional molecular model of a protein.

[Source: Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature, Toshimitsu Kawate, Jennifer Carlisle Michel, William T. Birdsong & Eric Gouaux, ‘Crystal structure of the ATP-gated P2X4 ion channel in the closed state’, 460, pp 592–598, © 2009. www.nature.com.]
Which bonds stabilize the shape of the area labelled X?
A. Covalent bonds between adjacent amino acids
B. Hydrogen bonds between N–H and C=O groups of amino acids
C. Hydrophobic interactions between R groups of amino acid
D. Disulphide bridges between cysteine molecules
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. The covalent bonds between adjacent amino acids are peptide bonds. These bonds determine the primary structure (the linear sequence) of the protein. Peptide bonds stabilize the amino acid sequence but not the three-dimensional shape of the folded region X.
B. Correct. Hydrogen bonds between the N–H and C=O groups of amino acids along the polypeptide chain are the main forces stabilizing secondary structure. The most common secondary structures are the α-helix and the β-pleated sheet. While individual hydrogen bonds are weak, many of them forming regularly along the chain are strong enough to stabilize these structures.
C. Incorrect. Hydrophobic interactions are one of the four main interactions between amino-acid side chains (R groups), contributing to the stability of the tertiary structure (the overall 3D shape). These interactions occur when non-polar R groups cluster inside the protein’s core or in the hydrophobic region of a membrane (as in ion-channel proteins). Although these interactions are important for the overall stability of membrane proteins, if X is a local α-helix, its local shape is stabilized mainly by hydrogen bonds.
D. Incorrect. Disulfide bridges are strong covalent bonds formed between pairs of cysteine residues. They stabilize the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. However, these bonds only form when cysteine residues are present and are not a general stabilizing force for every folded region in a protein.
Question 2
Which element is most common in proteins?
A. Sodium
B. Nitrogen
C. Phosphorus
D. Iron
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Sodium is not listed as one of the common elements that make up proteins or other basic biological macromolecules.
B. Correct. Nitrogen is an essential component of amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) and is the element that distinguishes proteins from carbohydrates and lipids.
Membrane potential comes from ion gradients maintained by protein pumps and ion channels, not by lipids.
C. Incorrect. Phosphorus is found in some biomolecules (for example, phospholipids and nucleic acids) but it is not a general component of all proteins the way nitrogen is.
D. Incorrect. Iron atoms appear in the haem group (a non-protein group) of hemoglobin, which is a conjugated protein. However, iron is not a common elemental component of the polypeptide chain itself.
Question 3
The image shows the structure of the protein hemoglobin?

What level of protein structure bonds the α and β chains together?
A. Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D.Quaternary
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. This option describes a single chain, not the association of multiple chains. The primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, linked by peptide bonds.
B. Incorrect. This option describes local folding within a single chain. Secondary structure occurs when a polypeptide chain interacts with itself through hydrogen bonds to form regions with coiled shapes (such as α-helices) or folded shapes (such as β-pleated sheets).
C. Incorrect. Tertiary structure is the overall folding of one entire polypeptide chain into a compact 3D shape, stabilized by interactions among R groups (such as hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, and hydrophobic interactions), which only involves only one polypeptide chain.
D. Correct. Quaternary structure arises when two or more polypeptide chains or proteins are held together, forming a larger, biologically functional molecule. Hemoglobin is an example of a protein with quaternary structure, consisting of four polypeptide chains, two α chains and two β chains. The three-dimensional arrangement of these subunits is the quaternary structure.
Question 4
Which is an effect of protein denaturation?
A. The order of amino acids is changed when the protein overheats.
B. The bonds between amino acids are broken by condensation.
C. Parts of the protein become linked together by hydrolysis.
D. The three-dimensional structure of the protein is altered.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. The sequence of amino acids is the protein’s primary structure, held together by peptide bonds. Peptide bonds do not break during denaturation, high temperature or extreme pH does not change the amino-acid sequence. Therefore, the primary structure remains unchanged when a protein is denatured.
B. Incorrect. The bonds between amino acids are peptide bonds.
A condensation reaction forms peptide bonds (joins two molecules and removes a molecule of water). Breaking peptide bonds requires hydrolysis, but even hydrolysis is not the mechanism of denaturation. So this statement is incorrect.
C. Incorrect. A hydrolysis reaction breaks molecules down into smaller units by adding hydrogen and hydroxide ions from water.
Hydrolysis breaks covalent bonds; it does not link parts of a protein together. Furthermore, denaturation involves changes in 3D structure, not the formation of new bonds or the breaking of peptide bonds, as would occur in hydrolysis.
D.Correct. Denaturation is a structural change in a protein that causes it to lose its biological properties, often permanently. It is a change in conformation that alters the three-dimensional shape of the protein, including the shape of the enzyme’s active site. This occurs because weak intramolecular interactions, such as hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds, that stabilize secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure are disrupted.
Question 5
Which row correctly matches the level of structure of a protein molecule with the bonds that stabilize it?
| Level of structure | Bonds | |
| A. | primary | peptide and hydrogen bonds between amine and carboxyl groups |
| B. | secondary | hydrogen bonds between R-groups of amino acids |
| C. | tertiary | disulfide, hydrogen and ionic bonds between R-groups of amino acids |
| D. | quaternary | covalent bonds between hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions on the polypeptide subunits |
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. The primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. This structure is stabilized by peptide bonds (covalent bonds). A peptide bond forms between the amine group (–NH₂) of one amino acid and the carboxyl group (–COOH) of another through a condensation reaction. Hydrogen bonds between N–H and C=O groups stabilize secondary structure, not primary structure.
B. Incorrect. Secondary structure is the local folding (such as α-helices or β-pleated sheets) that forms when the polypeptide chain interacts with itself. This structure is stabilized mainly by hydrogen bonds between the C=O and N–H groups along the polypeptide backbone, not between R groups. Interactions among R groups contribute to tertiary structure, not secondary.
C. Correct. The tertiary structure is the full three-dimensional folding of a single polypeptide chain into its unique, compact shape. This shape is stabilized by four major types of bonds/interactions between amino-acid side chains (R groups): Disulfide bonds, Ionic bonds, Hydrogen bonds, Hydrophobic interaction.
D. Incorrect. Quaternary structure arises when two or more polypeptide chains combine to form a larger, biologically functional molecule. These subunits are held together by the same types of interactions found in tertiary structure. While covalent bonds such as disulfide bridges can occur (e.g., in insulin), the key forces between hydrophobic regions are hydrophobic interactions, which are non-covalent, not covalent bonds.
Question 6
Which protein has the highest tensile strength (ability to resist breaking when stretched)?
A. Cellulose
B. Actin
C. Spider silk
D. Albumin
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Cellulose is a polysaccharide (a carbohydrate) made of β-glucose, not a protein. However, cellulose fibrils have very high tensile strength due to strong covalent bonds and extensive hydrogen bonding between the straight chains.
B. Incorrect. Actin is a thin filament protein in muscle cells, forming contractile filaments together with myosin. Actin does have a structural role, but it is not described in standard sources as having the highest tensile strength.
C. Correct. Although sources do not always directly compare its tensile strength with every other protein, they do identify fibrous proteins and their structural roles. Collagen, another fibrous protein, is noted for high tensile strength. Spider silk is a fibrous protein known for its exceptional strength, and in the context of typical exam questions, it is the correct answer as the protein with the highest tensile strength.
D. Incorrect. Albumin is a globular protein. Globular proteins are typically highly soluble and are involved in functions such as enzyme activity and transport in blood plasma. They have a compact, folded shape, not a long fibrous structure designed to withstand tension.
Question 7
Myoglobin is a globular protein in which nearly all the non-polar R-groups point towards the inside of the molecule. The outside surface contains all the polar R-groups. What can be deduced from this?
A. Disulfide bonds occur on the inside.
B. Hydrogen bonds form with water on the outside.
C. Ionic bonds form with water on the outside.
D. Covalent bonds occur on the inside.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Disulfide bonds are strong covalent bonds formed between pairs of cysteine residues and help stabilize tertiary structure. Although these bonds often occur deep within the folded structure, the arrangement of polar/non-polar groups is determined mainly by interactions with water (a weak, non-covalent effect), not by the location of strong covalent bonds like disulfide bridges.
B. Correct. Polar (hydrophilic) R groups are displayed on the outer surface of the protein so they can interact with water. Hydrogen bonds form between these polar R groups and surrounding water molecules. These interactions help stabilize the tertiary structure of the protein in an aqueous environment.
C. Incorrect. Ionic bonds form between oppositely charged R groups. Charged groups are a subset of polar groups. Polar groups include both neutral polar and charged R groups, and all polar groups interact with water. Although ionic groups are surrounded by water (solvation), hydrogen bonding is the broader and more general interaction for polar R groups on the surface.
D. Incorrect. Peptide covalent bonds hold amino acids together and form the primary structure. These bonds run along the entire polypeptide chain, both inside and outside the protein, therefore, they are not restricted to the interior.
Question 8
Diagrams of three different proteins, X, Y and Z, are shown

Which row describes the structure of each protein shown?
| X | Y | Z | |
| A. | quaternary | globular | secondary |
| B. | conjugated | fibrous | globular |
| C. | tertiary | quaternary | primary |
| D. | globular | secondary | fibrous |
Answer: B
Therefore option B is correct.
A, C, and D are incorrect.
Question 9
Outline the process of protein denaturation. [4]
Any four of the following:
a. change to conformation/shape/tertiary structure/3-D shape;
b. bonds within the protein/intramolecular bonds broken/changed;
c. pH and temperature (outside tolerated ranges) can cause denaturation;
d. vibrations/heat at high temperatures breaks bonds;
e. high pH/low pH/extreme pH alters ionization/charges (of amino acids and breaks ionic bonds);
f. protein cannot carry out its function OR active site of enzymes cannot bind substrates/catalyze reaction/no enzyme-substate complex;
g. Permanent/irreversible change (usually) OR Soluble proteins become insoluble/precipitate;
Sample answer:
Protein denaturation occurs when the conformation or 3-D tertiary structure [1] of a protein is altered. This happens because bonds within the protein are broken or changed [1], disrupting the stability of the molecule. pH or temperature outside the tolerated range can cause denaturation [1], as vibrations from high heat break intramolecular bonds, and extreme pH alters the ionization and charges of amino acids, breaking ionic bonds. As a result, the protein can no longer carry out its function [1], since the active site of an enzyme can no longer bind its substrate.
Question 10
Describe how the diversity of amino acids gives proteins a broad range of forms. [2]
Any two of the following:
a. properties/structure of the R groups vary;
b. may be hydrophobic or hydrophilic / polar or non-polar / acidic or basic;
c. cause different types of interactions/bonds between R-groups;
. affect how protein folds/solubility;
Sample answer:
The diversity of amino acids gives proteins a wide range of forms because the properties and structures of their R-groups vary [1]. Each R-group among the 20 amino acids differs chemically and determines the characteristics of the assembled polypeptide chain. These R-groups may be hydrophobic or hydrophilic, and the hydrophilic ones may be polar or charged, either acidic or basic [1]. This diversity influences how a protein folds and its solubility [1]. For example, in globular proteins that must dissolve in water, hydrophilic amino acids are positioned on the surface to form hydrogen bonds with water, while hydrophobic amino acids cluster inside the core, helping to stabilize the tertiary structure and define the protein’s final shape.
Question 1
The diagram is a three-dimensional molecular model of a protein.

[Source: Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature, Toshimitsu Kawate, Jennifer Carlisle Michel, William T. Birdsong & Eric Gouaux, ‘Crystal structure of the ATP-gated P2X4 ion channel in the closed state’, 460, pp 592–598, © 2009. www.nature.com.]
Which bonds stabilize the shape of the area labelled X?
A. Covalent bonds between adjacent amino acids
B. Hydrogen bonds between N–H and C=O groups of amino acids
C. Hydrophobic interactions between R groups of amino acid
D. Disulphide bridges between cysteine molecules
Question 2
Which element is most common in proteins?
A. Sodium
B. Nitrogen
C. Phosphorus
D. Iron
Question 3
The image shows the structure of the protein hemoglobin?

What level of protein structure bonds the α and β chains together?
A. Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D.Quaternary
Question 4
Which is an effect of protein denaturation?
A. The order of amino acids is changed when the protein overheats.
B. The bonds between amino acids are broken by condensation.
C. Parts of the protein become linked together by hydrolysis.
D. The three-dimensional structure of the protein is altered.
Question 5
Which row correctly matches the level of structure of a protein molecule with the bonds that stabilize it?
| Level of structure | Bonds | |
| A. | primary | peptide and hydrogen bonds between amine and carboxyl groups |
| B. | secondary | hydrogen bonds between R-groups of amino acids |
| C. | tertiary | disulfide, hydrogen and ionic bonds between R-groups of amino acids |
| D. | quaternary | covalent bonds between hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions on the polypeptide subunits |
Question 6
Which protein has the highest tensile strength (ability to resist breaking when stretched)?
A. Cellulose
B. Actin
C. Spider silk
D. Albumin
Question 7
Myoglobin is a globular protein in which nearly all the non-polar R-groups point towards the inside of the molecule. The outside surface contains all the polar R-groups. What can be deduced from this?
A. Disulfide bonds occur on the inside.
B. Hydrogen bonds form with water on the outside.
C. Ionic bonds form with water on the outside.
D. Covalent bonds occur on the inside.
Question 8
Diagrams of three different proteins, X, Y and Z, are shown

Which row describes the structure of each protein shown?
| X | Y | Z | |
| A. | quaternary | globular | secondary |
| B. | conjugated | fibrous | globular |
| C. | tertiary | quaternary | primary |
| D. | globular | secondary | fibrous |
Question 9
Outline the process of protein denaturation. [4]
Question 10
Describe how the diversity of amino acids gives proteins a broad range of forms. [2]