Question 1
The photograph shows a scorpion (Pandinus imperator).

What recognition features indicate that it is an arthropod?
A. Exoskeleton and articulated legs
B. Segmented body and endoskeleton
C. Soft body covered by calcium exoskeleton
D. Body divided into three parts and radial symmetry
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Movement of insects requires muscles in antagonistic pairs. The diagram shows an insect leg with muscles labelled X and Y.
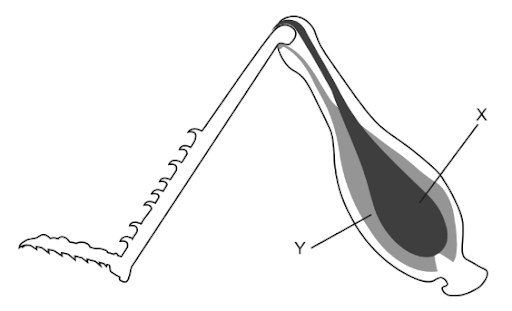
What actions in the human arm are equivalent to muscle X contracting and muscle Y relaxing?
A. triceps contracts, biceps relaxes, arm extends
B. biceps contracts, triceps relaxes, arm flexes
C. triceps contracts, biceps relaxes, arm flexes
D. biceps contracts, triceps relaxes, arm extends
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
What is the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction?
A. To enable actin to expose binding sites on myosin
B. To bind to troponin, exposing binding sites on actin
C. To prevent an action potential in the muscle membrane
D. To bind to tropomyosin, blocking binding sites on actin
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
What is the order of increasing size of muscle structures?
A. muscle, muscle fibre, myofibril, sarcomere
B. myofibril, muscle fibre, sarcomere, muscle
C. sarcomere, myofibril, muscle fibre, muscle
D. muscle fibre, sarcomere, myofibril, muscle
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
What is contained in skeletal muscle?
A. Cross bridges between muscle fibres
B. Sarcomeres formed of contractile myofibrils
C. Myosin filaments forming cross bridges with troponin and tropomyosin
D. Multinucleate cells with numerous microfibrils made of contractile sarcomeres
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
What are features of both endoskeletons of mammals and exoskeletons of insects?
A. They are both made of bone.
B. They both have cartilage.
C. They are both moved by antagonistic sets of muscles.
D. Both consist of dead tissue.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
What occurs during skeletal muscle contraction?
A. Myosin and actin filaments decrease in length.
B. Calcium ions bind to troponin.
C. ATP binds to actin heads.
D. The dark band gets shorter.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Outline the antagonistic action of the muscles of the elbow. [2]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Explain the roles of proteins in muscle contraction. [7]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Explain the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction. [3]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
The photograph shows a scorpion (Pandinus imperator).

What recognition features indicate that it is an arthropod?
A. Exoskeleton and articulated legs
B. Segmented body and endoskeleton
C. Soft body covered by calcium exoskeleton
D. Body divided into three parts and radial symmetry
Answer: A
A. Correct. Arthropods have a hard exoskeleton made of chitin and jointed (articulated) legs, which allow movement despite the rigid exoskeleton.
B. Incorrect. Arthropods do have segmented bodies, but they do not have an endoskeleton.
C. Incorrect. Arthropods have chitinous, not calcium-based, exoskeletons.
D. Incorrect. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical, not radially symmetrical.
Question 2
Movement of insects requires muscles in antagonistic pairs. The diagram shows an insect leg with muscles labelled X and Y.

What actions in the human arm are equivalent to muscle X contracting and muscle Y relaxing?
A. triceps contracts, biceps relaxes, arm extends
B. biceps contracts, triceps relaxes, arm flexes
C. triceps contracts, biceps relaxes, arm flexes
D. biceps contracts, triceps relaxes, arm extends
Answer: A
A. Correct. In insects, movement occurs through antagonistic muscle pairs, meaning one muscle contracts while the other relaxes to produce opposite movements. X = extensor muscle, Y = flexor muscle. The equivalent muscles on humans are triceps = extensor muscle and biceps = flexor muscle. Meaning triceps contracts, and biceps relax, leading to the extension of arms.
B. Incorrect. In insects, movement occurs through antagonistic muscle pairs, meaning one muscle contracts while the other relaxes to produce opposite movements. X = extensor muscle, Y = flexor muscle. The equivalent muscles on humans are triceps = extensor muscle and biceps = flexor muscle. Meaning triceps contracts, and biceps relax, leading to the extension of arms.
C. Incorrect. In insects, movement occurs through antagonistic muscle pairs, meaning one muscle contracts while the other relaxes to produce opposite movements. X = extensor muscle, Y = flexor muscle. The equivalent muscles on humans are triceps = extensor muscle and biceps = flexor muscle. Meaning triceps contracts, and biceps relax, leading to the extension of arms, not flexing.
D. Incorrect. In insects, movement occurs through antagonistic muscle pairs, meaning one muscle contracts while the other relaxes to produce opposite movements. X = extensor muscle, Y = flexor muscle. The equivalent muscles on humans are triceps = extensor muscle and biceps = flexor muscle. Meaning triceps contracts, and biceps relax, leading to the extension of arms. When biceps contracts and triceps relaxes, arm flexes, not extending.
Question 3
What is the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction?
A. To enable actin to expose binding sites on myosin
B. To bind to troponin, exposing binding sites on actin
C. To prevent an action potential in the muscle membrane
D. To bind to tropomyosin, blocking binding sites on actin
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Actin does not expose binding sites on myosin. Instead, myosin binds to exposed sites on actin.
B. Correct. Calcium binds to troponin, which moves tropomyosin away and exposes actin’s binding sites so myosin can attach.
C. Incorrect. Calcium does not prevent action potentials. Muscle contraction requires an action potential to release calcium.
D. Incorrect. Calcium does not bind to tropomyosin. Instead, it causes tropomyosin to move away and uncover the binding sites.
Question 4
What is the order of increasing size of muscle structures?
A. muscle, muscle fibre, myofibril, sarcomere
B. myofibril, muscle fibre, sarcomere, muscle
C. sarcomere, myofibril, muscle fibre, muscle
D. muscle fibre, sarcomere, myofibril, muscle
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. A whole muscle is made of many muscle fibers, each fiber contains many myofibrils, and each myofibril contains many sarcomeres. Meaning sarcomeres < myofibril < muscle fibers < muscle.
B. Incorrect. A whole muscle is made of many muscle fibers, each fiber contains many myofibrils, and each myofibril contains many sarcomeres. Meaning sarcomeres < myofibril < muscle fibers < muscle.
C. Correct. Incorrect. A whole muscle is made of many muscle fibers, each fiber contains many myofibrils, and each myofibril contains many sarcomeres. Meaning sarcomeres < myofibril < muscle fibers < muscle.
D. Incorrect. Incorrect. A whole muscle is made of many muscle fibers, each fiber contains many myofibrils, and each myofibril contains many sarcomeres. Meaning sarcomeres < myofibril < muscle fibers < muscle.
Question 5
What is contained in skeletal muscle?
A. Cross bridges between muscle fibres
B. Sarcomeres formed of contractile myofibrils
C. Myosin filaments forming cross bridges with troponin and tropomyosin
D. Multinucleate cells with numerous microfibrils made of contractile sarcomeres
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. Cross bridges form within sarcomeres between actin and myosin filaments inside a single muscle fiber, not between separate muscle fibers.
B. Incorrect. Sarcomeres are the repeating units of myofibrils, which are contractile structures inside the muscle fiber. Meaning myofibrils are formed of sarcomeres.
C. Incorrect. Myosin filaments form cross bridges with actin filaments, not troponin or tropomyosin. Troponin and tropomyosin regulate contraction.
D. Correct. Skeletal muscle is made of multinucleated muscle fibers that contain many myofibrils, which in turn are made of repeating sarcomeres.
Question 6
What are features of both endoskeletons of mammals and exoskeletons of insects?
A. They are both made of bone.
B. They both have cartilage.
C. They are both moved by antagonistic sets of muscles.
D. Both consist of dead tissue.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Mammal endoskeletons are made of bone, but insect exoskeletons are made of chitin, not bone.
B. Incorrect. Mammals have cartilage in joints and certain structures, but insects do not have cartilage at all.
C. Correct. Both rely on muscles arranged in antagonistic pairs (flexors/extensors) to produce movement. In mammals, muscles are inside, and in insects, muscles attach to the exoskeleton.
D. Incorrect. The exoskeleton of insects are largely dead chitin, but mammalian bone is living tissue with cells, nerves, and blood vessels.
Question 7
What occurs during skeletal muscle contraction?
A. Myosin and actin filaments decrease in length.
B. Calcium ions bind to troponin.
C. ATP binds to actin heads.
D. The dark band gets shorter.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. The filaments themselves do not shorten. Instead, they slide past each other, causing the sarcomere to shorten.
B. Correct. Calcium binds to troponin, moving tropomyosin off actin binding sites so myosin can form cross-bridges.
C. Incorrect. ATP binds to myosin heads, not actin. ATP provides energy for the myosin head to detach and recock.
D. Incorrect. The A band (dark band, mostly myosin) stays the same length. The I band and H zone get shorter as the sarcomere contracts.
Question 8
Outline the antagonistic action of the muscles of the elbow. [2]
Two of the following:
a. work in opposition to each other/cause opposite movements OR when one muscle contracts the other relaxes
b. biceps bends the elbow/flexes the arm/pulls the forearm upwards / is the flexor
c. triceps straightens/extends the arm/is the extensor
Sample answer:
The muscles of the elbow work antagonistically, meaning when one muscle contracts, the other relaxes, producing opposite movements [1]. The biceps muscle acts as the flexor of the elbow. When it contracts, it bends the elbow and pulls the forearm upwards [1]. In contrast, the triceps muscle acts as the extensor. When it contracts, it straightens the arm, performing the opposite movement of the biceps [1]. This coordinated action of flexor and extensor ensures smooth and controlled movement at the elbow joint.
Question 9
Explain the roles of proteins in muscle contraction. [7]
Seven of the following:
a. actin and myosin are protein filaments
b. actin/myosin/protein filaments form sarcomeres in muscle myofibrils
c. actin filaments are thin, and myosin filaments are thick
d. actin attached to Z lines / diagram showing overlapping actin and myosin in a sarcomere
e. actin has myosin binding sites
f. tropomyosin blocks myosin binding sites on actin (in relaxed muscle)
g. calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum when depolarization/ action potential arrives
h. calcium ions bind to troponin
i. troponin causes removal of tropomyosin from binding sites
j. myosin heads attach to/form cross-bridges with) actin
k. ATP activates/cocks/changes angle of/provides energy for detaching myosin heads
l. heads tilt to move actin towards center of sarcomere / filaments slide over each other
m. muscle contraction due to shortening of sarcomere/more overlapping of actin and myosin
Sample answer:
In muscle contraction, the proteins actin and myosin are filamentous proteins [1], with actin forming thin filaments and myosin forming thick filaments [1], and together these protein filaments are arranged into repeating units called sarcomeres within muscle myofibrils [1]. Actin filaments are anchored to the Z lines, creating a pattern where actin and myosin overlap inside each sarcomere [1. Actin contains myosin-binding sites [1], but in a relaxed muscle these sites are blocked by the regulatory protein tropomyosin [1]. When an action potential reaches the muscle, calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum [1], and these calcium ions bind to the protein troponin [1]. Troponin then shifts tropomyosin away from the binding sites on actin, exposing them [1]. Myosin heads can now attach to these sites, forming cross-bridges [1]. ATP provides the energy for the myosin heads to detach, reset, and change angle, enabling repeated cycles [1]. The pivoting of the myosin heads pulls the actin filaments toward the center of the sarcomere, causing them to slide past the myosin filaments [1]. As a result, the sarcomere shortens, increasing the overlap of actin and myosin and producing muscle contraction [1].
Question 10
Explain the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction. [3]
Three of the following:
a. calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum;
b. calcium binds to troponin;
c. causes tropomyosin to move;
d. uncovers binding sites;
e. myosin heads bind to the actin forming cross bridges;
Sample answer:
Muscle contraction begins when calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum [1]. These calcium ions then bind to troponin on the thin filaments [1], which causes tropomyosin to shift its position [1]. This movement uncovers the myosin-binding sites on actin [1], allowing myosin heads to attach to actin and form cross-bridges that initiate contraction [1].
Question 1
The photograph shows a scorpion (Pandinus imperator).

What recognition features indicate that it is an arthropod?
A. Exoskeleton and articulated legs
B. Segmented body and endoskeleton
C. Soft body covered by calcium exoskeleton
D. Body divided into three parts and radial symmetry
Question 2
Movement of insects requires muscles in antagonistic pairs. The diagram shows an insect leg with muscles labelled X and Y.

What actions in the human arm are equivalent to muscle X contracting and muscle Y relaxing?
A. triceps contracts, biceps relaxes, arm extends
B. biceps contracts, triceps relaxes, arm flexes
C. triceps contracts, biceps relaxes, arm flexes
D. biceps contracts, triceps relaxes, arm extends
Question 3
What is the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction?
A. To enable actin to expose binding sites on myosin
B. To bind to troponin, exposing binding sites on actin
C. To prevent an action potential in the muscle membrane
D. To bind to tropomyosin, blocking binding sites on actin
Question 4
What is the order of increasing size of muscle structures?
A. muscle, muscle fibre, myofibril, sarcomere
B. myofibril, muscle fibre, sarcomere, muscle
C. sarcomere, myofibril, muscle fibre, muscle
D. muscle fibre, sarcomere, myofibril, muscle
Question 5
What is contained in skeletal muscle?
A. Cross bridges between muscle fibres
B. Sarcomeres formed of contractile myofibrils
C. Myosin filaments forming cross bridges with troponin and tropomyosin
D. Multinucleate cells with numerous microfibrils made of contractile sarcomeres
Question 6
What are features of both endoskeletons of mammals and exoskeletons of insects?
A. They are both made of bone.
B. They both have cartilage.
C. They are both moved by antagonistic sets of muscles.
D. Both consist of dead tissue.
Question 7
What occurs during skeletal muscle contraction?
A. Myosin and actin filaments decrease in length.
B. Calcium ions bind to troponin.
C. ATP binds to actin heads.
D. The dark band gets shorter.
Question 8
Outline the antagonistic action of the muscles of the elbow. [2]
Question 9
Explain the roles of proteins in muscle contraction. [7]
Question 10
Explain the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction. [3]