Question 1
What occurs during competitive exclusion between two species?
I. They compete for the same resources so cannot coexist in the same niche.
II. Competing species are regulated by predators in the ecosystem.
III. Both species are restricted to a part of their fundamental niche.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. III only
D. I, II and III
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Hummingbirds eat flower nectar and small insects. To which nutritional group do they belong?
A. Autotrophs
B. Consumers
C. Detritivores
D. Saprotrophs
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
The Australian pitcher plant (Cephalotus follicularis) is a green plant that traps and feeds on flies and other live insects. What is this plant’s mode of nutrition?
A. Producer and saprotroph
B. Autotroph and detritivore
C. Autotroph and heterotroph
D. Consumer and saprotroph
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
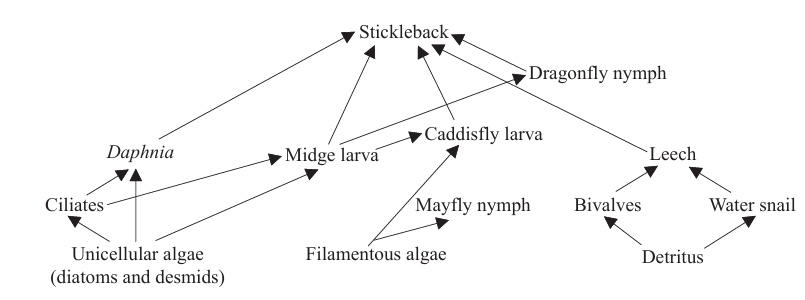
Question 4
What is the mode of nutrition of midge larva?
A. Autotroph
B. Detritivore
C. Heterotroph
D. Saprotroph.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
The image shows Prorocentrum, a coastal dinoflagellate that obtains energy from sunlight and from other organisms.
What best describes the mode of nutrition of Prorocentrum?
A. Mixotrophic
B. Autotrophic
C. Holozoic
D. Heterotrophic
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Dry rot fungus (Serpula lacrymans) secretes digestive enzymes to externally digest dead wood.

What type of nutrition is used by dry rot fungus?
A. Holozoic
B. Saprotrophic
C. Mixotrophic
D. Autotrophic
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
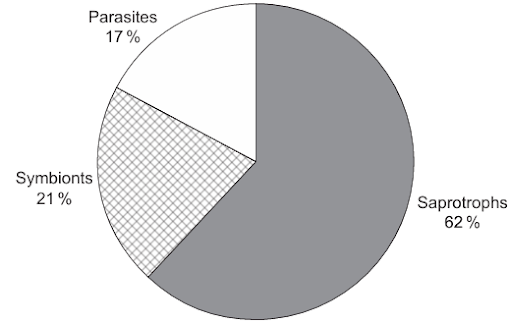
The pie chart shows the modes of nutrition of fungi in Huahu Lake wetland in China.
What is the most common mode of nutrition of fungi in this wetland?
A. Heterotrophic fungi that feed on living organisms by ingestion
B. Autotrophic fungi that obtain organic nutrients from detritus by internal digestion
C. Fungi that have either an autotrophic or heterotrophic method of nutrition
D. Heterotrophic fungi obtaining nutrients from dead organisms by external digestion
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What is the difference between a detritivore and a saprotroph?
A. Detritivores are animals, and saprotrophs are plants.
B. Detritivores feed on dead organic matter, and saprotrophs feed on living organisms.
C. Detritivores digest food internally, and saprotrophs digest it externally.
D. Detritivores are autotrophic, and saprotrophs are heterotrophic.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
The niches of the red and grey squirrels overlap. Explain the concept of competitive exclusion with respect to the changes in squirrel distribution shown in the maps. [3]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Outline the possible influence of a change in diet on hominid evolution. [2]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
What occurs during competitive exclusion between two species?
I. They compete for the same resources so cannot coexist in the same niche.
II. Competing species are regulated by predators in the ecosystem.
III. Both species are restricted to a part of their fundamental niche.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. III only
D. I, II and III
Answer: B
I. Correct. Competitive exclusion occurs when the fundamental niches of two species overlap. According to the competitive exclusion principle, two species cannot occupy the same niche indefinitely.
II. Incorrect. Regulation by predators is a density-dependent mechanism. The competitive exclusion principle focuses on the consequences of resource competition between species.
III. Correct. In some cases, competing species can coexist but are limited to a portion of their fundamental niche. Competition may restrict both species. The realized niche is the part of the potential range that a species actually occupies; this reduction is due to competition
Therefore, answer B that has statements I and II is correct.
A,C, and D are incorrect.
Question 2
Hummingbirds eat flower nectar and small insects. To which nutritional group do they belong?
A. Autotrophs
B. Consumers
C. Detritivores
D. Saprotrophs
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Autotrophs use external energy sources (e.g., light) to synthesize glucose from simple inorganic substances. Hummingbirds obtain food from other organisms.
B. Correct. Consumers feed on living or recently dead organic matter. Hummingbirds eat nectar and insects.
C. Incorrect. Detritivores feed on dead organic material (detritus). Hummingbirds eat nectar and living insects.
D. Incorrect. Saprotrophs secrete digestive enzymes onto dead organic matter outside the body and absorb the products. Hummingbirds digest their food internally (holozoic nutrition).
Question 3
The Australian pitcher plant (Cephalotus follicularis) is a green plant that traps and feeds on flies and other live insects. What is this plant’s mode of nutrition?
A. Producer and saprotroph
B. Autotroph and detritivore
C. Autotroph and heterotroph
D. Consumer and saprotroph
Answer: C
The pitcher plant is green, so it performs photosynthesis → Autotrophic. However, it also traps and digests insects to obtain other nutrients (e.g., nitrogen), meaning it obtains organic compounds from other organisms → Heterotrophic. This combined mode is called mixotrophic nutrition.
A. Incorrect. Although it is a producer, it is not a saprotroph (saprotrophs digest externally dead organic matter).
B. Incorrect. It eats live insects (heterotroph), not dead organic matter (detritivore).
C. Incorrect. It photosynthesizes and also feeds on insects.
D. Incorrect. It is an autotroph/producer.
Question 4
What is the mode of nutrition of midge larva?

A. Autotroph
B. Detritivore
C. Heterotroph
D. Saprotroph.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Autotrophs make their own food from simple inorganic substances. The midge larva feeds on detritus.
B. Correct. It feeds on detritus. Detritivory is a type of heterotrophic nutrition in which dead organic matter is ingested and digested internally.
C. Incorrect. Heterotrophs obtain carbon compounds from other organisms. Since detritivores are a type of heterotroph, the larva is heterotrophic. However, “Detritivore” is the more specific and appropriate answer based on the food source.
D. Incorrect. Saprotrophs digest externally by secreting enzymes onto dead organic matter. The Chironomidae larva is an invertebrate animal and digests internally → detritivore, not saprotroph.
Question 5
The image shows Prorocentrum, a coastal dinoflagellate that obtains energy from sunlight and from other organisms.

What best describes the mode of nutrition of Prorocentrum?
A. Mixotrophic
B. Autotrophic
C. Holozoic
D. Heterotrophic
Answer: A
A. Correct. Prorocentrum obtains energy from sunlight (autotrophic) and from other organisms (heterotrophic). Some unicellular eukaryotes (protists) are classified as mixotrophs. Another example is Euglena, which is a facultative mixotroph.
B. Incorrect. Autotrophs use external energy sources (such as light or chemical reactions) to synthesize glucose from simple inorganic substances. Although Prorocentrum uses sunlight, it also obtains energy from other organisms, so autotrophy alone is not a complete description.
C. Incorrect. Holozoic organisms do not produce food from sunlight; thus, this does not describe the dual nutritional mode of Prorocentrum.
D. Incorrect. Although Prorocentrum can do this, it also performs photosynthesis; therefore, heterotrophic is not the most complete description.
Question 6
Dry rot fungus (Serpula lacrymans) secretes digestive enzymes to externally digest dead wood.

What type of nutrition is used by dry rot fungus?
A. Holozoic
B. Saprotrophic
C. Mixotrophic
D. Autotrophic
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Holozoic nutrition involves ingesting food and digesting it internally. Dry rot fungus digests food externally by secreting enzymes; it does not ingest its food.
B. Correct. Fungi (along with bacteria) are major saprotrophs. Dry rot fungus digests dead wood externally, fitting the definition of saprotrophic nutrition.
C. Incorrect. Dry rot fungus obtains nutrients only from dead organic matter, making it purely heterotrophic.
D. Incorrect. Fungi are heterotrophic and rely on organic material such as dead wood.
Question 7
The pie chart shows the modes of nutrition of fungi in Huahu Lake wetland in China.

What is the most common mode of nutrition of fungi in this wetland?
A. Heterotrophic fungi that feed on living organisms by ingestion
B. Autotrophic fungi that obtain organic nutrients from detritus by internal digestion
C. Fungi that have either an autotrophic or heterotrophic method of nutrition
D. Heterotrophic fungi obtaining nutrients from dead organisms by external digestion
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. Although fungi are heterotrophs, saprotrophic fungi (which make up about 62%) do not feed on living organisms, they feed on dead organisms. More importantly, saprotrophic fungi secrete digestive enzymes externally and then absorb the products. They do not ingest (take in) food for internal digestion. Ingestion and internal digestion (holozoic nutrition) are characteristic of animals/consumers.
B. Incorrect. Fungi are heterotrophic, not autotrophic. Autotrophs use external energy sources (such as light) to synthesize glucose from simple inorganic substances. Fungi cannot photosynthesize because they lack chloroplasts. Saprotrophic fungi digest food by secreting enzymes externally, not by internal digestion.
C. Incorrect. This mode is called mixotrophic nutrition. Although some unicellular eukaryotes (protists) may be mixotrophs, fungi are generally classified as heterotrophs because they obtain carbon compounds from other organisms.
D. Incorrect. This is the saprotrophic mode of nutrition, which is the most common (about 62%). Fungi are heterotrophs and obtain carbon compounds from other organisms. Saprotrophs live on or in dead organic matter. They achieve this by secreting digestive enzymes onto dead organic material (external digestion) and absorbing the resulting products. This process helps break down complex carbon compounds into simpler substances.
Question 8
What is the difference between a detritivore and a saprotroph?
A. Detritivores are animals, and saprotrophs are plants.
B. Detritivores feed on dead organic matter, and saprotrophs feed on living organisms.
C. Detritivores digest food internally, and saprotrophs digest it externally.
D. Detritivores are autotrophic, and saprotrophs are heterotrophic.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Although detritivores are usually animals (such as earthworms), saprotrophs are mainly fungi and bacteria. Fungi and bacteria are not classified as plants.
B. Incorrect. Both detritivores and saprotrophs feed on dead organic matter or waste material. Organisms that feed on living or freshly killed organisms are called consumers, carnivores, or, if they live on a host, parasites.
C. Correct. The main difference between these two groups lies in how they process dead organic matter. Detritivores are organisms that ingest dead organic material (detritus), showing holozoic nutrition. They eat detritus and process it in their gut (internal digestion). Examples include earthworms and termites. Saprotrophs live on or within dead organic matter, secrete digestive enzymes onto that material (external digestion), and then absorb the digested products. Therefore, the key difference is that detritivores carry out internal digestion, while saprotrophs carry out external digestion.
D. Incorrect. Both groups are heterotrophs.
Question 9
The niches of the red and grey squirrels overlap. Explain the concept of competitive exclusion with respect to the changes in squirrel distribution shown in the maps. [3]
Any three of the following:
a. competitive exclusion states two species that occupy a similar niche in the same location cannot coexist;
b. one of the two competitors will always have an advantage over the other;
c. leads to extinction/displacement/evolution of the second competitor;
d. grey squirrels have replaced/occupied niches formerly occupied by red squirrels;
OR
habitats favour the grey squirrel in competition for the niche;
e. the niche of one competitor/both competitors becomes narrower;
Sample answer:
The principle of competitive exclusion explains the changes in squirrel distribution as a result of the overlap in their ecological niches. The competitive exclusion principle states that two species occupying a similar niche in the same location cannot coexist [1]. In this case, the grey squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis) is the invasive species, while the red squirrel (Sciurus vulgaris) is native. The grey squirrel has an advantage over the red squirrel because it has a broader diet, including the ability to digest polyphenolic compounds found in acorns, something the red squirrel cannot do. Therefore, one of the two competitors will always have an advantage over the other [1]. This advantage has allowed the grey squirrel to replace and occupy the ecological niches previously held by the red squirrel, causing red squirrel populations to decline rapidly [1]. Ultimately, this competitive exclusion leads to the red squirrel (the less effective competitor) being reduced in number or eliminated locally.
Question 10
Outline the possible influence of a change in diet on hominid evolution. [2]
Any two of the following:
a. more meat in diet correlates with larger brain size in hominids;
b. meat has much protein, fat and energy needed by brain to grow;
c. hunting animals requires more intelligence than gathering food/foraging / hunting
d. favours natural selection of larger brain;
Sample answer:
The change in diet among hominids is thought to have had a significant impact on their evolution. When the diet shifted to include more meat, this correlated with larger brain size in hominids [1]. The development of this larger brain could be nutritionally supported because meat contains high amounts of protein, fat, and energy needed for brain growth [2]. The brain requires a large amount of energy, and the concentrated energy provided by meat supplies these essential nutrients, thereby supporting the increase in brain size observed in species of the genus Homo compared with Australopithecus.
Question 1
What occurs during competitive exclusion between two species?
I. They compete for the same resources so cannot coexist in the same niche.
II. Competing species are regulated by predators in the ecosystem.
III. Both species are restricted to a part of their fundamental niche.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. III only
D. I, II and III
Question 2
Hummingbirds eat flower nectar and small insects. To which nutritional group do they belong?
A. Autotrophs
B. Consumers
C. Detritivores
D. Saprotrophs
Question 3
The Australian pitcher plant (Cephalotus follicularis) is a green plant that traps and feeds on flies and other live insects. What is this plant’s mode of nutrition?
A. Producer and saprotroph
B. Autotroph and detritivore
C. Autotroph and heterotroph
D. Consumer and saprotroph
Question 4
What is the mode of nutrition of midge larva?

A. Autotroph
B. Detritivore
C. Heterotroph
D. Saprotroph.
Question 5
The image shows Prorocentrum, a coastal dinoflagellate that obtains energy from sunlight and from other organisms.

What best describes the mode of nutrition of Prorocentrum?
A. Mixotrophic
B. Autotrophic
C. Holozoic
D. Heterotrophic
Question 6
Dry rot fungus (Serpula lacrymans) secretes digestive enzymes to externally digest dead wood.

What type of nutrition is used by dry rot fungus?
A. Holozoic
B. Saprotrophic
C. Mixotrophic
D. Autotrophic
Question 7
The pie chart shows the modes of nutrition of fungi in Huahu Lake wetland in China.

What is the most common mode of nutrition of fungi in this wetland?
A. Heterotrophic fungi that feed on living organisms by ingestion
B. Autotrophic fungi that obtain organic nutrients from detritus by internal digestion
C. Fungi that have either an autotrophic or heterotrophic method of nutrition
D. Heterotrophic fungi obtaining nutrients from dead organisms by external digestion
Question 8
What is the difference between a detritivore and a saprotroph?
A. Detritivores are animals, and saprotrophs are plants.
B. Detritivores feed on dead organic matter, and saprotrophs feed on living organisms.
C. Detritivores digest food internally, and saprotrophs digest it externally.
D. Detritivores are autotrophic, and saprotrophs are heterotrophic.
Question 9
The niches of the red and grey squirrels overlap. Explain the concept of competitive exclusion with respect to the changes in squirrel distribution shown in the maps. [3]
Question 10
Outline the possible influence of a change in diet on hominid evolution. [2]