Question 1
Which compound is a waste product of anaerobic respiration in humans?
A. Carbon dioxide
B. Ethanol
C. Lactate
D. Pyruvate
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The diagram shows a reaction that occurs during aerobic cell respiration.
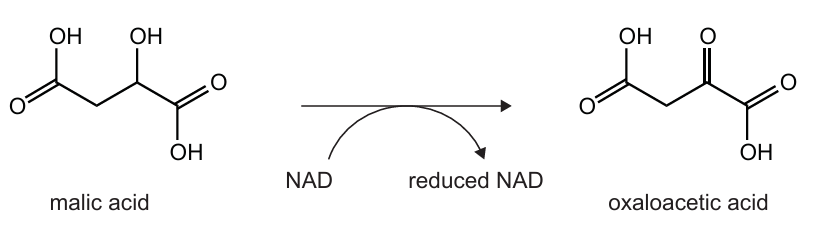
Which type of chemical change happens to malic acid?
A. Carboxylation
B. Decarboxylation
C. Oxidation
D. Reduction
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Bread dough is made by mixing flour, water and yeast. If the dough is then kept at about 30°C, it expands.
What is the main reason for choosing this temperature?
A. Carbon dioxide expands at this temperature.
B. This is the optimum temperature for the enzymes used in aerobic cell respiration.
C. Lactate produced by anaerobic cell respiration causes the release of carbon dioxide at this temperature.
D. At this temperature, yeast produces carbon dioxide rapidly by anaerobic cell respiration.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which part of aerobic respiration directly involves oxygen molecules?
A. Conversion of glucose to pyruvate
B. Accepting electrons from the electron transport chain
C. Oxidizing acetyl groups in the Krebs cycle
D. Production of NAD from reduced NAD
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Where are protons pumped, to allow chemiosmosis in aerobic respiration to occur?
A. From outside the mitochondrion through the double membranes
B. From carrier to carrier in the inner mitochondrial membrane
C. From the matrix of the mitochondrion to the space between the membranes
D. From the space between the membranes to the cytoplasm outside the mitochondrion
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
The diagram shows the link reaction between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
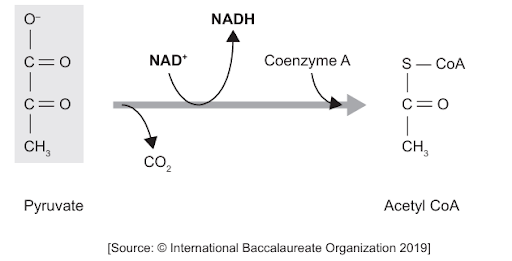
Which type of reaction is occurring?
A. Pyruvate is carboxylated.
B. CO2 is oxidized.
C. NAD+ is reduced.
D. Pyruvate is phosphorylated.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Two reactions of the Krebs cycle are shown.
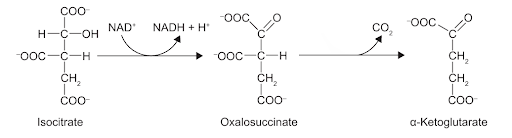
What type of reactions are isocitrate and oxalosuccinate undergoing?
| Isocitrate | Oxalosuccinate | |
| A. | oxidation | reduction |
| B. | reduction | decarboxylation |
| C. | reduction | oxidation |
| D. | oxidation | decarboxylation |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Lipids are more efficient energy stores than carbohydrates. What is a reason for this?
A. Lipids are bigger molecules than carbohydrates.
B. Lipids release more energy per gram than carbohydrates.
C. Lipids can be more easily mobilized than carbohydrates when needed.
D. Lipids can be used in aerobic and anaerobic respiration when needed.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Explain how animal cells produce the ATP that they need. [5]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Glucose is converted to pyruvate during the glycolysis stage of respiration.

(a) On the diagram, label
(i) with P where phosphorylation occurs; [1]
(ii) with O where oxidation occurs. [1]
(b) State where in the cell glycolysis takes place. [1]
(c) Outline how NAD is made available for glycolysis during anaerobic respiration in animal cells. [2]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Which compound is a waste product of anaerobic respiration in humans?
A. Carbon dioxide
B. Ethanol
C. Lactate
D. Pyruvate
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: Carbon dioxide is released during aerobic respiration (in the link reaction and Krebs cycle), not anaerobic respiration in humans.
B. Incorrect: Ethanol is the end product of anaerobic respiration in yeast and some plants, not in humans.
C. Correct: During anaerobic respiration in humans, glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen to release a small amount of energy (ATP). Because there is no oxygen, pyruvate (the end product of glycolysis) cannot enter the mitochondria for aerobic respiration. Instead, pyruvate is converted into lactate (lactic acid) in the cytoplasm. This process allows glycolysis to continue by regenerating NAD⁺, but lactate accumulates as a waste product that can cause muscle fatigue.
D. Incorrect: Pyruvate is an intermediate product of glycolysis, not the final waste product. In anaerobic conditions, it is further converted to lactate.
Question 2
The diagram shows a reaction that occurs during aerobic cell respiration.

Which type of chemical change happens to malic acid?
A. Carboxylation
B. Decarboxylation
C. Oxidation
D. Reduction
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: Because no CO2 group is added to the molecule. Carboxylation means the addition of a carboxyl (-COOH) group, which does not occur here
B. Incorrect: Because no carbon dioxide (CO2) is released from malic acid. The number of carbon atoms in malic acid and oxaloacetic acid remains the same (both have 4 carbons).
C. Correct: In this reaction, malic acid (malate) is converted into oxaloacetic acid (oxaloacetate) during the Krebs cycle of aerobic respiration. During this process, hydrogen atoms are removed from malic acid and transferred to NAD⁺, forming reduced NAD (NADH). The loss of hydrogen (and electrons) from malate means that malic acid is oxidized. Therefore, this reaction is an oxidation reaction.
D. Incorrect: Reduction involves gaining hydrogen or electrons, but in this reaction, malic acid loses hydrogen, meaning it is oxidized. Instead, NAD⁺ is the molecule being reduced.
Question 3
Bread dough is made by mixing flour, water and yeast. If the dough is then kept at about 30°C, it expands.

What is the main reason for choosing this temperature?
A. Carbon dioxide expands at this temperature.
B. This is the optimum temperature for the enzymes used in aerobic cell respiration.
C. Lactate produced by anaerobic cell respiration causes the release of carbon dioxide at this temperature.
D. At this temperature, yeast produces carbon dioxide rapidly by anaerobic cell respiration.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: The expansion of the dough is not due to gas expansion from heat, but rather production of new CO2 by yeast respiration.
B. Incorrect: The yeast in bread dough respires anaerobically, not aerobically. Oxygen is quickly used up inside the dough, so fermentation (anaerobic respiration) dominates.
C. Incorrect: Yeast does not produce lactate during anaerobic respiration - it produces ethanol and carbon dioxide. Lactate is produced in animal cells, not in yeast.
D. Correct: At around 30°C, yeast cells are at their optimum temperature for anaerobic respiration (fermentation). Under these conditions, yeast breaks down sugars in the dough without oxygen, producing carbon dioxide (CO2) and ethanol. The carbon dioxide gas forms bubbles in the dough, causing it to rise and expand. This temperature ensures that enzyme activity in yeast is high enough for rapid fermentation but not so high that the enzymes denature.
Question 4
Which part of aerobic respiration directly involves oxygen molecules?
A. Conversion of glucose to pyruvate
B. Accepting electrons from the electron transport chain
C. Oxidizing acetyl groups in the Krebs cycle
D. Production of NAD from reduced NAD
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: This occurs during glycolysis in the cytoplasm and does not require oxygen; it is an anaerobic process.
B. Correct: In aerobic respiration, oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, which occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Oxygen combines with electrons and hydrogen ions (H⁺) at the end of the chain to form water (H2O). This step is essential because it maintains the flow of electrons through the electron transport chain, allowing ATP production by oxidative phosphorylation to continue. Without oxygen to accept electrons, the chain would stop, and ATP production would cease.
C. Incorrect: Although this process is part of aerobic respiration, oxygen is not directly involved in the cycle. The Krebs cycle produces reduced NAD (NADH) and FADH2 that later donate electrons to the electron transport chain, where oxygen is used.
D. Incorrect: This depends indirectly on oxygen because NADH is oxidized back to NAD⁺ when electrons are passed to oxygen in the electron transport chain, but oxygen itself is not directly involved in the chemical step that forms NAD⁺; it is the final acceptor of the electrons that make this oxidation possible.
Question 5
Where are protons pumped, to allow chemiosmosis in aerobic respiration to occur?
A. From outside the mitochondrion through the double membranes
B. From carrier to carrier in the inner mitochondrial membrane
C. From the matrix of the mitochondrion to the space between the membranes
D. From the space between the membranes to the cytoplasm outside the mitochondrion
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: Protons are not pumped in from outside the mitochondrion. The proton pumping occurs within the organelle, between the matrix and intermembrane space.
B. Incorrect: Because while electrons are passed from carrier to carrier in the electron transport chain, protons are not; they are actively pumped across the membrane into the intermembrane space.
C. Correct: During aerobic respiration, the electron transport chain is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. As electrons move through the chain, energy is released and used by the carrier proteins to pump protons (H⁺ ions) from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space (the space between the inner and outer membranes). This creates a proton gradient - high proton concentration in the intermembrane space and low concentration in the matrix. The resulting electrochemical gradient (also called the proton motive force) drives chemiosmosis, where protons flow back into the matrix through ATP synthase, generating ATP.
D. Incorrect: Protons do not leave the mitochondrion. They remain in the intermembrane space to create the gradient necessary for ATP synthesis.
Question 6
The diagram shows the link reaction between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.

Which type of reaction is occurring?
A. Pyruvate is carboxylated.
B. CO2 is oxidized.
C. NAD+ is reduced.
D. Pyruvate is phosphorylated.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: Carboxylation means adding a carboxyl group (-COOH), but in this reaction, a carboxyl group is actually removed from pyruvate as CO2. This step is decarboxylation, not carboxylation.
B. Incorrect: CO2 is already fully oxidized (it has no more hydrogen or electrons to lose). It is the carbon from pyruvate that is oxidized to form CO2, not the other way around.
C. Correct: In the link reaction (which connects glycolysis to the Krebs cycle), pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA inside the mitochondrion. In this process, pyruvate is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons and hydrogen atoms. These electrons and hydrogen are transferred to NAD⁺, converting it into NADH. Since reduction is defined as the gain of electrons or hydrogen, NAD⁺ is reduced to NADH. This reduced NADH will later carry these high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain to generate ATP.
D. Incorrect: Because no phosphate group is added to pyruvate in this reaction. Instead, pyruvate is decarboxylated and oxidized, then combined with coenzyme A to form acetyl-CoA.
Question 7
Two reactions of the Krebs cycle are shown.

What type of reactions are isocitrate and oxalosuccinate undergoing?
| Isocitrate | Oxalosuccinate | |
| A. | oxidation | reduction |
| B. | reduction | decarboxylation |
| C. | reduction | oxidation |
| D. | oxidation | decarboxylation |
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: Oxalosuccinate is not reduced - it loses CO2, not gains electrons or hydrogen.
B. Incorrect: Isocitrate is oxidized, not reduced; it donates electrons to NAD⁺.
C. Incorrect: Neither molecule undergoes reduction; oxidation occurs first, followed by decarboxylation.
D. Correct: In the Krebs cycle, isocitrate is first oxidized to oxalosuccinate. During this oxidation, isocitrate loses hydrogen atoms and electrons, which are accepted by NAD⁺, reducing it to NADH + H⁺. This means isocitrate undergoes oxidation because it loses electrons (and hydrogen), while NAD⁺ is reduced. Next, oxalosuccinate undergoes decarboxylation, where it loses a molecule of carbon dioxide (CO2) to form α-ketoglutarate. The removal of a carboxyl group (-COOH) as CO2 is what defines a decarboxylation reaction. Thus, the correct sequence is oxidation (isocitrate) followed by decarboxylation (oxalosuccinate).
Question 8
Lipids are more efficient energy stores than carbohydrates. What is a reason for this?
A. Lipids are bigger molecules than carbohydrates.
B. Lipids release more energy per gram than carbohydrates.
C. Lipids can be more easily mobilized than carbohydrates when needed.
D. Lipids can be used in aerobic and anaerobic respiration when needed.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: Molecular size does not determine energy efficiency. The energy yield depends on chemical composition (types of bonds), not molecular mass.
B. Correct: Lipids are more efficient energy stores because they contain more carbon-hydrogen bonds than carbohydrates, meaning they are more reduced. When these bonds are broken during aerobic respiration, they release more energy per gram - approximately twice as much energy as carbohydrates. This makes lipids ideal for long-term energy storage in animals, such as in adipose tissue.
C. Incorrect: Carbohydrates (like glycogen) are mobilized more quickly for energy use. Lipids are stored in insoluble droplets and require more complex metabolic pathways to be broken down.
D. Incorrect: Lipids can only be used in aerobic respiration; they require oxygen to be broken down. In anaerobic conditions, only carbohydrates (like glucose) can be used.
Question 9
Explain how animal cells produce the ATP that they need. [5]
Any five of the following:
a. respiration/cell respiration;
b. energy released from glucose/lipids/organic compounds;
c. anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen;
d. lactate is produced in anaerobic respiration/word equation for anaerobic respiration;
e. oxygen used in aerobic respiration;
f. carbon dioxide and water produced in aerobic respiration/word equation for aerobic respiration;
g. mitochondria used for aerobic respiration;
h. larger yield of ATP from aerobic than anaerobic respiration;
Sample answer:
Animal cells produce ATP by cellular respiration [1], which harvests chemical energy from organic molecules (mainly glucose, but also lipids and other substrates) [1]. In aerobic respiration (requires oxygen) glucose is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water (a singe equation: `"glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide +water +ATP"`) [1], most of the ATP is generated in the mitochondria (oxidative phosphorylation), so aerobic pathways give a large yield of ATP per glucose [1]. When oxygen is limited, cells run anaerobic respiration, which does not require oxygen and yields much less ATP [1]; in human cells pyruvate is converted to lactate (a single equation: `"glucose → lactate +ATP"`) [1], regenerating NAD⁺ so glycolysis can continue. Thus, ATP comes from substrate breakdown (`"glycolysis 🡪 link cycle 🡪 Krebs 🡪 electron transport"`) with mitochondria central to aerobic ATP production [1], and anaerobic pathways giving a small, temporary ATP supply with lactate as the waste product.
Question 10
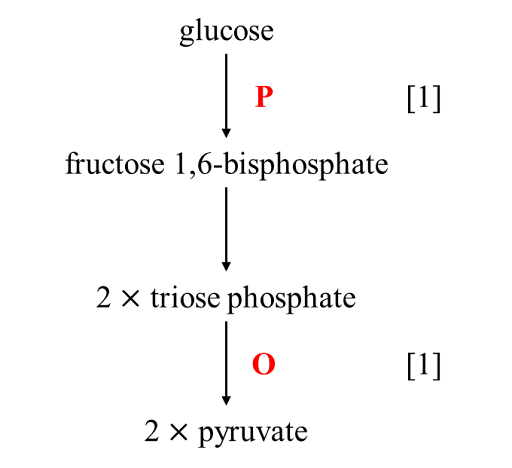
Glucose is converted to pyruvate during the glycolysis stage of respiration.

(a) On the diagram, label
(i) with P where phosphorylation occurs; [1]
(ii) with O where oxidation occurs. [1]
(b) State where in the cell glycolysis takes place. [1]
(c) Outline how NAD is made available for glycolysis during anaerobic respiration in animal cells. [2]
(a) (i) between glucose and fructose 1,6 – bisphosphate;
(a) (ii) between triose phosphate and pyruvate;
Sample answer:
(b) cytoplasm;
Sample answer:
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell [1].
(c) Any two of the following:
a. NADH transfers electrons to pyruvate OR pyruvate acts as electron acceptor / pyruvate is reduced;
b. (pyruvate) converted to lactate;
c. NADH oxidized/converted to NAD OR NAD available to be reduced/converted to NADH again (in glycolysis);
Sample answer:
During anaerobic respiration in animal cells, when oxygen is not available, NADH transfers its hydrogen (electrons) to pyruvate [1].
This converts pyruvate into lactate and oxidizes NADH back to NAD+ [2].
The regenerated NAD+ is then made available for glycolysis to continue, allowing ATP production to occur even in the absence of oxygen.
Question 1
Which compound is a waste product of anaerobic respiration in humans?
A. Carbon dioxide
B. Ethanol
C. Lactate
D. Pyruvate
Question 2
The diagram shows a reaction that occurs during aerobic cell respiration.

Which type of chemical change happens to malic acid?
A. Carboxylation
B. Decarboxylation
C. Oxidation
D. Reduction
Question 3
Bread dough is made by mixing flour, water and yeast. If the dough is then kept at about 30°C, it expands.

What is the main reason for choosing this temperature?
A. Carbon dioxide expands at this temperature.
B. This is the optimum temperature for the enzymes used in aerobic cell respiration.
C. Lactate produced by anaerobic cell respiration causes the release of carbon dioxide at this temperature.
D. At this temperature, yeast produces carbon dioxide rapidly by anaerobic cell respiration.
Question 4
Which part of aerobic respiration directly involves oxygen molecules?
A. Conversion of glucose to pyruvate
B. Accepting electrons from the electron transport chain
C. Oxidizing acetyl groups in the Krebs cycle
D. Production of NAD from reduced NAD
Question 5
Where are protons pumped, to allow chemiosmosis in aerobic respiration to occur?
A. From outside the mitochondrion through the double membranes
B. From carrier to carrier in the inner mitochondrial membrane
C. From the matrix of the mitochondrion to the space between the membranes
D. From the space between the membranes to the cytoplasm outside the mitochondrion
Question 6
The diagram shows the link reaction between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.

Which type of reaction is occurring?
A. Pyruvate is carboxylated.
B. CO2 is oxidized.
C. NAD+ is reduced.
D. Pyruvate is phosphorylated.
Question 7
Two reactions of the Krebs cycle are shown.

What type of reactions are isocitrate and oxalosuccinate undergoing?
| Isocitrate | Oxalosuccinate | |
| A. | oxidation | reduction |
| B. | reduction | decarboxylation |
| C. | reduction | oxidation |
| D. | oxidation | decarboxylation |
Question 8
Lipids are more efficient energy stores than carbohydrates. What is a reason for this?
A. Lipids are bigger molecules than carbohydrates.
B. Lipids release more energy per gram than carbohydrates.
C. Lipids can be more easily mobilized than carbohydrates when needed.
D. Lipids can be used in aerobic and anaerobic respiration when needed.
Question 9
Explain how animal cells produce the ATP that they need. [5]
Question 10
Glucose is converted to pyruvate during the glycolysis stage of respiration.

(a) On the diagram, label
(i) with P where phosphorylation occurs; [1]
(ii) with O where oxidation occurs. [1]
(b) State where in the cell glycolysis takes place. [1]
(c) Outline how NAD is made available for glycolysis during anaerobic respiration in animal cells. [2]