Question 1
What happens in the heart when epinephrine is secreted into the blood?
I. Pressure in the heart falls.
II. The pulmonary artery transports oxygenated blood at a faster rate.
III. The sinoatrial node increases the rate of electrical signals.
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. III only
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The graph shows changes in blood plasma glucose concentration before exercise, during exercise and during recovery with and without epinephrine (adrenaline) infusion. Epinephrine infusion was started 30 minutes into the exercise routine.
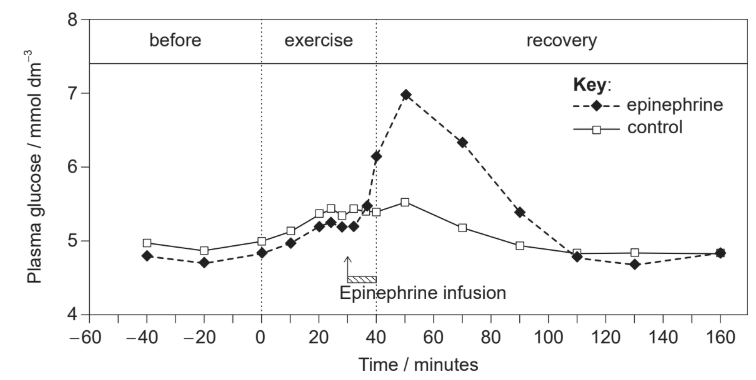
[Source: Kreisman, S.H., Ah Mew, N., Arsenault, M., Marliss, E.B., et al., 2000. AJP Endocrinology and Metabolism 278(5): E949–57. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.2000.278.5.E949. Reference redacted. Source adapted.]
Which action of epinephrine would result in the observed changes to plasma glucose concentration?
A. Second messenger is deactivated.
B. A G protein is activated, and cyclic AMP (cAMP) is produced.
C. Second messenger stimulates the production of ATP.
D. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) deactivates the G protein.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
What results from an unspecialized cell experiencing gradients of signaling chemicals?
A. Cell differentiation
B. Meiosis
C. Saltatory conduction
D. DNA replication
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Testosterone is a hormone that is important for male reproductive development.
To which group of compounds does testosterone belong?
A. Nucleotides
B. Carbohydrates
C. Lipids
D. Amino acids
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Compare and contrast hormonal and nervous communication. [7]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
B. subtilis colonies form biofilms through quorum sensing. Define quorum sensing. [1]
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Compare and contrast the mode of action of peptide hormones and steroid hormones. [6]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
State one function of epinephrine in the human body. [1]
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
The use of human growth hormone (HGH) to enhance athletic performance is now banned from most major sporting events including the Olympics. To investigate the effect of HGH on athletic performance, doctors in the US looked at changes in body composition and strength in a group of athletes taking the drug. This was compared with a control group of similar athletes who had never taken the drug.
| Mean change in mass compared with control group / kg | |
| Body fat | - 0.3 |
| Muscle | + 2.1 |
| Maximum mass that can be lifted using arm muscles | - 0.2 |
| Maximum mass that can be lifted using leg muscles | - 0.1 |
[Source: From Annals of Internal Medicine, H Liu and D M Bravata, Systematic Review: The Effects of Growth Hormone on Athletic Performance, 148., 10, 747–758. Copyright © 2008 American College of Physicians. All Rights Reserved. Reprinted with the permission of American College of Physicians, Inc.]
(a) Deduce from the results of the study whether HGH improves strength. [1]
(b) Suggest one reason that it is difficult to detect illegal use of HGH to enhance athletic performance. [1]
(c) HGH is a peptide hormone. Describe the mode of action of peptide hormones on target cells. [3]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Epinephrine stimulates the SA node, increasing the frequency of action potentials and therefore increasing the heart rate. [7]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
What happens in the heart when epinephrine is secreted into the blood?
I. Pressure in the heart falls.
II. The pulmonary artery transports oxygenated blood at a faster rate.
III. The sinoatrial node increases the rate of electrical signals.
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. III only
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. Epinephrine increases heart rate and stroke volume, which raises blood pressure and cardiac output. Therefore, it increases the pressure in the heart, not decreases it. (I = incorrect)
B. Incorrect. Epinephrine increases heart rate and stroke volume, which raises blood pressure and cardiac output. Therefore, it increases the pressure in the heart, not decreases it. The pulmonary artery always carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. Epinephrine can increase heart rate, but the pulmonary artery never carries oxygenated blood. (I, II = incorrect)
C. Incorrect. The pulmonary artery always carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. Epinephrine can increase heart rate, but the pulmonary artery never carries oxygenated blood. Epinephrine stimulates the SA node, increasing the frequency of action potential and therefore increasing the heart rate. (II = incorrect, III = correct).
D. Correct. Epinephrine stimulates the SA node, increasing the frequency of action potential and therefore increasing the heart rate. (III = correct).
Question 2
The graph shows changes in blood plasma glucose concentration before exercise, during exercise and during recovery with and without epinephrine (adrenaline) infusion. Epinephrine infusion was started 30 minutes into the exercise routine.

[Source: Kreisman, S.H., Ah Mew, N., Arsenault, M., Marliss, E.B., et al., 2000. AJP Endocrinology and Metabolism 278(5): E949–57. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.2000.278.5.E949. Reference redacted. Source adapted.]
Which action of epinephrine would result in the observed changes to plasma glucose concentration?
A. Second messenger is deactivated.
B. A G protein is activated, and cyclic AMP (cAMP) is produced.
C. Second messenger stimulates the production of ATP.
D. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) deactivates the G protein.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. If the second messenger (such as cAMP) were deactivated, glucose levels would not rise. cAMP must remain active to trigger glycogen breakdown and increase plasma glucose.
B. Correct. Epinephrine activates a G protein, which stimulates the production of cAMP. cAMP then activates enzymes that break down glycogen into glucose, raising plasma glucose concentration.
C. Incorrect. cAMP does not directly stimulate ATP production. Instead, it activates enzymes that release glucose into the blood. ATP production happens inside cells, not in the plasma.
D. Incorrect. cAMP does not deactivate G proteins. The rise in plasma glucose requires continued G-protein activity to keep producing cAMP and stimulating glycogen breakdown.
Question 3
What results from an unspecialized cell experiencing gradients of signaling chemicals?
A. Cell differentiation
B. Meiosis
C. Saltatory conduction
D. DNA replication
Answer: A
A. Correct. Gradients of signaling chemicals cause unspecialized cells to activate different genes depending on the concentration they detect. This leads to cell differentiation, where cells develop into different types with specialized functions.
B. Incorrect. Meiosis is the process of producing gametes. It is not triggered by signaling gradients during development.
C. Incorrect. Saltatory conduction refers to the jumping of action potentials along myelinated neurons. It has nothing to do with unspecialized cells or chemical gradients.
D. Incorrect. DNA replication happens during the cell cycle and is not caused by signaling gradients during embryonic development.
Question 4
Testosterone is a hormone that is important for male reproductive development.

To which group of compounds does testosterone belong?
A. Nucleotides
B. Carbohydrates
C. Lipids
D. Amino acids
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. A nucleotide is composed of a phosphate group, a pentose sugar (like deoxyribose or ribose), and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, guanine, or cytosine). These molecules are responsible for storing genetic information.
B. Incorrect. Carbohydrates are typically simple sugars or polymers formed from simple sugar monomers. Carbohydrates primarily function as structural material (like cellulose) or for energy storage (like starch and glycogen).
C. Correct. Testosterone is a steroid hormone, and all steroids are classified as lipids because they are derived from cholesterol, a lipid molecule.
D. Incorrect. Amino acids are the monomers that link together to form polypeptides and proteins. The basic structure of an amino acid includes an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain (R group). They link through peptide bonds.
Question 5
Compare and contrast hormonal and nervous communication. [7]
Seven of the following, with at least one similarity and difference:
Similarities:
a. both used for communication between cells/tissues/organs/parts of the body
b. both cause a response/change in specific/target cells OR both use chemicals that bind to receptors / hormones and neurotransmitters are both chemicals
c. both can stimulate or inhibit processes in target cells
d. both can work over long distances/between widely separated parts of the body
e. both under control of the brain/CNS / brain sending hormones and nerve impulses
f. both use feedback mechanisms/negative feedback/both used in homeostasis
Differences:
| Hormone | Nerves |
| chemical messenger | nerve impulse/electrical signal |
| transported in blood | transported by neurons |
| slower | faster |
| carried throughout body | carried to single/specific cell/muscle fiber |
| all/wide range of tissues/organs affected | only muscles/glands receive signals |
| long term |
Sample answer:
Hormonal and nervous communication share several similarities. Both are used for communication between different parts of the body [1], both rely on chemicals that bind to receptors on target cells [1], and both can stimulate or inhibit processes in those cells [1]. They can operate over long distances [1], and both systems are regulated by the brain and are important in homeostasis through feedback mechanisms [1].
However, they differ in important ways. Hormones are chemical messengers, whereas nerves transmit electrical impulses [1]. Hormones are transported in the bloodstream, while nerve signals travel along neurons [1]. Hormonal communication is typically slower, while nerve impulses are rapid [1]. Hormones may affect many tissues throughout the body, whereas nerves send signals to specific cells, such as muscles or glands [1]. Hormonal effects are generally long-lasting, whereas nervous responses are short-lived [1].
Question 6
B. subtilis colonies form biofilms through quorum sensing. Define quorum sensing. [1]
One of the following:
a system of behaviors triggered as a function of population density
Sample answer:
Quorum sensing is a system in which bacteria trigger specific behaviors when their population reaches a critical density, allowing them to coordinate activities such as biofilm formation.
Question 7
Compare and contrast the mode of action of peptide hormones and steroid hormones. [6]
Six of the following, with at least one similarity and difference:
Similarities:
a. both bring about changes in cell metabolism.
b. both carried by blood.
c. from endocrine gland OR to target organ/cells.
d. both (act by) binding to receptors.
Differences:
| Peptide hormone | Steroid hormone |
| remains outside target cell | enters target cell |
| receptor in/on plasma membrane | receptor in cytoplasm/nucleus/cell |
| does not form complex inside cytoplasm | forms receptor-hormone complex inside cell |
| involves secondary messenger/ cAMP | does not involve a secondary messenger/ cAMP; |
| activates cascade of reactions within cell OR activates/inhibits enzymes | regulates transcription |
Sample answer:
Peptide and steroid hormones share several similarities: both are transported in the blood from an endocrine gland to their target cells [1], both bind to receptors [1], and both ultimately alter cell metabolism [1]. However, their modes of action differ. Peptide hormones remain outside the target cell, binding to receptors on the plasma membrane, whereas steroid hormones enter the target cell and bind to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus [1]. Peptide hormones do not form receptor-hormone complexes inside the cytoplasm, while steroid hormones do form such complexes [1]. Peptide hormones rely on secondary messengers like cAMP and trigger a cascade of enzyme activations or inhibitions, whereas steroid hormones do not use secondary messengers and instead regulate transcription directly, altering gene expression [1].
Question 8
State one function of epinephrine in the human body. [1]
One of the following:
a. increases heart rate
b. prepares the body for action
Sample answer:
In the human body, epinephrine can increase the heart rate [1], and prepare the body for actions [1].
Question 9
The use of human growth hormone (HGH) to enhance athletic performance is now banned from most major sporting events including the Olympics. To investigate the effect of HGH on athletic performance, doctors in the US looked at changes in body composition and strength in a group of athletes taking the drug. This was compared with a control group of similar athletes who had never taken the drug.
| Mean change in mass compared with control group / kg | |
| Body fat | - 0.3 |
| Muscle | + 2.1 |
| Maximum mass that can be lifted using arm muscles | - 0.2 |
| Maximum mass that can be lifted using leg muscles | - 0.1 |
[Source: From Annals of Internal Medicine, H Liu and D M Bravata, Systematic Review: The Effects of Growth Hormone on Athletic Performance, 148., 10, 747–758. Copyright © 2008 American College of Physicians. All Rights Reserved. Reprinted with the permission of American College of Physicians, Inc.]
(a) Deduce from the results of the study whether HGH improves strength. [1]
(b) Suggest one reason that it is difficult to detect illegal use of HGH to enhance athletic performance. [1]
(c) HGH is a peptide hormone. Describe the mode of action of peptide hormones on target cells. [3]
(a) the drug does not appear to improve strength as less mass can be lifted by arms and legs
Sample answer:
No. The drug does not improve strength as less mass can be lifted by arm and leg muscles
(b) One of the following:
a. occurs naturally so hard to tell whether it has been injected
b. HGH has very short half life
Sample answer:
It is difficult to detect illegal use of HGH to enhance athletic performance because HGH is naturally produced in the body [1] and HGH has a very short half life [1].
(c) Three of the following:
a. peptide hormones do not enter the cell
b. they bind to receptors/proteins in the plasma membrane of the target cell
c. a secondary messenger initiates the cell response
d. causes a cascade of actions that changes the cell’s physiology
e. AMP is a common secondary messenger
Sample answer:
Peptide hormones such as HGH act on target cells by binding to receptors on the plasma membrane because they do not enter the cell [1]. Instead, they bind to specific receptor proteins on the cell surface, which triggers an internal signaling pathway [1]. When the receptor is activated, a secondary messenger inside the cell is produced to initiate the response [1], often involving cAMP, which is a common secondary messenger [1]. This internal signal activates a cascade of reactions that ultimately alters the cell physiology, producing the hormone’s effect [1].
Question 10
Epinephrine stimulates the SA node, increasing the frequency of action potentials and therefore increasing the heart rate. [7]
(a) epinephrine / adrenaline
(b) Three of the following:
a. epinephrine is a ligand / binds to (GPCR) receptors in cell membrane.
b. triggers G-protein activation / triggers G protein phosphorylation.
c. initiates a cascade of events producing cAMP / adenylyl cyclase enzymes
d. stimulates cAMP synthesis.
e. (cAMP) acts as a second messenger.
f. signals/influences/mediates specific cellular responses.
Sample answer:
Epinephrine acts by functioning as a ligand that binds to specific GPCR receptors on the cell membrane [1], where it activates a G-protein [1], triggering its phosphorylation and initiation of a signaling pathway. This activation stimulates adenylyl cyclase [1] to produce cAMP [1], and the resulting cAMP acts as a second messenger [1]. Through this pathway, cAMP mediates specific cellular responses, allowing epinephrine to exert its effects on the target cell [1].
(c) Two of the following:
a. the heart beats faster for more blood flow / blood pressure increases pushing more blood to the muscles / vasodilation allows more blood to reach muscles.
b. breathing rate increases providing the muscles with more oxygen.
c. bronchi/bronchioles dilate to allow more air/oxygen into the lungs for muscle contraction.
d. triggers the release of blood sugar/glucose supplying energy/ATP/cellular respiration for contraction OR triggers the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver for energy.
Sample answer:
Epinephrine increases the heart rate and blood pressure, causing more blood to flow to the muscles, and vasodilation in skeletal muscle allows a greater supply of oxygen and nutrients to reach the contracting muscle fibers [1]. Epinephrine also increases the availability of energy by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen into glucose in the liver and muscle, providing the ATP needed for intense and sustained muscle contraction [1].
Question 1
What happens in the heart when epinephrine is secreted into the blood?
I. Pressure in the heart falls.
II. The pulmonary artery transports oxygenated blood at a faster rate.
III. The sinoatrial node increases the rate of electrical signals.
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. III only
Question 2
The graph shows changes in blood plasma glucose concentration before exercise, during exercise and during recovery with and without epinephrine (adrenaline) infusion. Epinephrine infusion was started 30 minutes into the exercise routine.

[Source: Kreisman, S.H., Ah Mew, N., Arsenault, M., Marliss, E.B., et al., 2000. AJP Endocrinology and Metabolism 278(5): E949–57. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.2000.278.5.E949. Reference redacted. Source adapted.]
Which action of epinephrine would result in the observed changes to plasma glucose concentration?
A. Second messenger is deactivated.
B. A G protein is activated, and cyclic AMP (cAMP) is produced.
C. Second messenger stimulates the production of ATP.
D. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) deactivates the G protein.
Question 3
What results from an unspecialized cell experiencing gradients of signaling chemicals?
A. Cell differentiation
B. Meiosis
C. Saltatory conduction
D. DNA replication
Question 4
Testosterone is a hormone that is important for male reproductive development.

To which group of compounds does testosterone belong?
A. Nucleotides
B. Carbohydrates
C. Lipids
D. Amino acids
Question 5
Compare and contrast hormonal and nervous communication. [7]
Question 6
B. subtilis colonies form biofilms through quorum sensing. Define quorum sensing. [1]
Question 7
Compare and contrast the mode of action of peptide hormones and steroid hormones. [6]
Question 8
State one function of epinephrine in the human body. [1]
Question 9
The use of human growth hormone (HGH) to enhance athletic performance is now banned from most major sporting events including the Olympics. To investigate the effect of HGH on athletic performance, doctors in the US looked at changes in body composition and strength in a group of athletes taking the drug. This was compared with a control group of similar athletes who had never taken the drug.
| Mean change in mass compared with control group / kg | |
| Body fat | - 0.3 |
| Muscle | + 2.1 |
| Maximum mass that can be lifted using arm muscles | - 0.2 |
| Maximum mass that can be lifted using leg muscles | - 0.1 |
[Source: From Annals of Internal Medicine, H Liu and D M Bravata, Systematic Review: The Effects of Growth Hormone on Athletic Performance, 148., 10, 747–758. Copyright © 2008 American College of Physicians. All Rights Reserved. Reprinted with the permission of American College of Physicians, Inc.]
(a) Deduce from the results of the study whether HGH improves strength. [1]
(b) Suggest one reason that it is difficult to detect illegal use of HGH to enhance athletic performance. [1]
(c) HGH is a peptide hormone. Describe the mode of action of peptide hormones on target cells. [3]
Question 10
Epinephrine stimulates the SA node, increasing the frequency of action potentials and therefore increasing the heart rate. [7]