Question 1
What occurs during the transmission of an impulse at a synapse?
I. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis when calcium ions enter the presynaptic neuron.
II. Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
III. Acetylcholine is broken down by cholinesterase and resorbed into the presynaptic neuron once an impulse has been initiated on the postsynaptic membrane.
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Doctors often use drugs to restore normal action potentials. The oscilloscope trace shows the effect of one of these drugs, which acts on potassium (K) ion channels of cell membranes.
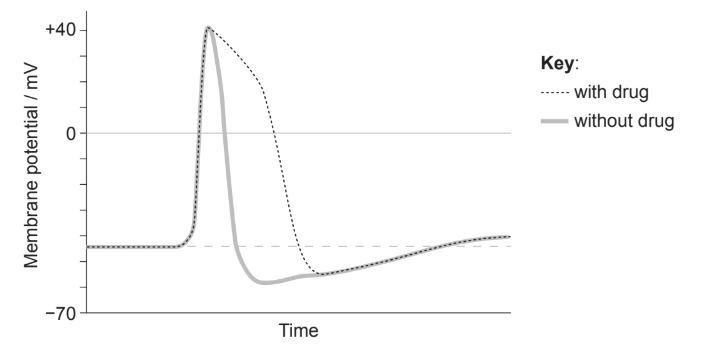
From the graph, what can be concluded about the effect of this drug on membrane potential?
A. It delays repolarization by preventing the influx of K ions towards the cytoplasm.
B. It delays depolarization due to a build-up of K ions outside the neuron.
C. It lengthens the resting potential as membrane permeability to K ions is decreased.
D. It lengthens the action potential by reducing the rate of K ions released from the cytoplasm.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
The image shows a neuron.
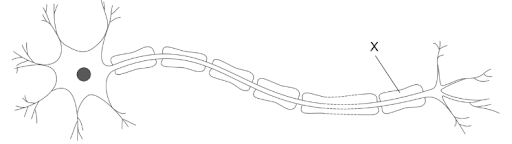
What is the function of X?
A. Increases the speed of transmission along the axon
B. Increases the rate of exchange of sodium and potassium ions
C. Holds bundles of neurons together to form a nerve
D. Determines the direction of the action potential
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
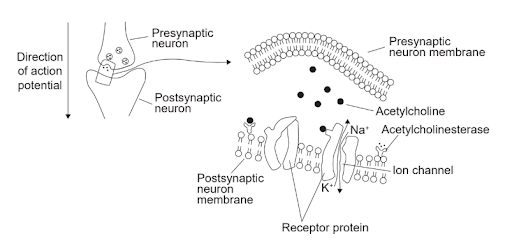
The diagram shows the synaptic transmission of nerve impulses by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
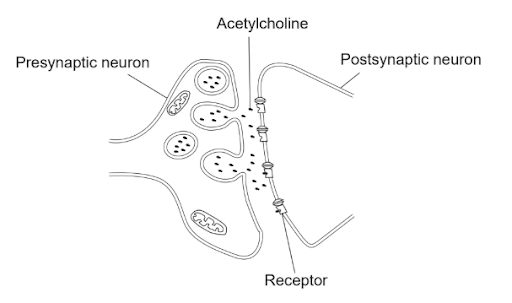
What is the fate of acetylcholine immediately after binding to the receptor?
A. It is pumped into the postsynaptic neuron.
B. It diffuses into the presynaptic neuron.
C. It is broken down in the synaptic cleft.
D. It binds to another receptor in the postsynaptic neuron.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
The diagram shows a neural synapse in the central nervous system of a honey bee (Apis mellifera).
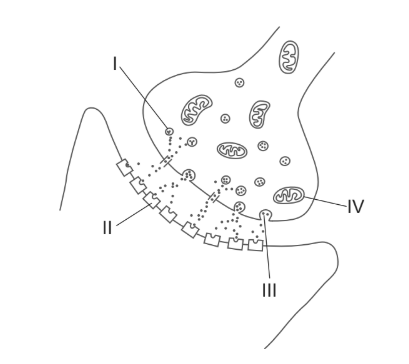
How do neonicotinoid pesticides cause paralysis and death of honey bees?
A. They destroy I.
B. They bind to II.
C. They inhibit the release of III.
D. They block the activity of IV.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
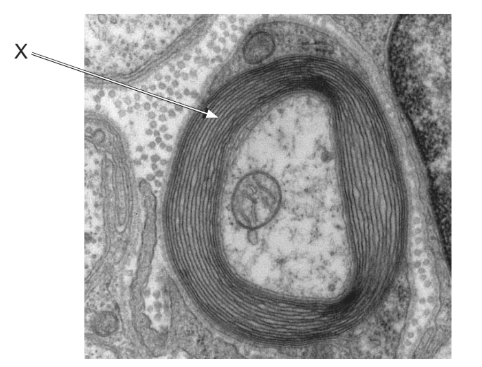
The electron micrograph shows a transverse section through a myelinated neuron.
What is the fate of acetylcholine immediately after binding to the receptor?
A. It is pumped into the postsynaptic neuron.
B. It diffuses into the presynaptic neuron.
C. It is broken down in the synaptic cleft.
D. It binds to another receptor in the postsynaptic neuron.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
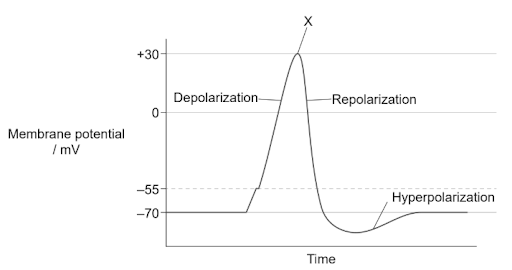
The diagram shows a graph of an action potential.
What is happening at X?
A. Sodium channels close.
B. Calcium channels open.
C. Sodium channels open.
D. Potassium channels close.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What occurs during the establishment of a resting membrane potential of a neuron?
A. Both sodium and potassium ions are pumped outside the neuron.
B. Sodium ions are pumped out while potassium ions are pumped into the neuron.
C. Both sodium and potassium ions are at rest inside the membrane of the neuron.
D. Sodium ions leave by diffusion and potassium ions enter the neuron by active transport.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Cholinergic synapses use acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter. They are widespread in the body, passing on signals to muscle cells. These synapses are affected by neonicotinoid pesticides.
The diagrams, which are not drawn to scale, show the synapse between two neurons and a detail of the synaptic cleft.
(a) Outline how depolarization of the membrane of an axon occurs. [2]
(b) Explain how acetylcholine initiates an action potential in a postsynaptic membrane. [2]
(c) State the action of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. [1]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Explain the mechanisms involved in the transmission of impulses between neurons. [6]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
What occurs during the transmission of an impulse at a synapse?
I. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis when calcium ions enter the presynaptic neuron.
II. Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
III. Acetylcholine is broken down by cholinesterase and resorbed into the presynaptic neuron once an impulse has been initiated on the postsynaptic membrane.
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. I true: Arrival of an action potential opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels; Ca2+ entry triggers vesicles to release acetylcholine by exocytosis. II true: Acetylcholine diffuse and bind receptors cause ion channels to open and initiates depolarization of the postsynaptic cell. However, III is also true: Cholinesterase breaks acetylcholine into acetate and choline; choline is reabsorbed for recycling, ensuring the signal stops.
B. Incorrect. II true: Acetylcholine diffuse and bind receptors cause ion channels to open and initiates depolarization of the postsynaptic cell. III true: Cholinesterase breaks acetylcholine into acetate and choline; choline is reabsorbed for recycling, ensuring the signal stops. However, I is also true: Arrival of an action potential opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels; Ca2+ entry triggers vesicles to release acetylcholine by exocytosis.
C. Incorrect. I true: Arrival of an action potential opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels; Ca2+ entry triggers vesicles to release acetylcholine by exocytosis. III true: Cholinesterase breaks acetylcholine into acetate and choline; choline is reabsorbed for recycling, ensuring the signal stops. However, II is also true: Acetylcholine diffuse and bind receptors cause ion channels to open and initiates depolarization of the postsynaptic cell.
D. Correct. I true: Arrival of an action potential opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels; Ca2+ entry triggers vesicles to release acetylcholine by exocytosis. II true: Acetylcholine diffuse and bind receptors cause ion channels to open and initiates depolarization of the postsynaptic cell. III true: Cholinesterase breaks acetylcholine into acetate and choline; choline is reabsorbed for recycling, ensuring the signal stops.
Question 2
Doctors often use drugs to restore normal action potentials. The oscilloscope trace shows the effect of one of these drugs, which acts on potassium (K) ion channels of cell membranes.

From the graph, what can be concluded about the effect of this drug on membrane potential?
A. It delays repolarization by preventing the influx of K ions towards the cytoplasm.
B. It delays depolarization due to a build-up of K ions outside the neuron.
C. It lengthens the resting potential as membrane permeability to K ions is decreased.
D. It lengthens the action potential by reducing the rate of K ions released from the cytoplasm.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. K⁺ does not move into the cytoplasm during repolarization; it moves out.
B. Incorrect. Depolarization is controlled by Na⁺ entry, not K⁺ buildup. Blocking K⁺ channels does not delay depolarization.
C. Incorrect. The resting potential is not a phase that “lengthens.” K⁺ channel blockers affect repolarization, not the resting state.
D. Correct. Repolarization requires K⁺ efflux. If K⁺ channels are slowed or blocked, repolarization is delayed, so the action potential lasts longer.
Question 3
The image shows a neuron.

What is the function of X?
A. Increases the speed of transmission along the axon
B. Increases the rate of exchange of sodium and potassium ions
C. Holds bundles of neurons together to form a nerve
D. Determines the direction of the action potential
Answer: A
A. Correct. X = myelin sheath. The myelin sheath insulates the axon and allows impulses to jump between nodes, greatly increasing transmission speed.
B. Incorrect. X = myelin sheath. Ion exchange happens at the nodes of Ranvier, not along the myelin itself.
C. Incorrect. X = myelin sheath. This is done by connective tissue, not by myelin.
D .Incorrect. X = myelin sheath. Action potential direction is determined by the refractory period, not by the myelin sheath.
Question 4
The diagram shows the synaptic transmission of nerve impulses by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.

What is the fate of acetylcholine immediately after binding to the receptor?
A. It is pumped into the postsynaptic neuron.
B. It diffuses into the presynaptic neuron.
C. It is broken down in the synaptic cleft.
D. It binds to another receptor in the postsynaptic neuron.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Acetylcholine does not enter the postsynaptic cell. It only binds to receptors on its membrane.
B. Incorrect. Acetylcholine cannot diffuse back; instead, it is broken down into choline, to be taken back up.
C. Correct. The enzyme acetylcholinesterase rapidly breaks acetylcholine into choline and acetate to stop the signal.
D. Incorrect. Once it has bound and activated a receptor, it is quickly broken down, not allowed to keep binding multiple receptors.
Question 5
The diagram shows a neural synapse in the central nervous system of a honey bee (Apis mellifera).

How do neonicotinoid pesticides cause paralysis and death of honey bees?
A. They destroy I.
B. They bind to II.
C. They inhibit the release of III.
D. They block the activity of IV.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Neonicotinoids do not physically destroy neurons, vesicles (I) or synaptic structures.
B. Correct. Neonicotinoids act as agonists of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (II) on the postsynaptic membrane. By binding here, they cause continuous stimulation of neurons, leading to paralysis and eventually death.
C. Incorrect. Neonicotinoids do not prevent acetylcholine release (III); they mimic its action instead.
D. Incorrect. They do not block the function of mitochondria (IV).
Question 6
The electron micrograph shows a transverse section through a myelinated neuron.

What is the fate of acetylcholine immediately after binding to the receptor?
A. It is pumped into the postsynaptic neuron.
B. It diffuses into the presynaptic neuron.
C. It is broken down in the synaptic cleft.
D. It binds to another receptor in the postsynaptic neuron.
Answer. C
A. Incorrect. X = myelin sheath. Repolarization occurs along the entire membrane due to K⁺ efflux, not specifically because of the myelin sheath.
B. Incorrect. X = myelin sheath. Action potentials can be generated in unmyelinated neurons as well; myelin speeds conduction but does not generate the impulse.
C. Correct. X = myelin sheath. Myelin insulates the axon and allows the action potential to “jump” between nodes of Ranvier, greatly increasing conduction speed.
D. Incorrect. X = myelin sheath. Synaptic transmission occurs at the axon terminal and involves neurotransmitters, not myelin.
Question 7
The diagram shows a graph of an action potential.

What is happening at X?
A. Sodium channels close.
B. Calcium channels open.
C. Sodium channels open.
D. Potassium channels close.
Answer: A
A. Correct. At the peak of the action potential (around +30 mV), voltage-gated Na⁺ channels inactivate/close, stopping Na⁺ influx and allowing repolarization to begin.
B. Incorrect. Calcium channels are not involved in generating the action potential along the axon; they are mainly at synaptic terminals.
C. Incorrect. Sodium channels open earlier, during the depolarization phase leading up to the peak.
D. Incorrect. Potassium channels are opening at the peak to allow K⁺ efflux, which drives repolarization.
Question 8
What occurs during the establishment of a resting membrane potential of a neuron?
A. Both sodium and potassium ions are pumped outside the neuron.
B. Sodium ions are pumped out while potassium ions are pumped into the neuron.
C. Both sodium and potassium ions are at rest inside the membrane of the neuron.
D. Sodium ions leave by diffusion and potassium ions enter the neuron by active transport.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. When establishing the resting membrane potential, only Na⁺ is pumped out, K⁺ is pumped in.
B. Correct. The sodium–potassium pump actively moves 3 Na⁺ out and 2 K⁺ in, creating a negative resting membrane potential inside the neuron.
C. Incorrect. Ions are not at rest. There is a constant electrochemical gradient maintained by the pump.
D. Incorrect. Sodium leaves primarily by active transport, not by simple diffusion, and K⁺ enters mainly by active transport.
Question 9
Cholinergic synapses use acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter. They are widespread in the body, passing on signals to muscle cells. These synapses are affected by neonicotinoid pesticides.
The diagrams, which are not drawn to scale, show the synapse between two neurons and a detail of the synaptic cleft.

(a) Outline how depolarization of the membrane of an axon occurs. [2]
(b) Explain how acetylcholine initiates an action potential in a postsynaptic membrane. [2]
(c) State the action of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. [1]
(a) Two of the following:
a. local depolarization causes ion / sodium / voltage gated channels to open
b. altering membrane permeability to sodium ions/Na+/positive ions / Na+ diffuses into the cytoplasm
c. membrane potential of the axon changes from negative to positive
d. a threshold potential is reached and an action potential is generated
Sample answer:
Depolarization of an axon begins when a local depolarization causes voltage-gated sodium channels to open [1]. This changes the membrane’s permeability to sodium ions, allowing Na⁺ to diffuse into the cytoplasm [1]. As sodium ions enter, the membrane potential of the axon shifts from negative to positive [1]. When the threshold potential is reached, an action potential is generated [1].
(b) Two of the following:
a. acetylcholine binds to the receptor protein
b. causing a change in tertiary structure / conformation of protein
c. diffusion/entry of ions / Na+ through the receptor/channel protein allowed
Sample answer:
Acetylcholine binds to receptor proteins on the postsynaptic membrane [1]. This causes a change in the tertiary structure or conformation of the receptor protein [1]. As a result, ions, mainly Na⁺, diffuse into the postsynaptic neuron through the receptor/channel protein [1], leading to depolarization and the initiation of an action potential.
(c) breaks down acetylcholine to acetyl and choline
Sample answer:
Enzyme acetylcholinesterase can break down acetylcholine into acetyl and choline [1].
Question 10
Explain the mechanisms involved in the transmission of impulses between neurons. [6]
Six of the following:
a. impulses transmitted between neurons across synapses.
b. presynaptic membrane depolarization/arrival of action potential causes release of neurotransmitter
c. Neurotransmitters may be excitatory or inhibitory
d. neurotransmitters diffuse across synapse/synaptic cleft / bind to receptors in postsynaptic membrane
e. postsynaptic membrane responds to sum effect/summation of all neurotransmitters
f. nerve impulse generated in postsynaptic neuron if threshold potential reached
g. neurotransmitter in synaptic cleft broken down to prevent continuous synaptic transmission OR excess neurotransmitter reabsorbed;
h. slow-acting neurotransmitters can affect groups of neuron OR slow-acting neurotransmitters release secondary messengers OR slow-acting neurotransmitters can modulate fast synaptic transmission
i. example of fast acting neurotransmitter e.g. acetylcholine / example of slow acting e.g. dopamine/serotonin/norepinephrine
j. psychoactive drugs affect brain by altering function of some synapses / by preventing breakdown of neurotransmitters / by mimicking action of neurotransmitters
Sample answer:
Impulses are transmitted between neurons across synapses [1]. When an action potential reaches the presynaptic membrane, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters [1]. These neurotransmitters may be excitatory or inhibitory [1]. They diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane [1]. The postsynaptic membrane responds to the summed effects of all neurotransmitters [1], and if the threshold potential is reached, a new nerve impulse is generated in the postsynaptic neuron [1]. To prevent continuous transmission, neurotransmitters are broken down or reabsorbed [1]. Slow-acting neurotransmitters can affect groups of neurons, release secondary messengers, or modulate fast synaptic transmission [1]. Examples include acetylcholine (fast-acting) and dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine (slow-acting) [1]. Psychoactive drugs can alter brain function by mimicking neurotransmitters, preventing their breakdown, or modifying synaptic activity [1].
Question 1
What occurs during the transmission of an impulse at a synapse?
I. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis when calcium ions enter the presynaptic neuron.
II. Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
III. Acetylcholine is broken down by cholinesterase and resorbed into the presynaptic neuron once an impulse has been initiated on the postsynaptic membrane.
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
Question 2
Doctors often use drugs to restore normal action potentials. The oscilloscope trace shows the effect of one of these drugs, which acts on potassium (K) ion channels of cell membranes.

From the graph, what can be concluded about the effect of this drug on membrane potential?
A. It delays repolarization by preventing the influx of K ions towards the cytoplasm.
B. It delays depolarization due to a build-up of K ions outside the neuron.
C. It lengthens the resting potential as membrane permeability to K ions is decreased.
D. It lengthens the action potential by reducing the rate of K ions released from the cytoplasm.
Question 3
The image shows a neuron.

What is the function of X?
A. Increases the speed of transmission along the axon
B. Increases the rate of exchange of sodium and potassium ions
C. Holds bundles of neurons together to form a nerve
D. Determines the direction of the action potential
Question 4
The diagram shows the synaptic transmission of nerve impulses by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.

What is the fate of acetylcholine immediately after binding to the receptor?
A. It is pumped into the postsynaptic neuron.
B. It diffuses into the presynaptic neuron.
C. It is broken down in the synaptic cleft.
D. It binds to another receptor in the postsynaptic neuron.
Question 5
The diagram shows a neural synapse in the central nervous system of a honey bee (Apis mellifera).

How do neonicotinoid pesticides cause paralysis and death of honey bees?
A. They destroy I.
B. They bind to II.
C. They inhibit the release of III.
D. They block the activity of IV.
Question 6
The electron micrograph shows a transverse section through a myelinated neuron.

What is the fate of acetylcholine immediately after binding to the receptor?
A. It is pumped into the postsynaptic neuron.
B. It diffuses into the presynaptic neuron.
C. It is broken down in the synaptic cleft.
D. It binds to another receptor in the postsynaptic neuron.
Question 7
The diagram shows a graph of an action potential.

What is happening at X?
A. Sodium channels close.
B. Calcium channels open.
C. Sodium channels open.
D. Potassium channels close.
Question 8
What occurs during the establishment of a resting membrane potential of a neuron?
A. Both sodium and potassium ions are pumped outside the neuron.
B. Sodium ions are pumped out while potassium ions are pumped into the neuron.
C. Both sodium and potassium ions are at rest inside the membrane of the neuron.
D. Sodium ions leave by diffusion and potassium ions enter the neuron by active transport.
Question 9
Cholinergic synapses use acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter. They are widespread in the body, passing on signals to muscle cells. These synapses are affected by neonicotinoid pesticides.
The diagrams, which are not drawn to scale, show the synapse between two neurons and a detail of the synaptic cleft.

(a) Outline how depolarization of the membrane of an axon occurs. [2]
(b) Explain how acetylcholine initiates an action potential in a postsynaptic membrane. [2]
(c) State the action of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. [1]
Question 10
Explain the mechanisms involved in the transmission of impulses between neurons. [6]