Question 1
An individual was presented with a stimulus resulting in the release of epinephrine. What was the most likely nature of the stimulus?
A. Sunset and the onset of darkness
B. An image of a close friend
C. The intake of glucose
D. A coach shouting to begin physical activity
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The image shows the changes in heart rate of an athlete during exercise.
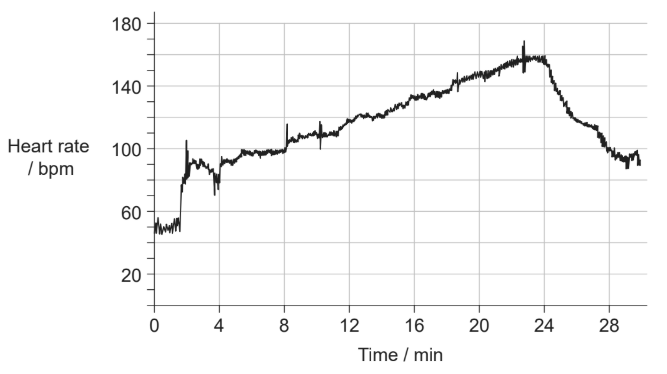
What is likely to have occurred between 0 and 4 minutes and between 24 and 28 minutes?
| Between 0 and 4 minutes | Between 24 and 28 minutes | |
| A. | Epinephrine is secreted | More blood is sent to the rest of the body than to the lungs |
| B. | More blood is sent to the rest of the lungs than to the body | Epinephrine is secreted |
| C. | Epinephrine is secreted | Impulses are sent from the medulla of the brain to the heart |
| D. | Impulses are sent from the medulla of the brain to the heart | Epinephrine is secreted |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
How does auxin contribute to phototropism?
A. It increases production of light-sensitive proteins.
B. It increases growth of cells on the shaded side of the stem.
C. It inhibits growth of axillary buds.
D. It inhibits stem elongation.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The diagram shows a plant shoot and the direction of the light which the shoot received.
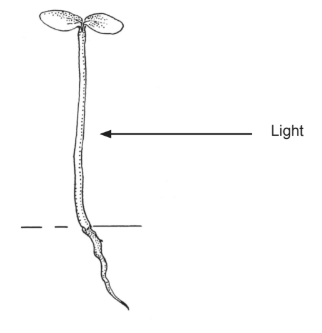
What are the direction of movement and the effect of auxin in the tip of a plant shoot when receiving light from one side?
| Direction of movement of auxin | Effect of auxin on cell elongation | |
| A. | Towards light | Promotes |
| B. | Towards light | Inhibits |
| C. | Away from light | Promotes |
| D. | Away from light | Inhibits |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
How does auxin exert its effect on plant cells?
A. Acts directly on the cell wall, causing expansion
B. Binds to a receptor resulting in expression of genes
C. Causes the vacuole to absorb water and expand the cell
D. Causes the cell to undergo cell division
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Explain the neural control of swallowing. [3]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Explain how breathing is controlled by the brain. [6]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Outline how the hormone auxin controls phototropism in plant shoots. [5]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Explain the control mechanism of the heart rate. [7]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Outline the role of melatonin in humans. [2]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
An individual was presented with a stimulus resulting in the release of epinephrine. What was the most likely nature of the stimulus?
A. Sunset and the onset of darkness
B. An image of a close friend
C. The intake of glucose
D. A coach shouting to begin physical activity
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. Darkness stimulates the release of melatonin, not epinephrine.
B. Incorrect. An image of a close friend would not trigger a sympathetic fight-or-flight response.
C. Incorrect. Food intake primarily affects insulin and glucagon, not epinephrine.
D. Correct. Sudden physical or emotional arousal triggers the sympathetic nervous system, causing the adrenal medulla to release epinephrine, preparing the body for action.
Question 2
The image shows the changes in heart rate of an athlete during exercise.

What is likely to have occurred between 0 and 4 minutes and between 24 and 28 minutes?
| Between 0 and 4 minutes | Between 24 and 28 minutes | |
| A. | Epinephrine is secreted | More blood is sent to the rest of the body than to the lungs |
| B. | More blood is sent to the rest of the lungs than to the body | Epinephrine is secreted |
| C. | Epinephrine is secreted | Impulses are sent from the medulla of the brain to the heart |
| D. | Impulses are sent from the medulla of the brain to the heart | Epinephrine is secreted |
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. 0-4 minute: adrenaline is released early to rapidly increase heart rate. However, 24-28 minute: during recovery, blood flow does not shift away from the lungs; ventilation and perfusion simply decrease together.
B. Incorrect. 0-4 minute: at the start of exercise, there is an increase in lung perfusion, but that is not the main driver of the rapid heart-rate rise. 24-28 minute: Epinephrine would not be secreted because the body is recovering, not beginning exercise.
C. Correct. 0-4 minute: early epinephrine release explains the sharp rise in heart rate at the start. 24-28 minute: during recovery, the medulla reduces sympathetic impulses and increases parasympathetic impulses to slow the heart.
D. Incorrect. 0-4 minute: The medulla always sends impulses to the heart, but this does not explain the very fast rise in heart rate at the start of exercise. 24-28 minute: Epinephrine would not be secreted because the body is recovering, not beginning exercise.
Question 3
How does auxin contribute to phototropism?
A. It increases production of light-sensitive proteins.
B. It increases growth of cells on the shaded side of the stem.
C. It inhibits growth of axillary buds.
D. It inhibits stem elongation.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Auxin does not affect the production of photoreceptors. Phototropins detect light, not auxin.
B. Correct. Auxin accumulates on the shaded side, causing those cells to elongate more, which bends the stem toward the light.
C. Incorrect. This describes the role of auxin in apical dominance, not phototropism.
D. Incorrect. Auxin promotes elongation in stems.
Question 4
The diagram shows a plant shoot and the direction of the light which the shoot received.

What are the direction of movement and the effect of auxin in the tip of a plant shoot when receiving light from one side?
| Direction of movement of auxin | Effect of auxin on cell elongation | |
| A. | Towards light | Promotes |
| B. | Towards light | Inhibits |
| C. | Away from light | Promotes |
| D. | Away from light | Inhibits |
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. When light shines on one side of a plant shoot, auxin moves away from the light, accumulating on the shaded side. Auxin promotes cell elongation in shoots, so the shaded side grows faster, causing the shoot to bend toward the light.
B. Incorrect. When light shines on one side of a plant shoot, auxin moves away from the light, accumulating on the shaded side. Auxin promotes cell elongation in shoots, so the shaded side grows faster, causing the shoot to bend toward the light.
C. Correct. When light shines on one side of a plant shoot, auxin moves away from the light, accumulating on the shaded side. Auxin promotes cell elongation in shoots, so the shaded side grows faster, causing the shoot to bend toward the light.
D. Incorrect. When light shines on one side of a plant shoot, auxin moves away from the light, accumulating on the shaded side. Auxin promotes cell elongation in shoots, so the shaded side grows faster, causing the shoot to bend toward the light.
Question 5
How does auxin exert its effect on plant cells?
A. Acts directly on the cell wall, causing expansion
B. Binds to a receptor resulting in expression of genes
C. Causes the vacuole to absorb water and expand the cell
D. Causes the cell to undergo cell division
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. Auxin does not act directly on the cell wall. Instead, it triggers signaling pathways that lead to proton pump activation, acidifying the cell wall and allowing expansion.
B. Correct. Auxin binds to specific receptors, which leads to the activation of gene expression. These genes promote the production of proteins involved in cell elongation, such as proton pumps that loosen the cell wall and allow growth.
C. Incorrect. Although vacuole water uptake contributes to cell elongation, auxin’s primary mechanism is not to directly cause water uptake. The water entry happens after wall loosening, not because of auxin acting on the vacuole.
D. Incorrect. Auxin primarily promotes cell elongation, not cell division. Cytokinins are the hormones most associated with stimulating cell division.
Question 6
Explain the neural control of swallowing. [3]
Three of the following:
a. voluntary passage of food through the mouth
b. bolus of food touches the walls of the pharynx
c. nerve sends message/impulse to brain
d. swallowing centre in the medulla oblongata
e. now involuntary/unconscious/autonomic responses/reflexes
f. triggers closing of epiglottis to prevent choking
g. leading to contraction of muscles/peristalsis in the pharynx and esophagus
Sample answer:
Swallowing begins with the voluntary movement of food through the mouth [1], and when the bolus touches the walls of the pharynx, sensory receptors are stimulated [1]. This triggers nerve impulses that are sent to the brain [1], specifically to the swallowing center located in the medulla oblongata [1]. At this point the process becomes involuntary and is controlled automatically as a reflex [1]. The medulla initiates the closing of the epiglottis to prevent food from entering the trachea and causing choking [1], and it triggers coordinated muscle contractions and peristalsis in the pharynx and esophagus to move the bolus downward [1].
Question 7
Explain how breathing is controlled by the brain. [6]
Six of the following:
a. breathing is an automatic process/can occur without conscious intervention/is involuntary/ autonomic
b. voluntary/conscious factors can override automatic functions for a limited time
c. control of the breathing comes from the respiratory centre
d. respiratory centre located in the medulla of the brain;
e. exercise results in higher CO2 levels in blood
f. breathing rate changes in response changes to blood pH/acidity/CO2 level
g. medulla contains chemoreceptors OR chemoreptors in aortic/carotid bodies send signals to medulla
h. respiratory centre/medulla sends nerve impulses to diaphragm/intercostal muscles
i. stimulates the intercostal muscles/diaphragm to control breathing rate/depth of inspiration/contraction
Sample answer:
Breathing is controlled as an automatic, involuntary process that does not require conscious input [1], although voluntary control can temporarily override this automatic mechanism [1]. The regulation of breathing comes from the respiratory center [1], which is in the medulla of the brain [1]. During exercise, rising levels of CO2 in the blood occur [1], and the breathing rate adjusts in response to changes in blood pH and acidity caused by altered CO2 levels [1]. The medulla contains chemoreceptors or receives signals from chemoreceptors in the aortic and carotid bodies, which detect these changes [1]. The respiratory center then sends nerve impulses to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles [1], stimulating their contraction to control the rate and depth of breathing [1].
Question 8
Outline how the hormone auxin controls phototropism in plant shoots. [5]
Five of the following:
a. grows/bends towards brightest light/sun
b. auxin moved from lighter to shadier side of shoot/stem tip/apex
c. moved by auxin efflux pumps
d. auxin promotes cell elongation/cell growth / auxin causes cell wall acidification/loosening
e. more growth on shady side of stem due to auxin concentration gradient
f. binds to auxin receptors in target cells
g. auxin/auxin receptors promote expression of genes for growth/for H+ secretion into wall
Sample answer:
Plant shoots bend toward the brightest light because auxin directs differential growth across the stem [1]. Auxin is transported from the illuminated side of the shoot tip toward the shadier side, creating an uneven distribution [1]. This lateral movement occurs through the action of auxin efflux pumps that actively shift the hormone across cells [1]. Once concentrated on the shaded side, auxin promotes cell elongation by loosening the cell wall through acidification mechanisms [1]. As a result, cells on the shaded side grow more than those on the lit side, causing the shoot to bend toward the light [1]. Auxin achieves this effect by binding to specific auxin receptors within target cells [1], which in turn activate the expression of genes involved in growth and the secretion of protons into the cell wall to facilitate elongation [1].
Question 9
Explain the control mechanism of the heart rate. [7]
Seven of the following:
a. sinoatrial node/SAN is a specialized group of muscle cells OR sinoatrial node/SAN is located in the right atrium
b. acts as a pacemaker/controls the heart rate OR initiates/generates the heart beat/starts the cardiac cycle
c. sends out electrical signal/impulses/depolarisations
d. electrical signal stimulates contraction of heart muscle
e. signal passes through walls of atria/passes to AV node
f. then through walls of the ventricles
g. medulla oblongata of brain can change/increase/decrease the rate
h. through nerves/named example of nerve/autonomic/sympathetic/ parasympathetic nervous system
i. one nerve increases the rate and the other decreases it
j. epinephrine/adrenaline increases heart rate/force of contraction
k. epinephrine/adrenaline prepares the body for vigorous activity/is part of fight or flight response
Sample answer:
The control of heart rate begins in the sinoatrial node (SAN), a specialized cluster of muscle cells located in the right atrium [1]. This SAN acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker because it initiates the heartbeat and sets the rhythm of the cardiac cycle [1]. It does this by sending out regular electrical impulses or depolarizations [1], which then trigger the contraction of the heart muscle [1]. The electrical signal first spreads through the atrial walls and then passes to the atrioventricular (AV) node [1], after which it travels through the walls of the ventricles to coordinate their contraction [1]. The medulla in the brain can adjust this rate by sending signals through the autonomic nervous system [1], using sympathetic nerves to increase heart rate and the vagus nerve to decrease it [1], and epinephrine further increases heart rate as part of the fight-or-flight response [1].
Question 10
Outline the role of melatonin in humans. [2]
Two of the following:
a. control/maintain/regulate circadian rhythms;
b. secreted/released late evening/end of day/in dark/night time/dim light/absence of blue light;
c. helps to induce sleep/sleepiness/influences timing of sleeping/waking/control sleep cycle;
Sample answer:
Melatonin helps regulate and maintain circadian rhythms in humans [1]. It is secreted in the late evening and during darkness, especially when blue light is absent [1]. This rise in melatonin induces sleepiness and helps control the timing of sleeping and waking in the sleep–wake cycle [1].
Question 1
An individual was presented with a stimulus resulting in the release of epinephrine. What was the most likely nature of the stimulus?
A. Sunset and the onset of darkness
B. An image of a close friend
C. The intake of glucose
D. A coach shouting to begin physical activity
Question 2
The image shows the changes in heart rate of an athlete during exercise.

What is likely to have occurred between 0 and 4 minutes and between 24 and 28 minutes?
| Between 0 and 4 minutes | Between 24 and 28 minutes | |
| A. | Epinephrine is secreted | More blood is sent to the rest of the body than to the lungs |
| B. | More blood is sent to the rest of the lungs than to the body | Epinephrine is secreted |
| C. | Epinephrine is secreted | Impulses are sent from the medulla of the brain to the heart |
| D. | Impulses are sent from the medulla of the brain to the heart | Epinephrine is secreted |
Question 3
How does auxin contribute to phototropism?
A. It increases production of light-sensitive proteins.
B. It increases growth of cells on the shaded side of the stem.
C. It inhibits growth of axillary buds.
D. It inhibits stem elongation.
Question 4
The diagram shows a plant shoot and the direction of the light which the shoot received.

What are the direction of movement and the effect of auxin in the tip of a plant shoot when receiving light from one side?
| Direction of movement of auxin | Effect of auxin on cell elongation | |
| A. | Towards light | Promotes |
| B. | Towards light | Inhibits |
| C. | Away from light | Promotes |
| D. | Away from light | Inhibits |
Question 5
How does auxin exert its effect on plant cells?
A. Acts directly on the cell wall, causing expansion
B. Binds to a receptor resulting in expression of genes
C. Causes the vacuole to absorb water and expand the cell
D. Causes the cell to undergo cell division
Question 6
Explain the neural control of swallowing. [3]
Question 7
Explain how breathing is controlled by the brain. [6]
Question 8
Outline how the hormone auxin controls phototropism in plant shoots. [5]
Question 9
Explain the control mechanism of the heart rate. [7]
Question 10
Outline the role of melatonin in humans. [2]