Question 1
In a stable natural ecosystem, how is the supply of nutrients and energy maintained?
A. Nutrients and energy are efficiently cycled within the ecosystem.
B. Energy from the Sun is cycled through the food chains, while nutrients are constantly lost.
C. Nutrients are efficiently cycled within the ecosystem, while there is a constant flow of energy.
D. Energy is cycled through photosynthesis and respiration, while food chains ensure that nutrients flow through the ecosystem.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The diagram shows flows of energy and matter in an ecosystem. What do the letters P, Q and R represent?
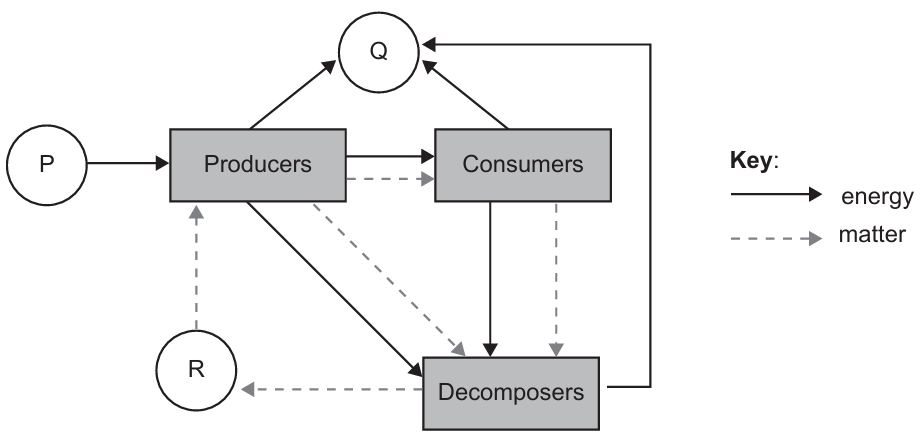
| P | Q | R | |
| A. | Light | Water vapour | Nitrates |
| B. | Chemical energy | Heat | Carbon dioxide |
| C. | Light | Heat | Inorganic nutrients |
| D. | Chemical energy | Carbon dioxide | Glucose |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
The diagram shows the carbon cycle.
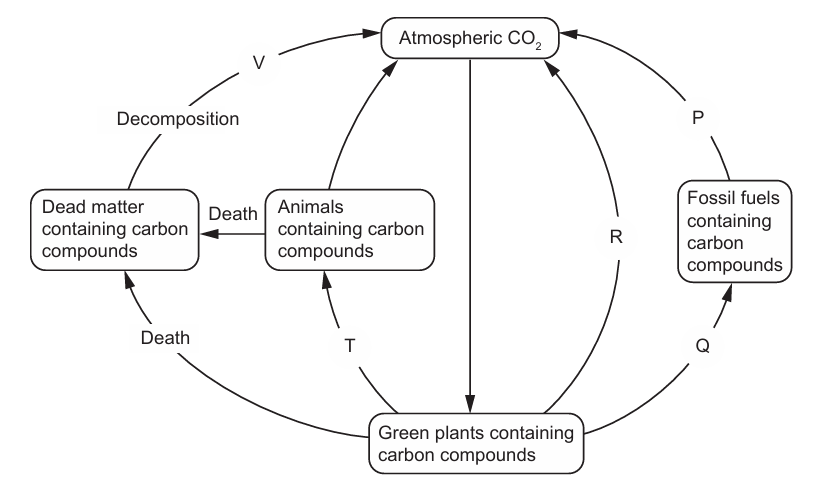
Which letters represent respiration?
A. R and T
B. P and V
C. Q and R
D. R and V
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The pyramid of energy shows the annual gross productivity for each trophic level in the Silver Springs ecosystem in Florida.
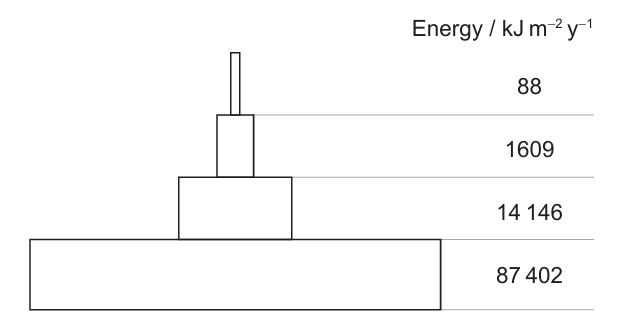
What does the pyramid show?
A. Most energy is lost by the autotrophs.
B. There are a larger number of herbivores than carnivores.
C. The biggest loss of energy is when sunlight reflects from plants.
D. The energy in the trophic levels is affected by seasonal changes.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Carbon sinks are any reservoirs that absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Which process increases the size of the carbon sink in oceans?
A. Photosynthesis
B. Respiration
C. Ocean acidification
D. Decomposition
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
The diagram shows the energy flow between five “sink” in a terrestrial ecosystem.
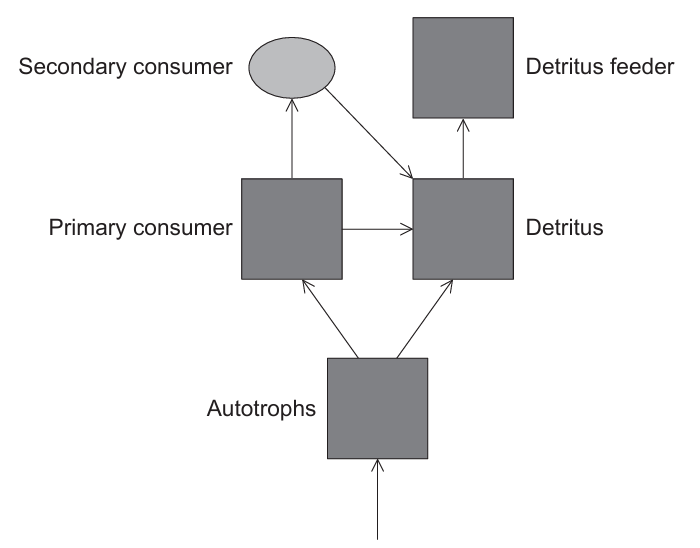
In a typical terrestrial ecosystem, which trophic level would have the highest biomass?
A. Autotrophs
B. Primary consumers
C. Secondary consumers
D. Detritus feeders
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
In a woodland ecosystem, each tree provides food for numerous aphids which feed on the sap of the tree.
The aphids are eaten by carnivorous beetles, as shown in the food chain.
Oak Tree → Aphids → Beetles
Which pyramid of energy represents this relationship?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
In an ecosystem, in the transfer of carbon from producers to consumers, what is carbon transferred as?
I. Carbon dioxide
II. Protein
III. Hydrogencarbonate ions
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II only
D. I and III only
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Outline the flow of energy through an ecosystem. [4]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Explain the transformations of carbon compounds in the carbon cycle. [7]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
In a stable natural ecosystem, how is the supply of nutrients and energy maintained?
A. Nutrients and energy are efficiently cycled within the ecosystem.
B. Energy from the Sun is cycled through the food chains, while nutrients are constantly lost.
C. Nutrients are efficiently cycled within the ecosystem, while there is a constant flow of energy.
D. Energy is cycled through photosynthesis and respiration, while food chains ensure that nutrients flow through the ecosystem.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: Energy cannot be cycled - it flows through the system and is lost as heat, so it must be continually replenished by sunlight.
B. Incorrect: The opposite is true: nutrients are recycled, while energy flows and is not cycled.
C. Correct: In a stable ecosystem, nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus are recycled through processes like decomposition and nutrient uptake, meaning they are reused repeatedly within the ecosystem. However, energy flows in one direction - from the Sun to producers (via photosynthesis) and then to consumers and decomposers, with energy being lost as heat at each trophic level. Therefore, the ecosystem depends on a constant input of solar energy rather than recycling energy.
D. Incorrect: Energy is not cycled between photosynthesis and respiration; rather, it flows and is gradually lost as heat. Nutrients, not energy, flow through food chains and are recycled.
Question 2
The diagram shows flows of energy and matter in an ecosystem. What do the letters P, Q and R represent?

| P | Q | R | |
| A. | Light | Water vapour | Nitrates |
| B. | Chemical energy | Heat | Carbon dioxide |
| C. | Light | Heat | Inorganic nutrients |
| D. | Chemical energy | Carbon dioxide | Glucose |
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: While P as light is correct, Q cannot be water vapour because the diagram shows Q as part of the energy flow, and water vapour is not a form of energy - it is part of the water cycle. R as nitrates is reasonable, but since Q is incorrect, this whole option is wrong.
B. Incorrect: Q as heat is correct, but producers do not receive chemical energy; they make it from light energy through photosynthesis. Also, R cannot be carbon dioxide because the dashed arrows show matter cycling back to producers, which represents nutrients in the soil, not a gas like carbon dioxide that leaves the system.
C. Correct: The diagram shows the flow of both energy and matter in an ecosystem. Producers receive energy from P, which must be light energy from the Sun used for photosynthesis. The energy leaving producers and consumers as Q represents heat, which is lost to the surroundings during respiration. Finally, decomposers break down dead organisms and return inorganic nutrients (such as nitrates and phosphates) to the soil, which are then reused by producers. Therefore, C correctly matches the flow of energy and matter shown in the diagram.
D. Incorrect: Producers receive light energy, not chemical energy. Q is also wrong because carbon dioxide represents matter, not energy, and the arrows for Q indicate energy loss. Finally, R cannot be glucose, as decomposers do not supply glucose to producers; they release inorganic nutrients. Therefore, D does not fit the diagram’s energy and matter flows.
Question 3
The diagram shows the carbon cycle.

Which letters represent respiration?
A. R and T
B. P and V
C. Q and R
D. R and V
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: R represents respiration from plants, which is correct, but T shows the transfer of carbon from green plants to animals, which happens through feeding, not respiration. So only R fits respiration, making this option incorrect.
B. Incorrect: P shows the release of carbon from fossil fuels to the atmosphere, which is combustion, not respiration. Although V does involve respiration by decomposers, P does not, so this option is incorrect.
C. Incorrect: Q represents the formation of fossil fuels from dead matter over long periods - this is a geological process, not respiration. While R is respiration by plants, Q is unrelated, making this option incorrect.
D. Correct: respiration is the process by which living organisms release carbon dioxide (CO2) back into the atmosphere. In the diagram, R represents the flow of carbon from green plants to atmospheric CO2 - this occurs when plants respire, releasing CO2. Similarly, V represents the flow of carbon from dead matter to atmospheric CO2 - this occurs when decomposers break down dead organisms and respire, also releasing CO2. Therefore, both R and V show carbon being returned to the atmosphere through respiration, which makes this option the correct answer.
Question 4
The pyramid of energy shows the annual gross productivity for each trophic level in the Silver Springs ecosystem in Florida.

What does the pyramid show?
A. Most energy is lost by the autotrophs.
B. There are a larger number of herbivores than carnivores.
C. The biggest loss of energy is when sunlight reflects from plants.
D. The energy in the trophic levels is affected by seasonal changes.
Answer: A
A. Correct: Autotrophs (producers) capture solar energy through photosynthesis, but most of the energy they absorb is not converted into chemical energy. A large proportion is lost through respiration, heat, and processes such as reflection and transmission of sunlight. The pyramid shows that the producers have the largest amount of energy (87,402 kJ m⁻² y⁻¹), but only a small fraction is passed on to herbivores (14,146 kJ m⁻² y⁻¹). This demonstrates that most of the energy is lost at the producer level before it can move up the food chain, mainly through respiration and inefficiencies in energy conversion.
B. Incorrect: The pyramid of energy represents the amount of energy at each trophic level, not the number of organisms. It tells us how much energy is available, not how many herbivores or carnivores there are.
C. Incorrect: The pyramid does not show energy losses due to reflection of sunlight; it shows biological energy transfer within the ecosystem (from producers to consumers). Reflection is not part of the trophic-level energy flow represented here.
D. Incorrect: While seasonal changes can influence productivity, the pyramid itself represents annual gross productivity (as stated in the question), which averages out seasonal variations. Therefore, the pyramid is not showing changes due to seasons but the overall energy structure of the ecosystem.
Question 5
Carbon sinks are any reservoirs that absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Which process increases the size of the carbon sink in oceans?
A. Photosynthesis
B. Respiration
C. Ocean acidification
D. Decomposition
Answer: A
A. Correct: Because photosynthesis by marine plants, algae, and phytoplankton removes carbon dioxide (CO2) from the ocean water (and indirectly from the atmosphere). These organisms use CO2 to make organic compounds, reducing the amount of dissolved CO2 and increasing the size of the oceanic carbon sink. As more CO2 is absorbed from the atmosphere to replace the CO2 used in photosynthesis, the ocean continues to act as a major sink for carbon. Thus, photosynthesis directly increases the ocean’s ability to store carbon.
B. Incorrect: Respiration does the opposite of photosynthesis - it releases CO2 back into the water and atmosphere as organisms break down organic molecules for energy. This process reduces, rather than increases, the ocean’s carbon sink capacity.
C. Incorrect: Ocean acidification occurs when CO2 dissolves in seawater to form carbonic acid. While this process involves CO2 entering the ocean, it does not enhance long-term carbon storage; instead, it changes the ocean’s chemistry, harming marine life and carbonate systems. It reflects a symptom of excess CO2, not an increase in carbon storage efficiency.
D. Incorrect: Because decomposition by microorganisms breaks down dead organic matter, releasing CO2 or methane back into the water or atmosphere. This returns carbon to circulation rather than storing it, so it decreases the size of the carbon sink instead of increasing it.
Question 6
The diagram shows the energy flow between five “sink” in a terrestrial ecosystem.

In a typical terrestrial ecosystem, which trophic level would have the highest biomass?
A. Autotrophs
B. Primary consumers
C. Secondary consumers
D. Detritus feeders
Answer: A
A. Correct: Autotrophs, or producers (such as plants), form the base of the food chain and have the highest biomass in a typical terrestrial ecosystem. They use sunlight to produce organic matter through photosynthesis, providing the primary source of energy and material for all other trophic levels. Since energy is lost as heat at each level of the food chain, only a small fraction of energy is transferred upward, meaning higher levels (consumers) must have less biomass to be sustained. Thus, autotrophs accumulate the most biomass because they directly harness solar energy and are more abundant than any consumer group.
B. Incorrect: Primary consumers (herbivores) rely on autotrophs for food, and only about 10% of the producers’ energy is transferred to them. Therefore, their total biomass is much smaller than that of autotrophs.
C. Incorrect: These are carnivores that feed on herbivores, obtaining even less energy. Since energy decreases up the trophic levels, secondary consumers have a much smaller biomass than both autotrophs and primary consumers.
D. Incorrect: Detritus feeders, such as decomposers, break down dead organic matter. While they play an essential role in nutrient recycling, their total biomass is generally much lower than that of autotrophs, as they depend on the organic material produced and left behind by other organisms.
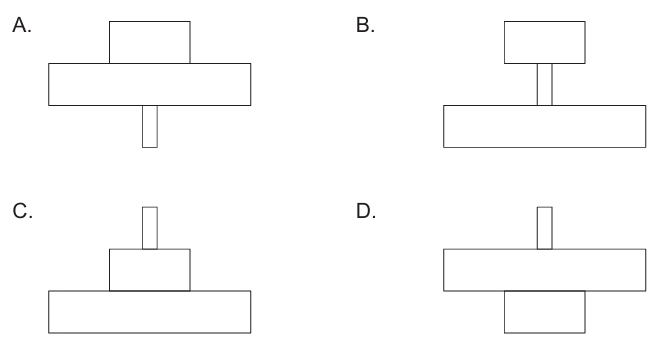
Question 7
In a woodland ecosystem, each tree provides food for numerous aphids which feed on the sap of the tree.
The aphids are eaten by carnivorous beetles, as shown in the food chain.
Oak Tree → Aphids → Beetles
Which pyramid of energy represents this relationship?

Answer: C
A. Incorrect: This pyramid is inverted, showing more energy at higher trophic levels, which is impossible - energy always decreases up the food chain due to losses through respiration and heat.
B. Incorrect: Although the diagram B appears roughly upright, the proportions are unrealistic - the producer’s energy bar should always be the largest. Here, it is too narrow to represent the true energy base of the ecosystem.
C. Correct: Pyramid of energy always shows the total energy available at each trophic level, and energy decreases from producers to higher consumers. In this food chain - oak tree 🡪 aphids 🡪 beetles - the oak tree (producer) provides the largest total energy input, even though there is only one tree. The aphids (primary consumers) and beetles (secondary consumers) each have less total energy available because much of the energy is lost as heat through respiration at every level. Therefore, the correct pyramid of energy must be upright, with the broadest base (oak tree) and progressively narrower bars for aphids and beetles, which is exactly what diagram C shows.
D. Incorrect: This diagram shows an inverted shape, with consumers appearing to have more energy than producers. This cannot occur in an energy pyramid since energy flow is unidirectional and diminishes at each transfer.
Question 8
In an ecosystem, in the transfer of carbon from producers to consumers, what is carbon transferred as?
I. Carbon dioxide
II. Protein
III. Hydrogencarbonate ions
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II only
D. I and III only
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: Carbon dioxide is used by producers (plants) during photosynthesis to make organic compounds. It is not transferred directly from producers to consumers, because consumers do not absorb CO2 from plants; they eat organic matter instead.
B. Correct: Carbon is transferred from producers to consumers when animals eat plants. In plants (the producers), carbon is found in organic molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins produced during photosynthesis. When consumers feed on plants, they take in these organic carbon compounds, including proteins, which contain carbon in their amino acid structure. Thus, carbon is transferred as part of organic molecules like proteins from producers to consumers through feeding.
C. Incorrect: Carbon dioxide (statement I) is not transferred between producers and consumers. Only organic compounds (e.g., proteins, carbohydrates) carry carbon between trophic levels.
D. Incorrect: Hydrogencarbonate (bicarbonate) ions are inorganic forms of carbon found dissolved in water and used by aquatic producers. They are not part of the direct transfer of carbon between producers and consumers in the food chain.
Question 9
Outline the flow of energy through an ecosystem. [4]
Any four of the following:
a. non-cyclical/one-way flow of energy / energy is not cycled/recycled;
b. plants/producers carry out photosynthesis / convert solar energy to chemical energy in carbon compounds / sun is the source of energy in an ecosystem;
c. chemical energy passes through food chains by feeding / through trophic levels;
d. energy released from carbon compounds through (cell) respiration;
e. some energy is released/lost as heat OR lost between levels due to excretion/uneaten material/death;
f. only 10%/small percentage/small amount of energy passes to the next trophic level;
g. food chains/webs are limited in length/size due to energy losses (between trophic levels);
Sample answer:
Energy flows through an ecosystem in a non-cyclical, one-way direction, starting from the Sun as the primary energy source [1].
Producers, such as plants, capture solar energy through photosynthesis, converting it into chemical energy stored in carbon compounds [1].
The energy is then transferred through food chains or trophic levels as organisms feed on one another [1].
Some of this energy is released during cellular respiration to support life processes [1].
A significant amount of energy is lost at each trophic level, leaving only a small percentage (around 10%) available to the next level [1].
Because of these continual losses, food chains are limited in length, and energy cannot be recycled, resulting in a one-way flow through the ecosystem [1].
Question 10
Explain the transformations of carbon compounds in the carbon cycle. [7]
Any seven of the following:
a. autotrophs/producers convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrates/carbon compounds in photosynthesis;
b. carbon dioxide diffuses/moves from the atmosphere /water into autotrophs/plants;
c. carbon compounds are transferred through food chains/OWTTE;
d. carbon dioxide produced by respiration diffuses out of organisms into water/atmosphere;
e. decomposers release carbon dioxide during decay/putrefaction;
f. methane is produced from organic matter in anaerobic conditions (by methanogens);
g. some methane diffuses into the atmosphere/accumulates in the ground;
h. methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide (and water) in the atmosphere;
i. peat forms when organic matter is not fully decomposed because of acidic/anaerobic conditions in waterlogged soils;
j. partially decomposed organic matter from past geological eras/fossils was converted into coal/oil/gas that accumulated in rocks;
k. carbon dioxide is produced by the combustion of biomass/fossilized organic matter/fuels;
l. hard parts of some animals/corals/molluscs are composed of calcium carbonate
m. can become fossilized in limestone;
Sample answer:
In the carbon cycle, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere or water diffuses into autotrophs, which convert it into carbohydrates and other carbon compounds by photosynthesis [1]. These compounds pass through food chains as organisms feed on one another [1]. All living things release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere or water through respiration, and decomposers further release it during decay [1]. In anaerobic conditions, methanogens produce methane [1], which may escape into the atmosphere or be oxidized back to carbon dioxide [1]. When organic matter does not fully decompose in waterlogged soils, peat forms, and over geological time, partially decomposed matter becomes fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas [1]. The combustion of these fuels returns carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, while some marine organisms store carbon as calcium carbonate in shells and skeletons that can become fossilized in limestone, locking away carbon for millions of years [2].
Question 1
In a stable natural ecosystem, how is the supply of nutrients and energy maintained?
A. Nutrients and energy are efficiently cycled within the ecosystem.
B. Energy from the Sun is cycled through the food chains, while nutrients are constantly lost.
C. Nutrients are efficiently cycled within the ecosystem, while there is a constant flow of energy.
D. Energy is cycled through photosynthesis and respiration, while food chains ensure that nutrients flow through the ecosystem.
Question 2
The diagram shows flows of energy and matter in an ecosystem. What do the letters P, Q and R represent?

| P | Q | R | |
| A. | Light | Water vapour | Nitrates |
| B. | Chemical energy | Heat | Carbon dioxide |
| C. | Light | Heat | Inorganic nutrients |
| D. | Chemical energy | Carbon dioxide | Glucose |
Question 3
The diagram shows the carbon cycle.

Which letters represent respiration?
A. R and T
B. P and V
C. Q and R
D. R and V
Question 4
The pyramid of energy shows the annual gross productivity for each trophic level in the Silver Springs ecosystem in Florida.

What does the pyramid show?
A. Most energy is lost by the autotrophs.
B. There are a larger number of herbivores than carnivores.
C. The biggest loss of energy is when sunlight reflects from plants.
D. The energy in the trophic levels is affected by seasonal changes.
Question 5
Carbon sinks are any reservoirs that absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Which process increases the size of the carbon sink in oceans?
A. Photosynthesis
B. Respiration
C. Ocean acidification
D. Decomposition
Question 6
The diagram shows the energy flow between five “sink” in a terrestrial ecosystem.

In a typical terrestrial ecosystem, which trophic level would have the highest biomass?
A. Autotrophs
B. Primary consumers
C. Secondary consumers
D. Detritus feeders
Question 7
In a woodland ecosystem, each tree provides food for numerous aphids which feed on the sap of the tree.
The aphids are eaten by carnivorous beetles, as shown in the food chain.
Oak Tree → Aphids → Beetles
Which pyramid of energy represents this relationship?

Question 8
In an ecosystem, in the transfer of carbon from producers to consumers, what is carbon transferred as?
I. Carbon dioxide
II. Protein
III. Hydrogencarbonate ions
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II only
D. I and III only
Question 9
Outline the flow of energy through an ecosystem. [4]
Question 10
Explain the transformations of carbon compounds in the carbon cycle. [7]