Question 1
The image shows a cell from the root tip of an onion (Allium cepa) (2n = 16) during late prophase of mitosis.

How many chromatids are present in the cell?
A.`8`
B. `16`
C. `32`
D. `64`
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
What occurs during the first division of meiosis?
A. Replication of DNA
B. Separation of chromatids
C. Having of the chromosome number
D. Production of two identical cells
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
How does mitosis produce two genetically identical nuclei?
A. By separation of homologous chromosomes
B. By separation of sister chromatids
C. By division of the cytoplasm into two equal cells
D. By division of the nuclear membrane into two equal parts
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Cisplatin is an anti-cancer drug that prevents tumour cells from dividing by mitosis as it inhibits cell processes at state S of interphrase. How does cisplatin prevent cancer cells from dividing?
A. It inhibits the replication of DNA.
B. It inhibits the growth of the spindle fibres.
C. It prevents the breakdown of the nuclear membrane.
D. It prevents the condensation of chromosomes.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
A cell in the testis of a male chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) contains 48 chromosomes. It is about to undergo meiosis. How many molecules of DNA will be present in the nucleus of the sperm cells just after meiosis?
A. `96`
B. `48`
C. `24`
D. `12`
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
What occurs during meiosis but not mitosis?
A. Spindles are formed from microtubules.
B. Chromosome number is conserved.
C. Homologous chromosomes pair up.
D. Centromeres split.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
The graph shows the mitotic index in the roots of lentil plants at different distances from the end of the root.
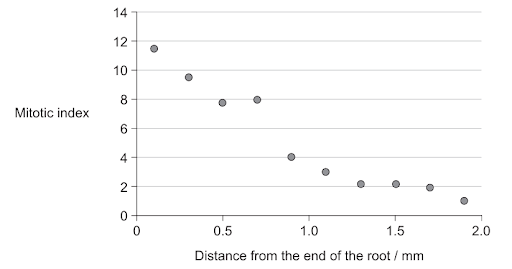
What can be deduced from the graph?
A. As the distance from the end of the root increases, more cells are undergoing mitosis.
B. At `0.5` mm form the end of the root, most of the cells are in prophase.
C. There were fewer cells observed at `1.5`mm than at `0.5`mm.
D. As the distance from the end of the root increases, the percentage of cells in interphrase increases.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which of the following take(s) place during either interphase or mitosis in animal cells?
I. Re-formation of nuclear membranes
II. Pairing of homologous chromosomes
III. DNA replication
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I and III only
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Describe the events that occur during mitosis. [9]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Explain the stages and processes of meiosis leading to genetic variation. [7]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
Explain how an error in meiosis can lead to Down syndrome. [8]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
The image shows a cell from the root tip of an onion (Allium cepa) (2n = 16) during late prophase of mitosis.

How many chromatids are present in the cell?
A.`8`
B. `16`
C. `32`
D. `64`
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: If there were `8` chromatids, that would mean there are only 4 duplicated chromosomes (`4 × 2 =8`) because the number of chromatids `=2 ×` number of chromosomes. But the onion has `2n = 16` chromosomes, not `4`.
B. Incorrect: If there were `16` chromatids, that would mean the cell has `8` chromosomes (`16/2 =8`), or that the chromosomes are not duplicated yet. However, the cell is in late prophase, after DNA replication. At this stage, each chromosome has two sister chromatids, so `16`chromatids means replication hasn’t occurred, which is wrong.
C. Correct: During late prophase (or prophase in general), each chromosome has already duplicated during S phase of interphase. Each duplicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined at a centromere.
So, the number of chromatids `=2 ×`number of chromosomes. Onion has`2n = 16`chromosomes 🡪 Total chromatids`=2 ×16 =32`. Therefore, during late prophase, there are`32` chromatids in the cell.
D. Incorrect: This would mean each chromosome has `4`chromatids, which never happens in normal mitosis. DNA replication produces `2` chromatids per chromosome, not `4`.
Question 2
What occurs during the first division of meiosis?
A. Replication of DNA
B. Separation of chromatids
C. Having of the chromosome number
D. Production of two identical cells
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: DNA replication occurs before meiosis begins, during the S phase of the cell cycle, to duplicate each chromosome into two sister chromatids. It does not occur during the first division of meiosis.
B. Incorrect: The separation of chromatids occurs during the second division of meiosis (meiosis II), which is analogous to mitosis, where sister chromatids are pulled apart to form haploid cells. The first division (meiosis I) involves the separation of homologous chromosomes, not chromatids.
C. Correct: The first division of meiosis, known as meiosis I, is a reductional division where homologous chromosomes (each consisting of two sister chromatids) are separated into two daughter cells. This process halves the chromosome number, reducing it from diploid (2n) to haploid (n), ensuring that gametes have half the original chromosome count.
D. Incorrect: The first division of meiosis produces two daughter cells, but they are not identical. Due to the separation of homologous chromosomes and processes like crossing over, these cells are haploid and genetically diverse, not identical to each other or the original cell.
Question 3
How does mitosis produce two genetically identical nuclei?
A. By separation of homologous chromosomes
B. By separation of sister chromatids
C. By division of the cytoplasm into two equal cells
D. By division of the nuclear membrane into two equal parts
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: he separation of homologous chromosomes occurs during meiosis I, not mitosis. Mitosis involves the division of a single cell into two identical daughter cells, and it does not involve the pairing or separation of homologous chromosomes, which are characteristic of the reductional division in meiosis.
B. Correct: Mitosis produces two genetically identical nuclei by ensuring that each sister chromatid - created during DNA replication prior to mitosis - is separated and distributed into one of the two daughter cells during anaphase. This process, driven by the mitotic spindle, ensures that each new nucleus receives an exact copy of the original genome, maintaining genetic identity.
C. Incorrect: The division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis, which occurs after mitosis. Cytokinesis produces two separate cells, but it does not ensure genetic identity - that’s determined by how chromatids are separated during mitosis. So, cytokinesis is about cell division, not genetic identity.
D. Incorrect: The nuclear membrane breaks down during prophase of mitosis and reforms around each set of chromosomes during telophase to create two nuclei. However, this division of the nuclear membrane is a structural event and not the primary mechanism for ensuring genetic identity, which relies on the accurate separation of sister chromatids.
Question 4
Cisplatin is an anti-cancer drug that prevents tumour cells from dividing by mitosis as it inhibits cell processes at state S of interphrase. How does cisplatin prevent cancer cells from dividing?
A. It inhibits the replication of DNA.
B. It inhibits the growth of the spindle fibres.
C. It prevents the breakdown of the nuclear membrane.
D. It prevents the condensation of chromosomes.
Answer: A
A. Correct: Cisplatin is an anti-cancer drug that prevents tumor cells from dividing by targeting the S phase of interphase, where DNA replication occurs. It works by cross-linking DNA strands, which inhibits the replication process by interfering with the ability of DNA polymerase to copy the genetic material accurately. This disruption halts the cell cycle, preventing the cancer cells from progressing to mitosis and ultimately leading to cell death.
B. Incorrect: The growth and function of spindle fibers occur during mitosis, particularly in the M phase, to separate chromosomes. Cisplatin's primary action is in the S phase, where it affects DNA replication, not the formation or function of spindle fibers, which are targeted by other drugs like taxanes.
C. Incorrect: The breakdown of the nuclear membrane happens during prophase of mitosis. Cisplatin does not interfere with this process, as its mechanism of action is focused on DNA replication in the S phase of interphase, not the structural changes associated with mitotic entry.
D. Incorrect: Chromosome condensation occurs during prophase of mitosis, preparing chromosomes for separation. Cisplatin’s effect is on DNA replication in the S phase, where it causes DNA damage and cross-linking, rather than preventing the physical condensation of chromosomes later in the cell cycle.
Question 5
A cell in the testis of a male chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) contains 48 chromosomes. It is about to undergo meiosis. How many molecules of DNA will be present in the nucleus of the sperm cells just after meiosis?
A. `96`
B. `48`
C. `24`
D. `12`
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: This is the number of DNA molecules after DNA replication but before the meiotic divisions (prophase I), not the number in the final sperm.
B. Incorrect: This would be the number of DNA molecules after meiosis I (`24` chromosomes each with two chromatids), or the number of chromosomes in the original cell if chromatids were not separated, not the final sperm count.
C. Correct: In a male chimpanzee, a diploid cell in the testis contains 48 chromosomes (`2n = 48`). Before the meiotic divisions the DNA is replicated in S phase, so each chromosome becomes two sister chromatids (two DNA molecules). That would give `48 ×2 =96` DNA molecules before the divisions. Meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes, halving the chromosome number so each daughter has `24` chromosomes, but each chromosome still consists of two sister chromatids (so `24 ×2 =48` DNA molecules after meiosis I). Meiosis II separates sister chromatids. After meiosis II (i.e. in the sperm cells just after meiosis) each chromosome is a single chromatid, so each sperm nucleus contains`24`chromosomes `= 24` DNA molecules.
D. Incorrect: This would imply the chromosome number was halved twice (`48` 🡪 `24` 🡪`12`), which is incorrect: meiosis reduces chromosome number only once (`2n`🡪 `n`), so each sperm has `24`, not `12`..
Question 6
What occurs during meiosis but not mitosis?
A. Spindles are formed from microtubules.
B. Chromosome number is conserved.
C. Homologous chromosomes pair up.
D. Centromeres split.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: Spindle formation from microtubules is a general feature of both mitosis and meiosis (spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores and move chromosomes). Because it happens in both processes, it is not unique to meiosis.
B. Incorrect: Mitosis conserves chromosome number (`2n` 🡪 `2n`); daughter nuclei have the same chromosome number as the parent. Meiosis is reductional (`2n` 🡪 `n`): chromosome number is halved to produce haploid gametes. So conservation of chromosome number is a property of mitosis, not meiosis.
C. Correct: In meiosis I, during prophase I, homologous chromosomes (one from each parent) undergo synapsis: they physically pair along their lengths to form bivalents/tetrads. This pairing enables crossing-over (recombination) between non-sister chromatids, which increases genetic variation. This pairing (synapsis) does not occur in mitosis - chromosomes do not form homologous pairs there.
D. Incorrect: Centromere splitting - the separation of sister chromatids at the centromere - occurs in both processes, but at different stages. In mitosis, it happens during anaphase, when sister chromatids are pulled apart. In meiosis, the centromeres remain intact in meiosis I because homologous chromosomes, not sister chromatids, separate at that stage. The centromeres split only in meiosis II. Therefore, centromere splitting is not unique to meiosis, and it doesn’t occur during the first meiotic division, making this statement incorrect.
Question 7
The graph shows the mitotic index in the roots of lentil plants at different distances from the end of the root.

What can be deduced from the graph?
A. As the distance from the end of the root increases, more cells are undergoing mitosis.
B. At `0.5` mm form the end of the root, most of the cells are in prophase.
C. There were fewer cells observed at `1.5`mm than at `0.5`mm.
D. As the distance from the end of the root increases, the percentage of cells in interphrase increases.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: The graph shows the opposite: mitotic index decreases with distance. That means fewer, not more, cells are in mitosis as you go away from the tip.
B. Incorrect: The mitotic index only tells you the percentage of cells in mitosis overall, not which mitotic stage (prophase, metaphase, etc.) they are in. You cannot deduce “most are in prophase” from this graph alone.
C. Incorrect: The mitotic index is a percentage (proportion), not the absolute number of cells counted. A lower mitotic index at `1.5` mm could occur even if the total number of observed cells was the same or larger — you cannot infer absolute cell counts from these percentages.
D. Correct: Calculating mitotic index `= frac{"Number of cells in mitosis"}{"Total number of cells"} ×100`. So a lower mitotic index means a smaller proportion (percentage) of cells are in mitosis, and therefore a larger proportion are in interphase (since total = mitosis + interphase). The graph shows the mitotic index falling as distance increases (from ~`11`–`12`at the tip down to ~`1` at`2.0` mm). If the percentage in mitosis decreases, the percentage in interphase must increase (they are complementary proportions of the cell cycle in this simple comparison). So this statement follows directly from the plotted decrease in mitotic index.
Question 8
Which of the following take(s) place during either interphase or mitosis in animal cells?
I. Re-formation of nuclear membranes
II. Pairing of homologous chromosomes
III. DNA replication
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I and III only
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: This option says that only re-formation of nuclear membranes happens during interphase or mitosis. It’s true that nuclear membranes re-form during telophase of mitosis, but DNA replication (III) also occurs during interphase (S phase). Therefore, this option is incorrect because it ignores the process of DNA replication.
B. Incorrect: It includes I (re-formation of nuclear membranes) - correct. But II (pairing of homologous chromosomes) is wrong, because this happens only in meiosis I, not in mitosis or interphase. Since homologous chromosomes do not pair up during mitosis, this option is incorrect.
C. Incorrect: II (pairing of homologous chromosomes) is false, as it occurs in meiosis I, not mitosis. III (DNA replication) is true (occurs in interphase). Because one part of the answer is wrong, this option is incorrect.
D. Correct: I (re-formation of nuclear membranes) - occurs during telophase of mitosis. III (DNA replication) - occurs during S phase of interphase before mitosis begins. Both are processes that take place during interphase or mitosis, so this option is correct.
Question 9
Describe the events that occur during mitosis. [9]
Any nine of the following:
a. sequence of stages is prophase 🡪 metaphase 🡪 anaphase 🡪 telophase;
b. chromosomes condense/supercoil/become shorter and fatter in prophase;
c. spindle microtubules grow (from poles to equator) in prophase/metaphase;
d. nuclear membrane breaks down in prophase/metaphase;
e spindle microtubules attach to the centromeres/chromosomes in metaphase;
f. chromosomes line up at equator in metaphase;
g. centromeres divide / (paired) chromatids separate / chromosomes separate into two chromatids in metaphase/anaphase;
h. (sister) chromatids/chromosomes pulled to opposite poles in anaphase;
j. spindle microtubules disappear in telophase;
k. nuclear membrane reforms around chromosomes/chromatids in telophase;
l. chromosomes/chromatids decondense in telophase;
Sample answer:
Mitosis progresses through a well-defined sequence of stages – prophase 🡪 metaphase 🡪 anaphase 🡪 telophase [1] - to ensure the accurate distribution of duplicated chromosomes. In prophase, chromosomes condense and become shorter and fatter [1], spindle microtubules extend from the poles to the equator [1], and the nuclear membrane breaks down to allow chromosome access [1]. During metaphase, spindle microtubules attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes [1], which then align precisely at the equator, setting the stage for their separation [1]. In anaphase, the centromeres divide, sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes [1], and these are pulled to opposite poles by the spindle microtubules [1]. Finally, in telophase, the spindle microtubules disappear [1], the nuclear membrane reforms around the decondensing chromosomes or chromatids [2], completing the formation of two identical nuclei ready for the next phase of the cell cycle.
Question 10
Explain the stages and processes of meiosis leading to genetic variation. [7]
(a) Any seven of the following:
a. meiosis divides a diploid nucleus to produce (4) haploid nuclei;
b. meiosis halves the chromosome number;
c. chromosomes consist of two sister chromatids at the start of meiosis;
d. homologous chromosomes are paired;
e. crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes;
f. crossing over promotes genetic variation/new gene/allele combinations;
g. pairs of homologous chromosomes are randomly oriented/assorted in the first
division of meiosis or sister chromatids are randomly assorted during the second division of meiosis;
h. in the first division of meiosis pairs of homologous chromosomes are separated;
i. random orientation promotes genetic variation/new gene/allele/chromosome
combinations;
j. meiosis produces haploid gametes (to ensure offspring have complete set of
chromosomes);
k. fusion of gametes from different parents promotes (genetic) variation;
Sample answer:
Meiosis is a specialized cell division process that reduces a diploid nucleus into four haploid nuclei [1], effectively halving the chromosome number to produce gametes [1], which ensures that the fusion of gametes from different parents during fertilization restores a complete set of chromosomes in the offspring. The process begins with chromosomes, each consisting of two sister chromatids, and involves the pairing of homologous chromosomes,where crossing over occurs, allowing segments of DNA to be exchanged between these homologous pairs, promoting genetic variation through new gene and allele combinations [3]. During the first division of meiosis, pairs of homologous chromosomes are separated after being randomly oriented [1], a process that further enhances genetic variation by creating new combinations of chromosomes [1], while the second division involves the random assortment of sister chromatids, adding to the diversity [1]. This random orientation and assortment, combined with the haploid nature of the resulting gametes, contribute significantly to genetic variation [1], which is further increased when gametes from different parents fuse, introducing a mix of genetic material that drives evolution and diversity in subsequent generations.
Question 11
Explain how an error in meiosis can lead to Down syndrome. [8]
Any eight of the following:
a. non-disjunction;
b. chromosomes/chromatids do not separate / go to same pole;
c. non-separation of (homologous) chromosomes during anaphase I;
d. due to incorrect spindle attachment;
e. non-separation of chromatids during anaphase II;
f. due to centromeres not dividing;
g. occurs during gamete/sperm/egg formation;
h. less common in sperm than egg formation / function of parents' age;
i. Down syndrome due to extra chromosome 21;
j. sperm/egg/gamete receives two chromosomes of same type;
k. zygote/offspring with three chromosomes of same type / trisomy / total 47 chromosomes;
Sample answer:
An error in meiosis can lead to Down syndrome through a process called non-disjunction [1], where chromosomes or chromatids fail to separate properly during cell division, often due to incorrect spindle attachment [2]. This non-separation can occur during anaphase I when homologous chromosomes do not move to opposite poles [1], or during anaphase II when chromatids fail to separate [1], typically because centromeres do not divide [1], and this error most commonly happens during gamete formation, such as in sperm or egg production [1], with a higher incidence in egg formation influenced by the age of the parents [1]. As a result, a gamete may receive two chromosomes of the same type, and if this involves chromosome 21, the affected gamete carries an extra copy [1]. Upon fertilization, the resulting zygote inherits three chromosomes of type 21 (trisomy), leading to a total of 47 chromosomes instead of the typical 46 [1], which manifests as Down syndrome in the offspring.
Question 1
The image shows a cell from the root tip of an onion (Allium cepa) (2n = 16) during late prophase of mitosis.

How many chromatids are present in the cell?
A.`8`
B. `16`
C. `32`
D. `64`
Question 2
What occurs during the first division of meiosis?
A. Replication of DNA
B. Separation of chromatids
C. Having of the chromosome number
D. Production of two identical cells
Question 3
How does mitosis produce two genetically identical nuclei?
A. By separation of homologous chromosomes
B. By separation of sister chromatids
C. By division of the cytoplasm into two equal cells
D. By division of the nuclear membrane into two equal parts
Question 4
Cisplatin is an anti-cancer drug that prevents tumour cells from dividing by mitosis as it inhibits cell processes at state S of interphrase. How does cisplatin prevent cancer cells from dividing?
A. It inhibits the replication of DNA.
B. It inhibits the growth of the spindle fibres.
C. It prevents the breakdown of the nuclear membrane.
D. It prevents the condensation of chromosomes.
Question 5
A cell in the testis of a male chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) contains 48 chromosomes. It is about to undergo meiosis. How many molecules of DNA will be present in the nucleus of the sperm cells just after meiosis?
A. `96`
B. `48`
C. `24`
D. `12`
Question 6
What occurs during meiosis but not mitosis?
A. Spindles are formed from microtubules.
B. Chromosome number is conserved.
C. Homologous chromosomes pair up.
D. Centromeres split.
Question 7
The graph shows the mitotic index in the roots of lentil plants at different distances from the end of the root.

What can be deduced from the graph?
A. As the distance from the end of the root increases, more cells are undergoing mitosis.
B. At `0.5` mm form the end of the root, most of the cells are in prophase.
C. There were fewer cells observed at `1.5`mm than at `0.5`mm.
D. As the distance from the end of the root increases, the percentage of cells in interphrase increases.
Question 8
Which of the following take(s) place during either interphase or mitosis in animal cells?
I. Re-formation of nuclear membranes
II. Pairing of homologous chromosomes
III. DNA replication
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I and III only
Question 9
Describe the events that occur during mitosis. [9]
Question 10
Explain the stages and processes of meiosis leading to genetic variation. [7]
Question 11
Explain how an error in meiosis can lead to Down syndrome. [8]