Question 1
The micrograph of a section through a plant stem shows at least ten different types of cells.
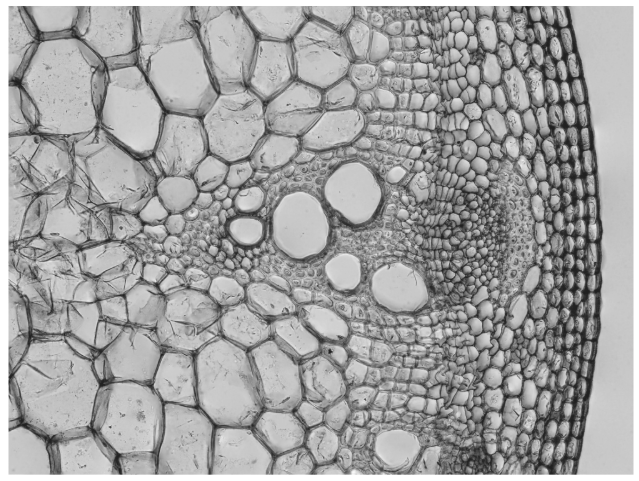
What explains the differences between these cells?
A. Only one gene is expressed in each cell type.
B. Different genes are expressed in each cell type.
C. Only useful genes remain in the DNA of each cell type.
D. Changes in the DNA sequence take place when these cells develop.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
What is a proteome?
A. The genes that code for all the proteins in the ribosome
B. The group of proteins that generate a proton gradient in mitochondria
C. The entire genome of a prokaryote
D. The entire set of proteins expressed by an organism at a certain time
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which statement correctly describes genome and proteome?
A. Only the genome but not the proteome can be analysed using gel electrophoresis.
B. The genome and the proteome are the same in all tissues in an organism.
C. In cells of different tissues, the genome is the same while the proteome varies.
D. Only mutations in the proteome but not in the genome cause any variability.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
The number of protein-coding genes in the human genome is estimated to be about 20000, which is much less than the size of the proteome. What is one reason for this?
A. Exons are removed from RNA before translation.
B. There are more types of amino acids than nucleotides.
C. mRNA can be spliced after transcription.
D. Base substitutions occur during transcription.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
DNA methylation profiles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) gametes were determined. The methylated areas were divided into three groups according to the amount of methylation: high, medium and low methylation.
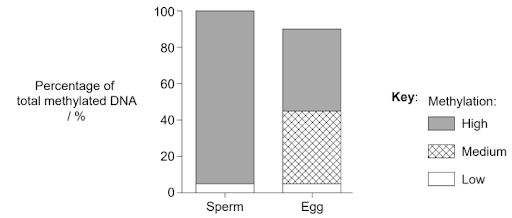
Methylation of DNA in sperm and egg is removed immediately after fertilization. What is the reason for this?
A. Methylation allows RNA polymerase to join the promoter.
B. It is needed to form homologous pairs of chromosomes.
C. It allows expression of genes linked to early development.
D. Transcription of promoters only occurs in methylated genes.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
What is the difference between the DNA of adult identical (monozygotic) twins?
A. Order of genes
B. Sequence of nucleotides
C. Methylation pattern
D. Ratio of complementary base pairs
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Explain how gene expression can be regulated during transcription to determine an organism’s phenotype. [7]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
DNA methylation has a critical role in gene regulation by affecting transcription. Samples were taken from two colon cancer tumors (T1 and T2) and two normal colon samples (N1 and N2). A particular gene was implicated as a possible cause of cancer. The promoter of this gene was cloned (A–J). The data show the DNA methylation patterns from these samples. The numbers (32–269) represent different markers in the promoter.
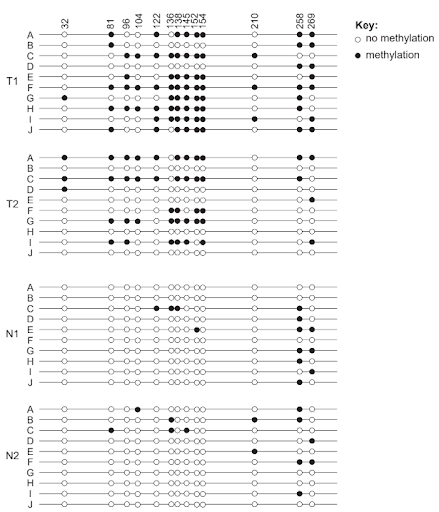
[Source: Philipp Schatz, Dimo Dietrich & Matthias Schuster. Rapid analysis of CpG methylation patterns using RNase T1 cleavage and MALDI-TOF. Nucleic Acids Research (2004) 32 (21): e167, doi:10.1093/nar/gnh165. Reproduced by permission of Oxford University Press]
a. Outline the difference in methylation pattern between tumorous and normal tissue samples. [2]
b. Suggest a way methylation may affect tumor cell genes. [1]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Insulin is produced in β cells of the pancreas and not in other cells of the human body. Explain how differentiation of cells and regulation of gene expression allow proteins such as insulin to be produced in only certain types of body cell. [7]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Outline how nucleosomes affect the transcription of DNA. [4]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
The micrograph of a section through a plant stem shows at least ten different types of cells.

What explains the differences between these cells?
A. Only one gene is expressed in each cell type.
B. Different genes are expressed in each cell type.
C. Only useful genes remain in the DNA of each cell type.
D. Changes in the DNA sequence take place when these cells develop.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect. All plant stem cells contain the same DNA, but the pattern of gene expression varies between cell types. Different cells switch on different sets of genes, leading to specialized structures and functions. This explains why xylem, phloem, cortex, and epidermal cells all look and behave differently despite having identical genomes. Cells express many genes, not just one. A xylem cell or phloem cell requires the expression of dozens to hundreds of genes to function properly.
B. Correct. All plant stem cells contain the same DNA, but the pattern of gene expression varies between cell types. Different cells switch on different sets of genes, leading to specialized structures and functions. This explains why xylem, phloem, cortex, and epidermal cells all look and behave differently despite having identical genomes.
C. Incorrect. All plant stem cells contain the same DNA, but the pattern of gene expression varies between cell types. Different cells switch on different sets of genes, leading to specialized structures and functions. This explains why xylem, phloem, cortex, and epidermal cells all look and behave differently despite having identical genomes. No DNA is removed during differentiation. All cells retain the full genome; they simply use different parts of it.
D. Incorrect. All plant stem cells contain the same DNA, but the pattern of gene expression varies between cell types. Different cells switch on different sets of genes, leading to specialized structures and functions. This explains why xylem, phloem, cortex, and epidermal cells all look and behave differently despite having identical genomes. Differentiation does not involve altering DNA sequences. Instead, it involves changes in gene regulation, not mutations.
Question 2
What is a proteome?
A. The genes that code for all the proteins in the ribosome
B. The group of proteins that generate a proton gradient in mitochondria
C. The entire genome of a prokaryote
D. The entire set of proteins expressed by an organism at a certain time
Answer: D
A. Incorrect. A proteome is not about the genes themselves, and it is not limited to ribosomal components. It concerns all proteins, not just those of one structure.
B. Incorrect. Components of the electron transport chain represent just one functional set of proteins within mitochondria. The proteome is far broader and includes every protein the organism, tissue, or cell expresses, not just those involved in ATP production.
C. Incorrect. genome refers to all DNA, not proteins. The proteome is about the proteins being expressed, while the genome is the full genetic code. Even in prokaryotes, the proteome changes with conditions, whereas the genome remains mostly constant.
D. Correct. The proteome is defined as all proteins currently being produced by a cell, tissue, or organism. It varies depending on environment, developmental stage, and cell type. It is dynamic, unlike the genome, which is mostly fixed.
Question 3
Which statement correctly describes genome and proteome?
A. Only the genome but not the proteome can be analysed using gel electrophoresis.
B. The genome and the proteome are the same in all tissues in an organism.
C. In cells of different tissues, the genome is the same while the proteome varies.
D. Only mutations in the proteome but not in the genome cause any variability.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Both DNA (genome) and proteins (proteome) can be analyzed using gel electrophoresis. DNA uses agarose gels; proteins use SDS-PAGE.
B. Incorrect. The genome is the same in all cells, but the proteome is different because different cell types express different proteins.
C. Correct. Different tissues have identical DNA, but they express different sets of proteins. For example, pancreatic β-cells express insulin, neurons express neurotransmitter-related proteins, muscle cells express actin and myosin.
D. Incorrect. Mutations occur in DNA, not proteins. Mutations in DNA can cause variation in both the genome and proteome.
Question 4
The number of protein-coding genes in the human genome is estimated to be about 20000, which is much less than the size of the proteome. What is one reason for this?
A. Exons are removed from RNA before translation.
B. There are more types of amino acids than nucleotides.
C. mRNA can be spliced after transcription.
D. Base substitutions occur during transcription.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. Introns are removed, not exons. Exons are kept and joined together. Removing exons would reduce, not increase, proteome diversity.
B. Incorrect. While true (20 amino acids vs. 4 nucleotides), this does not explain why the proteome is larger than the number of genes. It does not increase the number of different proteins produced per gene.
C. Correct. Alternative splicing allows a single gene to produce multiple different mRNA variants. Each variant can encode a different protein. This is one of the main reasons the proteome is much larger than the genome.
D. Incorrect. Transcription errors are rare and usually corrected; they do not systematically increase proteome size
Question 5
DNA methylation profiles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) gametes were determined. The methylated areas were divided into three groups according to the amount of methylation: high, medium and low methylation.

Methylation of DNA in sperm and egg is removed immediately after fertilization. What is the reason for this?
A. Methylation allows RNA polymerase to join the promoter.
B. It is needed to form homologous pairs of chromosomes.
C. It allows expression of genes linked to early development.
D. Transcription of promoters only occurs in methylated genes.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. DNA methylation usually inhibits binding of RNA polymerase, not promoting it.
B. Incorrect. Chromosome pairing during meiosis or fertilization does not depend on DNA methylation.
C. Correct. Removal of methylation after fertilization activates the zygotic genome, allowing genes necessary for early development to be transcribed.
D. Incorrect. Methylation generally represses transcription; promoters need to be unmethylated to be active.
Question 6
What is the difference between the DNA of adult identical (monozygotic) twins?
A. Order of genes
B. Sequence of nucleotides
C. Methylation pattern
D. Ratio of complementary base pairs
Answer: C
A. Incorrect. The order of genes is identical in monozygotic twins because they originate from the same zygote.
B. Incorrect. The DNA sequence is essentially the same; twins have nearly identical genomes. Minor mutations can occur over time, but generally the sequence is the same.
C. Correct. Epigenetic differences arise between twins as they age. Differences in DNA methylation patterns can affect gene expression and lead to phenotypic differences.
D. Incorrect. The ratio of A:T and G:C remains the same in both twins because their DNA sequences are the same.
Question 7
Explain how gene expression can be regulated during transcription to determine an organism’s phenotype. [7]
Seven of the following:
OR
Sample answer:
Gene expression can be regulated during transcription by transcription factors that bind to DNA and act as activators or repressors [1]. These transcription factors promote or block transcription [1]. A protein or transcription factor can bind to the promoter to activate transcription, where the promoter indicates where RNA polymerase binds to begin transcription [1]. Transcription factors or activators can bind to enhancers to increase transcription, while repressors can bind to silencers to decrease transcription [1]. Epigenetic tags, such as methylation, can alter gene expression [1]. Methylation of cytosine in the DNA of a promoter represses transcription [1]. Methylation of amino acids in histones can either repress or activate transcription [1]. These mechanisms regulate the production of proteins from the gene, which display phenotypic traits [1]. Additionally, gene expression can be altered by steroid hormones or biochemical signals that activate receptors to promote transcription [1]. Environmental factors, such as air pollution, can also alter methylation tags on DNA, affecting gene regulation [1].
Question 8
DNA methylation has a critical role in gene regulation by affecting transcription. Samples were taken from two colon cancer tumors (T1 and T2) and two normal colon samples (N1 and N2). A particular gene was implicated as a possible cause of cancer. The promoter of this gene was cloned (A–J). The data show the DNA methylation patterns from these samples. The numbers (32–269) represent different markers in the promoter.

[Source: Philipp Schatz, Dimo Dietrich & Matthias Schuster. Rapid analysis of CpG methylation patterns using RNase T1 cleavage and MALDI-TOF. Nucleic Acids Research (2004) 32 (21): e167, doi:10.1093/nar/gnh165. Reproduced by permission of Oxford University Press]
a. Outline the difference in methylation pattern between tumorous and normal tissue samples. [2]
b. Suggest a way methylation may affect tumor cell genes. [1]
a. Two of the following:
Sample answer:
Tumorous tissue samples show overall much higher levels of DNA methylation compared to normal tissue samples [1]. Some markers, such as 258 and 269, display similar methylation levels in both tumour and normal samples, indicating fewer differences at these sites [1]. In contrast, certain markers show methylation only in tumour cells—for example, marker 32—suggesting that methylation at specific loci may correlate with the presence of cancer [1].
b. One of the following:
Sample answer:
DNA methylation can inhibit the expression of cancer suppressor genes, leading to tumor formation [1] or can inhibit the expression of oncogenes, limiting cancer growth [1].
Question 9
Insulin is produced in β cells of the pancreas and not in other cells of the human body. Explain how differentiation of cells and regulation of gene expression allow proteins such as insulin to be produced in only certain types of body cell. [7]
Seven of the following:
Sample answer:
Insulin production is controlled by a specific gene that encodes the insulin protein [1]. This insulin gene is present in all human cells, but it is only activated in the β cells of the pancreas [1]. During development, stem cells differentiate into specialized cell types such as pancreatic β cells [1], and this differentiation involves switching some genes on while turning others off [1]. Insulin itself functions as a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels [1], and β cells contain specialized sensors that detect changes in blood glucose [1]. When glucose levels rise, these cells increase transcription of insulin mRNA [1], and this transcription occurs specifically within the β cells [1]. Gene expression is controlled by regulatory proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences such as enhancers, silencers, or promoter proximal elements [1], and these regulatory proteins are unique to the genes they control, meaning insulin-specific regulators exist only in β cells [1]. Chemical modifications such as DNA methylation, which typically suppresses gene expression, and histone acetylation, which promotes it, along with the degree of DNA coiling, also influence whether the insulin gene is expressed [1].
Question 10
Outline how nucleosomes affect the transcription of DNA. [4]
Four of the following:
Sample answer:
Nucleosomes can both promote and inhibit transcription by altering how tightly DNA is packaged [1]. When DNA is tightly condensed or supercoiled around histones, transcription is prevented because RNA polymerase and transcription factors cannot bind effectively [1]. Nucleosomes also influence transcription by allowing or blocking access of these enzymes to specific DNA regions [1]. Chemical tagging of histones, such as acetylation or methylation, can loosen or tighten chromatin, thereby promoting or inhibiting gene expression [1]. In addition, the movement or repositioning of nucleosomes along DNA can expose some genes while obscuring others, affecting which genes are transcribed [1].
Question 1
The micrograph of a section through a plant stem shows at least ten different types of cells.

What explains the differences between these cells?
A. Only one gene is expressed in each cell type.
B. Different genes are expressed in each cell type.
C. Only useful genes remain in the DNA of each cell type.
D. Changes in the DNA sequence take place when these cells develop.
Question 2
What is a proteome?
A. The genes that code for all the proteins in the ribosome
B. The group of proteins that generate a proton gradient in mitochondria
C. The entire genome of a prokaryote
D. The entire set of proteins expressed by an organism at a certain time
Question 3
Which statement correctly describes genome and proteome?
A. Only the genome but not the proteome can be analysed using gel electrophoresis.
B. The genome and the proteome are the same in all tissues in an organism.
C. In cells of different tissues, the genome is the same while the proteome varies.
D. Only mutations in the proteome but not in the genome cause any variability.
Question 4
The number of protein-coding genes in the human genome is estimated to be about 20000, which is much less than the size of the proteome. What is one reason for this?
A. Exons are removed from RNA before translation.
B. There are more types of amino acids than nucleotides.
C. mRNA can be spliced after transcription.
D. Base substitutions occur during transcription.
Question 5
DNA methylation profiles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) gametes were determined. The methylated areas were divided into three groups according to the amount of methylation: high, medium and low methylation.

Methylation of DNA in sperm and egg is removed immediately after fertilization. What is the reason for this?
A. Methylation allows RNA polymerase to join the promoter.
B. It is needed to form homologous pairs of chromosomes.
C. It allows expression of genes linked to early development.
D. Transcription of promoters only occurs in methylated genes.
Question 6
What is the difference between the DNA of adult identical (monozygotic) twins?
A. Order of genes
B. Sequence of nucleotides
C. Methylation pattern
D. Ratio of complementary base pairs
Question 7
Explain how gene expression can be regulated during transcription to determine an organism’s phenotype. [7]
Question 8
DNA methylation has a critical role in gene regulation by affecting transcription. Samples were taken from two colon cancer tumors (T1 and T2) and two normal colon samples (N1 and N2). A particular gene was implicated as a possible cause of cancer. The promoter of this gene was cloned (A–J). The data show the DNA methylation patterns from these samples. The numbers (32–269) represent different markers in the promoter.

[Source: Philipp Schatz, Dimo Dietrich & Matthias Schuster. Rapid analysis of CpG methylation patterns using RNase T1 cleavage and MALDI-TOF. Nucleic Acids Research (2004) 32 (21): e167, doi:10.1093/nar/gnh165. Reproduced by permission of Oxford University Press]
a. Outline the difference in methylation pattern between tumorous and normal tissue samples. [2]
b. Suggest a way methylation may affect tumor cell genes. [1]
Question 9
Insulin is produced in β cells of the pancreas and not in other cells of the human body. Explain how differentiation of cells and regulation of gene expression allow proteins such as insulin to be produced in only certain types of body cell. [7]
Question 10
Outline how nucleosomes affect the transcription of DNA. [4]