Question 1
Methane is one atmospheric gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
What are reasons for this?
I. It absorbs long wave radiation.
II. It is converted to carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
III. It allows more heat to leave the Earth’s atmosphere.
A. II only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III only
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
What results from global warming?
A. An increase in absorption of solar radiation decreases poleward shift of temperate species.
B. Release of carbon dioxide from the deep ocean causes decreased rates of decomposition.
C. Release of methane from melting permafrost causes a decrease in absorption of solar radiation.
D. Loss of snow and ice causes an increase in absorption of solar radiation.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
The graph shows how the worldwide use of fossil fuels has increased from 1800 to 2019.
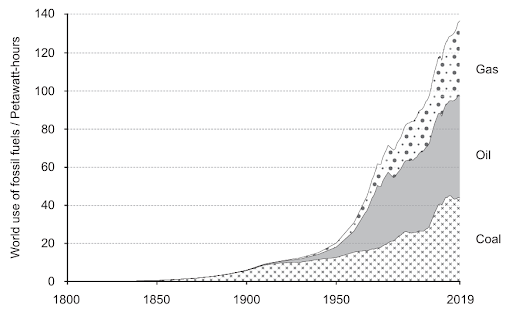
How has the increased combustion of fossil fuels contributed significantly to global warming?
A. The heat released raises the temperature of the air.
B. Combustion causes ozone depletion, which enhances the greenhouse effect.
C. Carbon dioxide produced by combustion prevents radiation from the Sun reaching Earth.
D. The products of combustion absorb long wave radiation.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
How do greenhouse gases contribute to global warming?
A. They destroy the ozone layer, allowing radiation to reach the Earth’s surface.
B. They prevent radiation from the Earth escaping into space.
C. They trap short wavelength radiation in the atmosphere.
D. They are a product of combustion, which generates heat.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
The oceans absorb much of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The combustion of fossil fuels has increased carbon dioxide ocean concentrations. What adverse effect does this have on marine life?
A. Heterotrophs consume more phytoplankton.
B. Phytoplankton have increased rates of photosynthesis.
C. Corals deposit less calcium carbonate to form skeletons.
D. Increased pH reduces enzyme activity in marine organisms.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
What material is formed when organic matter is not fully decomposed in acidic waterlogged soils?
A. Coal
B. Hydrogen
C. Oil
D. Peat
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Which expected effect of temperature increase on arctic ecosystems will increase carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
A. Greater production of plants due to warmer temperatures and changing vegetation
B. Greater decomposition of organic matter currently stored in permafrost
C. Less ice and snow will cause incoming radiation to be absorbed more readily
D. Melting ice from glaciers and icebergs will cause sea levels to rise
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
The enhanced greenhouse effect can cause a rise in atmospheric temperature.
(a) Outline two consequences of a global temperature rise on arctic ecosystems. [2]
(b) Outline one effect of a temperature rise on plants. [1]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Explain how increased carbon dioxide in the air leads to the greenhouse effect. [3]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Explain the impact of anthropogenic activity on climate change. [7]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Methane is one atmospheric gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
What are reasons for this?
I. It absorbs long wave radiation.
II. It is converted to carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
III. It allows more heat to leave the Earth’s atmosphere.
A. II only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III only
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: This option ignores statement I, which is actually the main reason methane is a greenhouse gas. Methane absorbs long-wave infrared radiation, trapping heat - this is essential to the greenhouse effect. While methane does eventually break down into `CO₂` (statement II, which is true), that process happens slowly and is secondary to its direct heat-trapping effect. Therefore, A is incorrect because it includes only one part of the correct explanation.
B. Correct: I is correct: Methane absorbs long-wave (infrared) radiation emitted from Earth’s surface, preventing heat from escaping. This is the main cause of its greenhouse effect. II is correct: Over time, methane oxidizes in the atmosphere to produce carbon dioxide (`CO₂`) and water vapor, which are also greenhouse gases, thus prolonging its warming influence. Together, these two mechanisms explain why methane contributes to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
C. Incorrect: While II is correct (conversion to `CO₂`), III is completely wrong. Statement III says methane “allows more heat to leave the atmosphere,” which is opposite to what greenhouse gases do. Greenhouse gases trap heat by absorbing and re-emitting infrared radiation - they do not let it escape. Hence, C is incorrect because it includes a false statement (III).
D. Incorrect: This includes III, which is incorrect because methane prevents heat from escaping - it does not allow more heat to leave. Although I and II are true, the inclusion of III makes this entire option wrong.
Question 2
What results from global warming?
A. An increase in absorption of solar radiation decreases poleward shift of temperate species.
B. Release of carbon dioxide from the deep ocean causes decreased rates of decomposition.
C. Release of methane from melting permafrost causes a decrease in absorption of solar radiation.
D. Loss of snow and ice causes an increase in absorption of solar radiation.
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: Global warming actually increases the poleward shift of temperate species (species move toward cooler regions). The statement says it decreases this shift, which is wrong. Also, increased absorption of solar radiation enhances, not reduces, temperature changes. So, this option contradicts actual climate patterns.
B. Incorrect: While global warming may cause release of `CO₂` from oceans, it does not decrease decomposition. In fact, warmer temperatures increase microbial activity, leading to higher decomposition rates, not lower. Additionally, most oceanic `CO₂` release is due to warming surface water reducing `CO₂`solubility - it doesn’t directly affect decomposition in this way.
C. Incorrect: Melting permafrost releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas that increases heat absorption, not decreases it. The released methane traps more longwave radiation, causing more warming. Therefore, saying it “causes a decrease in absorption of solar radiation” is completely opposite of what actually happens.
D. Correct: Snow and ice have a high albedo, meaning they reflect a large portion of sunlight back into space. When global warming causes snow and ice to melt, darker land or ocean surfaces are exposed - these have a lower albedo, so they absorb more solar radiation instead of reflecting it. This increases Earth’s heat absorption, accelerating warming even further - a positive feedback loop that enhances global warming.
Question 3
The graph shows how the worldwide use of fossil fuels has increased from 1800 to 2019.

How has the increased combustion of fossil fuels contributed significantly to global warming?
A. The heat released raises the temperature of the air.
B. Combustion causes ozone depletion, which enhances the greenhouse effect.
C. Carbon dioxide produced by combustion prevents radiation from the Sun reaching Earth.
D. The products of combustion absorb long wave radiation.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: While combustion releases heat, this local heat is very small compared to the global energy balance. It does not directly cause global warming - the main effect comes from greenhouse gases trapping radiation, not from the heat of combustion itself.
B. Correct: When fossil fuels burn, they release carbon dioxide (`CO₂`) and methane (`CH₄`) - both are greenhouse gases. These gases absorb longwave (infrared) radiation emitted from the Earth's surface. By trapping this heat in the atmosphere, they reduce heat loss to space, causing global warming. This is the mechanism of the greenhouse effect - the main cause of current climate change.
C. Incorrect: `CO₂` does not block radiation from the Sun. Solar (shortwave) radiation still reaches Earth’s surface. Instead, `CO₂` traps infrared (longwave) radiation leaving the Earth, not incoming sunlight.
D. Incorrect: Ozone depletion is caused by CFCs, not by the combustion of fossil fuels. Ozone depletion affects UV radiation, not the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is enhanced by gases like `CO₂`, `CH₄`, and `N₂O` - not by ozone loss.
Question 4
How do greenhouse gases contribute to global warming?
A. They destroy the ozone layer, allowing radiation to reach the Earth’s surface.
B. They prevent radiation from the Earth escaping into space.
C. They trap short wavelength radiation in the atmosphere.
D. They are a product of combustion, which generates heat.
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: Greenhouse gases do not destroy the ozone layer. Ozone depletion is mainly caused by CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons), not by `CO₂` or `CH₄`. The ozone layer controls UV radiation, while greenhouse gases affect infrared radiation - two different processes.
B. Correct: Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (`CO₂`), methane (`CH₄`), and water vapor (`H₂O`) allow shortwave solar radiation from the Sun to reach Earth’s surface. The Earth absorbs this energy and re-emits it as longwave infrared radiation (heat). Greenhouse gases absorb and re-radiate this longwave radiation, trapping heat in the atmosphere. This process reduces heat loss to space, keeping Earth warmer - the main mechanism of global warming.
C. Incorrect: Greenhouse gases do not trap short wavelength (solar) radiation. They are transparent to most incoming sunlight. What they trap is longwave (infrared) radiation emitted from Earth’s surface - this is what causes warming.
D. Incorrect: Although greenhouse gases are produced by combustion, the heat from combustion is not the main cause of global warming. The warming comes from radiation trapped by greenhouse gases, not from the heat of burning fuel itself.
Question 5
The oceans absorb much of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The combustion of fossil fuels has increased carbon dioxide ocean concentrations. What adverse effect does this have on marine life?
A. Heterotrophs consume more phytoplankton.
B. Phytoplankton have increased rates of photosynthesis.
C. Corals deposit less calcium carbonate to form skeletons.
D. Increased pH reduces enzyme activity in marine organisms.
Answer: C
A. Incorrect: The increase in `CO₂` does not directly cause heterotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms) to consume more phytoplankton. In fact, ocean acidification can negatively affect phytoplankton growth and food chain balance. The question asks for an adverse effect, and increased consumption by heterotrophs is not a harmful or direct consequence of `CO₂` rise.
B. Incorrect: While `CO₂` is needed for photosynthesis, high ocean `CO₂` levels do not necessarily increase phytoplankton photosynthesis, because acidification and lower pH can damage enzymes and cellular processes. Moreover, nutrient limitations often restrict phytoplankton growth, not `CO₂` levels. So, this statement does not describe the main harmful effect of higher `CO₂`.
C. Correct: When carbon dioxide (`CO₂`) dissolves in ocean water, it forms carbonic acid (`H₂CO₃`), which lowers the pH of seawater - a process known as ocean acidification. The increased acidity reduces the availability of carbonate ions (`CO₃²⁻`), which are essential for marine organisms like corals, mollusks, and some plankton to produce calcium carbonate (`CaCO₃`) for their shells and skeletons. As a result, corals cannot efficiently deposit calcium carbonate, leading to weaker skeletons, slower reef growth, and greater vulnerability to erosion and bleaching.
D. Incorrect: Ocean acidification decreases pH, not increases it. The question mentions an adverse effect - the problem is a drop in pH (more acidic water), not an increase. Lower pH can indeed reduce enzyme activity in marine organisms, but the statement is incorrect because it says “increased pH”.
Question 6
What material is formed when organic matter is not fully decomposed in acidic waterlogged soils?
A. Coal
B. Hydrogen
C. Oil
D. Peat
Answer: D
A. Incorrect: Coal forms from peat after millions of years of heat and pressure deep underground. It does not form directly in soils; it’s a later stage in fossil fuel formation.
B. Incorrect: Hydrogen is a gas, not an organic deposit. It is not produced by partial decomposition of organic matter in soils.
C. Incorrect: Oil forms from marine organisms (like plankton) buried under sediment in seas or oceans, not from plants in waterlogged soils. So, oil and peat form in different environments.
D. Correct: In acidic, waterlogged soils (like swamps or bogs), oxygen levels are very low, creating anaerobic conditions. Under these conditions, microorganisms cannot fully decompose dead organic matter (such as plant material). The partially decomposed organic matter accumulates over time, forming a dark, spongy material called peat. Peat is the first stage in the formation of fossil fuels like coal - over millions of years, with heat and pressure, peat can eventually turn into lignite and coal. Therefore, peat is the material formed when decomposition is incomplete in acidic, waterlogged environments.
Question 7
Which expected effect of temperature increase on arctic ecosystems will increase carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
A. Greater production of plants due to warmer temperatures and changing vegetation
B. Greater decomposition of organic matter currently stored in permafrost
C. Less ice and snow will cause incoming radiation to be absorbed more readily
D. Melting ice from glaciers and icebergs will cause sea levels to rise
Answer: B
A. Incorrect: Plant growth actually removes `CO₂` from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. This would decrease, not increase, atmospheric `CO₂`.
B. Correct: Permafrost is permanently frozen soil that contains large amounts of organic matter (dead plants and animals) that have not decomposed because of the cold temperatures. When global temperatures rise, permafrost melts, allowing microbes to decompose this stored organic matter. Decomposition releases carbon dioxide (`CO₂`) and sometimes methane (`CH₄`) into the atmosphere. These gases are greenhouse gases, so this process increases the concentration of `CO₂`, enhancing the greenhouse effect and global warming. Therefore, greater decomposition of organic matter in permafrost directly increases `CO₂` in the atmosphere.
C. Incorrect: This is the albedo effect, which increases heat absorption and causes further warming, but it does not directly release`CO₂` into the atmosphere.
D. Incorrect: This affects sea level, not atmospheric`CO₂`. Ice melting doesn’t release carbon dioxide because ice does not contain organic carbon.
Question 8
The enhanced greenhouse effect can cause a rise in atmospheric temperature.
(a) Outline two consequences of a global temperature rise on arctic ecosystems. [2]
(b) Outline one effect of a temperature rise on plants. [1]
(a) Any two of the following:
a. increased rates of decomposition (of detritus in permafrost);
b. expansion of the range of habitats available to temperate species;
c. loss of ice habitat;
d. changes in distribution of prey species affecting higher trophic levels;
e. increased success of pest species/pathogens;
f. rise in sea levels;
Sample answer:
Increased rates of decomposition of detritus in thawing permafrost [1];
Expansion of habitats suitable for temperate species [1];
Loss of ice habitats for organisms such as seals and polar bears [1];
Changes in prey distribution affecting predators [1].
(b) Any one of the following:
a. rate of photosynthesis increases as temperature increases;
b. rate of transpiration increases as temperature increases;
c. shift in plant distribution / OWTTE;
Sample answer:
As temperature increases, the rate of photosynthesis rises, leading to faster production of sugars and growth [1];
Transpiration rates also increase, which can lead to wilting or water stress in dry conditions [1].
Question 9
Explain how increased carbon dioxide in the air leads to the greenhouse effect. [3]
Any three of the following:
a. short wave radiation from sun passes through atmosphere / is not absorbed by `CO_2`;
b. infrared/long wave (radiation) / heat emitted from/released from (surface of) Earth;
c. `CO2` in the atmosphere absorbs infrared/long wave (radiation)/heat / cannot pass through the greenhouse gases;
d. this results in warm/increased temperatures on Earth/global warming;
Sample answer:
Increased carbon dioxide in the air leads to the greenhouse effect because short wave radiation from the Sun passes through the atmosphere and reaches the Earth’s surface without being absorbed by carbon dioxide [1]. The Earth then emits this absorbed energy as long wave infrared radiation (heat) back toward space [1]. However, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere absorbs some of this infrared radiation, preventing it from escaping [1]. As a result, heat becomes trapped within the atmosphere, leading to an increase in global temperatures and contributing to global warming [1].
Question 10
Explain the impact of anthropogenic activity on climate change. [7]
Any seven of the following:
a. greenhouse effect describes that greenhouse gases trap long-wave radiation from the Earth’s surface and absorbs it keeping the Earth warm OR increase in greenhouse gases trapped in atmosphere increases Earth’s temperature;
b. burning of fossil fuels/peat/coal/natural gas by humans has released more `CO_2` into the atmosphere causing temperature rise on Earth;
c. raising livestock for feed has added methane/greenhouse gas to the atmosphere causing more heat to be trapped on Earth;
d. industrial processes / fertilizer production has increased the concentration of nitrous oxides/greenhouse gases in the atmosphere;
e. deforestation has increased the amount of `CO_2` in the atmosphere/reduced an important sink for `CO_2`;
f. increased temperatures have caused melting of land ice leading to changes to polar habitats/decreasing species ability to survive OR melting of ice/snow causes reduction in albedo, so there is more insolation absorbed at Earth’s surface;
g. warmer surface water prevents upwelling of nutrients/decreases ocean productivity;
h. coral reef habitat destruction due to changes in water pH / temperature;
i. warmer temperatures/decreased snowfall has led to droughts and loss of life/habitats;
j. rates of decomposition of peat/organic matter increases greenhouse gases;
k. ocean/sea level rise from melting ice/thermal expansion of oceans has impacted coastal regions/loss of land;
l. changing weather patterns due to global warming has caused loss of life and infrastructure;
m. poleward migrations/migrations to more suitable places due to climate changes at lower latitudes;
Sample answer:
Human activities have significantly contributed to climate change by increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which enhances the greenhouse effect and raises global temperatures [1]. The burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas releases large amounts of carbon dioxide, while livestock farming produces methane, both of which trap heat in the atmosphere [1]. Industrial processes and the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers release nitrous oxides, further intensifying warming [1]. Deforestation reduces the number of trees available to absorb carbon dioxide, leading to higher atmospheric `CO₂` levels [1]. As temperatures rise, land ice melts, lowering the Earth’s albedo and causing more heat absorption [1]. The warming of oceans also leads to coral bleaching and habitat loss [1], while melting ice and thermal expansion cause sea levels to rise [1], threatening coastal ecosystems and human settlements.
Question 1
Methane is one atmospheric gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
What are reasons for this?
I. It absorbs long wave radiation.
II. It is converted to carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
III. It allows more heat to leave the Earth’s atmosphere.
A. II only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III only
Question 2
What results from global warming?
A. An increase in absorption of solar radiation decreases poleward shift of temperate species.
B. Release of carbon dioxide from the deep ocean causes decreased rates of decomposition.
C. Release of methane from melting permafrost causes a decrease in absorption of solar radiation.
D. Loss of snow and ice causes an increase in absorption of solar radiation.
Question 3
The graph shows how the worldwide use of fossil fuels has increased from 1800 to 2019.

How has the increased combustion of fossil fuels contributed significantly to global warming?
A. The heat released raises the temperature of the air.
B. Combustion causes ozone depletion, which enhances the greenhouse effect.
C. Carbon dioxide produced by combustion prevents radiation from the Sun reaching Earth.
D. The products of combustion absorb long wave radiation.
Question 4
How do greenhouse gases contribute to global warming?
A. They destroy the ozone layer, allowing radiation to reach the Earth’s surface.
B. They prevent radiation from the Earth escaping into space.
C. They trap short wavelength radiation in the atmosphere.
D. They are a product of combustion, which generates heat.
Question 5
The oceans absorb much of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The combustion of fossil fuels has increased carbon dioxide ocean concentrations. What adverse effect does this have on marine life?
A. Heterotrophs consume more phytoplankton.
B. Phytoplankton have increased rates of photosynthesis.
C. Corals deposit less calcium carbonate to form skeletons.
D. Increased pH reduces enzyme activity in marine organisms.
Question 6
What material is formed when organic matter is not fully decomposed in acidic waterlogged soils?
A. Coal
B. Hydrogen
C. Oil
D. Peat
Question 7
Which expected effect of temperature increase on arctic ecosystems will increase carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
A. Greater production of plants due to warmer temperatures and changing vegetation
B. Greater decomposition of organic matter currently stored in permafrost
C. Less ice and snow will cause incoming radiation to be absorbed more readily
D. Melting ice from glaciers and icebergs will cause sea levels to rise
Question 8
The enhanced greenhouse effect can cause a rise in atmospheric temperature.
(a) Outline two consequences of a global temperature rise on arctic ecosystems. [2]
(b) Outline one effect of a temperature rise on plants. [1]
Question 9
Explain how increased carbon dioxide in the air leads to the greenhouse effect. [3]
Question 10
Explain the impact of anthropogenic activity on climate change. [7]