Question 1
How many sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are there in CH₃CH₂CCCH₂COOH?
A. 13σ and 5π
B. 15σ and 2π
C. 15σ and 3π
D. 15σ only
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
What is the shape and the bond angle of the molecule BF3?
| Shape | Bond angle | |
| A. | Trigonal pyramidal | 109.5° |
| B. | Trigonal planar | 109.5° |
| C. | Trigonal pyramidal | 120° |
| D. | Trigonal planar | 120° |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
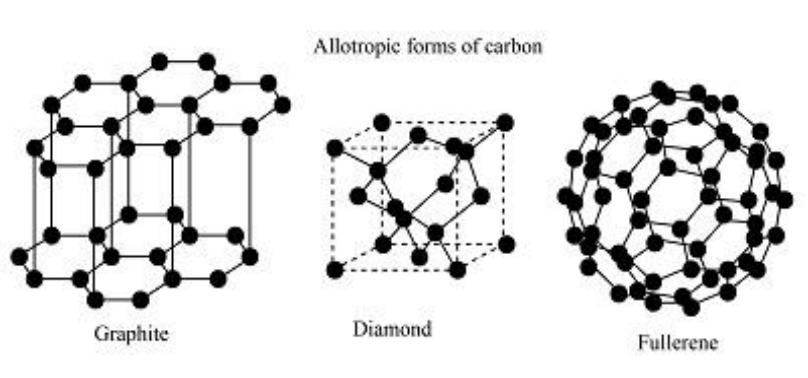
Diamond, C60 fullerene and graphite are allotropes of carbon.
Which statements are correct about these allotropes?
I. In diamond each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement.
II. In C60 fullerene each carbon is held in a trigonal arrangement.
III. In graphite each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which group of ions and molecules has delocalized electrons in all the species?
A. CH3COCH3, C2H5COO− and O3
B. NO3−, NO2− and CO2
C. C6H6, CO32− and graphite
D. C6H6, CO32− and C2H2
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
What is the correct number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in prop-2-enenitrile, CH₂CHCN?
| σ bonds | π bonds | |
| A. | 7 | 2 |
| B. | 4 | 5 |
| C. | 6 | 3 |
| D. | 3 | 3 |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
Which allotropes of carbon show sp2 hybridization?
I. Diamond
II. Graphite
III. C60 fullerene
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Which substance does not contain delocalized electrons?
A. Graphene.
B. Carbon-60, C₆₀.
C. Methylbenzene, C₆H₅CH₃.
D. Ethene, C₂H₄.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which species have resonance structures?
I. The azide ion, N₃⁻
II. The carbon dioxide molecule, CO₂
III. The methylbenzene molecule, C₆H₅CH₃
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Which of the following information about the specified central atom is correct?
| Atom | Number of electron domains around one central atom | Molecular geometry | Hybridization | |
| A. | C in C₂FCl | 2 | linear | sp |
| B. | C in C₂H₆ | 4 | square planar | sp³ |
| C. | P in PH₃ | 3 | trigonal pyramidal | sp³ |
| D. | O in H₂O | 4 | Bent / V-shaped | sp² |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
Which diagram shows the correct shape and relative energies of a p orbital and a sp³ hybrid orbital of a nitrogen atom?
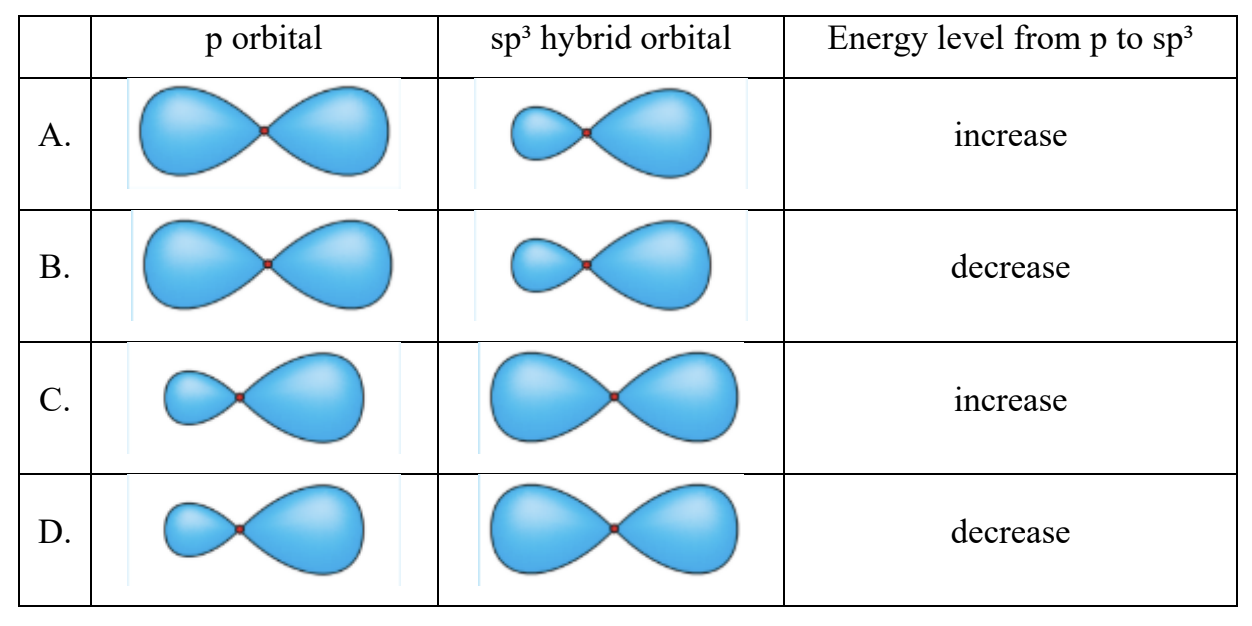
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
The diagrams below show s and p orbitals in different positions. Which combinations can form a σ-bond?
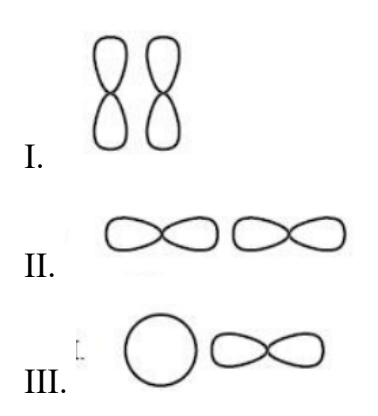
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
Which species contain delocalized electrons?
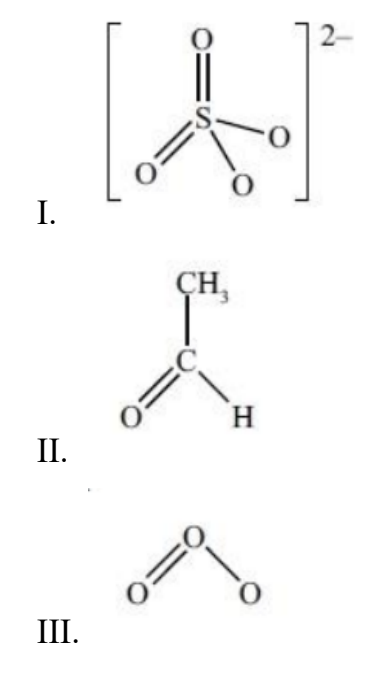
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
What is the hybridization of atoms X, Y and Z in epinephrine?
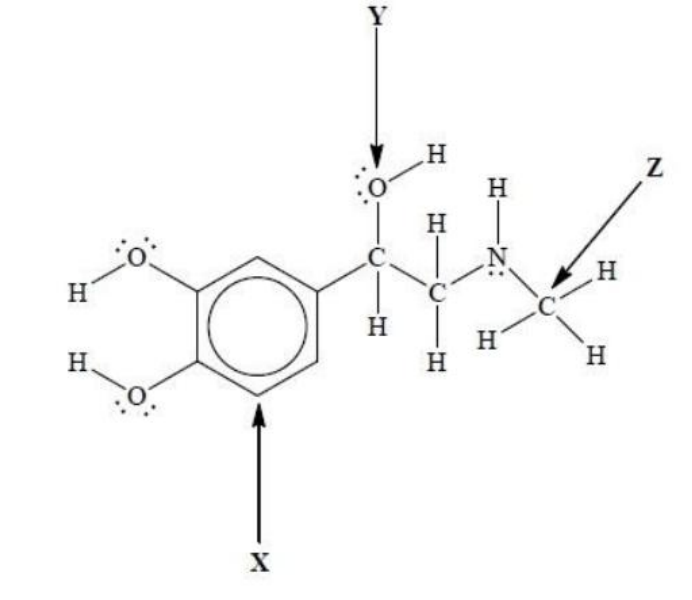
|
| X | Y | Z |
| A. | sp² | sp³ | sp³ |
| B. | sp² | sp | sp³ |
| C. | sp³ | sp² | sp² |
| D. | sp³ | sp³ | sp³ |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
Which diagram represents the bonding in SiO2?
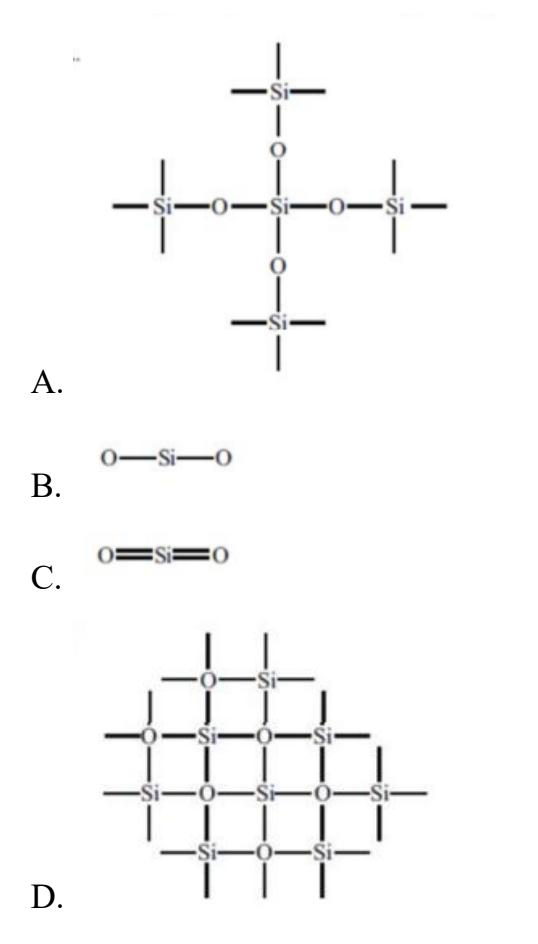
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 15
How many sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are there in CH₃CH₂CCCH₂COOH?
A. 13σ and 5π
B. 15σ and 2π
C. 15σ and 3π
D. 15σ only
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 16
What is the formal charge of boron in the borohydride ion, BH₄⁻?
A. –1
B. 0
C. +1
D. –4
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 17
Which one of the following contains the largest number of lone pairs on the central atom?
A. ClO₃⁻
B. XeF₄
C. I₃⁻
D. SF₄
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 18
Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon. State two empirical pieces of evidence that support a π electron delocalized structure of benzene.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 19
Two possible Lewis structures of the chlorate(VI) ion, ClO₃⁻ ion are shown below.
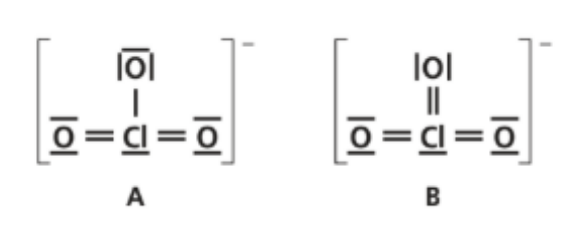
a. Outline the principles of the valence shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory.
b. Using VSEPR theory, state the electron domain geometry, molecular shape and the O–Cl–O bond angle in structure II.
c. Using formal charge, state and explain which is likely to be the Lewis structure of the ClO₃⁻ ion.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 20
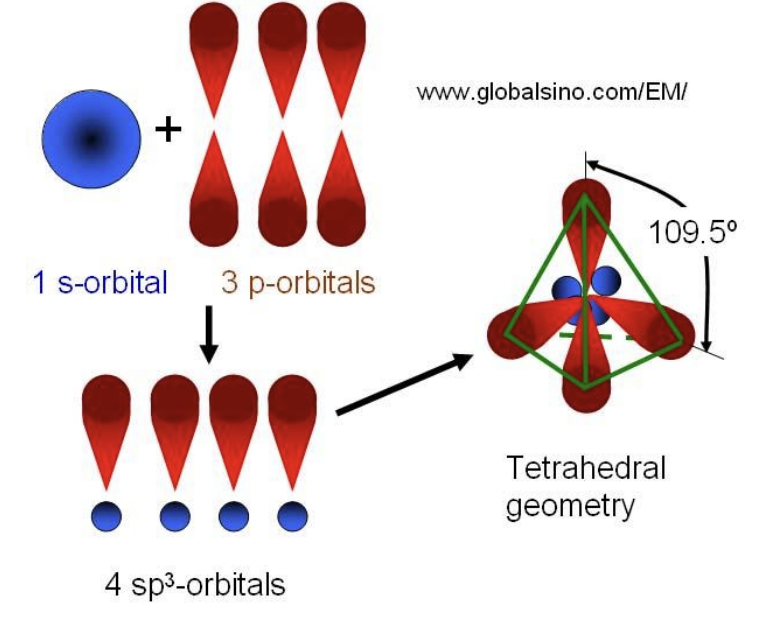
a. Draw a labelled diagram of sp³ orbitals.
b. Describe the bonding of sp³ carbon in terms of orbital overlap in propanone, (CH₃)₂C=O.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 21
Which molecule is trigonal bipyramidal in shape?
A. PCl₃
B. SiCl₄
C. PCl₅
D. SF₆
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 22
Ozone, O₃, in the upper atmosphere prevents harmful UV radiation reaching the surface of the Earth.
a. Draw the Lewis structure for ozone.
b. State the shape of the ozone molecule and estimate the bond angle.
c. State the hybridization of the central oxygen atom.
d. In terms of σ and π bonds, describe the two oxygen–oxygen bonds in the Lewis structure.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 23
Which of the following molecules does not have a π bond?
A. CO₂
B. CO
C. H₂O₂
D. SO₃
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 24
What is the hybridization state of carbon in ethyne (C₂H₂), graphite and diamond?
A. sp, sp², sp³
B. sp, sp³, sp²
C. sp³, sp², sp
D. sp, sp³, sp³
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 25
What is the number of σ and π bonds in (NC)₂C=C(CN)₂?
A. 5, 4
B. 6, 6
C. 9, 4
D. 9, 9
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 26
Boron nitride is found to exist in two possible forms, hexagonal boron nitride and cubic boron nitride as shown.
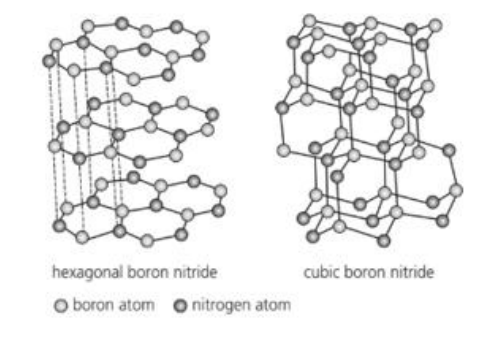
Carbon can also be found in two different forms (allotropes).
a. Name the allotropes of carbon which have a similar structure to hexagonal boron nitride and cubic boron nitride.
b. Based on the structures shown, explain the difference in one physical property of hexagonal and cubic boron nitride other than electrical conductivity.
c. Explain the difference in electrical conductivity between graphene and carbon-60.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 27
Which one of the following is correct for carbon suboxide, O=C=C=C=O?
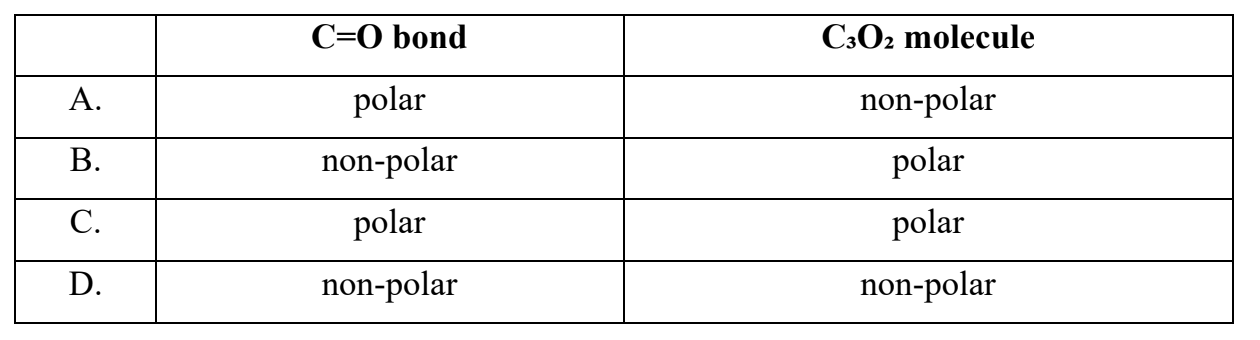
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 28
What are the approximate bond angles and structure of crystalline SiO2?
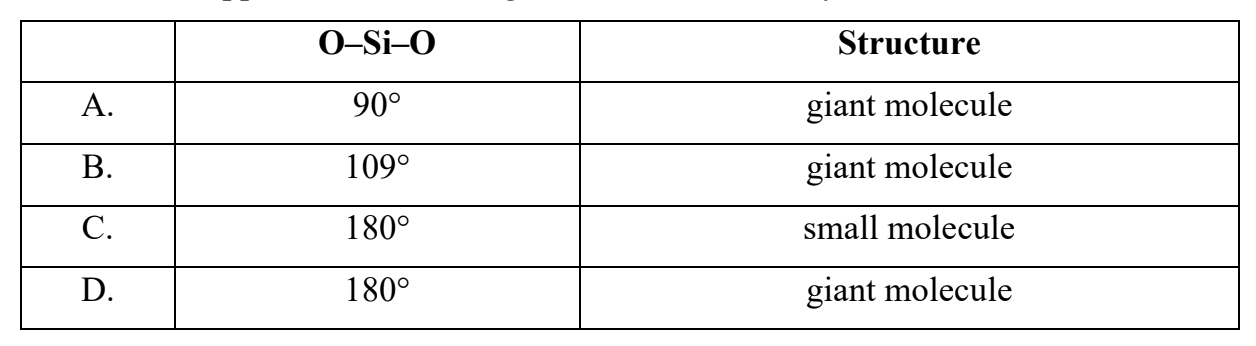
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 29
What describes the relationship between diamond, graphite and C60 fullerene?
A. Allotropes
B. Isomers
C. Isotopes
D. Polymers
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 30
Which combination describes the sulfate(IV) ion, SO32− (also known as sulfite ion)?
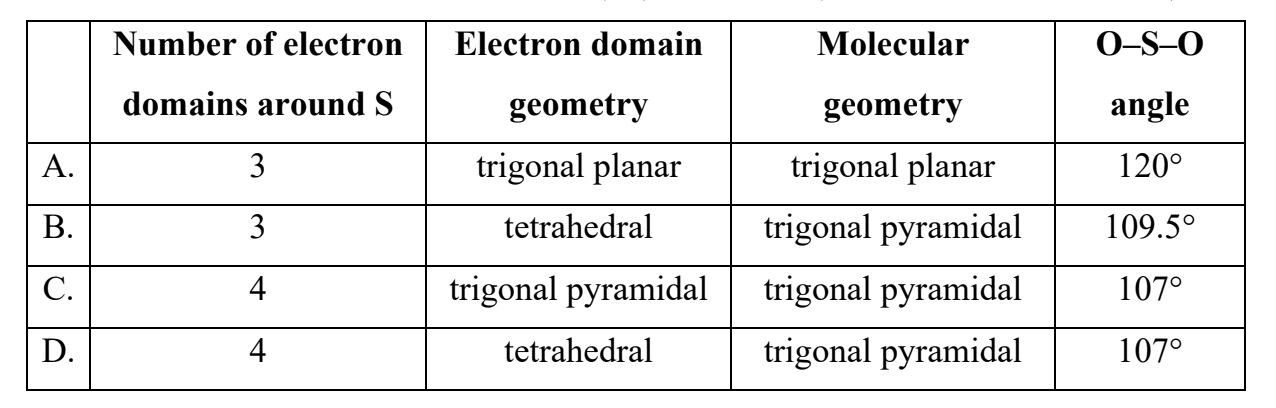
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 31
Which one of the following pairs of molecules has identical shapes for both species?
A. CCl4, SF4
B. XeF2, CO2
C. BCl3, PF3
D. PF5, IF5
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 32
Which molecules react to form a dative covalent (coordinate) bond?
A. CH4 and NH3
B. C2H2 and Cl2
C. NH3 and HF
D. Cl2 and HF
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 33
Which species contain a dative covalent (coordination or coordinate) bond?
I. Carbon monoxide, CO
II. Ammonia, NH3
III. Oxonium ion, H3O+
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 34
Which statement about intermolecular forces is correct?
A. The intermolecular force between H2 molecules is hydrogen bonding, because H2 has temporary dipoles.
B. The intermolecular forces between PH3 molecules are greater than the intermolecular forces between NH3 molecules, because they have a greater mass.
C. The intermolecular force between H2 molecules is hydrogen bonding, because H2 has permanent dipoles.
D. The intermolecular forces between Br2 molecules are van der Waals’, because Br2 has temporary dipoles.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 35
What describes the structure of silicon and silicon dioxide?
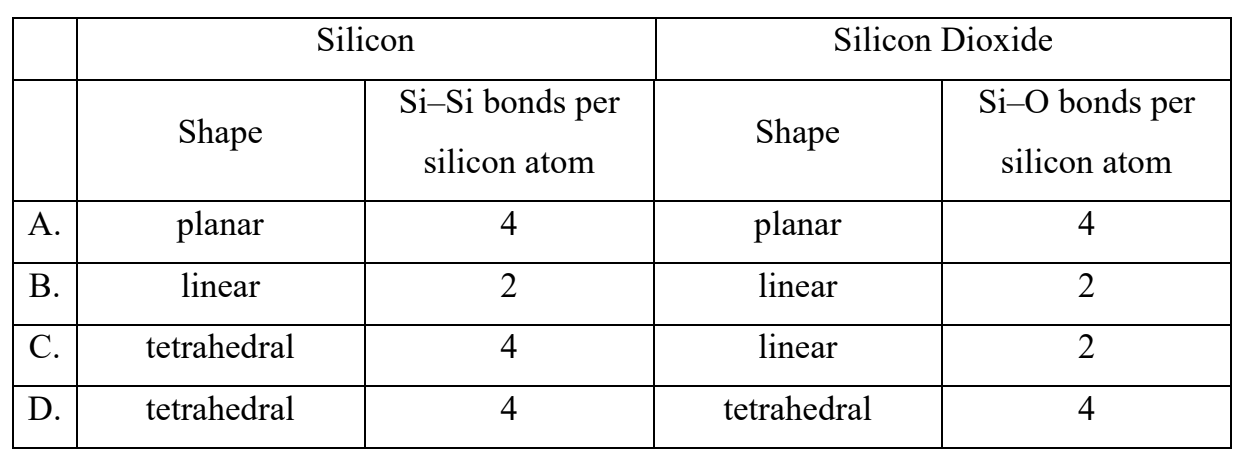
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 36
In which one of the following pairs does the first molecule have a larger dipole than the second?
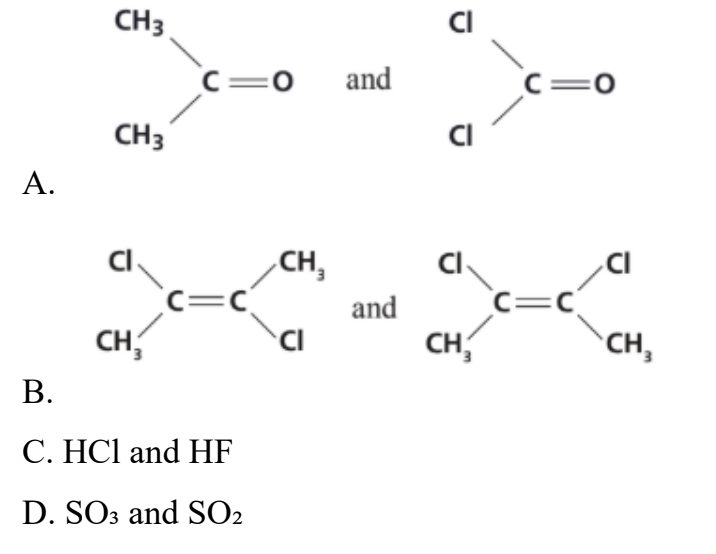
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 37
The structural formula of ethanediamide is shown below.
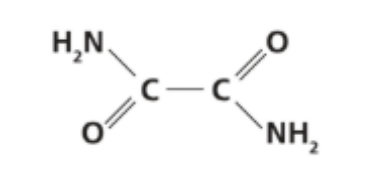
a. Predict the electron domain and molecular geometries at the nitrogen and carbon atoms, applying VSEPR theory.
b. State the hybridization of the carbon atoms.
c. State the number of sigma bonds, pi bonds and lone pairs in a molecule of ethanediamide.
d. Suggest why ethanediamide is a solid and ammonia is a gas under standard conditions.
e. Explain why ethanediamide is relatively soluble in water.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 38
Which molecule is non-polar?
A. H2CO
B. SO3
C. NFCl2
D. CHCl3
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 39
Silanes (see table below) are the silicon analogues of alkanes and follow a similar general formula.
They only have Si–H and Si–Si single bonds. Silanes can be used to prepare pure silicon.
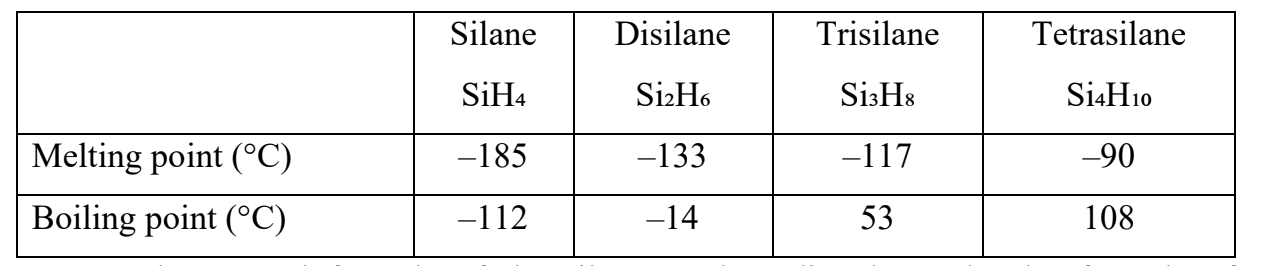
a. State the general formula of the silanes and predict the molecular formula of hexasilane.
b. State the general trend in the boiling and melting points of the silanes across the table from left to right.
c. State the name of one silane from the table which is a liquid under standard conditions.
d. Explain this general trend in boiling points for the silanes in terms of the type of structure and intermolecular forces.
e. Write an equation to show the combustion of silane.
f. State the molecular shape of silane, SiH4, and state the bond angle.
g. Explain why the Si–H bond is longer than the C–H bond.
h. Using the data booklet, compare the polarity of the bonds in a molecule of methane with those in silane and explain the difference.
i. Describe the structure of silicon and state one physical property of silicon.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 40
Explain why the solubility of trichloromethane (CHCl3) in water is ten times greater than that of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in water at the same temperature.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 41
Which of the following describes an observation that cannot be explained by hydrogen bonding?
A. Ice has a lower density than water at 0°C.
B. Hydrazine (N2H4) is more soluble in water than in ammonia.
C. CH3F has a lower boiling point than methanol CH3OH.
D. The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing number of carbon atoms.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 42
Which of the following compounds are arranged in decreasing order of their solubility in water?
A. CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2Cl
B. CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2Cl, CH3CH2CH2OH
C. CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2Cl
D. CH3CH2CH2Cl, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CO2Na
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 43
What type of bonding or intermolecular force is not present in NH3·BF3 (s)?
A. Hydrogen bonds
B. Coordination bonds
C. London (dispersion) forces
D. Ionic bonds
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 44
Which forces are present between molecules of carbon dioxide in the solid state?
A. Permanent dipole–permanent dipole interactions.
B. Temporary dipole–induced dipole interactions (London/dispersion forces).
C. Covalent bonding.
D. Ionic bonding.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 45
Which substance has a giant covalent structure?
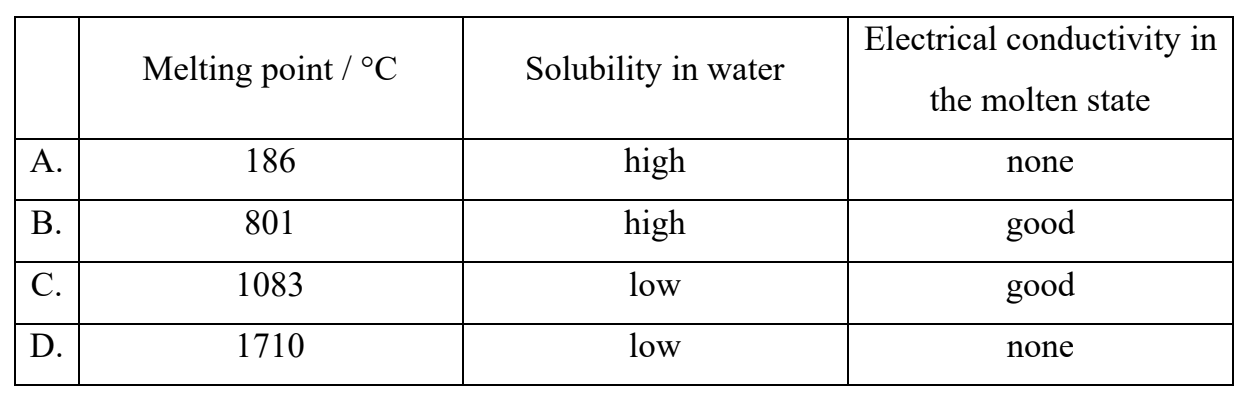
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 46
Which of the following are van der Waals’ forces?
I. Dipole–dipole forces
II. Hydrogen bonds
III. London (dispersion) forces
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 47
Which pair of molecules has the same bond angles?
A. PCl3 and BCl3
B. SO2 and CO2
C. H2O and NH3
D. CCl4 and SiH4
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 48
Based on electronegativity values, which bond is the most polar?
A. B–C
B. C–O
C. O–F
D. N–O
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 49
a. Outline the basic principle of all chromatographic techniques.
b. Paper chromatograms formed by two orange food colourings, A and B, are shown below.
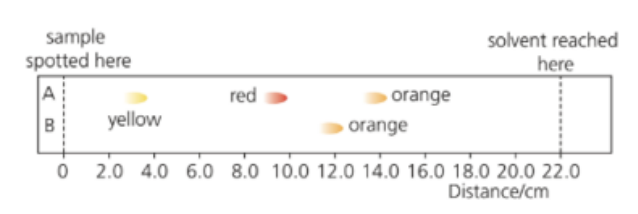
i. State which of these food colourings is a mixture of dyes.
ii. State which of these food colourings is a pure substance.
iii. Explain whether the same dye is present in each of the food colourings.
The RF value is the ratio of the distance moved by the solute/distance moved by solvent.
iv. Calculate the RF value of the substance responsible for the red spot in the chromatogram of A.
c. The results of a thin-layer chromatography separation on silica gel are shown below.
| Compound | Distance travelled / cm |
| Compound 1 | 1.6 |
| Compound 2 | 9.2 |
| Compound 3 | 12.6 |
i. Calculate the RF values of the compounds 1 and 2 and comment on their values.
ii. State one advantage of thin-layer chromatography over paper chromatography.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
How many sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are there in CH₃CH₂CCCH₂COOH?
A. 13σ and 5π
B. 15σ and 2π
C. 15σ and 3π
D. 15σ only
Answer: C. 15σ and 3π
C–C bonds:
• CH₃–CH₂ → 1 σ
• CH₂–C → 1 σ
• C≡C → 1 σ + 2 π
• C–CH₂ → 1 σ
• CH₂–C (of COOH) → 1 σ
⇒ Total C–C σ bonds = 5 σ, C–C π bonds = 2 π (from triple bond) C–H bonds:
• CH₃ → 3 σ
• CH₂ (next to CH₃) → 2 σ
• CH₂ (next to C≡C) → 2 σ
⇒ Total C–H σ bonds = 7 σ
C=O and O–H bonds (in COOH):
• C=O → 1 σ + 1 π
• C–O → 1 σ
• O–H → 1 σ
⇒ C–O and O–H total = 3 σ + 1 π
Add all together
| Type | Number |
| σ bonds | 5 (C–C) + 7 (C–H) + 3 (C–O, O–H) = 15 σ |
| π bonds | 2 (from C≡C) + 1 (from C=O) = 3 π |
Question 2
What is the shape and the bond angle of the molecule BF3?
| Shape | Bond angle | |
| A. | Trigonal pyramidal | 109.5° |
| B. | Trigonal planar | 109.5° |
| C. | Trigonal pyramidal | 120° |
| D. | Trigonal planar | 120° |
Answer: D. Shape: Trigonal planar; Bond angle: 120°
• Molecule: BF3 (boron trifluoride)
• Central atom: Boron (B)
• Valence electrons on B: 3
• Bond pairs: 3
• Lone pairs: 0
→ Therefore, according to VSEPR theory, three bonding pairs around boron arrange themselves as far apart as possible → trigonal planar geometry.
→ The ideal bond angle for trigonal planar = 120°.
Question 3
Diamond, C60 fullerene and graphite are allotropes of carbon.
Which statements are correct about these allotropes?
I. In diamond each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement.
II. In C60 fullerene each carbon is held in a trigonal arrangement.
III. In graphite each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: A. I and II only.
| Allotrope | Hybridization | Arrangement around each carbon | Type of bonding |
| Diamond | sp³ | Tetrahedral | Each carbon forms 4 single bonds → 3D giant covalent lattice |
| C₆₀ fullerene | sp² | Trigonal planar | Each carbon bonded to 3 others forming hexagons and pentagons |
| Graphite | sp² | Trigonal planar, not tetrahedral | Each carbon bonded to 3 others in flat layers |
Check each statement:
I. In diamond each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement. → Correct II.
II. In C₆₀ fullerene each carbon is held in a trigonal arrangement. → Correct III.
III. In graphite each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement. → Incorrect (it’s trigonal planar)
Question 4
Which group of ions and molecules has delocalized electrons in all the species?
A. CH3COCH3, C2H5COO− and O3
B. NO3−, NO2− and CO2
C. C6H6, CO32− and graphite
D. C6H6, CO32− and C2H2
Answer: C. C₆H₆, CO₃²⁻ and graphite
Delocalized electrons are electrons that are not confined to a single bond or atom, but are spread over several atoms through resonance or π-bond systems.
| Option | Species | Delocalization present? | Explanation |
| A. Incorrect: Not all have delocalization. | CH₃COCH₃ | No | No delocalization — localized C=O bond. |
| C₂H₅COO⁻ | Yes | Delocalized over two oxygens. | |
| O₃ | Yes | Delocalized π-electrons (resonance). | |
| B. Incorrect: Not all have delocalization. | NO₃⁻ | Yes | Resonance. |
| NO₂⁻ | Yes | Resonance. | |
| CO₂ | No | No delocalization — two localized C=O bonds. | |
| C. Correct: All have delocalized electrons. | C₆H₆ | Yes | Delocalized π-electrons in ring. |
| CO₃²⁻ | Yes | Resonance between three C=O bonds. | |
| Graphite | Yes | Delocalized π-electrons across layers. | |
| D. Incorrect: Not all have delocalization. | C₆H₆ | Yes | Delocalized π-electrons in ring. |
| CO₃²⁻ | Yes | Resonance between three C=O bonds. | |
| C₂H₂ | No | Localized triple bond (no delocalization). |
Question 5
What is the correct number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in prop-2-enenitrile, CH₂CHCN?
| σ bonds | π bonds | |
| A. | 7 | 2 |
| B. | 4 | 5 |
| C. | 6 | 3 |
| D. | 3 | 3 |
Answer: C. 6 σ and 3 π bonds.
1. Identify all bonds: Between CH₂=CH–C≡N:
• C₁=C₂ → 1 σ + 1 π
• C₂–C₃ → 1 σ
• C₃≡N → 1 σ + 2 π
• Each C–H → 1 σ
2. Count σ bonds:
| Type | Number | σ bonds |
| C–H | 2 (in CH₂) + 1 (in CH) = 3 | 3 σ |
| C=C | 1 | 1 σ |
| C–C | 1 | 1 σ |
| C≡N | 1 | 1 σ |
| Total σ bonds | 3 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 6 σ |
3. Count π bonds:
| Type | π bonds |
| C=C | 1 π |
| C≡N | 2 π |
| Total | 3 π |
Question 6
Which allotropes of carbon show sp2 hybridization?
I. Diamond
II. Graphite
III. C60 fullerene
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: C. II and III only.
| Allotrope | Type of hybridization | Structure |
| Diamond | sp³ | Each carbon forms 4 σ bonds (tetrahedral network). |
| Graphite | sp² | Each carbon forms 3 σ bonds in a planar hexagonal layer; the remaining p orbital overlaps to form delocalized π bonds. |
| C₆₀ fullerene | sp² (with slight distortion) | Each carbon forms 3 σ bonds to neighboring atoms in a curved surface (spherical structure). |
Question 7
Which substance does not contain delocalized electrons?
A. Graphene.
B. Carbon-60, C₆₀.
C. Methylbenzene, C₆H₅CH₃.
D. Ethene, C₂H₄.
Answer: D. Ethene, C₂H₄.
A. Incorrect:
• Structure: Each carbon atom in graphene is sp² hybridized, forming three σ bonds in a flat hexagonal layer.
• The remaining unhybridized p orbital on each carbon atom overlaps sideways with its neighbors.
B. Incorrect:
• Structure: C₆₀ has 60 carbon atoms forming a spherical cage of pentagons and hexagons (like a soccer ball). Each carbon is sp² hybridized, forming 3 σ bonds.
• The remaining p orbital electrons participate in π delocalization across the surface of the sphere.
C. Incorrect:
• Structure: The benzene ring (C₆H₆) part of methylbenzene is aromatic.
• In benzene, the six p orbitals on adjacent carbon atoms overlap sideways, forming a cyclic delocalized π system above and below the ring. The –CH₃ group (methyl) does not affect this delocalization.
D. Correct:
• Structure: Ethene has a double bond (C=C) made of one σ and one π bond.
• The π bond is formed by sideways overlap of two localized p orbitals — only between the two carbon atoms.
Question 8
Which species have resonance structures?
I. The azide ion, N₃⁻
II. The carbon dioxide molecule, CO₂
III. The methylbenzene molecule, C₆H₅CH₃
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: B. I and III only.
I. N₃⁻ has resonance.
• The azide ion has two equivalent resonance structures: ⁻N=N⁺=N ↔ N≡N⁺–N⁻
• The negative charge is delocalized over the terminal nitrogen atoms.
II. CO₂ does not have resonance. Although CO₂ can be drawn with different formal charge distributions (e.g. O=C=O or ⁻O–C≡O⁺), these are not resonance structures — they are different forms with distinct charge localizations, not equivalent contributors.
III. C₆H₅CH₃, methylbenzene:
• The benzene ring has delocalized π electrons shared among six carbon atoms. • The methyl group doesn’t destroy the aromatic delocalization.
Question 9
Which of the following information about the specified central atom is correct?
| Atom | Number of electron domains around one central atom | Molecular geometry | Hybridization | |
| A. | C in C₂FCl | 2 | linear | sp |
| B. | C in C₂H₆ | 4 | square planar | sp³ |
| C. | P in PH₃ | 3 | trigonal pyramidal | sp³ |
| D. | O in H₂O | 4 | Bent / V-shaped | sp² |
Answer: A
A. Correct:
C in C₂FCl is a carbon with one triple bond, the carbon has two electron domains → linear → sp hybridization
B. Incorrect:
Each carbon in ethane (C₂H₆) has four σ bonds (3 to H and 1 to C). → 4 electron domains, tetrahedral geometry, sp³ hybridization
C. Incorrect:
In PH₃, the phosphorus atom has 3 bonding pairs (to H) and 1 lone pair → 4 electron domains.
D. Incorrect:
• In H₂O, oxygen has 2 bonding pairs + 2 lone pairs = 4 electron domains (True)
• The molecular geometry is bent / V-shaped (True)
• But the hybridization is sp³, not sp².
Question 10
Which diagram shows the correct shape and relative energies of a p orbital and a sp³ hybrid orbital of a nitrogen atom?

Answer: B
A. Incorrect: sp³ orbitals have lower energy than p orbitals
B. Correct: Matches both the shape and energy relationship
C. Incorrect:
Both shape and energy are wrong:
• p orbital → symmetric dumbbell shape
• sp³ hybrid → asymmetric (one big, one small lobe)
• sp³ has lower energy than p (energy decreases)
D. Incorrect: Wrong p and sp³ shape
Question 11
The diagrams below show s and p orbitals in different positions. Which combinations can form a σ-bond?

A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: D. I, II and III.
| Option | Combos Included | Explanation |
| A. Incorrect | I and II only | I and II are correct, but III is also capable of forming a σ bond (s–p overlap) |
| B. Incorrect | I and III only | II also forms σ bonds (p–p overlap), so incomplete |
| C. Incorrect | II and III only | I also forms σ bonds (end-on p–p overlap) |
| D. Correct | I, II and III | All three combinations show end-to-end overlap → all form σ bonds |
Question 12
Which species contain delocalized electrons?

A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: B
I: Sulfate ion, SO4²⁻
• Sulfate has four oxygen atoms bonded to sulfur → One double bond and three single bonds in any resonance form.
• The π electrons are delocalized over all four S–O bonds.
II: Ethanal (CH₃CHO)
• The C=O bond is a localized double bond (one σ and one π bond).
• There is no conjugation or adjacent π system to delocalize electrons — the CH₃ group and H atom have only σ bonds.
III: Ozone (O₃)
• Structure: O=O–O ↔ O–O=O
• Two resonance forms can be drawn.
• The π electrons are delocalized across the three oxygen atoms.
Question 13
What is the hybridization of atoms X, Y and Z in epinephrine?

|
| X | Y | Z |
| A. | sp² | sp³ | sp³ |
| B. | sp² | sp | sp³ |
| C. | sp³ | sp² | sp² |
| D. | sp³ | sp³ | sp³ |
Answer: A
Atom X
• X is a carbon atom in the aromatic ring (benzene).
• In benzene, each carbon forms:
o 3 σ-bonds (two to neighboring carbons and one to hydrogen or a substituent), and
o 1 π-bond (as part of the delocalized aromatic π system).
• Each carbon atom in benzene is trigonal planar, with 120° bond angles. ⇒ Hybridization of X = sp²
Atom Y
• The O atom (Y) is attached to one hydrogen and one carbon, with two lone pairs of electrons.
• Total regions of electron density = 4 (2 σ-bonds + 2 lone pairs).
• The geometry is tetrahedral (bent shape).
⇒ Hybridization of Y = sp³
Atom Z
• Z is a carbon atom bonded to three hydrogens and one nitrogen.
• Total regions of electron density = 4 σ-bonds.
• The geometry is tetrahedral (bond angle ≈ 109.5°).
⇒ Hybridization of Z = sp³
Question 14
Which diagram represents the bonding in SiO2?

Question 15
How many sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are there in CH₃CH₂CCCH₂COOH?
A. 13σ and 5π
B. 15σ and 2π
C. 15σ and 3π
D. 15σ only
Answer: C. 15σ and 3π
C–C bonds:
• CH₃–CH₂ → 1 σ
• CH₂–C → 1 σ
• C≡C → 1 σ + 2 π
• C–CH₂ → 1 σ
• CH₂–C (of COOH) → 1 σ
⇒ Total C–C σ bonds = 5 σ, C–C π bonds = 2 π (from triple bond) C–H bonds:
• CH₃ → 3 σ
• CH₂ (next to CH₃) → 2 σ
• CH₂ (next to C≡C) → 2 σ
⇒ Total C–H σ bonds = 7 σ
C=O and O–H bonds (in COOH):
• C=O → 1 σ + 1 π
• C–O → 1 σ
• O–H → 1 σ
⇒ C–O and O–H total = 3 σ + 1 π
Add all together
| Type | Number |
| σ bonds | 5 (C–C) + 7 (C–H) + 3 (C–O, O–H) = 15 σ |
| π bonds | 2 (from C≡C) + 1 (from C=O) = 3 π |
Question 16
What is the formal charge of boron in the borohydride ion, BH₄⁻?
A. –1
B. 0
C. +1
D. –4
Answer: A. –1
Step 1. Determine valence electrons of boron
Boron (Group 13) → 3 valence electrons
Step 2. Determine bonding in BH₄⁻
• Structure: B is the central atom bonded to 4 hydrogens (each forming a single bond).
• Each B–H bond is a σ bond (shared pair of 2 electrons).
• The ion has an overall charge of –1, meaning there is one extra electron added to the molecule.
Total valence electrons = 3 (from B) + 4×1 (from H) + 1 (extra charge) = 8 electrons total → 4 bonding pairs → 4 single bonds
Step 3. Formal charge formula
Formal charge
= Valence electrons − (Nonbonding electrons) - `frac{1}{2}*("Bonding electrons")`
For boron:
• Valence electrons = 3
• Nonbonding electrons = 0 (all used in bonding)
• Bonding electrons = 8 (4 bonds × 2 e⁻ each)
Formal charge on B = 3 − 0 − `frac{8}{2}`= 3 − 4 = -1
Question 17
Which one of the following contains the largest number of lone pairs on the central atom?
A. ClO₃⁻
B. XeF₄
C. I₃⁻
D. SF₄
Answer: C. I₃⁻
A. Incorrect: ClO₃⁻
• Total valence electrons: Cl = 7, O₃ = 3×6 = 18, +1 (extra) = 26 electrons
• Cl is the central atom.
• Forms 3 bonds with oxygen.
• Remaining electrons after bonding → 26 − (3×2) = 20 → used for lone pairs on O atoms and maybe on Cl.
• Formal structure: ClO₃⁻ has 3 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair on Cl. ⇒ Lone pairs on Cl = 1
B. Incorrect: XeF₄
• Xe = 8 valence e⁻, F₄ = 4×7 = 28 → 36 electrons total
• 4 Xe–F bonds → 8 e⁻ used
• Remaining = 36 − 8 = 28 e⁻ → distributed: 24 e⁻ on F atoms (6 on each), 4 e⁻ left on Xe
• 4 e⁻ = 2 lone pairs on Xe
⇒ Lone pairs on Xe = 2
C. Correct: I₃⁻
• I = 7 valence e⁻ × 3 = 21, +1 = 22 e⁻
• Linear structure with central I bonded to two outer I atoms → 2 bonds (4 e⁻ used)
• Remaining 18 e⁻ → 6 on each outer I, leaving central I with 3 lone pairs. ⇒ Lone pairs on central I = 3
D. Incorrect: SF₄
• S = 6 valence e⁻, F₄ = 4×7 = 28 → total 34 e⁻
• 4 S–F bonds → 8 e⁻ used
• Remaining 26 e⁻ → 24 on F, 2 on S → 1 lone pair on S.
⇒ Lone pairs on S = 1
Question 18
Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon. State two empirical pieces of evidence that support a π electron delocalized structure of benzene.
All C–C bond lengths are equal (intermediate between single and double bonds). Therefore, benzene cannot have alternating single and double bonds; instead, the π electrons are delocalized over the ring.
Benzene is also a cyclic molecule in which all of the ring atoms are sp2-hybridized that allows the π electrons to be delocalized in molecular orbitals that extend all the way around the ring, above and below the plane of the ring. For this to happen, of course, the ring must be planar – otherwise the 2pz orbitals could not overlap properly. Benzene was experimentally confirmed to be flat molecule by Dame Kathleen Londsale with X-ray crystallography.
Question 19
Two possible Lewis structures of the chlorate(VI) ion, ClO₃⁻ ion are shown below.
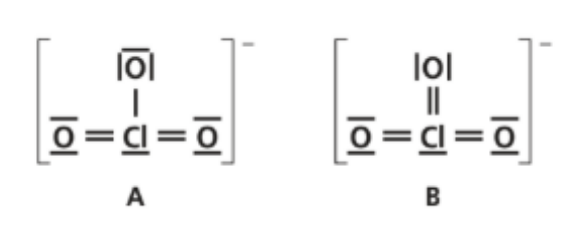
a. Outline the principles of the valence shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory.
b. Using VSEPR theory, state the electron domain geometry, molecular shape and the O–Cl–O bond angle in structure II.
c. Using formal charge, state and explain which is likely to be the Lewis structure of the ClO₃⁻ ion.
a. Principles of VSEPR theory
• Electron domains (bonding pairs and lone pairs) around a central atom repel each other and arrange to minimize repulsion (maximize separation).
• Lone pair–lone pair > lone pair–bond pair > bond pair–bond pair repulsions (so lone pairs compress bond angles more).
• A multiple bond counts as one electron domain for geometry.
b. Structure II (the right-hand drawing) – VSEPR description
• Around Cl there are 4 electron domains (three Cl–O double-bond domains + one lone pair) → tetrahedral electron-domain geometry.
• With one lone pair, the molecular shape is trigonal pyramidal.
• The O–Cl–O bond angle is slightly less than 109.5° (≈ 107°) due to the lone pair’s greater repulsion.
c. Which Lewis structure is more likely? Use formal charge
Compute formal charges (FC = valence – nonbonding – `frac{1}{2}` bonding):
• Structure A (two Cl=O and one Cl–O⁻, Cl has one lone pair):
o Cl: 7 – 2 – 5 = 0
o Two =O: 6 – 4 – 2 = 0 each
o O⁻ (single-bonded): 6 – 6 – 1 = –1
o Total: –1
• Structure II/B (three Cl=O, Cl has one lone pair):
o Cl: 7 – 2 – 6 = –1
o Each =O: 6 – 4 – 2 = 0
o Total: –1
Choice: Structure A is favored because the negative charge resides on oxygen, the more electronegative atom (and Cl carries 0). In II/B the negative charge is on chlorine (less favorable).
Question 20
a. Draw a labelled diagram of sp³ orbitals.
b. Describe the bonding of sp³ carbon in terms of orbital overlap in propanone, (CH₃)₂C=O.
a. Labelled diagram of sp³ orbitals
You should draw:
• A central atom (like carbon) with four equivalent sp³ orbitals arranged tetrahedrally around it.
• Each orbital is a large lobe (for bonding) and a small lobe (opposite direction).
• Bond angle = 109.5°
b. Bonding of sp³ carbon in propanone, (CH₃)₂C=O
In propanone:
• The two methyl carbons are sp³ hybridized.
• Each sp³ orbital on the methyl carbon overlaps end-on (σ overlap) with: o 1s orbital of hydrogen (forming C–H σ bonds)
o sp² orbital of the carbonyl carbon (forming C–C σ bond)
⇒ Each sp³ hybrid orbital of carbon overlaps head-on with either a hydrogen 1s orbital or an sp² orbital of the carbonyl carbon to form σ bonds.
Question 21
Which molecule is trigonal bipyramidal in shape?
A. PCl₃
B. SiCl₄
C. PCl₅
D. SF₆
Answer: C. PCl₅
A. Incorrect: PCl₃
• Central atom P has 5 valence electrons.
• Forms 3 bonds with Cl and has 1 lone pair → 4 electron domains.
• Electron geometry: tetrahedral; molecular shape: trigonal pyramidal. → Not trigonal bipyramidal.
B. Incorrect: SiCl₄
• Si has 4 bonding pairs, 0 lone pairs → 4 electron domains.
• Shape: tetrahedral (bond angle 109.5°). → Not trigonal bipyramidal.
C. Correct: PCl₅
• P has 5 bonding pairs, 0 lone pairs → 5 electron domains.
• Shape: trigonal bipyramidal (bond angles 90°, 120°, 180°).
D. Incorrect: SF₆
• S has 6 bonding pairs, 0 lone pairs → 6 electron domains.
• Shape: octahedral. → Not trigonal bipyramidal.
Question 22
Ozone, O₃, in the upper atmosphere prevents harmful UV radiation reaching the surface of the Earth.
a. Draw the Lewis structure for ozone.
b. State the shape of the ozone molecule and estimate the bond angle.
c. State the hybridization of the central oxygen atom.
d. In terms of σ and π bonds, describe the two oxygen–oxygen bonds in the Lewis structure.
a. Lewis structure of O₃
Draw either of the two resonance forms:
• O=O–O with a negative charge on the terminal single-bonded O and a positive formal charge on the central O; lone pairs on each O. (Also indicate the second resonance O–O=O or state “resonance between two equivalent structures.”)
b. Shape and bond angle
• Shape: Bent (V-shaped) around the central oxygen (electron-domain geometry trigonal planar).
• Bond angle: ≈117° (less than 120° due to lone-pair repulsion).
c. Hybridization of the central O
• sp² (three electron domains: two bonding pairs + one lone pair).
d. Nature of the O–O bonds (σ and π)
• Each O–O link contains one σ bond; the π bond is delocalized over the two O–O connections (resonance), so both bonds are equivalent and intermediate between single and double.
Question 23
Which of the following molecules does not have a π bond?
A. CO₂
B. CO
C. H₂O₂
D. SO₃
Answer: C. H₂O₂
A. Incorrect: CO₂
• Structure: O=C=O
• Contains two double bonds, each with one σ and one π bond.
→ Has π bonds.
B. Incorrect: CO
Structure: C≡O (triple bond: one σ and two π bonds).
→ Has π bonds.
C. Correct: H₂O₂
• Structure: H–O–O–H
• All bonds are single σ bonds; there are no double or triple bonds, hence no π bonds.
D. Incorrect: SO₃
• Structure: Resonance forms with double bonds between S and O.
• Each S–O bond has partial π character due to delocalization.
→ Has π bonds.
Question 24
What is the hybridization state of carbon in ethyne (C₂H₂), graphite and diamond?
A. sp, sp², sp³
B. sp, sp³, sp²
C. sp³, sp², sp
D. sp, sp³, sp³
Answer: A. sp, sp², sp³
Ethyne (C₂H₂)
• Structure: H–C≡C–H
• Each carbon forms two σ bonds (one with H, one with the other C) and two π bonds in the triple bond.
→ Hybridization: sp
Graphite: Each carbon forms three σ bonds with other carbons in the same plane, and one delocalized π electron.
→ Hybridization: sp²
Diamond: Each carbon forms four σ bonds (tetrahedral structure).
→ Hybridization: sp³
Question 25
What is the number of σ and π bonds in (NC)₂C=C(CN)₂?
A. 5, 4
B. 6, 6
C. 9, 4
D. 9, 9
Answer: C. 9, 4
i. Each C≡N bond
• 1 σ bond
• 2 π bonds
⇒ Each –C≡N contributes 1 σ + 2 π
Since there are 4 C≡N groups total:
→ σ = 4 × 1 = 4
→ π = 4 × 2 = 8
ii. The central C=C bond
• 1 σ bond
• 1 π bond
Add these to the total.
| Bond type | Count |
| σ bonds | 4 (from C≡N) + 1 (C=C) = 5 σ |
| π bonds | 8 (from C≡N) + 1 (C=C) = 9 π |
Question 26
Boron nitride is found to exist in two possible forms, hexagonal boron nitride and cubic boron nitride as shown.

Carbon can also be found in two different forms (allotropes).
a. Name the allotropes of carbon which have a similar structure to hexagonal boron nitride and cubic boron nitride.
b. Based on the structures shown, explain the difference in one physical property of hexagonal and cubic boron nitride other than electrical conductivity.
c. Explain the difference in electrical conductivity between graphene and carbon-60.
a.
• Hexagonal BN — like graphite/graphene (layered hexagonal sheets).
• Cubic BN — like diamond (3-D tetrahedral network).
b.
• Hexagonal BN is soft/slippery because layers are held together only by weak vander Waals forces, so they slide.
• Cubic BN is very hard (diamond-like) because of a 3-D covalent network of strong B–N bonds throughout.
c.
• Graphene conducts electricity very well: its π-electrons are delocalized over an extended 2-D sheet, giving a near-zero band gap.
• C60 (buckminsterfullerene) is a molecular solid: electrons are mostly localized within each molecule and there’s a band gap between molecules, so it is a poor conductor/semiconductor compared with graphene.
Question 27
Which one of the following is correct for carbon suboxide, O=C=C=C=O?

Answer: A. C=O bond: polar; C3O2 molecule: non-polar.
• Nature of the C=O bond
The carbon–oxygen double bond (C=O) is polar because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon.
→ Each C=O bond has a dipole directed toward oxygen.
`=>` C=O bond is polar.
• Nature of the C3O2 molecule
Carbon suboxide (O=C=C=C=O) is linear and symmetrical.
The molecule has two identical polar C=O bonds pointing in opposite directions, so their dipole moments cancel out.
`=>` Molecule is non-polar.
Question 28
What are the approximate bond angles and structure of crystalline SiO2?

Answer: B. O–Si–O: 109°; Structure: giant molecule.
Crystalline silicon dioxide (SiO2) (quartz) has a giant covalent (network) structure, not a small molecular one.
• Each Si atom is covalently bonded to four O atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement.
• Each O atom is bonded to two Si atoms.
Bond angle:
• The O–Si–O bond angle is approximately 109.5°, characteristic of a tetrahedral
geometry.
Question 29
What describes the relationship between diamond, graphite and C60 fullerene?
A. Allotropes
B. Isomers
C. Isotopes
D. Polymers
Answer: A. Allotropes
• Diamond, graphite, and C60 fullerene are all different structural forms of the same element, carbon.
• They have the same element (C) but different atomic arrangements and hence different physical properties.
Question 30
Which combination describes the sulfate(IV) ion, SO32− (also known as sulfite ion)?

Answer: D. 4 electron domains – tetrahedral – trigonal pyramidal – 107°
For the sulfite ion, SO32−:
1. Lewis structure:
• Central S atom bonded to 3 O atoms.
• One lone pair on sulfur.
→ Total of 4 electron domains (3 bonding pairs + 1 lone pair).
2. Electron domain geometry: 4 domains → tetrahedral (from VSEPR theory).
3. Molecular geometry: Because one of the four domains is a lone pair, the actual molecular shape is trigonal pyramidal.
4. Bond angle: Slightly less than 109.5°, typically around 107°, due to lone-pair repulsion.
Question 31
Which one of the following pairs of molecules has identical shapes for both species?
A. CCl4, SF4
B. XeF2, CO2
C. BCl3, PF3
D. PF5, IF5
Answer: B. XeF2, CO2
A. Incorrect: CCl4 (tetrahedral) vs SF4 (seesaw)
B. Correct:
• XeF2 (linear) vs CO2 (linear) → identical shape (linear)
• Even though Xe has lone pairs, both molecules are linear geometrically.
C. Incorrect: BCl3 (trigonal planar) vs PF3 (trigonal pyramidal)
D. Incorrect: PF5 (trigonal bipyramidal) vs IF5 (square pyramidal)
Question 32
Which molecules react to form a dative covalent (coordinate) bond?
A. CH4 and NH3
B. C2H2 and Cl2
C. NH3 and HF
D. Cl2 and HF
Answer: C. NH3 and HF
A. Incorrect: CH4 and NH3 → both have complete octets; no lone pair donation.
B. Incorrect: C2H2 and Cl2 → forms covalent bonds, not coordinate.
C. Correct:
A dative covalent bond (coordinate bond) is formed when one atom donates both electrons to a shared bond pair.
In this case:
• NH3 (ammonia) has a lone pair on nitrogen.
• HF (hydrogen fluoride) can produce H+ (a proton) when the H–F bond breaks.
When they react:
NH3 + H+ → NH4+
The nitrogen donates its lone pair to form a dative covalent bond with H+, giving the ammonium ion (NH4+).
D. Incorrect:
Cl2 and HF → no lone pair donation to form coordinate bond.
Question 33
Which species contain a dative covalent (coordination or coordinate) bond?
I. Carbon monoxide, CO
II. Ammonia, NH3
III. Oxonium ion, H3O+
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Answer: B. I and III only
I. Carbon monoxide (CO)
• Structure: :C≡O:
• Contains one normal covalent bond, one double bond, and one dative (coordinate) bond, where oxygen donates a lone pair to carbon.
`=>` Contains a dative covalent bond.
II. Ammonia (NH3)
• All three N–H bonds are normal covalent bonds (each atom contributes one electron).
• However, NH3 can form a dative bond (e.g., in NH4+), but it does not contain one by itself.
`=>` Does not contain a dative bond (but can form one).
III. Oxonium ion (H3O+)
• Formed when H2O donates a lone pair to an H+ ion: H2O + H+ → H3O+
• The O–H bond formed by donation is a dative covalent bond.
`=>` Contains a dative covalent bond.
Question 34
Which statement about intermolecular forces is correct?
A. The intermolecular force between H2 molecules is hydrogen bonding, because H2 has temporary dipoles.
B. The intermolecular forces between PH3 molecules are greater than the intermolecular forces between NH3 molecules, because they have a greater mass.
C. The intermolecular force between H2 molecules is hydrogen bonding, because H2 has permanent dipoles.
D. The intermolecular forces between Br2 molecules are van der Waals’, because Br2 has temporary dipoles.
Answer: D. The intermolecular forces between Br2 molecules are van der Waals’, because Br2 has temporary dipoles.
A. Incorrect:
H2 has no hydrogen bonding — it’s nonpolar. It only has weak London dispersion (vander Waals) forces due to temporary dipoles
B. Incorrect:
NH3 forms hydrogen bonds, which are much stronger than van der Waals forces in PH3.
So, NH3 has stronger intermolecular forces.
C. Incorrect:
H2 is nonpolar (no permanent dipole). It only has temporary dipoles.
D. Correct:
Br2 is nonpolar, but temporary dipoles (instantaneous dipoles) induce vander Waals’ forces.
Question 35
What describes the structure of silicon and silicon dioxide?

Answer: D
Elemental silicon (Si):
• Has a giant covalent structure.
• Each Si atom is covalently bonded to 4 other Si atoms.
• The shape around each Si atom is tetrahedral.
Silicon dioxide (SiO2):
• Also has a giant covalent (network) structure.
• Each Si atom is covalently bonded to 4 oxygen atoms.
• Each O atom bonds to 2 Si atoms.
• The shape around each Si atom is also tetrahedral.
Question 36
In which one of the following pairs does the first molecule have a larger dipole than the second?

Answer: A
A. Correct:
The first molecule has a polar C=O bond, and the molecule is symmetric, so the dipole moment is primarily due to the C=O bond. The second molecule also has a polar C=O bond, but it has two highly electronegative chlorine atoms attached to the same carbon.
The C-Cl bond dipoles point in the opposite direction to the C=O dipole moment. Due to the geometry, the vector sum of the C-Cl bond dipoles and the C=O bond dipole results in a smaller net dipole moment for the second molecule compared to the first. Therefore, the first molecule has a larger dipole than the second.
B. Incorrect:
The second molecule has the cis configuration. The C-Cl bond dipoles do not cancel out, resulting in a net dipole moment. The first molecule has the trans configuration. The C-Cl bond dipoles are equal in magnitude and point in opposite directions, so they cancel each other out, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero. Therefore, the second molecule
has a larger dipole moment than the first.
C. Incorrect:
Fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine, so the H-F bond is more polar than the H-Cl bond. As a result, HF has a larger dipole moment than HCl.
D. Incorrect:
The first molecule is sulfur trioxide SO3. It has a trigonal planar geometry, and the S=O bond dipoles are arranged symmetrically and cancel each other out, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero. The second molecule is sulfur dioxide SO2. It has a bent
molecular geometry, and the S=O bond dipoles do not cancel each other out, resulting in a net dipole moment greater than zero. Therefore, SO2 has a larger dipole moment than SO3.
Question 37
The structural formula of ethanediamide is shown below.

a. Predict the electron domain and molecular geometries at the nitrogen and carbon atoms, applying VSEPR theory.
b. State the hybridization of the carbon atoms.
c. State the number of sigma bonds, pi bonds and lone pairs in a molecule of ethanediamide.
d. Suggest why ethanediamide is a solid and ammonia is a gas under standard conditions.
e. Explain why ethanediamide is relatively soluble in water.
a. VSEPR at N and C
• Nitrogen (amide N): Lone pair delocalized into C=O → 3 electron domains; electron-domain geometry: trigonal planar; molecular geometry: trigonal planar (≈120° around N).
• Carbonyl carbon (each C of C=O): Three regions (C=O, C–N, C–C) → 3 electron domains; trigonal planar (≈120°).
b. Hybridization of the carbon atoms
Each carbonyl carbon is sp2.
c. Count of σ bonds, π bonds and lone pairs (whole molecule)
• σ bonds: 9 (4N–H) + (2C–N) + (1C–C) + (2C=O σ)
• π bonds: 2 (one in each C=O)
• Lone pairs: 6 (2 on O of each C=O → 4) + (one on each N → 2)
d. Why ethanediamide is a solid but ammonia is a gas (r.t.p.)
Ethanediamide forms an extensive H-bonding network (N–H···O=C) and is more polar/higher Mr → much stronger intermolecular forces → solid.
NH3 has fewer/weaker H-bonding interactions → gas at standard conditions.
e. Why ethanediamide is relatively soluble in water
It can both donate (N–H) and accept (C=O) hydrogen bonds with water; it is highly polar, so it mixes well via H-bonding and dipole–dipole interactions.
Question 38
Which molecule is non-polar?
A. H2CO
B. SO3
C. NFCl2
D. CHCl3
Answer: B. SO3
A molecule is non-polar if:
• Its bonds are arranged symmetrically, and
• The dipole moments cancel each other out.
A. Incorrect:
Trigonal planar, but oxygen is more electronegative → molecule is polar
B. Correct:
• Trigonal planar molecule (120° bond angles).
• All S=O bonds are identical and symmetrically arranged → dipoles cancel out → non-polar.
C. Incorrect:
Different atoms around the central N → asymmetric molecule → polar.
D. Incorrect:
Tetrahedral but substituents (Cl, H) are different → dipoles do not cancel → polar.
Question 39
Silanes (see table below) are the silicon analogues of alkanes and follow a similar general formula.
They only have Si–H and Si–Si single bonds. Silanes can be used to prepare pure silicon.

a. State the general formula of the silanes and predict the molecular formula of hexasilane.
b. State the general trend in the boiling and melting points of the silanes across the table from left to right.
c. State the name of one silane from the table which is a liquid under standard conditions.
d. Explain this general trend in boiling points for the silanes in terms of the type of structure and intermolecular forces.
e. Write an equation to show the combustion of silane.
f. State the molecular shape of silane, SiH4, and state the bond angle.
g. Explain why the Si–H bond is longer than the C–H bond.
h. Using the data booklet, compare the polarity of the bonds in a molecule of methane with those in silane and explain the difference.
i. Describe the structure of silicon and state one physical property of silicon.
a. General formula: SinH2n+2 (silanes). Hexasilane: Si6H14.
b. Both melting points and boiling points increase from SiH4 → Si4H10.
c. A liquid at standard conditions: trisilane (Si3H8) (also tetrasilane, Si4H10).
d. Silanes are simple molecular substances; as chain length increases, molecules are larger/more polarizable with greater surface area, so London dispersion forces become stronger → higher b.p. (and m.p.)
e. Combustion of silane:
SiH4 + 2O2 → SiO2 + 2H2O
f. Shape of SiH4: tetrahedral; bond angle ≈ 109.5°.
g. Si–H bond is longer than C–H because Si is larger (3p valence orbitals) giving longer, poorer orbital overlap than C (2p).
h. Bond polarity:
• In CH4, C is slightly more electronegative than H → Cδ−–Hδ+ (very small polarity).
• In SiH4, H is more electronegative than Si → Siδ+–Hδ− (opposite direction, each bond more polar).
Both molecules are overall non-polar due to tetrahedral symmetry.
i. Structure of silicon: giant covalent (network); each Si bonded to four Si atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. Property (any one): very high melting point, hard/brittle, insoluble, semiconductor (poor conductor at low T).
Question 40
Explain why the solubility of trichloromethane (CHCl3) in water is ten times greater than that of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in water at the same temperature.
Trichloromethane (CHCl3, chloroform) is more soluble in water than carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) because:
1. Polarity difference
• CHCl3 is polar, since the C–H bond gives a small dipole moment that does not cancel out the C–Cl dipoles.
• CCl4 is non-polar — the four identical C–Cl bonds are symmetrically arranged, so their dipoles cancel.
2. Intermolecular interactions
• CHCl3 molecules can form weak hydrogen bonds with water due to the slightly positive hydrogen (δ+ on H) interacting with the lone pairs of oxygen in water.
• CCl4 cannot form hydrogen bonds and interacts with water only by weak London dispersion forces.
3. Resulting solubility
Because of these dipole–dipole and weak hydrogen-bond interactions, CHCl3 mixes with water much better, giving a solubility about ten times higher than that of non-polar CCl4.
Question 41
Which of the following describes an observation that cannot be explained by hydrogen bonding?
A. Ice has a lower density than water at 0°C.
B. Hydrazine (N2H4) is more soluble in water than in ammonia.
C. CH3F has a lower boiling point than methanol CH3OH.
D. The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing number of carbon atoms.
Answer: D. The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing number of carbon atoms.
A. Incorrect: Hydrogen bonding forms an open hexagonal lattice in ice → lower density.
B. Incorrect: Both N2H4 and H2O form strong hydrogen bonds, explaining high mutual solubility.
C. Incorrect: CH3OH forms hydrogen bonds, while CH3F does not, explaining the higher boiling point of methanol.
D. Correct: This trend is due mainly to increasing London dispersion (van der Waals) forces from larger molecular mass/surface area, not hydrogen bonding.
Question 42
Which of the following compounds are arranged in decreasing order of their solubility in water?
A. CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2Cl
B. CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2Cl, CH3CH2CH2OH
C. CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2Cl
D. CH3CH2CH2Cl, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CO2Na
Answer: A. CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2Cl
• CH3CH2CO2Na is ionic → dissolves easily in water due to strong ion–dipole interactions → most soluble.
• CH3CH2CH2OH is polar and forms hydrogen bonds with water → moderately soluble.
• CH3CH2CH2Cl is nearly nonpolar, interacts only via weak London dispersion forces → least soluble.
Question 43
What type of bonding or intermolecular force is not present in NH3·BF3 (s)?
A. Hydrogen bonds
B. Coordination bonds
C. London (dispersion) forces
D. Ionic bonds
Answer: D. Ionic bonds
In solid NH3·BF3, the bonding and forces present are:
• Coordination (dative covalent) bond: Nitrogen in NH3 donates a lone pair to the empty orbital of boron in BF3 → N → B coordinate bond.
• Hydrogen bonds: Between NH3 molecules, due to N–H···N interactions.
• London (dispersion) forces: Present between all molecules due to temporary dipoles.
• Ionic bonds: No ions are formed; all bonding is covalent or coordinate, not ionic.
Question 44
Which forces are present between molecules of carbon dioxide in the solid state?
A. Permanent dipole–permanent dipole interactions.
B. Temporary dipole–induced dipole interactions (London/dispersion forces).
C. Covalent bonding.
D. Ionic bonding.
Answer: B. Temporary dipole–induced dipole interactions (London/dispersion forces).
• CO2 is a linear, non-polar molecule because the two polar C=O bonds are equal and opposite, cancelling each other’s dipoles.
• In solid CO2 (dry ice), the molecules are held together by weak intermolecular forces — specifically London dispersion forces (also called temporary dipole–induced dipole forces).
• There are no permanent dipoles, no ionic bonds, and no covalent bonds between molecules.
`=>` The only forces between CO2 molecules in the solid state are London (dispersion) forces.
Question 45
Which substance has a giant covalent structure?

Answer: D
A giant covalent structure (also called a network covalent structure) has the following properties:
• Very high melting point (due to strong covalent bonds throughout the lattice).
• Insoluble in water (since no ions are present).
• Does not conduct electricity, even when molten (no free electrons or ions).
| Melting point / °C | Solubility in water | Electrical conductivity in the molten state | Type | |
| A. | 186 | high | none | molecular solid (e.g., sugar) |
| B. | 801 | high | good | ionic (e.g., NaCl) |
| C. | 1083 | low | good | metallic (e.g., Cu) |
| D. | 1710 | low | none | giant covalent (e.g., SiO₂ or Si) |
Question 46
Which of the following are van der Waals’ forces?
I. Dipole–dipole forces
II. Hydrogen bonds
III. London (dispersion) forces
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: B. I and III only.
Van der Waals’ forces (also called intermolecular forces) include:
I. Dipole–dipole interactions — between polar molecules.
II. Hydrogen bonds are stronger and more specific than ordinary van der Waals’ forces— they occur only when H is bonded to N, O, or F.
III. London (dispersion) forces — between all molecules, caused by temporary dipoles.
`=>` Van der Waals’ forces include dipole–dipole and London dispersion forces only.
Question 47
Which pair of molecules has the same bond angles?
A. PCl3 and BCl3
B. SO2 and CO2
C. H2O and NH3
D. CCl4 and SiH4
Answer: D. CCl4 and SiH4
| Molecule | Shape | Bond angle | Reason |
| PCl₃ | Trigonal pyramidal | ~107° | Has one lone pair on P |
| BCl₃ | Trigonal planar | 120° | No lone pairs |
| SO₂ | Bent | ~119° | Double bonds + lone pairs |
| CO₂ | Linear | 180° | No lone pairs |
| H₂O | Bent | 104.5° | Two lone pairs |
| NH₃ | Trigonal pyramidal | 107° | One lone pair |
| CCl₄ | Tetrahedral | 109.5° | 4 bonding pairs |
| SiH₄ | Tetrahedral | 109.5° | 4 bonding pairs |
`=>` Both CCl4 and SiH4 are tetrahedral molecules with bond angles of 109.5°.
Question 48
Based on electronegativity values, which bond is the most polar?
A. B–C
B. C–O
C. O–F
D. N–O
Answer: B. C–O
The polarity of a bond depends on the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN) between the two bonded atoms.
| Bond | Electronegativity values | ΔEN | Polarity | |
| A. | B–C | B = 2.0, C = 2.5 | 0.5 | weakly polar |
| B. | C–O | C = 2.5, O = 3.5 | 1.0 | strongly polar |
| C. | O–F | O = 3.5, F = 4.0 | 0.5 | weakly polar |
| D. | N–O | N = 3.0, O = 3.5 | 0.5 | weakly polar |
The C–O bond has the largest electronegativity difference (1.0), so it is the most polar bond.
Question 49
a. Outline the basic principle of all chromatographic techniques.
b. Paper chromatograms formed by two orange food colourings, A and B, are shown below.

i. State which of these food colourings is a mixture of dyes.
ii. State which of these food colourings is a pure substance.
iii. Explain whether the same dye is present in each of the food colourings.
The RF value is the ratio of the distance moved by the solute/distance moved by solvent.
iv. Calculate the RF value of the substance responsible for the red spot in the chromatogram of A.
c. The results of a thin-layer chromatography separation on silica gel are shown below.
| Compound | Distance travelled / cm |
| Compound 1 | 1.6 |
| Compound 2 | 9.2 |
| Compound 3 | 12.6 |
i. Calculate the RF values of the compounds 1 and 2 and comment on their values.
ii. State one advantage of thin-layer chromatography over paper chromatography.
a. Basic principle of all chromatographic techniques
Chromatography separates substances based on their different affinities for two phases:
A stationary phase, which does not move, and a mobile phase, which moves through or over the stationary phase. Substances that interact more strongly with the stationary phase move more slowly, while those that interact more strongly with the mobile phase move faster — resulting in separation.
b. Paper chromatography
i. A — because it separates into two spots (red and yellow).
ii. B — because it shows only one spot (orange).
iii. The yellow dye in A and the orange dye in B travel the same distance on the chromatogram, suggesting they have the same Rf value. ⇒ The same yellow dye is present in both A and B.
iv. Calculate the Rf value for the red spot in A.
`"R_f`=`frac{"distance moved by solute"}{"distance moved by solvent"} = frac{10.0}{22.0} = 0.45`
c. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC)
i. Calculate the Rf values and comment.
| Compound | Distance travelled (cm) | Solvent (cm) | Rf value |
| 1 | 1.6 | 12.6 | `frac{1.6}{12.6}=0.13` |
| 2 | 9.2 | 12.6 | `frac{9.2}{12.6}=0.73` |
Compound 2 travels much further than compound 1, meaning it has a stronger affinity for the mobile phase and weaker attraction to the stationary phase.
ii. TLC gives better separation and faster results because the silica gel layer has smaller particles and provides greater resolution than paper.
Question 1
How many sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are there in CH₃CH₂CCCH₂COOH?
A. 13σ and 5π
B. 15σ and 2π
C. 15σ and 3π
D. 15σ only
Question 2
What is the shape and the bond angle of the molecule BF3?
| Shape | Bond angle | |
| A. | Trigonal pyramidal | 109.5° |
| B. | Trigonal planar | 109.5° |
| C. | Trigonal pyramidal | 120° |
| D. | Trigonal planar | 120° |
Question 3
Diamond, C60 fullerene and graphite are allotropes of carbon.
Which statements are correct about these allotropes?
I. In diamond each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement.
II. In C60 fullerene each carbon is held in a trigonal arrangement.
III. In graphite each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 4
Which group of ions and molecules has delocalized electrons in all the species?
A. CH3COCH3, C2H5COO− and O3
B. NO3−, NO2− and CO2
C. C6H6, CO32− and graphite
D. C6H6, CO32− and C2H2
Question 5
What is the correct number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in prop-2-enenitrile, CH₂CHCN?
| σ bonds | π bonds | |
| A. | 7 | 2 |
| B. | 4 | 5 |
| C. | 6 | 3 |
| D. | 3 | 3 |
Question 6
Which allotropes of carbon show sp2 hybridization?
I. Diamond
II. Graphite
III. C60 fullerene
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 7
Which substance does not contain delocalized electrons?
A. Graphene.
B. Carbon-60, C₆₀.
C. Methylbenzene, C₆H₅CH₃.
D. Ethene, C₂H₄.
Question 8
Which species have resonance structures?
I. The azide ion, N₃⁻
II. The carbon dioxide molecule, CO₂
III. The methylbenzene molecule, C₆H₅CH₃
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 9
Which of the following information about the specified central atom is correct?
| Atom | Number of electron domains around one central atom | Molecular geometry | Hybridization | |
| A. | C in C₂FCl | 2 | linear | sp |
| B. | C in C₂H₆ | 4 | square planar | sp³ |
| C. | P in PH₃ | 3 | trigonal pyramidal | sp³ |
| D. | O in H₂O | 4 | Bent / V-shaped | sp² |
Question 10
Which diagram shows the correct shape and relative energies of a p orbital and a sp³ hybrid orbital of a nitrogen atom?

Question 11
The diagrams below show s and p orbitals in different positions. Which combinations can form a σ-bond?

A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 12
Which species contain delocalized electrons?

A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 13
What is the hybridization of atoms X, Y and Z in epinephrine?

|
| X | Y | Z |
| A. | sp² | sp³ | sp³ |
| B. | sp² | sp | sp³ |
| C. | sp³ | sp² | sp² |
| D. | sp³ | sp³ | sp³ |
Question 14
Which diagram represents the bonding in SiO2?

Question 15
How many sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are there in CH₃CH₂CCCH₂COOH?
A. 13σ and 5π
B. 15σ and 2π
C. 15σ and 3π
D. 15σ only
Question 16
What is the formal charge of boron in the borohydride ion, BH₄⁻?
A. –1
B. 0
C. +1
D. –4
Question 17
Which one of the following contains the largest number of lone pairs on the central atom?
A. ClO₃⁻
B. XeF₄
C. I₃⁻
D. SF₄
Question 18
Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon. State two empirical pieces of evidence that support a π electron delocalized structure of benzene.
Question 19
Two possible Lewis structures of the chlorate(VI) ion, ClO₃⁻ ion are shown below.
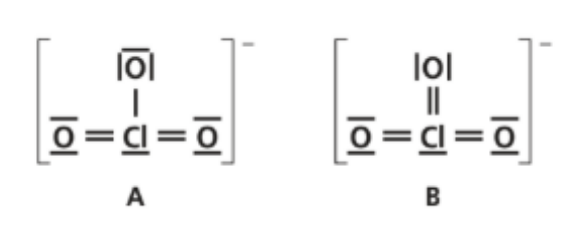
a. Outline the principles of the valence shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory.
b. Using VSEPR theory, state the electron domain geometry, molecular shape and the O–Cl–O bond angle in structure II.
c. Using formal charge, state and explain which is likely to be the Lewis structure of the ClO₃⁻ ion.
Question 20
a. Draw a labelled diagram of sp³ orbitals.
b. Describe the bonding of sp³ carbon in terms of orbital overlap in propanone, (CH₃)₂C=O.
Question 21
Which molecule is trigonal bipyramidal in shape?
A. PCl₃
B. SiCl₄
C. PCl₅
D. SF₆
Question 22
Ozone, O₃, in the upper atmosphere prevents harmful UV radiation reaching the surface of the Earth.
a. Draw the Lewis structure for ozone.
b. State the shape of the ozone molecule and estimate the bond angle.
c. State the hybridization of the central oxygen atom.
d. In terms of σ and π bonds, describe the two oxygen–oxygen bonds in the Lewis structure.
Question 23
Which of the following molecules does not have a π bond?
A. CO₂
B. CO
C. H₂O₂
D. SO₃
Question 24
What is the hybridization state of carbon in ethyne (C₂H₂), graphite and diamond?
A. sp, sp², sp³
B. sp, sp³, sp²
C. sp³, sp², sp
D. sp, sp³, sp³
Question 25
What is the number of σ and π bonds in (NC)₂C=C(CN)₂?
A. 5, 4
B. 6, 6
C. 9, 4
D. 9, 9
Question 26
Boron nitride is found to exist in two possible forms, hexagonal boron nitride and cubic boron nitride as shown.

Carbon can also be found in two different forms (allotropes).
a. Name the allotropes of carbon which have a similar structure to hexagonal boron nitride and cubic boron nitride.
b. Based on the structures shown, explain the difference in one physical property of hexagonal and cubic boron nitride other than electrical conductivity.
c. Explain the difference in electrical conductivity between graphene and carbon-60.
Question 27
Which one of the following is correct for carbon suboxide, O=C=C=C=O?

Question 28
What are the approximate bond angles and structure of crystalline SiO2?

Question 29
What describes the relationship between diamond, graphite and C60 fullerene?
A. Allotropes
B. Isomers
C. Isotopes
D. Polymers
Question 30
Which combination describes the sulfate(IV) ion, SO32− (also known as sulfite ion)?

Question 31
Which one of the following pairs of molecules has identical shapes for both species?
A. CCl4, SF4
B. XeF2, CO2
C. BCl3, PF3
D. PF5, IF5
Question 32
Which molecules react to form a dative covalent (coordinate) bond?
A. CH4 and NH3
B. C2H2 and Cl2
C. NH3 and HF
D. Cl2 and HF
Question 33
Which species contain a dative covalent (coordination or coordinate) bond?
I. Carbon monoxide, CO
II. Ammonia, NH3
III. Oxonium ion, H3O+
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Question 34
Which statement about intermolecular forces is correct?
A. The intermolecular force between H2 molecules is hydrogen bonding, because H2 has temporary dipoles.
B. The intermolecular forces between PH3 molecules are greater than the intermolecular forces between NH3 molecules, because they have a greater mass.
C. The intermolecular force between H2 molecules is hydrogen bonding, because H2 has permanent dipoles.
D. The intermolecular forces between Br2 molecules are van der Waals’, because Br2 has temporary dipoles.
Question 35
What describes the structure of silicon and silicon dioxide?

Question 36
In which one of the following pairs does the first molecule have a larger dipole than the second?

Question 37
The structural formula of ethanediamide is shown below.

a. Predict the electron domain and molecular geometries at the nitrogen and carbon atoms, applying VSEPR theory.
b. State the hybridization of the carbon atoms.
c. State the number of sigma bonds, pi bonds and lone pairs in a molecule of ethanediamide.
d. Suggest why ethanediamide is a solid and ammonia is a gas under standard conditions.
e. Explain why ethanediamide is relatively soluble in water.
Question 38
Which molecule is non-polar?
A. H2CO
B. SO3
C. NFCl2
D. CHCl3
Question 39
Silanes (see table below) are the silicon analogues of alkanes and follow a similar general formula.
They only have Si–H and Si–Si single bonds. Silanes can be used to prepare pure silicon.

a. State the general formula of the silanes and predict the molecular formula of hexasilane.
b. State the general trend in the boiling and melting points of the silanes across the table from left to right.
c. State the name of one silane from the table which is a liquid under standard conditions.
d. Explain this general trend in boiling points for the silanes in terms of the type of structure and intermolecular forces.
e. Write an equation to show the combustion of silane.
f. State the molecular shape of silane, SiH4, and state the bond angle.
g. Explain why the Si–H bond is longer than the C–H bond.
h. Using the data booklet, compare the polarity of the bonds in a molecule of methane with those in silane and explain the difference.
i. Describe the structure of silicon and state one physical property of silicon.
Question 40
Explain why the solubility of trichloromethane (CHCl3) in water is ten times greater than that of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in water at the same temperature.
Question 41
Which of the following describes an observation that cannot be explained by hydrogen bonding?
A. Ice has a lower density than water at 0°C.
B. Hydrazine (N2H4) is more soluble in water than in ammonia.
C. CH3F has a lower boiling point than methanol CH3OH.
D. The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing number of carbon atoms.
Question 42
Which of the following compounds are arranged in decreasing order of their solubility in water?
A. CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2Cl
B. CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2Cl, CH3CH2CH2OH
C. CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CO2Na, CH3CH2CH2Cl
D. CH3CH2CH2Cl, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CO2Na
Question 43
What type of bonding or intermolecular force is not present in NH3·BF3 (s)?
A. Hydrogen bonds
B. Coordination bonds
C. London (dispersion) forces
D. Ionic bonds
Question 44
Which forces are present between molecules of carbon dioxide in the solid state?
A. Permanent dipole–permanent dipole interactions.
B. Temporary dipole–induced dipole interactions (London/dispersion forces).
C. Covalent bonding.
D. Ionic bonding.
Question 45
Which substance has a giant covalent structure?

Question 46
Which of the following are van der Waals’ forces?
I. Dipole–dipole forces
II. Hydrogen bonds
III. London (dispersion) forces
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 47
Which pair of molecules has the same bond angles?
A. PCl3 and BCl3
B. SO2 and CO2
C. H2O and NH3
D. CCl4 and SiH4
Question 48
Based on electronegativity values, which bond is the most polar?
A. B–C
B. C–O
C. O–F
D. N–O
Question 49
a. Outline the basic principle of all chromatographic techniques.
b. Paper chromatograms formed by two orange food colourings, A and B, are shown below.

i. State which of these food colourings is a mixture of dyes.
ii. State which of these food colourings is a pure substance.
iii. Explain whether the same dye is present in each of the food colourings.
The RF value is the ratio of the distance moved by the solute/distance moved by solvent.
iv. Calculate the RF value of the substance responsible for the red spot in the chromatogram of A.
c. The results of a thin-layer chromatography separation on silica gel are shown below.
| Compound | Distance travelled / cm |
| Compound 1 | 1.6 |
| Compound 2 | 9.2 |
| Compound 3 | 12.6 |
i. Calculate the RF values of the compounds 1 and 2 and comment on their values.
ii. State one advantage of thin-layer chromatography over paper chromatography.