Question 1
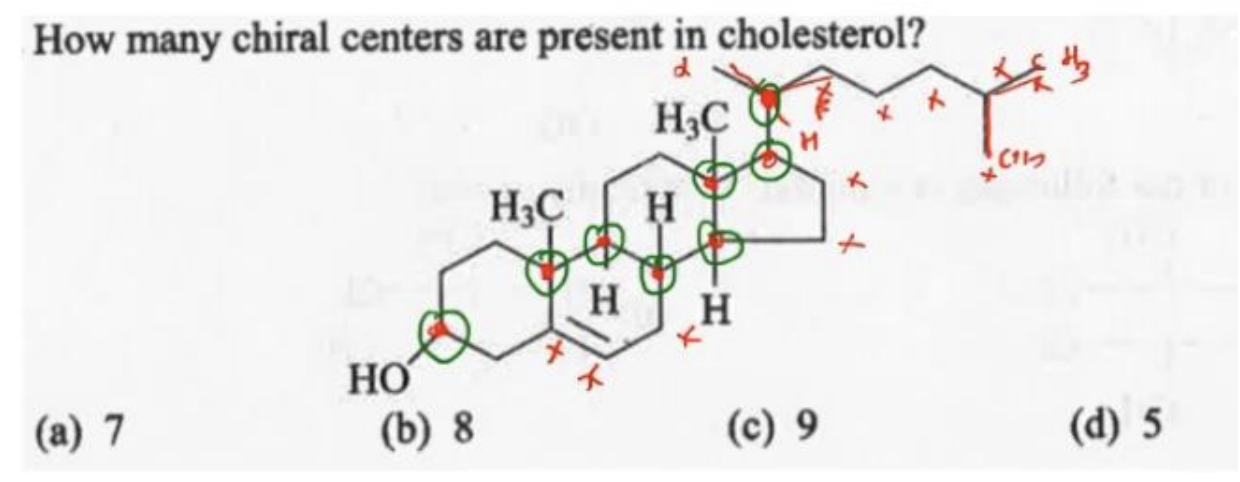
How many chiral centres are present in the cholesterol molecule?
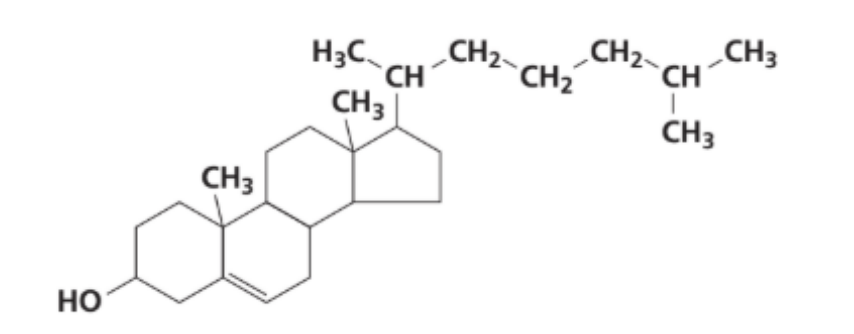
A. 9
B. 8
C. 7
D. 6
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The formula C₄H₉Br represents more than one compound. Using this formula, draw a structure (showing all bonds between carbon atoms) to represent a halogenoalkane that is
i. Primary.
ii. Secondary.
iii. Tertiary.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which analytical technique is used to measure bond lengths in solid compounds?
A. IR spectroscopy.
B. Mass spectroscopy.
C. NMR spectroscopy.
D. X-ray crystallography.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which compound gives this ¹H NMR spectrum?
A. CH₃CH₂OCH₂CH₃
B. CH₃CH₂OH
C. CH₃CH₂CH₃
D. CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
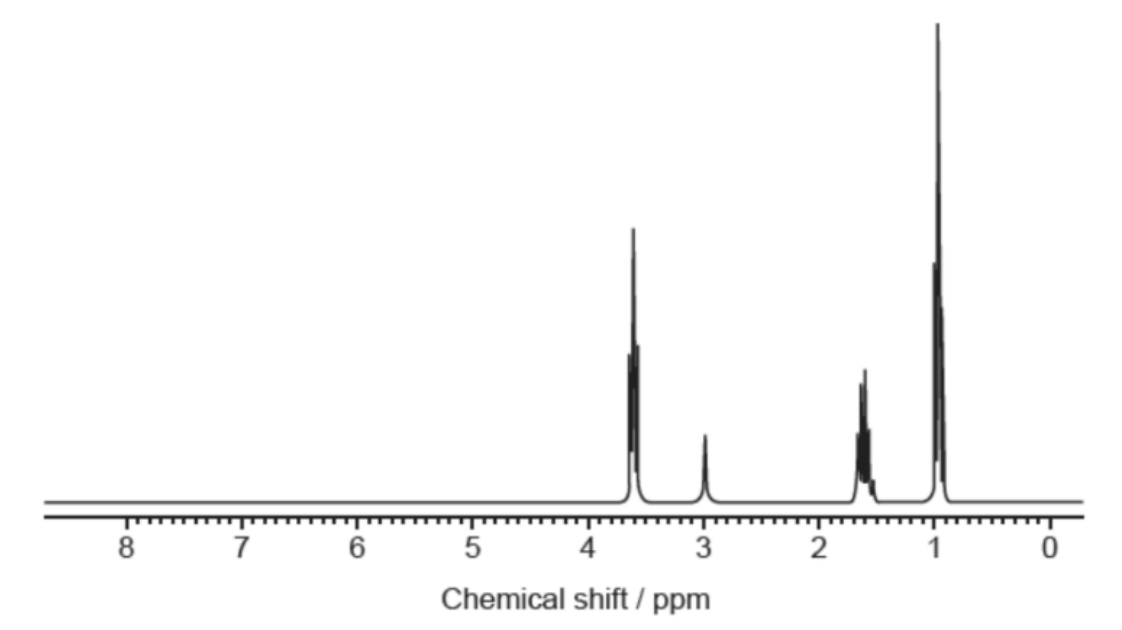
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
a. Explain why IR spectroscopy cannot be used to distinguish between propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol for wavenumbers outside the fingerprint region.
b. Describe how the ¹H NMR spectra of propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol will be different.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
¹H NMR spectroscopy can be used to obtain information about the structure of molecules. The ¹H NMR spectrum of a compound with the formula C₄H₈O₂ exhibits three major peaks. The chemical shifts, areas and splitting patterns of the peaks are given below.
| Chemical shift / ppm | Peak area | Splitting pattern |
| 0.9 | 3 | triplet |
| 2.0 | 2 | quartet |
| 4.1 | 3 | singlet |
a. State the information that can be obtained from the number of signals (peaks) and splitting pattern.
b. Use chemical shifts from the data booklet and the information given above, to deduce the structure of the compound. Explain your answer.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
There are four structural isomers that are alcohols with the formula C₄H₉OH.
a. Explain why the infrared spectra of all four alcohols show very similar absorptions around 3350 cm-1 and 2900 cm-1.
b. Describe how these alcohols can be distinguished using their infrared spectra.
c. Explain why the mass spectra of all four alcohols show a peak at m/z = 74.
d. Suggest the formulas of the fragments formed from C₄H₉OH with the following m/z values:
i. m/z = 57
ii. m/z = 45
e. The numbers of signals (peaks), and the areas under them, in the ¹H NMR spectra of these alcohols can be used to identify them.
i. Explain why the ¹H NMR spectrum of (CH₃)₂CHCH₂OH has four signals (peaks). Predict the ratio of the areas under the peaks.
ii. Deduce the structure of the alcohol whose ¹H NMR spectrum has two signals (peaks) with areas in the ratio 9:1.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Given equimolar concentrations, which substance would produce the largest integral trace (strongest signal)?
A. Si(CH₃)₄.
B. C₇H₁₆.
C. C₆H₆.
D. (CH₃)₃CH.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
How many signals (peaks) are observed in the ¹H NMR spectrum?
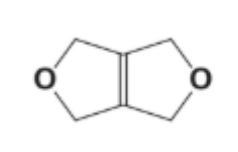
A. 6
B. 4
C. 1
D. 2
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
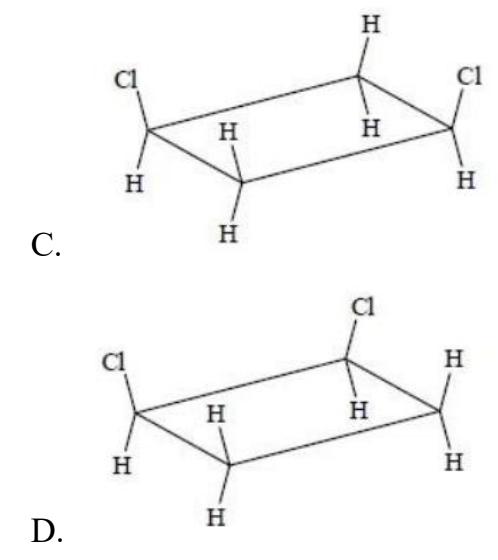
Which structure is a geometric isomer of cis-1,2-dichlorocyclobutane?
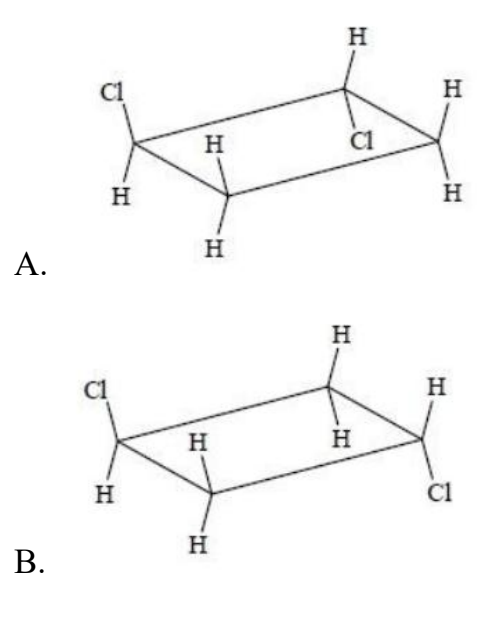
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
Which compound exists as two cis–trans isomers?
A. CF₂=CF₂.
B. CH₂=CHF.
C. CHF₂CH₂F.
D. CHF=CHF.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
Which molecule can show optical activity?
A. CHBrCHF.
B. CH₃CH₂CHFCH₂CH₃.
C. (CH₃)₂CBrF.
D. CH₃CH₂CH(CH₃)F.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
Which types of stereoisomers are shown by 2,4-dimethylhex-2-ene?
A. Enantiomers only.
B. Cis and trans isomers.
C. Cis and trans isomers and enantiomers.
D. Neither cis and trans isomers nor enantiomers.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
What is the name of this compound using the IUPAC rules?
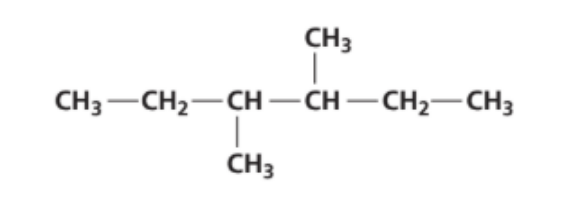
A. 2-ethyl-3-methylpentane.
B. 2,3-diethylbutane.
C. 3-methyl-4-ethylpentane.
D. 3,4-dimethylhexane.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 15
What is the IUPAC name for (CH₃)₂COH(CH₂)₂CH₃?
A. Hexan-3-ol.
B. 2-methylpentan-2-ol.
C. 2-methylpentan-3-ol.
D. Dimethylpentan-1-ol.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 16
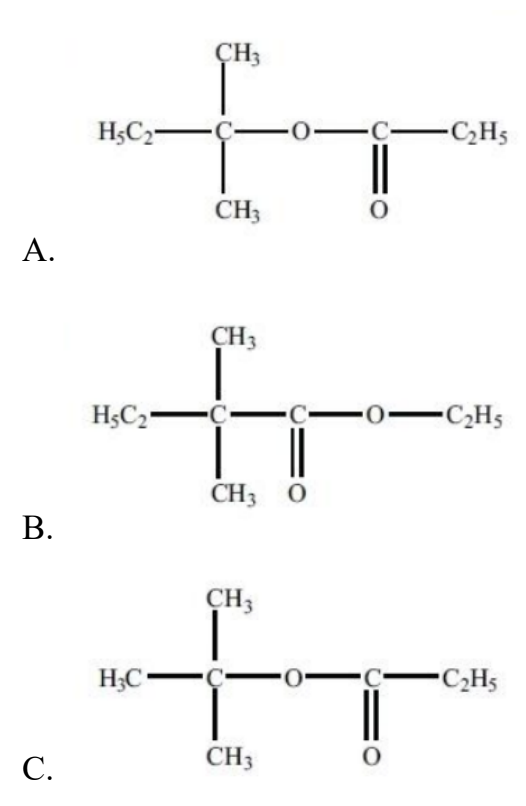
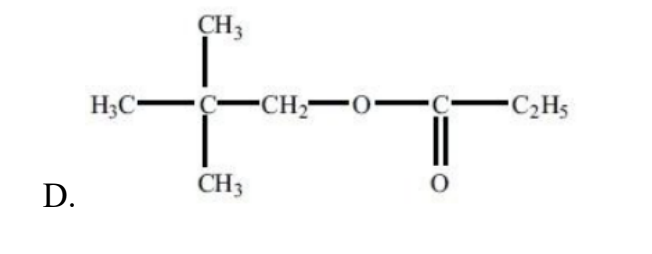
What is the structural formula of the ester formed by reacting propanoic acid with 2- methylbutan-2-ol under appropriate conditions?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 17
Which monomer is used to form the polymer with the following repeating unit?
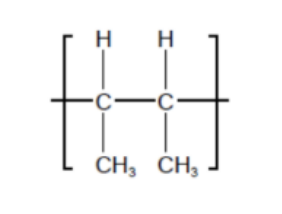
A. CH₃CH=CHCH₃
B. CH₃CH₂CH=CH₂
C. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₃
D. (CH₃)₂C=CH₂
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 18
The biopharmaceutical industry is now a global contributor to the world economy. Atorvastatin, a drug used to lower cholesterol, recently gained attention from the global media. Atorvastatin has the structure shown below.
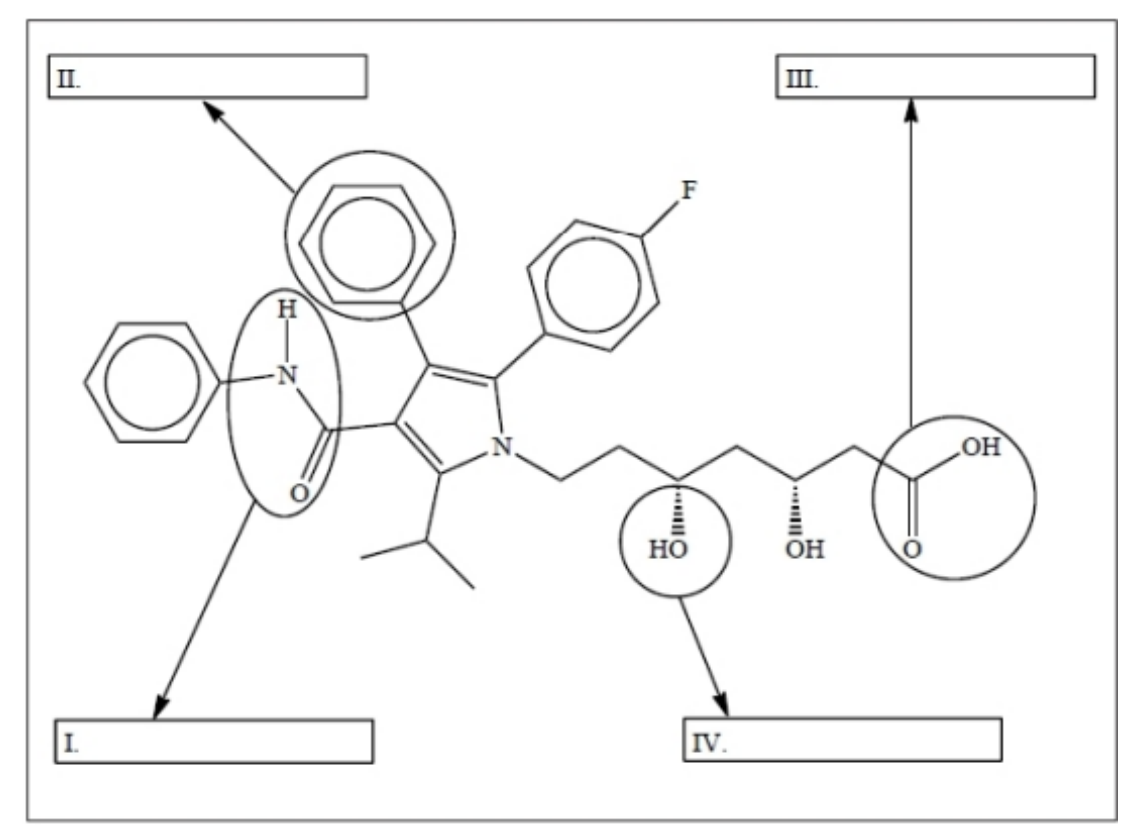
Identify the four functional groups, I, II, III, and IV.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 19
C₈H₁₈ boiling points
| Isomer | Structural formula | Boiling point / °C |
| n-octane | 125.6 | |
| 2-methylheptane | 117.7 | |
| 2,2,4-trimethylpentane | 99.2 |
For a given group of isomers of a particular alkane, how does the boiling point change as the number of carbon side-chains increases?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 20
Which one of the following organic compounds does not exist?
A. An ester which is a structural isomer of a carboxylic acid, C3H6O2.
B. A carboxylic acid which is a structural isomer of an ester, C2H4O2.
C. An aldehyde which is a structural isomer of a ketone, C3H6O.
D. A ketone which is a structural isomer of an aldehyde, C2H4O.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 21
What is the number of structural isomers of C₄H₉I?
A. 4.
B. 5.
C. 7.
D. 8.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 22
In which pair are the compounds not structural isomers?
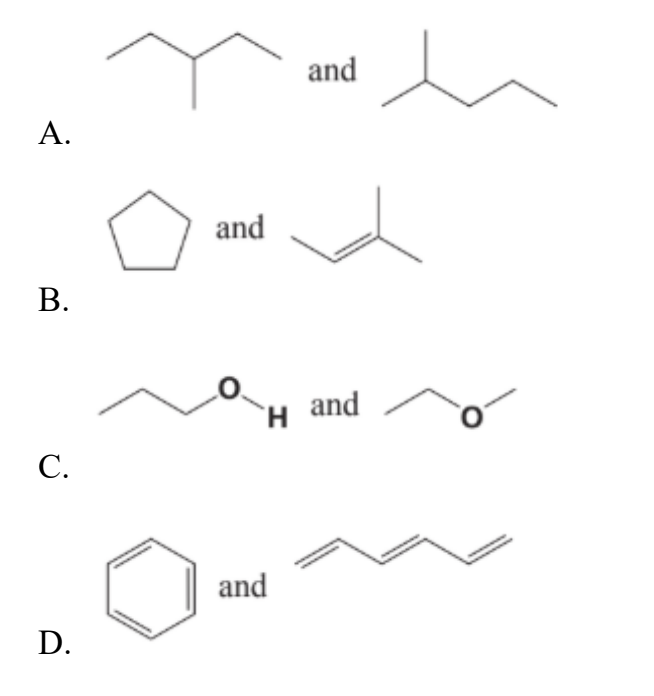
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 23
Which one of the following is a ketone?
A. CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3.
B. CH3CH2COCH3.
C. CH3CH2O(CH2)3CH3.
D. CH3CH2CH2CHO.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 24
Which three compounds form part of a homologous series?
A. C2H2, C2H4, C2H6
B. CH3OH, C3H7OH, CH3(CH2)5OH
C. CH3(CH2)4OH, CH3(CH2)2CH(OH)CH3, CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2OH
D. C2H5CHO, CH3COCH3, CH3(CH2)2OH
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 25
What is the IUPAC name for CH₃(CH₂)₄CHO?
A. Hexan-1-ol.
B. 2-hexanone.
C. Hexanal.
D. Hexanoic acid.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
How many chiral centres are present in the cholesterol molecule?

A. 9
B. 8
C. 7
D. 6
Answer: B. 8
Question 2
The formula C₄H₉Br represents more than one compound. Using this formula, draw a structure (showing all bonds between carbon atoms) to represent a halogenoalkane that is
i. Primary.
ii. Secondary.
iii. Tertiary.
i. Primary halogenoalkane
A primary halogenoalkane has the carbon bonded to bromine attached to only one other carbon
Example: 1-bromobutane → CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–CH₂–Br
ii. Secondary halogenoalkane
A secondary halogenoalkane has the carbon bonded to bromine attached to two other carbons.
Example: 2-bromobutane → CH₃–CH(Br)–CH₂–CH₃
iii. Tertiary halogenoalkane
A tertiary halogenoalkane has the carbon bonded to bromine attached to three other carbons.
Example: 2-bromo-2-methylpropane
CH₃
|
CH₃–C(Br)–CH₃
Question 3
Which analytical technique is used to measure bond lengths in solid compounds?
A. IR spectroscopy.
B. Mass spectroscopy.
C. NMR spectroscopy.
D. X-ray crystallography.
Answer: D. X-ray crystallography.
A. Incorrect:
IR identifies functional groups by detecting bond vibrations (stretching and bending). It provides information about types of bonds but not exact bond lengths or angles.
B. Incorrect:
Mass spectrometry measures the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of ions. It is used to determine molecular mass and structure, not geometric details like bond lengths.
C. Incorrect:
NMR reveals information about the chemical environment of nuclei (e.g., hydrogen or carbon). It helps deduce connectivity and electronic environments, but not precise bond distances in solids.
D. Correct:
X-rays are diffracted by the electron clouds in a crystalline solid. Analysis of the diffraction pattern gives a three-dimensional model of the molecule, showing accurate bond lengths and bond angles.
Question 4
Which compound gives this ¹H NMR spectrum?
A. CH₃CH₂OCH₂CH₃
B. CH₃CH₂OH
C. CH₃CH₂CH₃
D. CH₃CH₂CH₂OH

Answer: B. CH₃CH₂OH
A. Incorrect: CH₃CH₂OCH₂CH₃ (diethyl ether)
Two equivalent ethyl groups → only two signals (CH₃ triplet ~1.1 ppm, O–CH₂ quartet ~3.4–3.6 ppm) with integrals 6H and 4H.
The spectrum has three signals → not A.
B. Correct:
Three sets of protons → three signals expected: CH₃ (3H), CH₂ (2H), and OH (1H). Splitting:
• CH₃ next to CH₂ → triplet near 1.1 ppm (3H)
• CH₂ next to CH₃ and O → quartet near 3.5–3.7 ppm (2H)
• OH → broad singlet around 2–5 ppm (1H, position varies, weak) The spectrum shows exactly: a big triplet ≈1.1 ppm, a quartet ≈3.6 ppm, and a small broad signal ~2–3 ppm → matches ethanol.
C. Incorrect: CH₃CH₂CH₃ (propane)
No oxygen → no downfield peak at 3–4 ppm. Expected two signals: CH₃ (triplet) and central CH₂ (septet/multiplet), both ~0.9–1.6 ppm only.
Spectrum shows a clear downfield signal ~3.6 ppm → not C.
D. Incorrect: CH₃CH₂CH₂OH (propan-1-ol)
Four proton environments (CH₃, CH₂–CH₃, CH₂–OH, OH) → four signals expected. The O–CH₂ would be a triplet (~3.3–3.6 ppm) from coupling to the adjacent CH₂ (2H), not a quartet.
Spectrum shows three signals with a quartet near 3.6 ppm → not D. Why the others are incorrect
Question 5
a. Explain why IR spectroscopy cannot be used to distinguish between propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol for wavenumbers outside the fingerprint region.
b. Describe how the ¹H NMR spectra of propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol will be different.
a. Both propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol are alcohols, so they have the same key functional groups. Each shows a broad O–H stretch around 3200–3600 cm⁻¹, and a C–O stretch around 1050–1150 cm⁻¹.These absorptions occur outside the fingerprint region and are very similar for both molecules. Therefore, IR spectroscopy cannot distinguish them (only the fingerprint region could).
b. Propan-1-ol (CH₃CH₂CH₂OH):
4 sets of proton environments:
• CH₃– (triplet, 3H)
• CH₂– next to CH₃ (sextet or multiplet, 2H)
• CH₂– next to OH (triplet, 2H)
• OH (broad singlet, 1H)
Propan-2-ol (CH₃CHOHCH₃):
3 sets of proton environments:
• Two equivalent CH₃ groups (doublet, 6H)
• CH (multiplet, 1H)
• OH (broad singlet, 1H)
⇒ Propan-1-ol gives four proton environments, while propan-2-ol gives three. In propan-2-ol, there are two equivalent CH₃ groups (6H doublet), unlike in propan-1-ol, which has two different CH₃/CH₂ groups.
Question 6
¹H NMR spectroscopy can be used to obtain information about the structure of molecules. The ¹H NMR spectrum of a compound with the formula C₄H₈O₂ exhibits three major peaks. The chemical shifts, areas and splitting patterns of the peaks are given below.
| Chemical shift / ppm | Peak area | Splitting pattern |
| 0.9 | 3 | triplet |
| 2.0 | 2 | quartet |
| 4.1 | 3 | singlet |
a. State the information that can be obtained from the number of signals (peaks) and splitting pattern.
b. Use chemical shifts from the data booklet and the information given above, to deduce the structure of the compound. Explain your answer.
a. Information from number of signals and splitting pattern
Number of signals (3):
→ The molecule contains three distinct sets of equivalent hydrogen atoms. Splitting pattern:
• Triplet → hydrogens adjacent to a CH₂ group (n+1 = 3 → n = 2 neighboring H).
• Quartet → hydrogens adjacent to a CH₃ group (n+1 = 4 → n = 3 neighboring H).
• Singlet → hydrogens with no neighboring H atoms on adjacent carbon. b. Determine structure using chemical shifts and formula
• Peak at 0.9 ppm (triplet, 3H): typical for CH₃–CH₂– group.
• Peak at 2.0 ppm (quartet, 2H): typical for –CH₂– next to C=O (like in an ester or ketone).
• Peak at 4.1 ppm (singlet, 3H): typical for –OCH₃ group.
• Formula C₄H₈O₂ suggests an ester (fits both oxygen atoms).
Hence, the structure that fits is ethyl methanoate (methyl formate)? Check again: C₃H₆O₂ for methyl acetate, but we have C₄H₈O₂ → that’s ethyl acetate (CH₃COOCH₂CH₃). Let’s match:
• CH₃– next to CH₂ → 0.9 ppm triplet (3H)
• CH₂– next to CH₃ and C=O → 2.0 ppm quartet (2H)
• CH₃–O– (ester methoxy) → 4.1 ppm singlet (3H)
⇒ All matches with ethyl acetate (CH₃COOCH₂CH₃).
Question 7
There are four structural isomers that are alcohols with the formula C₄H₉OH.
a. Explain why the infrared spectra of all four alcohols show very similar absorptions around 3350 cm-1 and 2900 cm-1.
b. Describe how these alcohols can be distinguished using their infrared spectra.
c. Explain why the mass spectra of all four alcohols show a peak at m/z = 74.
d. Suggest the formulas of the fragments formed from C₄H₉OH with the following m/z values:
i. m/z = 57
ii. m/z = 45
e. The numbers of signals (peaks), and the areas under them, in the ¹H NMR spectra of these alcohols can be used to identify them.
i. Explain why the ¹H NMR spectrum of (CH₃)₂CHCH₂OH has four signals (peaks). Predict the ratio of the areas under the peaks.
ii. Deduce the structure of the alcohol whose ¹H NMR spectrum has two signals (peaks) with areas in the ratio 9:1.
a. All show a broad O–H stretch around 3200–3600 cm⁻¹ (≈3350 cm⁻¹) and sp³ C–H stretches at ≈2850–2960 cm⁻¹ (≈2900 cm⁻¹), because each isomer has the same functional groups (O–H and alkyl C–H).
b. They can be distinguished by their fingerprint region (<1500 cm⁻¹) and by the C–O stretch, which shifts with class of alcohol:
primary < secondary < tertiary (≈1050–1150 cm⁻¹).
c. All have the same molecular formula (C₄H₁₀O), so each mass spectrum shows an M⁺ molecular ion at m/z = 74.
d. Likely fragment ions
i. m/z 57: C₄H₉⁺ (tert-butyl/butyl cation)
ii. m/z 45: C₂H₅O⁺ (ethoxy/CH₃CHOH⁺)
e. ¹H NMR
i. For (CH₃)₂CHCH₂OH: four sets of protons → 4 signals.
Integration (including OH) = 6 : 1 : 2 : 1 (two equivalent CH₃; one methine CH; one CH₂ next to OH; one OH).
ii. Two signals with ratio 9 : 1 corresponds to (CH₃)₃COH (2-methyl-2-propanol, tert butanol): nine equivalent methyl H and one OH.
Question 8
Given equimolar concentrations, which substance would produce the largest integral trace (strongest signal)?
A. Si(CH₃)₄.
B. C₇H₁₆.
C. C₆H₆.
D. (CH₃)₃CH.
Answer: B. C₇H₁₆.
For equimolar samples, the total integral in a ¹H NMR spectrum is proportional to the total number of hydrogens in the molecule (since the integral sums all proton signals).
• Si(CH₃)₄ → 12 H
• C₇H₁₆ → 16 H ← largest
• C₆H₆ → 6 H
• (CH₃)₃CH → 10 H
Thus C₇H₁₆ gives the largest integral (strongest overall signal).
Question 9
How many signals (peaks) are observed in the ¹H NMR spectrum?

A. 6
B. 4
C. 1
D. 2
Answer: D. 2
Each CH₂ group next to oxygen (–CH₂–O–) experiences the same environment because of symmetry. All hydrogen atoms on these CH₂ groups are equivalent. Therefore, there is only one unique proton environment in the molecule. Therefore, only one signal will be observed in the compound. However, 1H NMR spectra need a reference so that the chemical shift can be measured in ppm. This reference is often tetramethylsilane Si(CH3)4 which gives a strong single signal at 0 ppm due to the 12 equivalent hydrogen atoms so actually two signals may well be observed, one from the compound and one from the reference.
Question 10
Which structure is a geometric isomer of cis-1,2-dichlorocyclobutane?


Answer: A
A. Correct: A has one Cl up, one Cl is down → trans-1,2-dichlorocyclobutane, which is the geometric isomer of the cis compound.
B. Incorrect: Although B has one Cl up, one Cl is down, the two Cl atoms are at positions 1 and 3.
C. Incorrect: The two Cl atoms are at positions 1 and 3.
D. Incorrect: Both Cl are up → cis-1,2-dichlorocyclobutane
Question 11
Which compound exists as two cis–trans isomers?
A. CF₂=CF₂.
B. CH₂=CHF.
C. CHF₂CH₂F.
D. CHF=CHF.
Answer: D. CHF=CHF.
A. Incorrect: CF₂=CF₂
Each carbon of the double bond is bonded to two identical atoms (two fluorines) → No cis–trans (`frac{E}{Z}`) isomerism possible.
B. Incorrect: CH₂=CHF
The left carbon has two identical H atoms → No geometric isomerism.
C. Incorrect: CHF₂CH₂F
This is a saturated molecule (no double bond) → No cis–trans isomerism.
D. Correct: CHF=CHF
Each carbon in the double bond is attached to:
one H and one F → two different substituents.
⇒ CHF=CHF can exist as cis–CHF=CHF (Z) and trans–CHF=CHF (E) isomers.
Question 12
Which molecule can show optical activity?
A. CHBrCHF.
B. CH₃CH₂CHFCH₂CH₃.
C. (CH₃)₂CBrF.
D. CH₃CH₂CH(CH₃)F.
Answer: D. CH₃CH₂CH(CH₃)F.
A. Incorrect:
CHBrCHF → This is an alkene (CHBr=CHF). Alkenes don’t have an sp³ stereogenic center; `frac{E}{Z}` isomerism is not optical activity. Not chiral.
B. Incorrect:
CH₃CH₂CHFCH₂CH₃ → The carbon bearing F is attached to two identical ethyl groups (CH₃CH₂– on both sides), plus H and F → Not four different groups. Achiral. C. Incorrect:
(CH₃)₂CBrF → Central carbon has Br, F, and two methyls → two identical substituents. Achiral.
D. Correct:
CH₃CH₂CH(CH₃)F → The starred carbon is attached to four different groups (H, F, CH₃, CH₃CH₂). → Chiral → optically active.
Question 13
Which types of stereoisomers are shown by 2,4-dimethylhex-2-ene?
A. Enantiomers only.
B. Cis and trans isomers.
C. Cis and trans isomers and enantiomers.
D. Neither cis and trans isomers nor enantiomers.
Answer: D. Neither cis and trans isomers nor enantiomers.
Step 1. Write the structure of 2,4-dimethylhex-2-ene
CH₃–C(CH₃)=C(CH₃)–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃
Step 2. Check for cis–trans (`frac{E}{Z}`) isomerism
• Cis–trans (geometric) isomerism requires each carbon of the C=C to have two different substituents.
• The left carbon of the C=C has two methyl groups → identical substituents Therefore, no cis–trans () is`frac{E}{Z}`omerism possible.
Step 3. Check for chiral (enantiomeric) centers
There is no sp³ carbon bonded to four different groups. → There are no chiral centers, hence no enantiomers.
⇒ 2,4-dimethylhex-2-ene shows neither cis–trans isomerism nor enantiomerism
Question 14
What is the name of this compound using the IUPAC rules?

A. 2-ethyl-3-methylpentane.
B. 2,3-diethylbutane.
C. 3-methyl-4-ethylpentane.
D. 3,4-dimethylhexane.
Answer: D. 3,4-dimethylhexane.
• Longest continuous chain has 6 carbons → hexane.
• There are two methyl substituents: one on the 3rd carbon and one on the 4th carbon (whichever end you start from gives 3,4).
→ The correct IUPAC name is 3,4-dimethylhexane.
Question 15
What is the IUPAC name for (CH₃)₂COH(CH₂)₂CH₃?
A. Hexan-3-ol.
B. 2-methylpentan-2-ol.
C. 2-methylpentan-3-ol.
D. Dimethylpentan-1-ol.
Answer: B. 2-methylpentan-2-ol.
(CH₃)₂C(OH)(CH₂)₂CH₃ has a longest continuous chain of five carbons that must include the carbon bearing the –OH. Number from the end giving the –OH the lowest locant → the –OH is on C-2. At that same carbon there is one extra methyl substituent (the other methyl is counted as the chain terminus).
→ 2-methylpentan-2-ol.
Question 16
What is the structural formula of the ester formed by reacting propanoic acid with 2- methylbutan-2-ol under appropriate conditions?


Answer: A
Propanoic acid + 2-methylbutan-2-ol → an ester of the form
CH₃CH₂C(=O)O–C(CH₃)₂CH₂CH₃
Question 17
Which monomer is used to form the polymer with the following repeating unit?

A. CH₃CH=CHCH₃
B. CH₃CH₂CH=CH₂
C. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₃
D. (CH₃)₂C=CH₂
Answer: D. (CH₃)₂C=CH₂
The repeating unit shows:
–CH(CH3)–CH(CH3)–ₙ
That means each carbon in the polymer chain bears one methyl group (–CH₃). Therefore, the monomer must be 2-methylpropene, also known as isobutene. Its structure is: (CH₃)₂C = CH₂
Question 18
The biopharmaceutical industry is now a global contributor to the world economy. Atorvastatin, a drug used to lower cholesterol, recently gained attention from the global media. Atorvastatin has the structure shown below.

Identify the four functional groups, I, II, III, and IV.
I – Amide (a cyclic amide/lactam: –CONH–)
II – Aromatic (benzene/phenyl) ring
III – Carboxylic acid (–COOH)
IV – Alcohol (–OH, secondary alcohol on the side chain)
Question 19
C₈H₁₈ boiling points
| Isomer | Structural formula | Boiling point / °C |
| n-octane | 125.6 | |
| 2-methylheptane | 117.7 | |
| 2,2,4-trimethylpentane | 99.2 |
For a given group of isomers of a particular alkane, how does the boiling point change as the number of carbon side-chains increases?
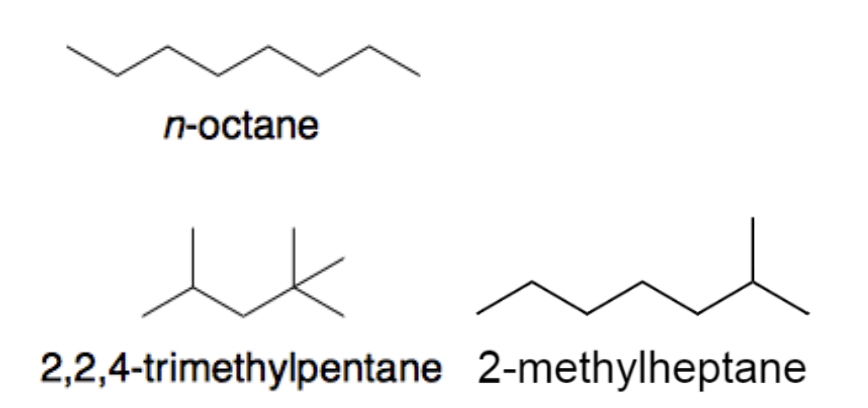
As the number of carbon side-chains (branching) increases, the molecule becomes more compact with a smaller surface area, so London dispersion forces are weaker → lower boiling point.
Question 20
Which one of the following organic compounds does not exist?
A. An ester which is a structural isomer of a carboxylic acid, C3H6O2.
B. A carboxylic acid which is a structural isomer of an ester, C2H4O2.
C. An aldehyde which is a structural isomer of a ketone, C3H6O.
D. A ketone which is a structural isomer of an aldehyde, C2H4O.
Answer: D. A ketone which is a structural isomer of an aldehyde, C2H4O.
A. Incorrect:
An ester (C₃H₆O₂) structural isomer of a carboxylic acid (C₃H₆O₂) → Exists. Examples:
• Ester: methyl ethanoate (CH₃COOCH₃)
• Acid: propanoic acid (CH₃CH₂COOH)
→ Both have formula C₃H₆O₂
B. Incorrect:
A carboxylic acid (C₂H₄O₂) structural isomer of an ester (C₂H₄O₂) → Exists. Examples:
• Acid: ethanoic acid (CH₃COOH)
• Ester: methyl formate (HCOOCH₃)
C. Incorrect:
An aldehyde (C₃H₆O) structural isomer of a ketone (C₃H₆O) → Exists. Examples:
• Aldehyde: propanal (CH₃CH₂CHO)
• Ketone: propanone (CH₃COCH₃)
D. Correct:
A ketone (C₂H₄O) structural isomer of an aldehyde (C₂H₄O) → Does not exist.
• The formula C₂H₄O corresponds to ethanal (CH₃CHO), an aldehyde.
• You cannot form a ketone with only 2 carbons, since a ketone requires at least 3 carbons (–CO– group must be between two carbon atoms).
Question 21
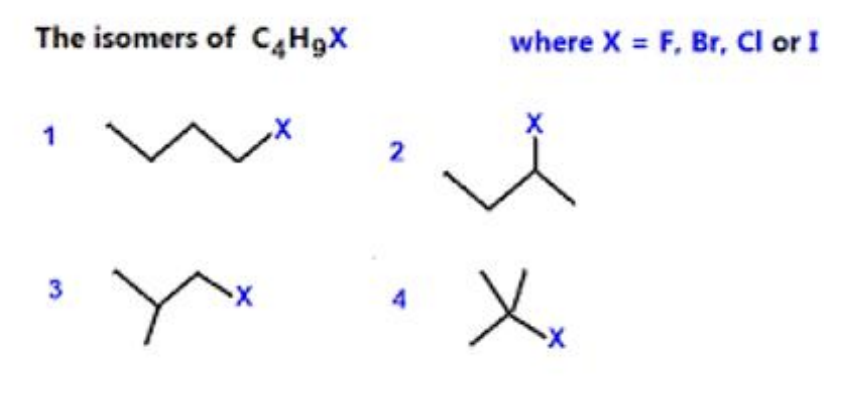
What is the number of structural isomers of C₄H₉I?
A. 4.
B. 5.
C. 7.
D. 8.
Answer: A. 4.
Question 22
In which pair are the compounds not structural isomers?

Answer: D
A. Incorrect:
Both compounds have the same formula C6H14. But they have different structure, one is 3-methylpentane, one is 2-methylpentane. Therefore, they are structure isomers. B. Incorrect:
The ring and the alkene shown have the same molecular formula (cycloalkane vs alkene) but different connectivity → Structural isomers.
C. Incorrect:
Alcohol vs ether with the same molecular formula (C₃H₈O) → functional (structural) isomers.
D. Correct:
• Benzene = C₆H₆
• The chain on the right is 1,3,5-hexatriene = C₆H₈
Different formulas (C₆H₆ vs C₆H₈) ⇒ they are not isomers.
Question 23
Which one of the following is a ketone?
A. CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3.
B. CH3CH2COCH3.
C. CH3CH2O(CH2)3CH3.
D. CH3CH2CH2CHO.
Answer: B. CH3CH2COCH3.
A. Incorrect: CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3. → Has –OH group → alcohol, not a ketone.
B. Correct: CH3CH2COCH3 → Has C=O in the middle of the chain (propan-2-one structure) → ketone.
C. Incorrect: CH3CH2O(CH2)3CH3. → Has –O– linkage → ether, not a ketone.
D. Incorrect: CH3CH2CH2CHO → Has –CHO at the end → aldehyde, not a ketone
Question 24
Which three compounds form part of a homologous series?
A. C2H2, C2H4, C2H6
B. CH3OH, C3H7OH, CH3(CH2)5OH
C. CH3(CH2)4OH, CH3(CH2)2CH(OH)CH3, CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2OH
D. C2H5CHO, CH3COCH3, CH3(CH2)2OH
Answer: B. CH3OH, C3H7OH, CH3(CH2)5OH
A. Incorrect:
C2H2, C2H4, C2H6 – Different functional groups (alkyne, alkene, alkane) → Not one homologous series.
B. Correct:
CH3OH, C3H7OH, CH3(CH2)5OH - All alcohols (same functional group –OH, same general formula CnH2n+2O). They are simply different members (methanol, propanol, hexanol), i.e., part of the same homologous series.
C. Incorrect:
Contains alcohols but mixes primary and secondary alcohols; these do not belong to the same homologous series in typical syllabus definitions (their chemical properties differ, e.g., oxidation).
D. Incorrect:
Mixes aldehyde, ketone, and alcohol → Different functional groups → Not a homologous series.
Question 25
What is the IUPAC name for CH₃(CH₂)₄CHO?
A. Hexan-1-ol.
B. 2-hexanone.
C. Hexanal.
D. Hexanoic acid.
Answer: C. Hexanal.
Given: CH3(CH2)4CHO
= CH3–CH2–CH2–CH2–CH2–CHO
• Identify the longest carbon chain including the aldehyde group: 6 carbons → prefix = hex-
• Functional group: –CHO = aldehyde, suffix = -al
• No other substituents → name is simply hexanal.
Question 1
How many chiral centres are present in the cholesterol molecule?

A. 9
B. 8
C. 7
D. 6
Question 2
The formula C₄H₉Br represents more than one compound. Using this formula, draw a structure (showing all bonds between carbon atoms) to represent a halogenoalkane that is
i. Primary.
ii. Secondary.
iii. Tertiary.
Question 3
Which analytical technique is used to measure bond lengths in solid compounds?
A. IR spectroscopy.
B. Mass spectroscopy.
C. NMR spectroscopy.
D. X-ray crystallography.
Question 4
Which compound gives this ¹H NMR spectrum?
A. CH₃CH₂OCH₂CH₃
B. CH₃CH₂OH
C. CH₃CH₂CH₃
D. CH₃CH₂CH₂OH

Question 5
a. Explain why IR spectroscopy cannot be used to distinguish between propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol for wavenumbers outside the fingerprint region.
b. Describe how the ¹H NMR spectra of propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol will be different.
Question 6
¹H NMR spectroscopy can be used to obtain information about the structure of molecules. The ¹H NMR spectrum of a compound with the formula C₄H₈O₂ exhibits three major peaks. The chemical shifts, areas and splitting patterns of the peaks are given below.
| Chemical shift / ppm | Peak area | Splitting pattern |
| 0.9 | 3 | triplet |
| 2.0 | 2 | quartet |
| 4.1 | 3 | singlet |
a. State the information that can be obtained from the number of signals (peaks) and splitting pattern.
b. Use chemical shifts from the data booklet and the information given above, to deduce the structure of the compound. Explain your answer.
Question 7
There are four structural isomers that are alcohols with the formula C₄H₉OH.
a. Explain why the infrared spectra of all four alcohols show very similar absorptions around 3350 cm-1 and 2900 cm-1.
b. Describe how these alcohols can be distinguished using their infrared spectra.
c. Explain why the mass spectra of all four alcohols show a peak at m/z = 74.
d. Suggest the formulas of the fragments formed from C₄H₉OH with the following m/z values:
i. m/z = 57
ii. m/z = 45
e. The numbers of signals (peaks), and the areas under them, in the ¹H NMR spectra of these alcohols can be used to identify them.
i. Explain why the ¹H NMR spectrum of (CH₃)₂CHCH₂OH has four signals (peaks). Predict the ratio of the areas under the peaks.
ii. Deduce the structure of the alcohol whose ¹H NMR spectrum has two signals (peaks) with areas in the ratio 9:1.
Question 8
Given equimolar concentrations, which substance would produce the largest integral trace (strongest signal)?
A. Si(CH₃)₄.
B. C₇H₁₆.
C. C₆H₆.
D. (CH₃)₃CH.
Question 9
How many signals (peaks) are observed in the ¹H NMR spectrum?

A. 6
B. 4
C. 1
D. 2
Question 10
Which structure is a geometric isomer of cis-1,2-dichlorocyclobutane?


Question 11
Which compound exists as two cis–trans isomers?
A. CF₂=CF₂.
B. CH₂=CHF.
C. CHF₂CH₂F.
D. CHF=CHF.
Question 12
Which molecule can show optical activity?
A. CHBrCHF.
B. CH₃CH₂CHFCH₂CH₃.
C. (CH₃)₂CBrF.
D. CH₃CH₂CH(CH₃)F.
Question 13
Which types of stereoisomers are shown by 2,4-dimethylhex-2-ene?
A. Enantiomers only.
B. Cis and trans isomers.
C. Cis and trans isomers and enantiomers.
D. Neither cis and trans isomers nor enantiomers.
Question 14
What is the name of this compound using the IUPAC rules?

A. 2-ethyl-3-methylpentane.
B. 2,3-diethylbutane.
C. 3-methyl-4-ethylpentane.
D. 3,4-dimethylhexane.
Question 15
What is the IUPAC name for (CH₃)₂COH(CH₂)₂CH₃?
A. Hexan-3-ol.
B. 2-methylpentan-2-ol.
C. 2-methylpentan-3-ol.
D. Dimethylpentan-1-ol.
Question 16
What is the structural formula of the ester formed by reacting propanoic acid with 2- methylbutan-2-ol under appropriate conditions?


Question 17
Which monomer is used to form the polymer with the following repeating unit?

A. CH₃CH=CHCH₃
B. CH₃CH₂CH=CH₂
C. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₃
D. (CH₃)₂C=CH₂
Question 18
The biopharmaceutical industry is now a global contributor to the world economy. Atorvastatin, a drug used to lower cholesterol, recently gained attention from the global media. Atorvastatin has the structure shown below.

Identify the four functional groups, I, II, III, and IV.
Question 19
C₈H₁₈ boiling points
| Isomer | Structural formula | Boiling point / °C |
| n-octane | 125.6 | |
| 2-methylheptane | 117.7 | |
| 2,2,4-trimethylpentane | 99.2 |
For a given group of isomers of a particular alkane, how does the boiling point change as the number of carbon side-chains increases?
Question 20
Which one of the following organic compounds does not exist?
A. An ester which is a structural isomer of a carboxylic acid, C3H6O2.
B. A carboxylic acid which is a structural isomer of an ester, C2H4O2.
C. An aldehyde which is a structural isomer of a ketone, C3H6O.
D. A ketone which is a structural isomer of an aldehyde, C2H4O.
Question 21
What is the number of structural isomers of C₄H₉I?
A. 4.
B. 5.
C. 7.
D. 8.
Question 22
In which pair are the compounds not structural isomers?

Question 23
Which one of the following is a ketone?
A. CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3.
B. CH3CH2COCH3.
C. CH3CH2O(CH2)3CH3.
D. CH3CH2CH2CHO.
Question 24
Which three compounds form part of a homologous series?
A. C2H2, C2H4, C2H6
B. CH3OH, C3H7OH, CH3(CH2)5OH
C. CH3(CH2)4OH, CH3(CH2)2CH(OH)CH3, CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2OH
D. C2H5CHO, CH3COCH3, CH3(CH2)2OH
Question 25
What is the IUPAC name for CH₃(CH₂)₄CHO?
A. Hexan-1-ol.
B. 2-hexanone.
C. Hexanal.
D. Hexanoic acid.