Question 1
The following mechanism is proposed for a reaction:
A + B → C + D slow step
D + B → A + E fast step
a. Classify substances B and D as reactant, product, catalyst, or intermediate, based on the proposed mechanism.
b. Deduce the rate expression.
c. Calculate the initial rate of reaction for experiment 2, if measured under the same conditions.
| Experiment | [A] / mol dm-3 | [B] / mol dm-3 | Initial rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 1 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 1.20 |
| 2 | 0.300 | 0.200 |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Determine the orders of reaction of the reactants and the overall rate expression for the reaction between 2-bromobutane and aqueous sodium hydroxide using the data in the table.
| Experiment | [NaOH] / mol dm-3 | [C₄H₉Br] / mol dm-3 | Rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.66 × 10-3 |
| 2 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 8.31 × 10-4 |
| 3 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1.02 × 10-4 |
| 4 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 8.29 × 10-4 |
a. Determine the rate constant, k, with its units, using the data from experiment 3.
b. Identify the molecularity of the rate-determining step in this reaction.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
a. Nitrogen oxide is in equilibrium with dinitrogen dioxide.
2NO(g) ⇌ N₂O₂(g) ΔH° < 0
Deduce, giving a reason, the effect of increasing the temperature on the concentration of N₂O₂.
b. A two-step mechanism is proposed for the formation of NO₂(g) from NO(g) that involves an exothermic equilibrium process.
First step: 2NO(g) ⇌ N₂O₂(g) fast
Second step: N₂O₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2NO₂(g) slow
Deduce the rate expression for the mechanism.
c. The rate constant for a reaction doubles when the temperature is increased from 25.0 °C to 35 °C. Calculate the activation energy, Eₐ, in kJ mol⁻¹ for the reaction using section 1 and 2 of the data booklet.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which statement about a reaction best describes the relationship between the temperature, T, and the rate constant, k?
A. As T increases, k decreases linearly.
B. As T increases, k decreases non-linearly.
C. As T increases, k increases linearly.
D. As T increases, k increases non-linearly.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
For the gas phase reaction:
A(g) + B(g) → C(g)
The experimentally determined rate expression is: rate = k[A][B]²
By what factor will the rate change if the concentration of A is tripled and the concentration of B is halved?
A. 0.75
B. 1.5
C. 6
D. 12
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
The diagram below shows the energy changes for a reaction with and without a catalyst. Which symbols represent the activation energy, Eₐ, and the enthalpy change, ΔH, for the reaction with a catalyst?

| Eₐ (with a catalyst) | ΔH | |
| A. | x | z |
| B. | y | z |
| C. | z | x |
| D. | y − x | z |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Which statement is correct?
A. The value of the rate constant, k, is independent of temperature and is deduced from the equilibrium constant, Kc.
B. The value of the rate constant, k, is independent of temperature and the overall reaction order determines its units.
C. The value of the rate constant, k, is temperature dependent and is deduced from the equilibrium constant, Kc.
D. The value of the rate constant, k, is temperature dependent and the overall reaction order determines its units.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
What is the intercept on the y-axis when a graph of ln k is plotted against `frac{1}{T}` on the x axis?
ln k = `- frac{E_a){RT}+ln A`
A. ln A
B. `-frac{E_a}{R}`
C. `-frac{R}{E_a}`
D. Ea
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Sodium bisulfite, NaHSO₃, reacts with methanal, converting it into a non-toxic compound which can be disposed safely. The overall equation is:
HSO₃⁻(aq) + H₂CO(aq) → CH₂(OH)SO₃⁻
The initial rate of this reaction can be studied by the ‘clock’ method using phenolphthalein as an indicator. The sudden appearance of the pink colour indicates the time to stop the stopwatch.
A series of experiments was carried out using different concentrations of HSO₃⁻ and H₂CO. The results obtained are shown below:
| Experiment | [HSO₃⁻]/mol dm-3 | [H₂CO]/mol dm-3 | Time for appearance of pink colour /s |
| 1 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 60 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 0.050 | 48 |
| 3 | 0.050 | 0.060 | 40 |
| 4 | 0.040 | 0.070 | 34 |
a. State the relationship between the time taken for the pink colour to appear and the initial rate of reaction.
b. Calculate the relative rates (1/time) for each of these four experiments and use them to deduce the order of reaction with respect to the two reactants.
c. State the rate equation for the reaction and state the units for the rate constant. Kinetic studies suggest that the mechanism involves the following two elementary steps:
Step 1: Bisulfite ion reacts with a water molecule via an acid-base reaction, forming sulfite ions, SO₃2-.
Step 2: The resulting sulfite ions react with methanal to produce the non-toxic product, CH₂(OH)SO₃⁻, and hydroxide ions.
d. Formulate balanced equations for these two elementary steps.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
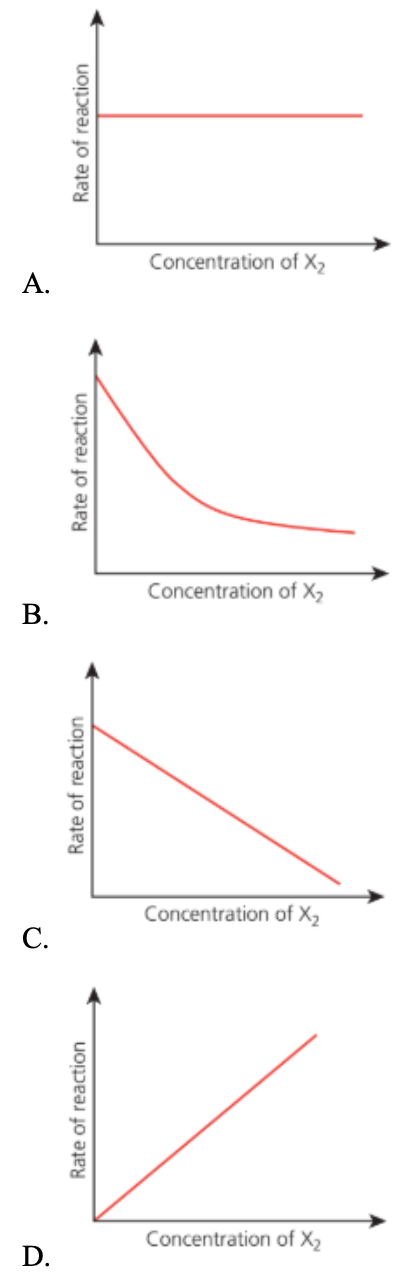
Question 10
The equation of a reaction involving X₂ is:
2X₂ → X + X₃
Which graph shows that the reaction is first order with respect to X₂?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
Which of the following statements of an Arrhenius plot of lnk against `frac{1}{T}*K^(-1)`is correct?
ln k = `(frac{-E_a}{R})*frac{1}{T}+lnA`
A. The graph has a positive gradient.
B. The activation energy can be calculated from the gradient.
C. The y-intercept is the Arrhenius factor, A.
D. The gradient becomes steeper when a catalyst is added.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
Under acidic conditions hydrogen peroxide oxidizes iodide ions to iodine molecules in the following reaction:
H₂O₂(aq) + 2H⁺(aq) + 2I⁻(aq) → 2H₂O(l) + I₂(aq)
Kinetic studies of this reaction using different initial concentrations of reactants at a constant temperature:
| Initial [H₂O₂(aq)] / mol dm-3 | Initial [H⁺(aq)] / mol dm-3 | Initial [I⁻(aq)] / mol dm-3 | Initial rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 0.005 | 0.05 | 0.015 | 1.31 × 10⁻⁶ |
| 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.015 | 2.63 × 10⁻⁶ |
| 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 5.25 × 10⁻⁶ |
| 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 5.25 × 10⁻⁶ |
What is the overall order of the reaction?
A. Zero (zeroth) order.
B. First order.
C. Second order.
D. Third order.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
A reaction proceeds by the following mechanism:
Step 1: A + B ⇌ X fast
Step 2: X + A → P slow
Which rate equation is consistent with this mechanism?
A. rate = k[A]²[B].
B. rate = k[A]²[B][X].
C. rate = k[X][P].
D. rate = k[A][B].
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
The reaction between X and Y, in aqueous solution, follows the general rate equation:
rate = k[X]a[Y]b
The initial rate of this reaction was measured for different concentrations of X and Y, and the following results were obtained.
| [X] / mol dm-3 | [Y] / mol dm-3 | Initial rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 0.040 | 2.40 | 2.63 × 10-3 |
| 0.040 | 4.80 | 1.05 × 10-2 |
| 0.040 | 7.20 | 2.37 × 10-2 |
| 0.160 | 2.40 | 1.05 × 10-2 |
What are the values of a and b for the rate equation?
| a | b | |
| A. | 1 | 1 |
| B. | 0 | 2 |
| C. | 1 | 2 |
| D. | 2 | 1 |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
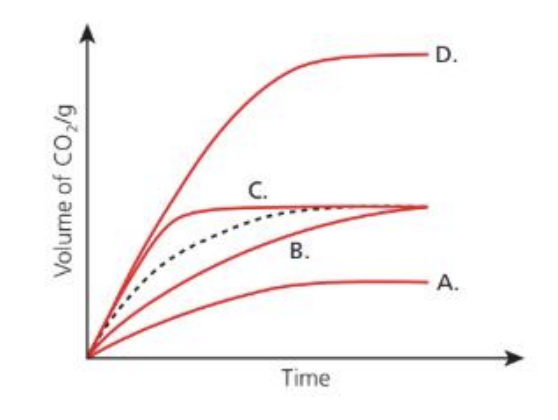
Question 15
The dotted line represents the volume of carbon dioxide released when excess magnesium carbonate is added to dilute nitric acid.
Which graph represents the production of carbon dioxide when excess magnesium carbonate is added to the same volume of nitric acid of double concentration?
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 16
The energy profile diagram of the reversible reaction between M and N is shown in the figure.
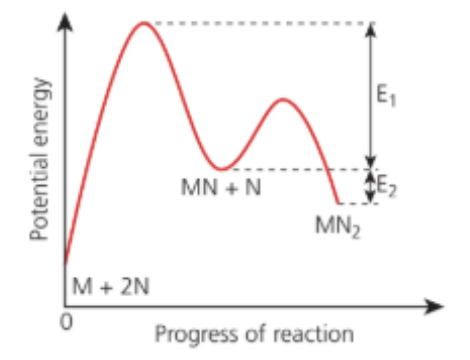
Which of the following statements are correct?
I. The activation energy of the reverse reaction is E1 + E2.
II. Rate equation of the reaction is rate = k[M][N]2.
III. The equilibrium [MN2] increases as temperature increases.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 17
Which is correct for the reaction mechanism shown?
2A → B + 2C slow
B + C → D + E fast
C + D → E + F fast
| Equation of overall reaction | Rate equation | |
| A. | 2A → E + F | rate = k[A]² |
| B. | 2A → 2E + F | rate = k[C][D] |
| C. | 2A + B + 2C + D → 2E + F | rate = k[A]²[B][C]²[D] |
| D. | 2A → 2E + F | rate = k[A]² |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
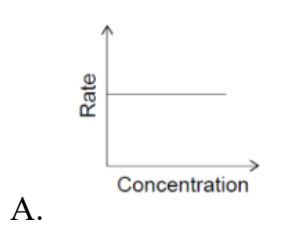
Question 18
Which graph is obtained from a first order reaction?

Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 19
The energy profile diagram of a reaction is shown in the figure.

Which of the following is true about the reaction?
A. The reaction occurs in two elementary steps.
B. The reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings.
C. The last step of the reaction is the rate-determining step.
D. The products are energetically more stable than the reactants.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 20
The dotted line represents the formation of oxygen, O₂ (g), from the uncatalysed complete decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H₂O₂ (aq).

Which curve represents a catalysed reaction under the same conditions?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 21
Which conditions must be met for a reaction to take place?
I. Reactants collide with sufficient energy.
II. Reactants collide with correct orientation.
III. Reactants must be in the same state.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 22
Magnesium reacts with sulfuric acid:
Mg(s) + H₂SO₄(aq) → MgSO₄(aq) + H₂(g)
The graph shows the results of an experiment using excess magnesium ribbon and dilute sulfuric acid.

a. Outline why the rate of the reaction decreases with time.
b. Sketch, on the same graph, the expected results if the experiment were repeated using powdered magnesium, keeping its mass and all other variables unchanged.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 23
The graph below shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies at a particular temperature.

The rate at which dinitrogen monoxide decomposes is significantly increased by a metal oxide catalyst.
Annotate and use the graph to outline why a catalyst has this effect.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 24
The reaction between ammonium iodide and potassium nitrite in aqueous solution can be represented by the equation:
NH₄I (aq) + KNO₂ (aq) → N₂ (g) + 2H₂O (l) + KI (aq)
The graph below shows the total volume of nitrogen gas produced in a sealed gas syringe at 30 second intervals from a mixture of ammonium iodide and potassium nitrite in aqueous solution at 25°C.

a. i. State how the rate of formation of nitrogen changes with time. Explain your answer in terms of collision theory.
ii. Explain why the volume of nitrogen eventually remains constant.
b. i. State and explain how the rate of formation of nitrogen would change if the temperature were increased from 25°C to 40°C.
ii. State and explain how the rate of formation of nitrogen would change if the same mass of ammonium iodide was used as large lumps instead of as a fine powder.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 25
The diagram represents the Boltzmann distribution of molecular kinetic energies at a given temperature.
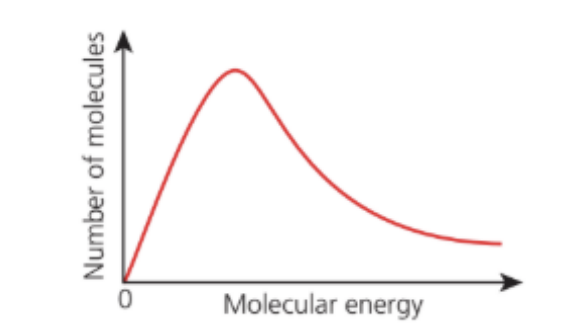
How does the shape of the graph change when the temperature decreases?
A. The peak is higher and further to the left.
B. The peak is higher and further to the right.
C. The peak is lower and further to the left.
D. The peak is lower and further to the right.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 26
Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron:
2H+(aq) + Fe(s) → H2(g) + Fe2+(aq)
What will increase the rate of this reaction but not change the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of kinetic energies?
I. Addition of a suitable catalyst
II. An increase in the concentration of hydrochloric acid
III. An increase in the temperature of hydrochloric acid
A. Only I is correct.
B. I and II are correct.
C. II and III are correct.
D. I, II and III are correct.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 27
Which change does not increase the initial rate of reaction when magnesium carbonate is added to excess hydrochloric?
MgCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
A. An increase in the temperature of the reaction mixture.
B. A decrease in the size of the magnesium carbonate particles.
C. An increase in the concentration of hydrochloric acid.
D. Addition of deionized water into the reaction mixture.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 28
Which of the graphs below shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of kinetic energies for the same amount of gas molecules (behaving ideally) at two temperatures, where T2 is greater than T1?
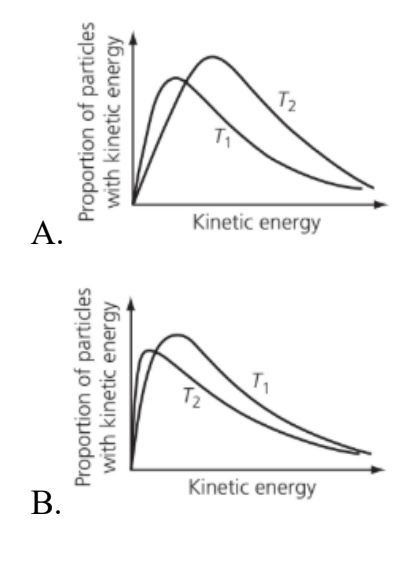
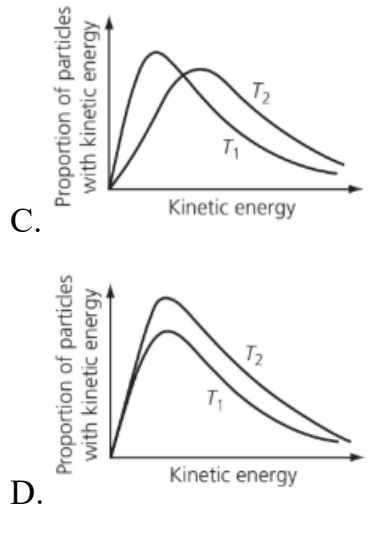
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
The following mechanism is proposed for a reaction:
A + B → C + D slow step
D + B → A + E fast step
a. Classify substances B and D as reactant, product, catalyst, or intermediate, based on the proposed mechanism.
b. Deduce the rate expression.
c. Calculate the initial rate of reaction for experiment 2, if measured under the same conditions.
| Experiment | [A] / mol dm-3 | [B] / mol dm-3 | Initial rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 1 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 1.20 |
| 2 | 0.300 | 0.200 |
a. Classify B and D
• B: Reactant — it is consumed overall; overall reaction is 2B → C + E.
• D: Intermediate — formed in step 1 and used up in step 2; not present in the overall reaction.
b. Rate expression
Slow (rate-determining) step:
A + B → C + D
Therefore,
rate = k[A][B]
c. Initial rate for experiment 2
Using the relationship:
rate ∝ [A][B]
`frac{r_2]{r_1} = frac{[A]_2[B]_2}{[A]_1[B]_1}=frac{0.300*0.200}{0.200*0.200}=1.5`
r2 = 1.5 × 1.20 = 1.80 mol dm−3s−1
Question 2
Determine the orders of reaction of the reactants and the overall rate expression for the reaction between 2-bromobutane and aqueous sodium hydroxide using the data in the table.
| Experiment | [NaOH] / mol dm-3 | [C₄H₉Br] / mol dm-3 | Rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.66 × 10-3 |
| 2 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 8.31 × 10-4 |
| 3 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1.02 × 10-4 |
| 4 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 8.29 × 10-4 |
a. Determine the rate constant, k, with its units, using the data from experiment 3.
b. Identify the molecularity of the rate-determining step in this reaction.
a.
• Orders and rate expression
Compare Expt 1 → 2 (halve [NaOH], keep [C₄H₉Br] constant): rate halves 1.66 × 10-3 → 8.31 × 10-4 ⇒ first order in [NaOH].
Compare Expt 1 → 4 (halve [C₄H₉Br], keep [NaOH] constant): rate halves 1.66 × 10-3 → 8.29 × 10-4 ⇒ first order in [C₄H₉Br].
rate = k[NaOH][C₄H₉Br]
Overall order = 1 + 1 = 2.
• Rate constant k (use experiment 3)
1.02 × 10−4 = k(0.25)(0.25) = 0.0625k ⇒ k = `frac{1.02*10^-4}{0.0625}` = 1.63 × 10-3
• Units for second order:
k = 1.63 × 10-3 dm3 mol−1s−1.
b. Molecularity of the rate-determining step
Two species in the rate law ⇒ bimolecular
Question 3
a. Nitrogen oxide is in equilibrium with dinitrogen dioxide.
2NO(g) ⇌ N₂O₂(g) ΔH° < 0
Deduce, giving a reason, the effect of increasing the temperature on the concentration of N₂O₂.
b. A two-step mechanism is proposed for the formation of NO₂(g) from NO(g) that involves an exothermic equilibrium process.
First step: 2NO(g) ⇌ N₂O₂(g) fast
Second step: N₂O₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2NO₂(g) slow
Deduce the rate expression for the mechanism.
c. The rate constant for a reaction doubles when the temperature is increased from 25.0 °C to 35 °C. Calculate the activation energy, Eₐ, in kJ mol⁻¹ for the reaction using section 1 and 2 of the data booklet.
a. The concentration of N₂O₂ decreases when temperature increases. Reason: The forward reaction 2NO ⇌ N₂O₂ is exothermic (ΔH° < 0). By Le Châtelier’s principle, raising T shifts equilibrium to the endothermic direction (back to NO), reducing [N₂O₂].
b. Rate expression from the mechanism
Slow (rate-determining) step:
N₂O₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2NO₂(g)
⇒ rate = k[N₂O₂][O₂]
Fast pre-equilibrium:
2NO ⇌ N₂O₂
k = `frac{[N_2O_2]}{[NO]^2}` ⇒ [N₂O₂] = [NO]2
Substitute:
rate = k′[NO]2 [O₂]
where k′ = kK.
c. Activation energy when k doubles from 25.0°C to 35.0°C
Use Arrhenius equation:
`ln frac{k_2}{k_1}=frac{E_a}{R}*(frac{1}{T_1}-frac{1}{T_2})`
With `frac{k_2}{k_1}=2`, T1 = 298 K, T2 = 308 K:
Ea = `frac{R*ln2}{frac{1}{T_1}-frac{1}{T_2}}≈frac{8.314*0.693}{frac{1}{298}-frac{1}{308}}`≈ 5.34 × 104J mol-1 = 53 to 54 kJ mol-1.
Question 4
Which statement about a reaction best describes the relationship between the temperature, T, and the rate constant, k?
A. As T increases, k decreases linearly.
B. As T increases, k decreases non-linearly.
C. As T increases, k increases linearly.
D. As T increases, k increases non-linearly.
Answer: D. As T increases, k increases non-linearly.
k = `Ae^frac{-E_a}{RT}`
Interpretation
• As temperature T increases, the exponential term `e^frac{-E_a}{RT}` increases, because the negative exponent becomes smaller in magnitude.
• Therefore, k increases with increasing temperature.
• The relationship is not linear, because of the exponential dependence on `frac{1}{T}`.
Question 5
For the gas phase reaction:
A(g) + B(g) → C(g)
The experimentally determined rate expression is: rate = k[A][B]²
By what factor will the rate change if the concentration of A is tripled and the concentration of B is halved?
A. 0.75
B. 1.5
C. 6
D. 12
Answer: A. 0.75
Given rate law:
rate = k[A][B]²
Change in concentrations:
• [A] is tripled → ×3
• [B] is halved → ×12
New rate relative to old rate:
`frac{"new rate"}{"old rate"}=frac{k(3[A])(frac{1}{2}[B])^2}{k[A][B]^2`
Simplify:
`frac{"new rate"}{"old rate"}=3*(frac{1}{2})^2=3*frac{1}{4}=frac{3}{4}` = 0.75
Question 6
The diagram below shows the energy changes for a reaction with and without a catalyst. Which symbols represent the activation energy, Eₐ, and the enthalpy change, ΔH, for the reaction with a catalyst?

| Eₐ (with a catalyst) | ΔH | |
| A. | x | z |
| B. | y | z |
| C. | z | x |
| D. | y − x | z |
Answer: A
1. Understanding the diagram
• The higher curve = reaction without a catalyst.
• The lower curve = reaction with a catalyst.
• The reactants start at the same energy.
• The products end at a lower energy (exothermic reaction).
Label meanings:
• x = activation energy with a catalyst (lower peak).
• y = activation energy without a catalyst (higher peak).
• z = energy difference between reactants and products → enthalpy change (ΔH).
2. Recall key facts
• A catalyst lowers activation energy but does not change ΔH.
Eₐ (with catalyst) = x, ΔH = z
Question 7
Which statement is correct?
A. The value of the rate constant, k, is independent of temperature and is deduced from the equilibrium constant, Kc.
B. The value of the rate constant, k, is independent of temperature and the overall reaction order determines its units.
C. The value of the rate constant, k, is temperature dependent and is deduced from the equilibrium constant, Kc.
D. The value of the rate constant, k, is temperature dependent and the overall reaction order determines its units.
Answer: D. The value of the rate constant, k, is temperature dependent and the overall reaction order determines its units.
A. Incorrect: k depends on temperature and is unrelated to the equilibrium constant Kc.
B. Incorrect: Units part is right, but k is temperature dependent.
C. Incorrect: k and Kc are unrelated (kinetic vs equilibrium).
D. Correct: Both points correct.
Question 8
What is the intercept on the y-axis when a graph of ln k is plotted against `frac{1}{T}` on the x axis?
ln k = `- frac{E_a){RT}+ln A`
A. ln A
B. `-frac{E_a}{R}`
C. `-frac{R}{E_a}`
D. Ea
Answer: A. ln A
ln k = `-frac{E_a}{R}*frac{1}{T}`+ ln A
This is in the linear form y = mx + c, where:
• y = ln k
• x =`frac{1}{T}`
• m = `-frac{E_a}{R}`(slope)
• c = ln A (y-intercept)
Question 9
Sodium bisulfite, NaHSO₃, reacts with methanal, converting it into a non-toxic compound which can be disposed safely. The overall equation is:
HSO₃⁻(aq) + H₂CO(aq) → CH₂(OH)SO₃⁻
The initial rate of this reaction can be studied by the ‘clock’ method using phenolphthalein as an indicator. The sudden appearance of the pink colour indicates the time to stop the stopwatch.
A series of experiments was carried out using different concentrations of HSO₃⁻ and H₂CO. The results obtained are shown below:
| Experiment | [HSO₃⁻]/mol dm-3 | [H₂CO]/mol dm-3 | Time for appearance of pink colour /s |
| 1 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 60 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 0.050 | 48 |
| 3 | 0.050 | 0.060 | 40 |
| 4 | 0.040 | 0.070 | 34 |
a. State the relationship between the time taken for the pink colour to appear and the initial rate of reaction.
b. Calculate the relative rates (1/time) for each of these four experiments and use them to deduce the order of reaction with respect to the two reactants.
c. State the rate equation for the reaction and state the units for the rate constant. Kinetic studies suggest that the mechanism involves the following two elementary steps:
Step 1: Bisulfite ion reacts with a water molecule via an acid-base reaction, forming sulfite ions, SO₃2-.
Step 2: The resulting sulfite ions react with methanal to produce the non-toxic product, CH₂(OH)SO₃⁻, and hydroxide ions.
d. Formulate balanced equations for these two elementary steps.
a. The initial rate is inversely proportional to the time taken for the pink colour to appear, i.e.
rate ∝ `frac{1}{t}`
b. Relative rates = `frac{1}{t}` (arb. units):
| Exp | `frac{1}{s*(t^-1)` |
| 1 | `frac{1}{60}`= 1.67 × 10⁻² |
| 2 | `frac{1}{48}`= 2.08 × 10⁻² |
| 3 | `frac{1}{40}`= 2.50 × 10⁻² |
| 4 | `frac{1}{34}`= 2.94 × 10⁻² |
Use these to get orders:
• From 1 → 2: [H₂CO] × 1.25, rate × 1.25 → first order in [H₂CO].
• From 2 → 3: [HSO₃⁻] increases but predicted rate from first-order [H₂CO] already matches → zero order in [HSO₃⁻].
c. Rate equation and units of k
rate = k[H₂CO]
Since [H₂CO] has units of mol dm-3 and rate is mol dm-3 s-1,
[k] = s-1
d. Elementary steps (balanced):
1. Acid–base step forming sulfite:
HSO₃⁻ + H₂O ⇌ SO₃2- + H3O+
2. Addition of sulfite to methanal, producing the non-toxic adduct and hydroxide:
SO₃2- + H₂CO + H₂O → CH₂(OH)SO₃⁻ + OH⁻
Question 10
The equation of a reaction involving X₂ is:
2X₂ → X + X₃
Which graph shows that the reaction is first order with respect to X₂?

Answer: C.
Given reaction
2X₂ → X + X₃
We’re told the reaction is first order with respect to X₂.
That means:
Rate ∝ [2X₂]1
So, if the concentration of X₂ doubles, the rate doubles — it’s a directly proportional, linear relationship.
A. Incorrect: Zero order — rate independent of [X₂].
B. Incorrect: Inverse/negative dependence — not first order.
C. Correct: Rate ∝ [X₂] → first order.
D. Incorrect: The concentration of X₂ should decrease, not increase.
Question 11
Which of the following statements of an Arrhenius plot of lnk against `frac{1}{T}*K^(-1)`is correct?
ln k = `(frac{-E_a}{R})*frac{1}{T}+lnA`
A. The graph has a positive gradient.
B. The activation energy can be calculated from the gradient.
C. The y-intercept is the Arrhenius factor, A.
D. The gradient becomes steeper when a catalyst is added.
Answer: B. The activation energy can be calculated from the gradient.
Arrhenius Equation (log form):
ln k = `(frac{-E_a}{R})*frac{1}{T}+ln A`
This is in the form y = mx + c, where:
A. Incorrect: The gradient m = `frac{-E_a}{R}` is negative, since Ea and R are positive.
B. Correct: Ea = −(slope) × R
C. Incorrect: The intercept is ln A, not A itself.
D. Incorrect: A catalyst lowers Ea, making the slope less steep (less negative).
Question 12
Under acidic conditions hydrogen peroxide oxidizes iodide ions to iodine molecules in the following reaction:
H₂O₂(aq) + 2H⁺(aq) + 2I⁻(aq) → 2H₂O(l) + I₂(aq)
Kinetic studies of this reaction using different initial concentrations of reactants at a constant temperature:
| Initial [H₂O₂(aq)] / mol dm-3 | Initial [H⁺(aq)] / mol dm-3 | Initial [I⁻(aq)] / mol dm-3 | Initial rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 0.005 | 0.05 | 0.015 | 1.31 × 10⁻⁶ |
| 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.015 | 2.63 × 10⁻⁶ |
| 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 5.25 × 10⁻⁶ |
| 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 5.25 × 10⁻⁶ |
What is the overall order of the reaction?
A. Zero (zeroth) order.
B. First order.
C. Second order.
D. Third order.
Answer: C. Second order.
Rate law (general form):
rate = k[H2O2]a[H+]b[I-]c
Step 1 - Compare Experiments 1 and 2
• [H2O2] doubles (0.005 → 0.010)
• [H+] and [I-]constant
• Rate doubles (1.31×10⁻⁶ → 2.63×10⁻⁶)
2a = 2 ⇒ a = 1
⇒ First order in H₂O₂
Step 2 - Compare Experiments 2 and 3
• [I-] doubles (0.015 → 0.030)
• [H2O2], [H+] constant
• Rate doubles (2.63×10⁻⁶ → 5.25×10⁻⁶)
2c = 2 ⇒ c = 1
⇒ First order in I-
Step 3 - Compare Experiments 3 and 4
• [H+] doubles (0.05 → 0.10)
• [H2O2] and [I-] constant
• Rate remains constant (5.25×10⁻⁶ → 5.25×10⁻⁶)
2b = 1 ⇒ b = 0
⇒ Zero order in H+
Step 4 - Determine overall order
Overall order = a + b + c = 1 + 0 + 1 = 2
Question 13
A reaction proceeds by the following mechanism:
Step 1: A + B ⇌ X fast
Step 2: X + A → P slow
Which rate equation is consistent with this mechanism?
A. rate = k[A]²[B].
B. rate = k[A]²[B][X].
C. rate = k[X][P].
D. rate = k[A][B].
Answer: A. rate = k[A]²[B].
Step 1 – The slow step (Step 2) controls the rate
rate = k[X][A]
But [X] is an intermediate, so we must eliminate it.
Step 2 – Express [X] in terms of A and B
From the fast equilibrium in Step 1:
A + B ⇌ X
k =`frac{[X]}{[A][B]}`⇒ [X] = K[A][B]
Step 3 – Substitute [X] into the rate equation
rate = k[X][A] = k(K[A][B])[A] = (kK)[A]²[B]
⇒ rate = k′[A]²[B]
Reasoning:
The rate depends on the slow step, and the intermediate X is replaced using the equilibrium from the fast step. Hence, the rate equation consistent with this mechanism is:
rate = k[A]²[B]
Question 14
The reaction between X and Y, in aqueous solution, follows the general rate equation:
rate = k[X]a[Y]b
The initial rate of this reaction was measured for different concentrations of X and Y, and the following results were obtained.
| [X] / mol dm-3 | [Y] / mol dm-3 | Initial rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 0.040 | 2.40 | 2.63 × 10-3 |
| 0.040 | 4.80 | 1.05 × 10-2 |
| 0.040 | 7.20 | 2.37 × 10-2 |
| 0.160 | 2.40 | 1.05 × 10-2 |
What are the values of a and b for the rate equation?
| a | b | |
| A. | 1 | 1 |
| B. | 0 | 2 |
| C. | 1 | 2 |
| D. | 2 | 1 |
Answer: C.
Given rate law:
Rate = k[X]a[Y]b
Step 1: Determine order with respect to Y (b)
Keep [X] constant (use experiments 1–2).
| Exp | [X] | [Y] | Rate (mol dm-3 s-1) |
| 1 | 0.040 | 2.40 | 2.63 × 10-3 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 4.80 | 1.05 × 10-2 |
From 1 → 2:
`frac{[Y]_2}{[Y_1]}=frac{4.80}{2.40}=2`
`frac{Rate_2}{Rate_1}=frac{1.05*10^(-2)}{2.63*10^(-3)}`≈ 4
So rate increases by a factor of 4 when [Y] doubles:
2b = 4 ⇒ b = 2
Step 2: Determine order with respect to X (a)
Keep [Y] constant (use experiments 1 and 4).
| Exp | [X] | [Y] | Rate (mol dm-3 s-1) |
| 1 | 0.040 | 2.40 | 2.63 × 10-3 |
| 4 | 0.160 | 2.40 | 1.05 × 10-2 |
From 1 → 4:
`frac{[X]_4}{[X_1]}=frac{0.160}{0.040}=4`
`frac{Rate_4}{Rate_1}=frac{1.05*10^(-2)}{2.63*10^(-3)}`≈ 4
So rate increases by a factor of 4 when [X] increases fourfold:
4a = 4 ⇒ a = 1
Question 15
The dotted line represents the volume of carbon dioxide released when excess magnesium carbonate is added to dilute nitric acid.
Which graph represents the production of carbon dioxide when excess magnesium carbonate is added to the same volume of nitric acid of double concentration?

Answer: D
Reaction:
MgCO3 + 2HNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2
MgCO3 is in excess, so acid is the limiting reagent. Therefore, the total volume of CO2 depends on the amount of acid (i.e., number of moles of HNO3).
Effect of Doubling Acid Concentration: If we use the same volume but double the concentration:
• Number of moles of HNO3 doubles.
• Since acid is limiting, twice as many moles of CO2 will be produced.
• The rate will also increase because the solution is more concentrated → more H+ ions per unit volume → faster reaction.
Therefore:
• The final CO2 volume doubles.
• The curve rises faster and levels off at a higher value.
Question 16
The energy profile diagram of the reversible reaction between M and N is shown in the figure.

Which of the following statements are correct?
I. The activation energy of the reverse reaction is E1 + E2.
II. Rate equation of the reaction is rate = k[M][N]2.
III. The equilibrium [MN2] increases as temperature increases.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: A. I and II only.
I. From the diagram the forward reaction is exothermic (products lower than reactants; ΔH = −E2). The activation energy for the reverse reaction is the energy gap from products up to the highest transition state, i.e.
Ea,rev = Ea,fwd + ∣ ΔH ∣ = E1 + E2
⇒ Correct.
II. The overall stoichiometry is M + 2N → MN2. If that overall step is elementary (as implied by the rate expression given), the rate law is
rate = k[M][N]2
⇒ Correct.
III. Since the reaction is exothermic (products at lower energy), increasing temperature shifts equilibrium toward reactants (Le Châtelier), so the equilibrium concentration of MN2 decreases, not increases.
⇒ Incorrect.
Hence, I and II are correct; III is not.
Question 17
Which is correct for the reaction mechanism shown?
2A → B + 2C slow
B + C → D + E fast
C + D → E + F fast
| Equation of overall reaction | Rate equation | |
| A. | 2A → E + F | rate = k[A]² |
| B. | 2A → 2E + F | rate = k[C][D] |
| C. | 2A + B + 2C + D → 2E + F | rate = k[A]²[B][C]²[D] |
| D. | 2A → 2E + F | rate = k[A]² |
Answer: D.
• Overall reaction: Add the three elementary steps and cancel intermediates (B, C, D):
1. 2A → B + 2C (slow)
2. B + C → D + E (fast)
3. C + D → E + F (fast)
⇒ Net: 2A → 2E + F
• Rate law: Determined by the slow (rate-determining) step, which is elementary: 2A → B + 2C
⇒ rate = k[A]2
Question 18
Which graph is obtained from a first order reaction?


Answer: B.
For a first-order reaction:
Rate = k[A]1
So the rate is directly proportional to concentration. That means a straight-line grap through the origin.
Question 19
The energy profile diagram of a reaction is shown in the figure.

Which of the following is true about the reaction?
A. The reaction occurs in two elementary steps.
B. The reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings.
C. The last step of the reaction is the rate-determining step.
D. The products are energetically more stable than the reactants.
Answer: D. The products are energetically more stable than the reactants.
A. Incorrect: There are more than two peaks, so more than two steps.
B. Incorrect: Products are lower in energy → exothermic reaction, releases heat, not absorbs.
C. Incorrect: The rate-determining step is the slowest, corresponding to the highest activation energy peak, which is the first one, not the last.
D. Correct: Products have lower potential energy, hence more stable.
Question 20
The dotted line represents the formation of oxygen, O₂ (g), from the uncatalysed complete decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H₂O₂ (aq).

Which curve represents a catalysed reaction under the same conditions?
Answer: A.
Effect of a Catalyst
• A catalyst increases the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy.
• It does not change the total amount of product formed — only how fast it is reached.
So compared to the uncatalysed (dotted) line:
• The catalysed curve will rise more steeply (faster rate).
• It will reach the same final volume (same total oxygen produced).
• It levels off sooner because the reaction finishes faster.
Interpretation of the Graph
| Curve | Behavior | Explanation |
| A. Correct | Steeper and same final volume | Catalysed reaction. |
| B. Incorrect | Reaches same final volume, slightly slower | Too similar to uncatalysed; not fast enough. |
| C. Incorrect | Below uncatalysed curve | Slower reaction, not catalysed. |
| D. Incorrect | Much lower final volume | Incomplete or inhibited reaction, not catalysed. |
Question 21
Which conditions must be met for a reaction to take place?
I. Reactants collide with sufficient energy.
II. Reactants collide with correct orientation.
III. Reactants must be in the same state.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: A. I and II only.
I. Reactants collide with sufficient energy.
→ Correct – Particles must collide with at least the activation energy (Eₐ) to break existing bonds and start the reaction.
II. Reactants collide with correct orientation.
→ Correct – Even with enough energy, collisions must have the right alignment so that bonds can form between the correct atoms.
III. Reactants must be in the same state.
→ Incorrect – Many reactions occur between different states (e.g., solid + liquid, gas + solid). Being in the same state is not necessary.
Question 22
Magnesium reacts with sulfuric acid:
Mg(s) + H₂SO₄(aq) → MgSO₄(aq) + H₂(g)
The graph shows the results of an experiment using excess magnesium ribbon and dilute sulfuric acid.

a. Outline why the rate of the reaction decreases with time.
b. Sketch, on the same graph, the expected results if the experiment were repeated using powdered magnesium, keeping its mass and all other variables unchanged.
a. Because the acid is being used up, its concentration of H⁺ ions falls with time → fewer effective collisions with Mg → the reaction rate decreases.
b. Powdered Mg, same mass
Draw a curve that:
• Starts with a steeper initial slope (faster rate due to larger surface area), lies above the original curve early on, levels off at the same final volume of H₂ (acid is still the limiting reagent), reaches that plateau sooner than the dashed curve.

Question 23
The graph below shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies at a particular temperature.

The rate at which dinitrogen monoxide decomposes is significantly increased by a metal oxide catalyst.
Annotate and use the graph to outline why a catalyst has this effect.
• Explanation:
A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy (Eₐ). It does not change the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution itself (i.e., the shape of the curve or the temperature), but it changes the position of the activation energy threshold on the graph.
• How to Annotate the Graph:
Draw two vertical lines on the x-axis to represent activation energy: o One for the uncatalysed reaction (Eₐ₁) — further to the right.
o One for the catalysed reaction (Eₐ₂) — further to the left.
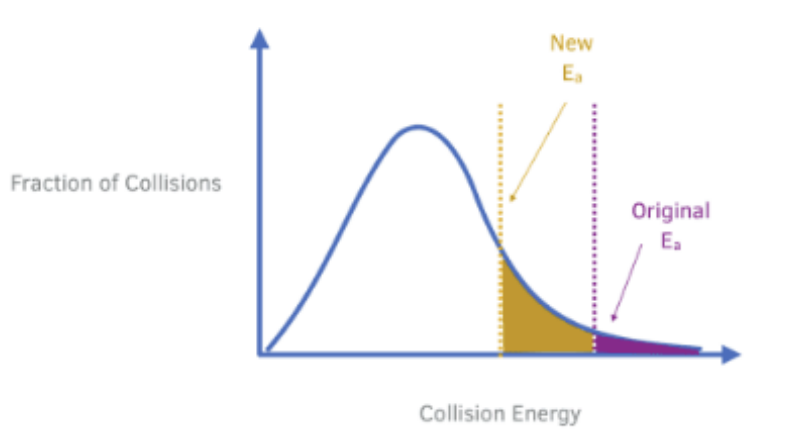
Question 24
The reaction between ammonium iodide and potassium nitrite in aqueous solution can be represented by the equation:
NH₄I (aq) + KNO₂ (aq) → N₂ (g) + 2H₂O (l) + KI (aq)
The graph below shows the total volume of nitrogen gas produced in a sealed gas syringe at 30 second intervals from a mixture of ammonium iodide and potassium nitrite in aqueous solution at 25°C.

a. i. State how the rate of formation of nitrogen changes with time. Explain your answer in terms of collision theory.
ii. Explain why the volume of nitrogen eventually remains constant.
b. i. State and explain how the rate of formation of nitrogen would change if the temperature were increased from 25°C to 40°C.
ii. State and explain how the rate of formation of nitrogen would change if the same mass of ammonium iodide was used as large lumps instead of as a fine powder.
a. i. How the rate changes: It decreases with time (the slope of the N₂–time curve gets smaller).
Collision-theory explanation: As the reaction proceeds, the concentrations of the reactants in solution fall, so particles collide less frequently and fewer collisions per second have the required energy and orientation → the rate drops.
ii. The volume of N₂ eventually becomes constant because the reaction stops – a limiting reactant is used up, so no more gas is produced.
b. i. Raising the temperature from 25 °C to 40 °C increases the rate (steeper initial slope, gas produced faster).
Explain: At higher T, particles have higher kinetic energy; a larger fraction has E ≥ Eₐ, and collisions occur more often and are more energetic, so the frequency of successful collisions increases.
ii. Using the same mass of ammonium iodide as large lumps instead of a fine powder makes the rate slower.
Explain: Larger particles give a smaller surface area in contact with solution (and dissolve more slowly), so there are fewer collisions per second between reactants. (Final volume of N₂ would be unchanged; it’s only produced more slowly.)
Question 25
The diagram represents the Boltzmann distribution of molecular kinetic energies at a given temperature.

How does the shape of the graph change when the temperature decreases?
A. The peak is higher and further to the left.
B. The peak is higher and further to the right.
C. The peak is lower and further to the left.
D. The peak is lower and further to the right.
Answer: A. The peak is higher and further to the left.
A. Correct: Lower temperature → lower average energy → peak moves left and becomes higher.
B. Incorrect: Rightward shift = higher temperature, not lower.
C. Incorrect: Lower temperature = higher, not lower, peak.
D. Incorrect: This describes higher temperature, not lower.
Question 26
Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron:
2H+(aq) + Fe(s) → H2(g) + Fe2+(aq)
What will increase the rate of this reaction but not change the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of kinetic energies?
I. Addition of a suitable catalyst
II. An increase in the concentration of hydrochloric acid
III. An increase in the temperature of hydrochloric acid
A. Only I is correct.
B. I and II are correct.
C. II and III are correct.
D. I, II and III are correct.
Answer: B. I and II are correct.
The Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution describes how kinetic energies of particles are distributed. Only temperature changes this distribution, because it alters the average kinetic energy of the particles.
• Temperature ↑ → curve shifts right and flattens (particles have more kinetic energy).
• Concentration ↑ → does not affect the shape of the distribution (same energy distribution, just more particles).
• Catalyst → does not affect the energy distribution either; it only lowers the activation energy.
| Change | Effect on rate | Effect on M–B distribution | |
| I. | Addition of a catalyst | Increases rate | No change |
| II. | Increase in acid concentration | Increases rate | No change |
| III. | Increase in temperature | Increases rate | Changes distribution |
Question 27
Which change does not increase the initial rate of reaction when magnesium carbonate is added to excess hydrochloric?
MgCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
A. An increase in the temperature of the reaction mixture.
B. A decrease in the size of the magnesium carbonate particles.
C. An increase in the concentration of hydrochloric acid.
D. Addition of deionized water into the reaction mixture.
Answer: D. Addition of deionized water into the reaction mixture.
• A, B, and C all increase the rate by increasing temperature, surface area, or reactant concentration.
• D decreases the rate because dilution reduces collision frequency.
Question 28
Which of the graphs below shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of kinetic energies for the same amount of gas molecules (behaving ideally) at two temperatures, where T2 is greater than T1?


Answer: C.
When temperature increases:
• Average kinetic energy increases → the curve shifts to the right.
• Distribution spreads out → curve becomes flatter and wider.
• Peak height decreases because particles are more spread across a wider range of energies.
• The area under the curve stays constant (since total number of particles is the same).
So, at higher temperature (T₂):
• Curve is broader and lower.
• Peak shifts to higher kinetic energy.
Question 1
The following mechanism is proposed for a reaction:
A + B → C + D slow step
D + B → A + E fast step
a. Classify substances B and D as reactant, product, catalyst, or intermediate, based on the proposed mechanism.
b. Deduce the rate expression.
c. Calculate the initial rate of reaction for experiment 2, if measured under the same conditions.
| Experiment | [A] / mol dm-3 | [B] / mol dm-3 | Initial rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 1 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 1.20 |
| 2 | 0.300 | 0.200 |
Question 2
Determine the orders of reaction of the reactants and the overall rate expression for the reaction between 2-bromobutane and aqueous sodium hydroxide using the data in the table.
| Experiment | [NaOH] / mol dm-3 | [C₄H₉Br] / mol dm-3 | Rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.66 × 10-3 |
| 2 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 8.31 × 10-4 |
| 3 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1.02 × 10-4 |
| 4 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 8.29 × 10-4 |
a. Determine the rate constant, k, with its units, using the data from experiment 3.
b. Identify the molecularity of the rate-determining step in this reaction.
Question 3
a. Nitrogen oxide is in equilibrium with dinitrogen dioxide.
2NO(g) ⇌ N₂O₂(g) ΔH° < 0
Deduce, giving a reason, the effect of increasing the temperature on the concentration of N₂O₂.
b. A two-step mechanism is proposed for the formation of NO₂(g) from NO(g) that involves an exothermic equilibrium process.
First step: 2NO(g) ⇌ N₂O₂(g) fast
Second step: N₂O₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2NO₂(g) slow
Deduce the rate expression for the mechanism.
c. The rate constant for a reaction doubles when the temperature is increased from 25.0 °C to 35 °C. Calculate the activation energy, Eₐ, in kJ mol⁻¹ for the reaction using section 1 and 2 of the data booklet.
Question 4
Which statement about a reaction best describes the relationship between the temperature, T, and the rate constant, k?
A. As T increases, k decreases linearly.
B. As T increases, k decreases non-linearly.
C. As T increases, k increases linearly.
D. As T increases, k increases non-linearly.
Question 5
For the gas phase reaction:
A(g) + B(g) → C(g)
The experimentally determined rate expression is: rate = k[A][B]²
By what factor will the rate change if the concentration of A is tripled and the concentration of B is halved?
A. 0.75
B. 1.5
C. 6
D. 12
Question 6
The diagram below shows the energy changes for a reaction with and without a catalyst. Which symbols represent the activation energy, Eₐ, and the enthalpy change, ΔH, for the reaction with a catalyst?

| Eₐ (with a catalyst) | ΔH | |
| A. | x | z |
| B. | y | z |
| C. | z | x |
| D. | y − x | z |
Question 7
Which statement is correct?
A. The value of the rate constant, k, is independent of temperature and is deduced from the equilibrium constant, Kc.
B. The value of the rate constant, k, is independent of temperature and the overall reaction order determines its units.
C. The value of the rate constant, k, is temperature dependent and is deduced from the equilibrium constant, Kc.
D. The value of the rate constant, k, is temperature dependent and the overall reaction order determines its units.
Question 8
What is the intercept on the y-axis when a graph of ln k is plotted against `frac{1}{T}` on the x axis?
ln k = `- frac{E_a){RT}+ln A`
A. ln A
B. `-frac{E_a}{R}`
C. `-frac{R}{E_a}`
D. Ea
Question 9
Sodium bisulfite, NaHSO₃, reacts with methanal, converting it into a non-toxic compound which can be disposed safely. The overall equation is:
HSO₃⁻(aq) + H₂CO(aq) → CH₂(OH)SO₃⁻
The initial rate of this reaction can be studied by the ‘clock’ method using phenolphthalein as an indicator. The sudden appearance of the pink colour indicates the time to stop the stopwatch.
A series of experiments was carried out using different concentrations of HSO₃⁻ and H₂CO. The results obtained are shown below:
| Experiment | [HSO₃⁻]/mol dm-3 | [H₂CO]/mol dm-3 | Time for appearance of pink colour /s |
| 1 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 60 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 0.050 | 48 |
| 3 | 0.050 | 0.060 | 40 |
| 4 | 0.040 | 0.070 | 34 |
a. State the relationship between the time taken for the pink colour to appear and the initial rate of reaction.
b. Calculate the relative rates (1/time) for each of these four experiments and use them to deduce the order of reaction with respect to the two reactants.
c. State the rate equation for the reaction and state the units for the rate constant. Kinetic studies suggest that the mechanism involves the following two elementary steps:
Step 1: Bisulfite ion reacts with a water molecule via an acid-base reaction, forming sulfite ions, SO₃2-.
Step 2: The resulting sulfite ions react with methanal to produce the non-toxic product, CH₂(OH)SO₃⁻, and hydroxide ions.
d. Formulate balanced equations for these two elementary steps.
Question 10
The equation of a reaction involving X₂ is:
2X₂ → X + X₃
Which graph shows that the reaction is first order with respect to X₂?

Question 11
Which of the following statements of an Arrhenius plot of lnk against `frac{1}{T}*K^(-1)`is correct?
ln k = `(frac{-E_a}{R})*frac{1}{T}+lnA`
A. The graph has a positive gradient.
B. The activation energy can be calculated from the gradient.
C. The y-intercept is the Arrhenius factor, A.
D. The gradient becomes steeper when a catalyst is added.
Question 12
Under acidic conditions hydrogen peroxide oxidizes iodide ions to iodine molecules in the following reaction:
H₂O₂(aq) + 2H⁺(aq) + 2I⁻(aq) → 2H₂O(l) + I₂(aq)
Kinetic studies of this reaction using different initial concentrations of reactants at a constant temperature:
| Initial [H₂O₂(aq)] / mol dm-3 | Initial [H⁺(aq)] / mol dm-3 | Initial [I⁻(aq)] / mol dm-3 | Initial rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 0.005 | 0.05 | 0.015 | 1.31 × 10⁻⁶ |
| 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.015 | 2.63 × 10⁻⁶ |
| 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 5.25 × 10⁻⁶ |
| 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 5.25 × 10⁻⁶ |
What is the overall order of the reaction?
A. Zero (zeroth) order.
B. First order.
C. Second order.
D. Third order.
Question 13
A reaction proceeds by the following mechanism:
Step 1: A + B ⇌ X fast
Step 2: X + A → P slow
Which rate equation is consistent with this mechanism?
A. rate = k[A]²[B].
B. rate = k[A]²[B][X].
C. rate = k[X][P].
D. rate = k[A][B].
Question 14
The reaction between X and Y, in aqueous solution, follows the general rate equation:
rate = k[X]a[Y]b
The initial rate of this reaction was measured for different concentrations of X and Y, and the following results were obtained.
| [X] / mol dm-3 | [Y] / mol dm-3 | Initial rate / mol dm-3 s-1 |
| 0.040 | 2.40 | 2.63 × 10-3 |
| 0.040 | 4.80 | 1.05 × 10-2 |
| 0.040 | 7.20 | 2.37 × 10-2 |
| 0.160 | 2.40 | 1.05 × 10-2 |
What are the values of a and b for the rate equation?
| a | b | |
| A. | 1 | 1 |
| B. | 0 | 2 |
| C. | 1 | 2 |
| D. | 2 | 1 |
Question 15
The dotted line represents the volume of carbon dioxide released when excess magnesium carbonate is added to dilute nitric acid.
Which graph represents the production of carbon dioxide when excess magnesium carbonate is added to the same volume of nitric acid of double concentration?

Question 16
The energy profile diagram of the reversible reaction between M and N is shown in the figure.

Which of the following statements are correct?
I. The activation energy of the reverse reaction is E1 + E2.
II. Rate equation of the reaction is rate = k[M][N]2.
III. The equilibrium [MN2] increases as temperature increases.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 17
Which is correct for the reaction mechanism shown?
2A → B + 2C slow
B + C → D + E fast
C + D → E + F fast
| Equation of overall reaction | Rate equation | |
| A. | 2A → E + F | rate = k[A]² |
| B. | 2A → 2E + F | rate = k[C][D] |
| C. | 2A + B + 2C + D → 2E + F | rate = k[A]²[B][C]²[D] |
| D. | 2A → 2E + F | rate = k[A]² |
Question 18
Which graph is obtained from a first order reaction?


Question 19
The energy profile diagram of a reaction is shown in the figure.

Which of the following is true about the reaction?
A. The reaction occurs in two elementary steps.
B. The reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings.
C. The last step of the reaction is the rate-determining step.
D. The products are energetically more stable than the reactants.
Question 20
The dotted line represents the formation of oxygen, O₂ (g), from the uncatalysed complete decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H₂O₂ (aq).

Which curve represents a catalysed reaction under the same conditions?
Question 21
Which conditions must be met for a reaction to take place?
I. Reactants collide with sufficient energy.
II. Reactants collide with correct orientation.
III. Reactants must be in the same state.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 22
Magnesium reacts with sulfuric acid:
Mg(s) + H₂SO₄(aq) → MgSO₄(aq) + H₂(g)
The graph shows the results of an experiment using excess magnesium ribbon and dilute sulfuric acid.

a. Outline why the rate of the reaction decreases with time.
b. Sketch, on the same graph, the expected results if the experiment were repeated using powdered magnesium, keeping its mass and all other variables unchanged.
Question 23
The graph below shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies at a particular temperature.

The rate at which dinitrogen monoxide decomposes is significantly increased by a metal oxide catalyst.
Annotate and use the graph to outline why a catalyst has this effect.
Question 24
The reaction between ammonium iodide and potassium nitrite in aqueous solution can be represented by the equation:
NH₄I (aq) + KNO₂ (aq) → N₂ (g) + 2H₂O (l) + KI (aq)
The graph below shows the total volume of nitrogen gas produced in a sealed gas syringe at 30 second intervals from a mixture of ammonium iodide and potassium nitrite in aqueous solution at 25°C.

a. i. State how the rate of formation of nitrogen changes with time. Explain your answer in terms of collision theory.
ii. Explain why the volume of nitrogen eventually remains constant.
b. i. State and explain how the rate of formation of nitrogen would change if the temperature were increased from 25°C to 40°C.
ii. State and explain how the rate of formation of nitrogen would change if the same mass of ammonium iodide was used as large lumps instead of as a fine powder.
Question 25
The diagram represents the Boltzmann distribution of molecular kinetic energies at a given temperature.

How does the shape of the graph change when the temperature decreases?
A. The peak is higher and further to the left.
B. The peak is higher and further to the right.
C. The peak is lower and further to the left.
D. The peak is lower and further to the right.
Question 26
Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron:
2H+(aq) + Fe(s) → H2(g) + Fe2+(aq)
What will increase the rate of this reaction but not change the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of kinetic energies?
I. Addition of a suitable catalyst
II. An increase in the concentration of hydrochloric acid
III. An increase in the temperature of hydrochloric acid
A. Only I is correct.
B. I and II are correct.
C. II and III are correct.
D. I, II and III are correct.
Question 27
Which change does not increase the initial rate of reaction when magnesium carbonate is added to excess hydrochloric?
MgCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
A. An increase in the temperature of the reaction mixture.
B. A decrease in the size of the magnesium carbonate particles.
C. An increase in the concentration of hydrochloric acid.
D. Addition of deionized water into the reaction mixture.
Question 28
Which of the graphs below shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of kinetic energies for the same amount of gas molecules (behaving ideally) at two temperatures, where T2 is greater than T1?

