Question 1
H₂(g) and I₂(g) react according to the following equilibrium:
H₂(g) + I₂(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
When 0.10 mol of H₂(g) and 0.10 mol of I₂(g) are heated in a sealed vessel at 600 K, 0.06 mol of HI is present at equilibrium.
What is the K value for the reaction at 600 K?
A. 0.184
B. 1.360
C. 0.360
D. 0.735
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
Urea can also be made by the direct combination of ammonia and carbon dioxide gases.
2NH₃(g) + CO₂(g) ⇌ (H₂N)₂CO(g) + H₂O(g) ΔH < 0
a. State the equilibrium constant expression, Kc.
b. Predict, with a reason, the effect on the equilibrium constant, Kc, when the temperature is increased.
c. Determine an approximate order of magnitude for Kc, using sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet. Assume ΔG° for the forward reaction is approximately +50 kJ at 298 K.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
The graph shows values of ΔG for a reaction at different temperatures.
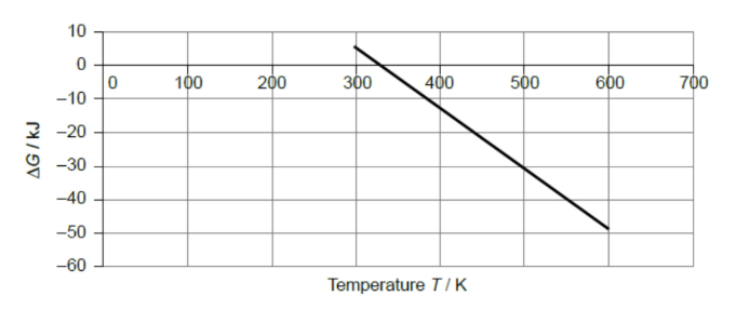
Which statement is correct?
A. The standard entropy change of the reaction is negative.
B. The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is positive.
C. At higher temperatures, the reaction becomes less spontaneous.
D. The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is negative.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which is correct for a redox reaction where the standard electrode potential is negative?
ΔG° = −nFE° and ΔG° = −RTln K
A. ΔG° is negative and K is less than 1.
B. ΔG° is negative and K is greater than 1.
C. ΔG° is positive and K is less than 1.
D. ΔG° is positive and K is greater than 1.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Methanol can be formed from carbon monoxide and hydrogen:
CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g)
The reaction was investigated by mixing 3.20 mol of carbon monoxide and 3.20 mol of hydrogen in a 10.0 dm³ sealed vessel, and equilibrium was established at 120°C under a pressure of 1.60 × 10⁶ Pa.
a. Assuming ideal gas behaviour, determine the total amount of gas in moles, at equilibrium.
b. Calculate the amounts (mol) of CO, H₂, and CH₃OH in moles, present at equilibrium.
c. Calculate the value (to 3 s.f.) for the equilibrium constant, K.
d. Calculate the change in Gibbs energy (kJ mol⁻¹), ΔG, for the formation of methanol from carbon monoxide and hydrogen at 120°C.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
N₂O₄ dissociates into NO₂ as shown in the equation below.
N₂O₄(g) ⇌ 2NO₂(g)
The equilibrium constant, K, for this dissociation at 373 K is 0.210 mol dm-3. Which of the following statements is true?
A. ΔG for the forward reaction is negative at 373 K.
B. ΔG for the forward reaction is zero at 373 K.
C. ΔH for the forward reaction is zero at 373 K.
D. ΔH for the forward reaction is positive at 373 K.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Methanol is an important industrial solvent and fuel. It can be produced from carbon monoxide and hydrogen according to the following equation:
CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g) ΔH = –91 kJ mol-1
The effect of different catalysts on this reaction is investigated using the following apparatus:
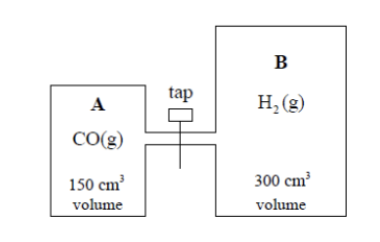
A contains 1 mole of carbon monoxide and B contains 2 moles of hydrogen. The gases in both containers are at the same temperature and pressure. The tap is closed at the start of the experiment.
a. What will happen to the concentration of methanol if the system is allowed to reach equilibrium at a lower temperature?
b. i. Write the equilibrium expression for the above reaction, and give the units for Kc.
ii. Calculate a value for Kc if the maximum yield of methanol is 85%.
iii. When this reaction is carried out on an industrial scale, the yield is about 60%. Suggest a reason for this.
iv. Copper is a good catalyst for this reaction. What effect, if any, will the addition of copper have on the value of Kc?
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
An equilibrium can be represented by the following chemical equation:
A(aq) + B(aq) ⇌ 2C(aq) + D(aq)
In a certain 1.0 dm³ mixture, the equilibrium concentration of B is 10.0 mol dm-3.
What will be the new equilibrium concentration of B if 5 moles of pure B is dissolved in the mixture?
A. 15.0 mol dm-3.
B. Between 10.0 mol dm-3 and 15.0 mol dm-3.
C. Between 5.0 mol dm-3 and 10.0 mol dm-3.
D. 10.0 mol dm-3.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Iodine and bromine gases were mixed and allowed to reach equilibrium.
I₂(g) + Br₂(g) ⇌ 2IBr(g)
| [I₂] | [Br₂] | [IBr] | |
| Initial concentration | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.00 |
| Equilibrium concentration | 0.10 | 0.10 | x |
What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
A. 0.05
B. 1
C. 4
D. 10
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
At 445°C, the equilibrium constant (K) for the following reaction is 0.020.
2HI(g) ⇌ H₂(g) + I₂(g)
A mixture of H₂, I₂, and HI in a vessel at 445°C has the following concentrations: [HI] = 2.0 mol dm-3, [H₂] = 0.50 mol dm-3, [I₂] = 0.10 mol dm-3.
Which one of the following statements concerning the reaction quotient, Q, is correct for this equilibrium system?
A. Q = K and the system is at equilibrium.
B. Q is less than K and more H₂ and I₂ will be produced.
C. Q is less than K and more HI will be produced.
D. Q is greater than K and more H₂ and I₂ will be produced.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
When silver bromide, AgBr, is mixed with water, a very small amount of silver bromide will dissolve in water in an equilibrium process.
AgBr (s) ⇌ Ag⁺ (aq) + Br⁻ (aq); K = [Ag⁺(aq)][Br⁻(aq)]
How will the concentration of Ag⁺ (aq) and K change when some solid sodium bromide is dissolved into a mixture of silver bromide and water at equilibrium?
| Solubility | Equilibrium constant, K | |
| A. | Increase | Increase |
| B. | Increase | No change |
| C. | Constant | No change |
| D. | Decrease | Increase |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
Methanol is an important alcohol used in fuel mixtures, making methyl esters and oxidation to methanol (formaldehyde) to make urea–formaldehyde resin glues.
Methanol is manufactured industrially from carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas in an enclosed system according to the following reaction:
CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g); ΔH = –90 kJ mol-1
The reaction is typically subjected to the following industrial conditions:
| Pressure | 50 MPa |
| Temperature | 250 °C |
| Catalyst | copper–zinc oxide mixture |
a. Describe what happens at dynamic equilibrium.
b. Suggest the effect of the high pressure and catalyst used under industrial conditions have on the position of equilibrium and the rate of reaction.
c. The reaction is performed at a moderately high temperature of 250 °C. Suggest why a low temperature is not used industrially instead.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
The equilibrium between nitrogen dioxide, NO₂, and dinitrogen tetroxide, N₂O₄, is shown below.
2NO₂(g) ⇌ N₂O₄(g), Kc = 0.01
What happens when the volume of a mixture at equilibrium is decreased at a constant temperature?
I. The value of Kc increases
II. More N₂O₄ is formed
III. The ratio of `frac{[NO_2]}{[N_2O_4]}` decreases
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
Kc for 2N₂O(g) ⇌ 2N₂(g) + O₂(g) is 7.3 × 10³⁴.
What is Kc for the following reaction, at the same temperature?
N₂(g) + `frac{1}{2}`O₂(g) ⇌ N₂O(g)
A. 7.3 × 10³⁴
B. `frac{1}{sqrt(7.3*10^34)}`
C. `frac{1}{7.3*10^34}`
D. `frac{1}{2*7.3*10^34}`
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 15
Consider the following equilibrium system:
2AlCl₃(g) ⇌ Al₂Cl₆(g); ΔH° < 0
Which of the following statements will cause the position of the above equilibrium to shift to the left?
A. Decreasing the volume of the vessel.
B. Increasing the temperature.
C. Pumping inert gas into the vessel at constant volume.
D. Pumping AlCl₃ gas into the vessel.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 16
The table gives information about the percentage yield of ammonia obtained in the Haber process under different conditions.
| Pressure (atm) | 200°C | 300°C | 400°C | 500°C |
| 10 | 50.7 | 14.7 | 3.9 | 1.2 |
| 100 | 81.7 | 52.5 | 25.2 | 10.6 |
| 200 | 89.1 | 66.7 | 38.8 | 18.3 |
| 300 | 89.9 | 71.1 | 47.1 | 24.4 |
| 400 | 94.6 | 79.7 | 55.4 | 31.9 |
| 600 | 95.4 | 84.2 | 65.2 | 42.3 |
a. From the table, identify which combination of temperature and pressure gives the highest yield of ammonia.
b. The equation for the main reaction in the Haber process is:
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) ⇌ 2NH₃(g); ΔH° is negative
Use this information to state and explain the effect on the yield of ammonia of increasing
i. pressure
ii. temperature
c. In practice, typical conditions used in the Haber process are a temperature of 500 °C and a pressure of 200 atmospheres. Explain why these conditions are used rather than those that give the highest yield.
d. Write the equilibrium constant expression, K, for the production of ammonia.
e. i Suggest why this reaction is important for humanity.
ii. A chemist claims to have developed a new catalyst for the Haber process, which, unlike iron, increases the yield of ammonia. Evaluate the claim made by this chemist.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 17
Consider the following reaction:
2A (g) ⇌ C (g); K = 1.1
Which statement is correct when the reaction is at equilibrium?
A. [A] >> [C]
B. [A] > [C]
C. [A] = [C]
D. [A] < [C]
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 18
For a gaseous reaction, the equilibrium constant expression is:
K = `frac{[O_2]^5[NH_3]^4}{[NO]^4[H_2O]^6}`
Which equation corresponds to this equilibrium expression?
A. 4NH₃ + 5O₂ ⇌ 4NO + 6H₂O
B. 4NO + 6H₂O ⇌ 4NH₃ + 5O₂
C. 8NH₃ + 10O₂ ⇌ 8NO + 12H₂O
D. 2NO + 3H₂O ⇌ 2NH₃ + O₂
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 19
The smaller the value of an equilibrium constant, K
A. The slower the reaction rate.
B. The more endothermic the reaction.
C. The lower the concentration of products at equilibrium.
D. The faster the reactants are converted to products.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 20
A sealed container at room temperature is half full of water with only water vapour above it. The temperature of the sealed container is slowly decreased in an ice bath. The set-up is left for equilibrium to establish while more ice is continually added. Which statement is correct when the equilibrium of the water and water vapour mixture reached equilibrium at the lower temperature?
A. The rate of condensation is the same as the rate of vaporization.
B. The number of moles of water will be equal to the number of moles of water vapour in the sealed container.
C. The pressure in the sealed container increases.
D. The volume of water in the container remains the same throughout the entire process
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
H₂(g) and I₂(g) react according to the following equilibrium:
H₂(g) + I₂(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
When 0.10 mol of H₂(g) and 0.10 mol of I₂(g) are heated in a sealed vessel at 600 K, 0.06 mol of HI is present at equilibrium.
What is the K value for the reaction at 600 K?
A. 0.184
B. 1.360
C. 0.360
D. 0.735
Answer: D. 0.735
1. Find the change in moles
For every 2 mol HI formed, 1 mol H₂ and 1 mol I₂ are used.
Change in HI = +0.06 ⇒ Change in H₂ = Change in I₂ = −0.03
2. Calculate equilibrium moles
| Species | Initial (mol) | Change (mol) | Equilibrium (mol) |
| H₂ | 0.10 | −0.03 | 0.07 |
| I₂ | 0.10 | −0.03 | 0.07 |
| HI | 0 | +0.06 | 0.06 |
3. Write the equilibrium constant expression
K = `frac{[HI]^2}{[H_2][I_2]}`
Because the volume is constant, we can use moles instead of concentrations (the volume term cancels out):
K = `frac{(0.06)^2}{(0.07)*(0.07)}=frac{0.0036}{0.0049}`= 0.735
Question 2
Urea can also be made by the direct combination of ammonia and carbon dioxide gases.
2NH₃(g) + CO₂(g) ⇌ (H₂N)₂CO(g) + H₂O(g) ΔH < 0
a. State the equilibrium constant expression, Kc.
b. Predict, with a reason, the effect on the equilibrium constant, Kc, when the temperature is increased.
c. Determine an approximate order of magnitude for Kc, using sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet. Assume ΔG° for the forward reaction is approximately +50 kJ at 298 K.
a. Equilibrium constant expression, Kc
Given reaction:
2NH₃(g) + CO₂(g) ⇌ (H₂N)₂CO(g) + H₂O(g)
Kc = `frac{[(H_2N)_2CO][H_2O]}{[NH_3]^2[CO_2]`
`=>`Kc = `frac{[(H_2N)_2CO][H_2O]}{[NH_3]^2[CO_2]`
b. Effect of temperature increase on Kc
Given: ΔH < 0 → the reaction is exothermic.
When temperature increases, equilibrium shifts to the left (endothermic direction) to oppose the temperature rise (Le Chatelier’s principle).
Therefore, the equilibrium constant Kc decreases with increasing temperature.
c. Approximate order of magnitude for Kc
Given:
ΔGo = +50 kJ mol−1, T = 298 K
Use the relationship:
ΔGo = −RTln K
ln K = `- frac{ΔG^o}{RT} = -frac{50000}{(8.314)(298)}`= -20.1
K = e-20.1 ≈ 2 × 10−9
Question 3
The graph shows values of ΔG for a reaction at different temperatures.

Which statement is correct?
A. The standard entropy change of the reaction is negative.
B. The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is positive.
C. At higher temperatures, the reaction becomes less spontaneous.
D. The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is negative.
Answer: B. The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is positive.
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
Observation from graph:
• As temperature (T) increases, ΔG decreases (becomes more negative).
• At T = 300 K, ΔG ≈ +10 kJ (non-spontaneous).
• At T = 700 K, ΔG ≈ −55 kJ (spontaneous).
So, increasing temperature makes the reaction more spontaneous.
From the Gibbs equation:
• If ΔG decreases (becomes more negative) as T increases, then the term −TΔS must be negative and large.
• That means ΔS is positive (entropy increases).
Since at low temperature ΔG is positive and becomes negative only at higher T, → the reaction becomes spontaneous only when TΔS outweighs ΔH. Thus, ΔH must be positive (endothermic), because at low T, ΔG is positive.
Question 4
Which is correct for a redox reaction where the standard electrode potential is negative?
ΔG° = −nFE° and ΔG° = −RTln K
A. ΔG° is negative and K is less than 1.
B. ΔG° is negative and K is greater than 1.
C. ΔG° is positive and K is less than 1.
D. ΔG° is positive and K is greater than 1.
Answer: C. ΔG° is positive and K is less than 1.
Step 1: When E° is negative
• ΔG°< 0 ⇒ −nFE° > 0
• Therefore, ΔG° > 0
→ The reaction is non-spontaneous under standard conditions.
Step 2: Link ΔG° and K
ΔG° = −RTln K
If ΔG° > 0 ⇒ ln K < 0 ⇒ K < 1
Question 5
Methanol can be formed from carbon monoxide and hydrogen:
CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g)
The reaction was investigated by mixing 3.20 mol of carbon monoxide and 3.20 mol of hydrogen in a 10.0 dm³ sealed vessel, and equilibrium was established at 120°C under a pressure of 1.60 × 10⁶ Pa.
a. Assuming ideal gas behaviour, determine the total amount of gas in moles, at equilibrium.
b. Calculate the amounts (mol) of CO, H₂, and CH₃OH in moles, present at equilibrium.
c. Calculate the value (to 3 s.f.) for the equilibrium constant, K.
d. Calculate the change in Gibbs energy (kJ mol⁻¹), ΔG, for the formation of methanol from carbon monoxide and hydrogen at 120°C.
a. Total moles of gas at equilibrium
Ideal gas:
n= `frac{PV}{RT}=frac{(1.60*10^6)*(0.0100)}{(8.314)*(393)}`= 4.90 mol (3 s.f.)
ntotal = 4.90 mol
b. Amounts of each species at equilibrium
Let x = mol of CH₃OH formed.
Initial moles: CO = 3.20, H₂ = 3.20, CH₃OH = 0
Change: CO − x, H₂ − 2x, CH₃OH + x
Total moles = 6.40 − 2x = 4.90 ⇒ x = 0.752 mol
Thus:
• CO = 3.20 − x = 2.45 mol
• H₂ = 3.20 − 2x = 1.70 mol
• CH₃OH = x = 0.752 mol
c. Equilibrium constant, K(3 s.f.)
K = `frac{[CH_3OH]}{[CO][H_2]^2}`
Concentrations in 10.0 dm³:
[CH₃OH] = 0.0752,[CO] = 0.245,[H₂] = 0.170 mol dm−3
K = `frac{0.0752}{(0.245)*(0.170)^2}`= 10.7
d) Gibbs energy change at 120 °C
ΔG = −RTln K = −(8.314)(393)ln (10.7) = −7.73 × 103 J mol−1
ΔG = −7.73 kJ mol−1
Question 6
N₂O₄ dissociates into NO₂ as shown in the equation below.
N₂O₄(g) ⇌ 2NO₂(g)
The equilibrium constant, K, for this dissociation at 373 K is 0.210 mol dm-3. Which of the following statements is true?
A. ΔG for the forward reaction is negative at 373 K.
B. ΔG for the forward reaction is zero at 373 K.
C. ΔH for the forward reaction is zero at 373 K.
D. ΔH for the forward reaction is positive at 373 K.
Answer: D. ΔH for the forward reaction is positive at 373 K.
Step 1: Interpret K
• K < 1means reactants (N₂O₄) are favored at equilibrium.
• Thus, the forward reaction (dissociation) is not strongly spontaneous at 373 K – equilibrium lies toward N₂O₄.
Step 2: Relate K to Gibbs free energy
ΔG = −RTlnK
Since K = 0.210 < 1,
ln K < 0 ⟹ − RTln K > 0 ⟹ ΔG > 0
→ ΔG is positive, not negative.
At equilibrium, ΔG for the overall system = 0, but ΔGo (standard Gibbs free energy) corresponds to the equilibrium constant — and is positive here.
Step 3: Consider ΔH
The dissociation of N₂O₄ → 2NO₂ requires breaking bonds and increases moles of gas → it is endothermic → ΔH > 0
Question 7
Methanol is an important industrial solvent and fuel. It can be produced from carbon monoxide and hydrogen according to the following equation:
CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g) ΔH = –91 kJ mol-1
The effect of different catalysts on this reaction is investigated using the following apparatus:

A contains 1 mole of carbon monoxide and B contains 2 moles of hydrogen. The gases in both containers are at the same temperature and pressure. The tap is closed at the start of the experiment.
a. What will happen to the concentration of methanol if the system is allowed to reach equilibrium at a lower temperature?
b. i. Write the equilibrium expression for the above reaction, and give the units for Kc.
ii. Calculate a value for Kc if the maximum yield of methanol is 85%.
iii. When this reaction is carried out on an industrial scale, the yield is about 60%. Suggest a reason for this.
iv. Copper is a good catalyst for this reaction. What effect, if any, will the addition of copper have on the value of Kc?
a. Lowering the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right (exothermic forward reaction), so the equilibrium concentration of methanol increases.
b. i. Equilibrium expression and units
Kc = `frac{[CH_3OH]}{[CO][H_2]^2}`
Units:
`frac{mol*dm^(-3)}{(mol*dm^(-3))*(mol*dm^(-3))^2}=dm^6*mol^(-2)`
ii. Value of Kc if the maximum methanol yield is 85%
With 1.0 mol CO and 2.0 mol H₂ (stoichiometric), an 85% yield
gives: `""n_(CH_3OH)` = 0.85 mol
`""n_(CO)` = 0.15 mol
`""n_(H_2)` = 2 − 2(0.85) = 0.30 mol
Total volume after mixing:
150 + 300 = 450 cm3 = 0.450 dm3
Concentrations:
[CH3OH] = `frac{0.85}{0.450}`= 1.889; [CO] = `frac{0.15}{0.450}`= 0.333; [H2] = `frac{0.30}(0.450}`= 0.667
Kc = `frac{1.889}{(0.333)*(0.667)^2`≈ 12.8 dm6 mol−2
iii. Industrial yield is ~60% because conditions are a compromise:
• Lower T would give higher yield but too slow rate.
• Very high pressure would improve yield but is costly and hazardous.
• Industry runs at moderate `frac{T}{P}` with recycle of unreacted gases, giving a lower single-pass yield.
iv. Adding a copper catalyst does not change Kc (Catalysts speed up the approach to equilibrium but do not alter the equilibrium position).
Question 8
An equilibrium can be represented by the following chemical equation:
A(aq) + B(aq) ⇌ 2C(aq) + D(aq)
In a certain 1.0 dm³ mixture, the equilibrium concentration of B is 10.0 mol dm-3.
What will be the new equilibrium concentration of B if 5 moles of pure B is dissolved in the mixture?
A. 15.0 mol dm-3.
B. Between 10.0 mol dm-3 and 15.0 mol dm-3.
C. Between 5.0 mol dm-3 and 10.0 mol dm-3.
D. 10.0 mol dm-3.
Answer: B. Between 10.0 mol dm-3 and 15.0 mol dm-3.
At equilibrium:
[B] = 10.0 mol dm-3
We add 5 moles of B into a 1.0 dm3 solution
→ New initial [B] = 10.0 + 5.0 = 15.0 mol dm-3
Effect on equilibrium:
• When we add more B, the system now has excess reactant.
• According to Le Chatelier’s principle, the equilibrium will shift to the right (toward products) to use up some of the added B.
• This means some of the extra B will react and its concentration will decrease slightly from 15 mol dm-3 - but not all the way back to 10 mol dm-3.
→ At the new equilibrium:
[B] will be between 10.0 and 15.0 mol dm-3.
Question 9
Iodine and bromine gases were mixed and allowed to reach equilibrium.
I₂(g) + Br₂(g) ⇌ 2IBr(g)
| [I₂] | [Br₂] | [IBr] | |
| Initial concentration | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.00 |
| Equilibrium concentration | 0.10 | 0.10 | x |
What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
A. 0.05
B. 1
C. 4
D. 10
Answer: C. 4
ICE Table (Initial–Change–Equilibrium)
| Substance | Initial (mol dm-3) | Change | Equilibrium |
| I₂ | 0.20 | −0.10 | 0.10 |
| Br₂ | 0.20 | −0.10 | 0.10 |
| IBr | 0.00 | +0.20 | 0.20 |
Because for every 1 mol I₂ and 1 mol Br₂ consumed, 2 mol IBr are produced. So equilibrium [IBr] = 0.20.
Expression for Kc:
Kc =`frac{[IBr]^2}{[I_2][Br_2]}`
Substitute values:
Kc = `frac{[0.20]^2}{(0.10)*(0.10)}`= `frac{0.04){0.01} = 4`
Question 10
At 445°C, the equilibrium constant (K) for the following reaction is 0.020.
2HI(g) ⇌ H₂(g) + I₂(g)
A mixture of H₂, I₂, and HI in a vessel at 445°C has the following concentrations: [HI] = 2.0 mol dm-3, [H₂] = 0.50 mol dm-3, [I₂] = 0.10 mol dm-3.
Which one of the following statements concerning the reaction quotient, Q, is correct for this equilibrium system?
A. Q = K and the system is at equilibrium.
B. Q is less than K and more H₂ and I₂ will be produced.
C. Q is less than K and more HI will be produced.
D. Q is greater than K and more H₂ and I₂ will be produced.
Answer: B. Q is less than K and more H₂ and I₂ will be produced.
Step 1: Write the expression for Q
Q = `frac{[H_2][I_2]}{[HI]^2}`
Step 2: Substitute the values
Q = `frac{(0.50}*(0.10)}{(2.0)^2}=frac{0.05}{4}`= 0.0125
Step 3: Compare Q with K
Q = 0.0125 < K = 0.020
Step 4: Interpret
When Q < K, the reaction shifts to the right, producing more products (H₂ and I₂) until equilibrium is reached.
Question 11
When silver bromide, AgBr, is mixed with water, a very small amount of silver bromide will dissolve in water in an equilibrium process.
AgBr (s) ⇌ Ag⁺ (aq) + Br⁻ (aq); K = [Ag⁺(aq)][Br⁻(aq)]
How will the concentration of Ag⁺ (aq) and K change when some solid sodium bromide is dissolved into a mixture of silver bromide and water at equilibrium?
| Solubility | Equilibrium constant, K | |
| A. | Increase | Increase |
| B. | Increase | No change |
| C. | Constant | No change |
| D. | Decrease | Increase |
Answer: C.
• NaBr is a soluble ionic compound, which dissociates completely: NaBr → Na⁺ + Br⁻
• This increases the [Br⁻] in solution.
Le Châtelier’s Principle
• The equilibrium will shift to the left (toward solid AgBr) to reduce the added Br⁻.
• As a result, the concentration of Ag⁺ decreases.
Effect on equilibrium constant (K)
• K depends only on temperature, not on concentrations of ions or solids.
• Since temperature is constant, K remains unchanged.
Question 12
Methanol is an important alcohol used in fuel mixtures, making methyl esters and oxidation to methanol (formaldehyde) to make urea–formaldehyde resin glues.
Methanol is manufactured industrially from carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas in an enclosed system according to the following reaction:
CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g); ΔH = –90 kJ mol-1
The reaction is typically subjected to the following industrial conditions:
| Pressure | 50 MPa |
| Temperature | 250 °C |
| Catalyst | copper–zinc oxide mixture |
a. Describe what happens at dynamic equilibrium.
b. Suggest the effect of the high pressure and catalyst used under industrial conditions have on the position of equilibrium and the rate of reaction.
c. The reaction is performed at a moderately high temperature of 250 °C. Suggest why a low temperature is not used industrially instead.
a. At dynamic equilibrium the forward and reverse reactions continue at equal rates; concentrations/pressures of reactants and products stay constant (not zero rate).
b. High pressure (50 MPa): Favors the side with fewer gas moles (3 → 1), so it shifts the equilibrium to methanol and also increases the rate by giving more frequent collisions.
Catalyst (Cu–ZnO): Does not change the equilibrium position; it increases the rate of both forward and reverse reactions by lowering Ea, so equilibrium is reached faster.
c. The reaction is exothermic, so a lower temperature would give a higher equilibrium yield of CH₃OH, but the reaction rate would be too slow (and throughput uneconomical).
Hence, a moderately high temperature (~250 °C) is used as a compromise between reasonable rate and acceptable yield.
Question 13
The equilibrium between nitrogen dioxide, NO₂, and dinitrogen tetroxide, N₂O₄, is shown below.
2NO₂(g) ⇌ N₂O₄(g), Kc = 0.01
What happens when the volume of a mixture at equilibrium is decreased at a constant temperature?
I. The value of Kc increases
II. More N₂O₄ is formed
III. The ratio of `frac{[NO_2]}{[N_2O_4]}` decreases
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: C. II and III only.
2NO₂(g) ⇌ N₂O₄(g), Kc = 0.01
When the volume decreases (pressure increases):
• System shifts to fewer moles of gas to reduce pressure.
• Here, left side = 2 mol gas, right side = 1 mol gas.
→ Shifts to the right (forms more N₂O₄).
I. The value of Kc increases
→ Incorrect: Kc depends only on temperature, not volume or pressure.
II. More N₂O₄ is formed
→ Correct: Shift to the right due to pressure increase.
III. The ratio `frac{[NO_2]}{[N_2O_4]}` decreases
→ Correct: [NO₂] decreases, [N₂O₄] increases. Ratio goes down.
Question 14
Kc for 2N₂O(g) ⇌ 2N₂(g) + O₂(g) is 7.3 × 10³⁴.
What is Kc for the following reaction, at the same temperature?
N₂(g) + `frac{1}{2}`O₂(g) ⇌ N₂O(g)
A. 7.3 × 10³⁴
B. `frac{1}{sqrt(7.3*10^34)}`
C. `frac{1}{7.3*10^34}`
D. `frac{1}{2*7.3*10^34}`
Answer: B. `frac{1}{sqrt(7.3*10^34)}`
Step 1: Reverse the original reaction
Reversing flips reactants and products:
2N₂(g) + O₂(g) ⇌ 2N₂O(g)
So:
K' = `frac{1}{7.3*10^34}`
Step 2: Adjust for coefficients
We want half of this reaction (divide all coefficients by 2):
N₂(g) + `frac{1}{2}`O₂(g) ⇌ N₂O(g)
When we divide the stoichiometric coefficients by 2, we take the square root of
K = `(K')^frac{1}{2}`= `(frac{1}{7.3*10^34})^frac{1}{2} = frac{1}{sqrt(7.3*10^34)}`
Question 15
Consider the following equilibrium system:
2AlCl₃(g) ⇌ Al₂Cl₆(g); ΔH° < 0
Which of the following statements will cause the position of the above equilibrium to shift to the left?
A. Decreasing the volume of the vessel.
B. Increasing the temperature.
C. Pumping inert gas into the vessel at constant volume.
D. Pumping AlCl₃ gas into the vessel.
Answer: B. Increasing the temperature.
A. Incorrect:
• Decreasing volume → increases pressure.
• System shifts to fewer moles of gas to reduce pressure.
• Forward side: 2 mol → 1 mol.
• So it would shift right, not left.
B. Correct:
• Reaction is exothermic forward.
• Increasing T favors the endothermic (reverse) direction.
→ Shifts equilibrium to the left.
C. Incorrect: At constant volume, total pressure increases but partial pressures of reactants/products stay the same, so no shift.
D. Incorrect: Adding more reactant drives equilibrium right (toward products).
Question 16
The table gives information about the percentage yield of ammonia obtained in the Haber process under different conditions.
| Pressure (atm) | 200°C | 300°C | 400°C | 500°C |
| 10 | 50.7 | 14.7 | 3.9 | 1.2 |
| 100 | 81.7 | 52.5 | 25.2 | 10.6 |
| 200 | 89.1 | 66.7 | 38.8 | 18.3 |
| 300 | 89.9 | 71.1 | 47.1 | 24.4 |
| 400 | 94.6 | 79.7 | 55.4 | 31.9 |
| 600 | 95.4 | 84.2 | 65.2 | 42.3 |
a. From the table, identify which combination of temperature and pressure gives the highest yield of ammonia.
b. The equation for the main reaction in the Haber process is:
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) ⇌ 2NH₃(g); ΔH° is negative
Use this information to state and explain the effect on the yield of ammonia of increasing
i. pressure
ii. temperature
c. In practice, typical conditions used in the Haber process are a temperature of 500 °C and a pressure of 200 atmospheres. Explain why these conditions are used rather than those that give the highest yield.
d. Write the equilibrium constant expression, K, for the production of ammonia.
e. i Suggest why this reaction is important for humanity.
ii. A chemist claims to have developed a new catalyst for the Haber process, which, unlike iron, increases the yield of ammonia. Evaluate the claim made by this chemist.
a. Highest % NH₃ from the table 600 atm and 200 °C (95.4%)
b. Effect on equilibrium yield
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) ⇌ 2NH₃(g); ΔH° < 0
i. Pressure ↑ → yield ↑. Fewer gas moles on the right (4 → 2), so higher pressure shifts equilibrium to ammonia.
ii. Temperature ↑ → yield ↓. The reaction is exothermic; raising T favors the reverse (endothermic) direction.
c. Why use ~500 °C and ~200 atm rather than the “best-yield” conditions? They are a compromise:
• Lower T would give higher yield but too slow a rate.
• Much higher pressure would give higher yield but is very costly and hazardous (thick vessels, energy).
• At ~500 °C with an Fe catalyst and ~200 atm you get acceptable rate with reasonable yield and cost.
d. Equilibrium constant for ammonia formation
K = `frac{[NH_3]^2}{[N_2][H_2]^3}`
(or with partial pressures for Kp:Kp =`frac{p_(NH_3)^2}{p_(N_2)*p_(H_2)^3}`).
e. i. Ammonia is the feedstock for fertilisers (ammonium salts / urea) → essential for global food production.
ii. Evaluating the catalyst claim
A catalyst does not change equilibrium yield at fixed T and P; it only increases the rate of reaching equilibrium. The claim “increases the yield” is therefore incorrect as stated. A better catalyst could allow operation at lower temperature, which indirectly could give a higher equilibrium yield, but the equilibrium position itself is unchanged by the catalyst.
Question 17
Consider the following reaction:
2A (g) ⇌ C (g); K = 1.1
Which statement is correct when the reaction is at equilibrium?
A. [A] >> [C]
B. [A] > [C]
C. [A] = [C]
D. [A] < [C]
Answer: C. [A] = [C]
K = 1.1
Meaning of K
• K = `frac{[C]}{[A]^2}`
• K = 1.1 means the ratio of products to reactants squared is roughly 1.
→ [C] and [A] are of comparable magnitude — neither side dominates much.
A. Incorrect: [A] ≫ [C] would make K ≪ 1 (product much smaller than reactants).
B. Incorrect: [A] > [C] would make K slightly < 1.
C. Correct: [A] = [C] approximately true when K ≈ 1.
D. Incorrect: [A] < [C] would make K much > 1.
Question 18
For a gaseous reaction, the equilibrium constant expression is:
K = `frac{[O_2]^5[NH_3]^4}{[NO]^4[H_2O]^6}`
Which equation corresponds to this equilibrium expression?
A. 4NH₃ + 5O₂ ⇌ 4NO + 6H₂O
B. 4NO + 6H₂O ⇌ 4NH₃ + 5O₂
C. 8NH₃ + 10O₂ ⇌ 8NO + 12H₂O
D. 2NO + 3H₂O ⇌ 2NH₃ + O₂
Answer: B. 4NO + 6H₂O ⇌ 4NH₃ + 5O₂
Step 1: Recall that
K = `frac{["products"]^"coefficients"}{["reactants"]^"coefficients"}`
So the numerator represents products, and the denominator represents reactants.
Step 2: Identify from the expression
Products: O₂ and NH₃
Reactants: NO and H₂O
Hence, the reaction must be:
4NO + 6H₂O ⇌ 4NH₃ + 5O₂
Question 19
The smaller the value of an equilibrium constant, K
A. The slower the reaction rate.
B. The more endothermic the reaction.
C. The lower the concentration of products at equilibrium.
D. The faster the reactants are converted to products.
Answer: C. The lower the concentration of products at equilibrium.
A. Incorrect: K gives equilibrium position, not speed (rate depends on activation energy).
B. Incorrect: K depends on ΔG°, not directly on endothermic/exothermic nature.
C. Correct: Small K → reaction favors reactants → fewer products.
D. Incorrect: Speed is unrelated to K.
Question 20
A sealed container at room temperature is half full of water with only water vapour above it. The temperature of the sealed container is slowly decreased in an ice bath. The set-up is left for equilibrium to establish while more ice is continually added. Which statement is correct when the equilibrium of the water and water vapour mixture reached equilibrium at the lower temperature?

A. The rate of condensation is the same as the rate of vaporization.
B. The number of moles of water will be equal to the number of moles of water vapour in the sealed container.
C. The pressure in the sealed container increases.
D. The volume of water in the container remains the same throughout the entire process
Answer: A. The rate of condensation is the same as the rate of vaporization.
At equilibrium: H₂O(l) ⇌ H₂O(g)
The rates of evaporation (vaporization) and condensation are equal. As temperature decreases:
• The vapour pressure of water decreases.
• Some water vapour condenses into liquid to maintain equilibrium.
• Eventually, less vapour and lower pressure exist.
A. Correct: This is the definition of equilibrium.
B. Incorrect: The liquid contains far more moles than vapour.
C. Incorrect: Cooling reduces vapour pressure → pressure decreases.
D. Incorrect: Some vapour condenses → liquid water volume increases slightly.
Question 1
H₂(g) and I₂(g) react according to the following equilibrium:
H₂(g) + I₂(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
When 0.10 mol of H₂(g) and 0.10 mol of I₂(g) are heated in a sealed vessel at 600 K, 0.06 mol of HI is present at equilibrium.
What is the K value for the reaction at 600 K?
A. 0.184
B. 1.360
C. 0.360
D. 0.735
Question 2
Urea can also be made by the direct combination of ammonia and carbon dioxide gases.
2NH₃(g) + CO₂(g) ⇌ (H₂N)₂CO(g) + H₂O(g) ΔH < 0
a. State the equilibrium constant expression, Kc.
b. Predict, with a reason, the effect on the equilibrium constant, Kc, when the temperature is increased.
c. Determine an approximate order of magnitude for Kc, using sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet. Assume ΔG° for the forward reaction is approximately +50 kJ at 298 K.
Question 3
The graph shows values of ΔG for a reaction at different temperatures.

Which statement is correct?
A. The standard entropy change of the reaction is negative.
B. The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is positive.
C. At higher temperatures, the reaction becomes less spontaneous.
D. The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is negative.
Question 4
Which is correct for a redox reaction where the standard electrode potential is negative?
ΔG° = −nFE° and ΔG° = −RTln K
A. ΔG° is negative and K is less than 1.
B. ΔG° is negative and K is greater than 1.
C. ΔG° is positive and K is less than 1.
D. ΔG° is positive and K is greater than 1.
Question 5
Methanol can be formed from carbon monoxide and hydrogen:
CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g)
The reaction was investigated by mixing 3.20 mol of carbon monoxide and 3.20 mol of hydrogen in a 10.0 dm³ sealed vessel, and equilibrium was established at 120°C under a pressure of 1.60 × 10⁶ Pa.
a. Assuming ideal gas behaviour, determine the total amount of gas in moles, at equilibrium.
b. Calculate the amounts (mol) of CO, H₂, and CH₃OH in moles, present at equilibrium.
c. Calculate the value (to 3 s.f.) for the equilibrium constant, K.
d. Calculate the change in Gibbs energy (kJ mol⁻¹), ΔG, for the formation of methanol from carbon monoxide and hydrogen at 120°C.
Question 6
N₂O₄ dissociates into NO₂ as shown in the equation below.
N₂O₄(g) ⇌ 2NO₂(g)
The equilibrium constant, K, for this dissociation at 373 K is 0.210 mol dm-3. Which of the following statements is true?
A. ΔG for the forward reaction is negative at 373 K.
B. ΔG for the forward reaction is zero at 373 K.
C. ΔH for the forward reaction is zero at 373 K.
D. ΔH for the forward reaction is positive at 373 K.
Question 7
Methanol is an important industrial solvent and fuel. It can be produced from carbon monoxide and hydrogen according to the following equation:
CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g) ΔH = –91 kJ mol-1
The effect of different catalysts on this reaction is investigated using the following apparatus:

A contains 1 mole of carbon monoxide and B contains 2 moles of hydrogen. The gases in both containers are at the same temperature and pressure. The tap is closed at the start of the experiment.
a. What will happen to the concentration of methanol if the system is allowed to reach equilibrium at a lower temperature?
b. i. Write the equilibrium expression for the above reaction, and give the units for Kc.
ii. Calculate a value for Kc if the maximum yield of methanol is 85%.
iii. When this reaction is carried out on an industrial scale, the yield is about 60%. Suggest a reason for this.
iv. Copper is a good catalyst for this reaction. What effect, if any, will the addition of copper have on the value of Kc?
Question 8
An equilibrium can be represented by the following chemical equation:
A(aq) + B(aq) ⇌ 2C(aq) + D(aq)
In a certain 1.0 dm³ mixture, the equilibrium concentration of B is 10.0 mol dm-3.
What will be the new equilibrium concentration of B if 5 moles of pure B is dissolved in the mixture?
A. 15.0 mol dm-3.
B. Between 10.0 mol dm-3 and 15.0 mol dm-3.
C. Between 5.0 mol dm-3 and 10.0 mol dm-3.
D. 10.0 mol dm-3.
Question 9
Iodine and bromine gases were mixed and allowed to reach equilibrium.
I₂(g) + Br₂(g) ⇌ 2IBr(g)
| [I₂] | [Br₂] | [IBr] | |
| Initial concentration | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.00 |
| Equilibrium concentration | 0.10 | 0.10 | x |
What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
A. 0.05
B. 1
C. 4
D. 10
Question 10
At 445°C, the equilibrium constant (K) for the following reaction is 0.020.
2HI(g) ⇌ H₂(g) + I₂(g)
A mixture of H₂, I₂, and HI in a vessel at 445°C has the following concentrations: [HI] = 2.0 mol dm-3, [H₂] = 0.50 mol dm-3, [I₂] = 0.10 mol dm-3.
Which one of the following statements concerning the reaction quotient, Q, is correct for this equilibrium system?
A. Q = K and the system is at equilibrium.
B. Q is less than K and more H₂ and I₂ will be produced.
C. Q is less than K and more HI will be produced.
D. Q is greater than K and more H₂ and I₂ will be produced.
Question 11
When silver bromide, AgBr, is mixed with water, a very small amount of silver bromide will dissolve in water in an equilibrium process.
AgBr (s) ⇌ Ag⁺ (aq) + Br⁻ (aq); K = [Ag⁺(aq)][Br⁻(aq)]
How will the concentration of Ag⁺ (aq) and K change when some solid sodium bromide is dissolved into a mixture of silver bromide and water at equilibrium?
| Solubility | Equilibrium constant, K | |
| A. | Increase | Increase |
| B. | Increase | No change |
| C. | Constant | No change |
| D. | Decrease | Increase |
Question 12
Methanol is an important alcohol used in fuel mixtures, making methyl esters and oxidation to methanol (formaldehyde) to make urea–formaldehyde resin glues.
Methanol is manufactured industrially from carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas in an enclosed system according to the following reaction:
CO(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g); ΔH = –90 kJ mol-1
The reaction is typically subjected to the following industrial conditions:
| Pressure | 50 MPa |
| Temperature | 250 °C |
| Catalyst | copper–zinc oxide mixture |
a. Describe what happens at dynamic equilibrium.
b. Suggest the effect of the high pressure and catalyst used under industrial conditions have on the position of equilibrium and the rate of reaction.
c. The reaction is performed at a moderately high temperature of 250 °C. Suggest why a low temperature is not used industrially instead.
Question 13
The equilibrium between nitrogen dioxide, NO₂, and dinitrogen tetroxide, N₂O₄, is shown below.
2NO₂(g) ⇌ N₂O₄(g), Kc = 0.01
What happens when the volume of a mixture at equilibrium is decreased at a constant temperature?
I. The value of Kc increases
II. More N₂O₄ is formed
III. The ratio of `frac{[NO_2]}{[N_2O_4]}` decreases
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 14
Kc for 2N₂O(g) ⇌ 2N₂(g) + O₂(g) is 7.3 × 10³⁴.
What is Kc for the following reaction, at the same temperature?
N₂(g) + `frac{1}{2}`O₂(g) ⇌ N₂O(g)
A. 7.3 × 10³⁴
B. `frac{1}{sqrt(7.3*10^34)}`
C. `frac{1}{7.3*10^34}`
D. `frac{1}{2*7.3*10^34}`
Question 15
Consider the following equilibrium system:
2AlCl₃(g) ⇌ Al₂Cl₆(g); ΔH° < 0
Which of the following statements will cause the position of the above equilibrium to shift to the left?
A. Decreasing the volume of the vessel.
B. Increasing the temperature.
C. Pumping inert gas into the vessel at constant volume.
D. Pumping AlCl₃ gas into the vessel.
Question 16
The table gives information about the percentage yield of ammonia obtained in the Haber process under different conditions.
| Pressure (atm) | 200°C | 300°C | 400°C | 500°C |
| 10 | 50.7 | 14.7 | 3.9 | 1.2 |
| 100 | 81.7 | 52.5 | 25.2 | 10.6 |
| 200 | 89.1 | 66.7 | 38.8 | 18.3 |
| 300 | 89.9 | 71.1 | 47.1 | 24.4 |
| 400 | 94.6 | 79.7 | 55.4 | 31.9 |
| 600 | 95.4 | 84.2 | 65.2 | 42.3 |
a. From the table, identify which combination of temperature and pressure gives the highest yield of ammonia.
b. The equation for the main reaction in the Haber process is:
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) ⇌ 2NH₃(g); ΔH° is negative
Use this information to state and explain the effect on the yield of ammonia of increasing
i. pressure
ii. temperature
c. In practice, typical conditions used in the Haber process are a temperature of 500 °C and a pressure of 200 atmospheres. Explain why these conditions are used rather than those that give the highest yield.
d. Write the equilibrium constant expression, K, for the production of ammonia.
e. i Suggest why this reaction is important for humanity.
ii. A chemist claims to have developed a new catalyst for the Haber process, which, unlike iron, increases the yield of ammonia. Evaluate the claim made by this chemist.
Question 17
Consider the following reaction:
2A (g) ⇌ C (g); K = 1.1
Which statement is correct when the reaction is at equilibrium?
A. [A] >> [C]
B. [A] > [C]
C. [A] = [C]
D. [A] < [C]
Question 18
For a gaseous reaction, the equilibrium constant expression is:
K = `frac{[O_2]^5[NH_3]^4}{[NO]^4[H_2O]^6}`
Which equation corresponds to this equilibrium expression?
A. 4NH₃ + 5O₂ ⇌ 4NO + 6H₂O
B. 4NO + 6H₂O ⇌ 4NH₃ + 5O₂
C. 8NH₃ + 10O₂ ⇌ 8NO + 12H₂O
D. 2NO + 3H₂O ⇌ 2NH₃ + O₂
Question 19
The smaller the value of an equilibrium constant, K
A. The slower the reaction rate.
B. The more endothermic the reaction.
C. The lower the concentration of products at equilibrium.
D. The faster the reactants are converted to products.
Question 20
A sealed container at room temperature is half full of water with only water vapour above it. The temperature of the sealed container is slowly decreased in an ice bath. The set-up is left for equilibrium to establish while more ice is continually added. Which statement is correct when the equilibrium of the water and water vapour mixture reached equilibrium at the lower temperature?

A. The rate of condensation is the same as the rate of vaporization.
B. The number of moles of water will be equal to the number of moles of water vapour in the sealed container.
C. The pressure in the sealed container increases.
D. The volume of water in the container remains the same throughout the entire process