Question 1
Consider the following standard electrode potential values:
Fe³⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Fe²⁺(aq); E° = +0.77 V
Ni²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Ni(s); E° = −0.26 V
Fe²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Fe(s); E° = −0.45 V
Ca²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Ca(s); E° = −2.87 V
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
3-hydroxybutanoic acid is a metabolite which the body can use to provide energy when it is low on glucose.
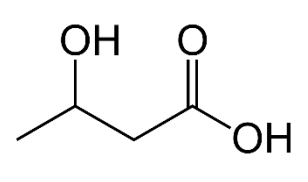
a. Name the functional groups present in 3-hydroxybutanoic acid.
b. Draw the two stereoisomers of 3-hydroxybutanoic acid.
c. Draw the organic product formed when 3-hydroxybutanoic acid is left to react with an excess of a reducing agent and the mixture is quenched with acid.
d. i. When 3-hydroxybutanoic acid is reacted with potassium manganate(VII) (an oxidizing agent) an unstable compound with a degree of unsaturation of 2 is formed. Suggest the structure of this unstable compound.
ii. The unstable compound produced decomposes to form carbon dioxide and one other product with a degree of unsaturation of 1. Identify the product formed in this decomposition reaction.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which statement is correct for a voltaic but not for an electrolytic cell?
A. An electrolyte is required.
B. The anode is where oxidation occurs.
C. Ions move in the electrolyte.
D. Electrons flow from the negative. electrode to the positive electrode.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Which compound can be oxidized when heated with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate(VI)?
A. CH₃C(O)CH₂CH₃
B. CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃
C. (CH₃)₃COH
D. CH₃(CH₂)₂COOH
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Which of these functional groups will react with a reducing agent?
I. Alkoxy
II. Carboxyl
III. Carbonyl
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
All non-cyclic structural isomers of alcohols with molecular formula C₄H₁₀O are reacted with hot acidified KMnO₄. How many will decolourize the purple KMnO₄?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
What is the oxidation half-equation in the redox reaction?
2S₂O₃²⁻(aq) + I₂(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2I⁻(aq)
A. I₂(aq) + 2e⁻ → 2I⁻(aq)
B. 2I⁻(aq) →. I₂(aq) + 2e⁻
C. 2S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2e⁻
D. S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2e⁻ → 2S₂O₃²⁻(aq)
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Which compounds are susceptible to oxidation with potassium manganate(VII)?
I. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂OH
II. (CH₃)₃CCH₂OH
III. CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Consider the following standard electrode potential values:
Cu⁺(aq) + e⁻ ⇌ Cu(s) E° = +0.52 V
MnO₄⁻(aq) + 8H⁺(aq) + 5e⁻ ⇌ Mn²⁺(aq) + 4H₂O(l) E° = +1.51 V
What is the cell potential for this reaction?
MnO₄⁻(aq) + 8H⁺(aq) + 5Cu(s) → Mn²⁺(aq) + 4H₂O(l) + 5Cu⁺(aq)
A. +2.03
B. +0.99
C. −0.99
D. −2.03
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
During a titrimetric analysis, 25.00 cm³ of an aqueous solution containing ethanol required 37.50 cm³ of 1.50 mol dm⁻³ of acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution for complete reaction. The density of ethanol is 0.790 g cm⁻³.
During the reaction, ethanol, CH₃CH₂OH, is oxidized to ethanoic acid, CH₃COOH, while dichromate(VI) ions, Cr₂O₇²⁻, react as shown in the following half-equation:
Cr₂O₇²⁻(aq) + 14H⁺(aq) + 6e⁻ → 2Cr³⁺(aq) + 7H₂O(l)
a. Explain, in terms of change in oxidation state, why dichromate(VI) ions undergo reduction.
b. Write the half-equation for the oxidation of ethanol, CH₃CH₂OH, to ethanoic acid, CH₃COOH.
c. Use the half-equations to construct an ionic equation for the above redox reaction.
d. Using the titration results and relevant data, calculate the volume of ethanol in 25.00 cm³ of the alcoholic solution.
e. Determine the concentration as a percentage by volume of the alcoholic solution.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
For which of the reactions below will the Gibbs energy change ΔG° be the most negative?
A. Cu(s) + 2Ag⁺(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) E° = +0.46 V
B. Co(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Cu(s) + Co²⁺(aq) E° = +0.62 V
C. Fe²⁺(aq) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Fe³⁺(aq) + Cu⁺(aq) E° = −0.61 V
D. H₂(g) + Cr²⁺(aq) → Cr(s) + 2H⁺(aq) E° = −0.74 V
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
Using the standard electrode potentials given, calculate the standard cell potential when an I₂, I⁻ half-cell (E° = +0.54 V) is connected to a Cl₂/Cl⁻ half-cell (E° = +1.36 V).
A. +3.80 V
B. +1.90 V
C. +1.64 V
D. +0.82 V
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
a. i. Draw a diagram for the voltaic cell formed by connecting the following standard half-cells:
Ni(s) | Ni²⁺(aq) || Mn²⁺(aq) | Mn(s)
ii. Describe the key features of the hydrogen half-cell.
b. i. Write an equation for the reaction in each half-cell, identifying the species which is oxidized and the oxidizing agent.
ii. State which electrode is the anode and state the direction of electron flow in the external circuit.
iii. For the overall cell, calculate its voltage and state the sign of ΔG.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
In copper-plating, orchids are coated with a thin layer of graphite paste before placing them in a bath of aqueous copper(II) sulfate and electroplating with copper as the anode.
a. Suggest a reason why orchids are first coated with graphite.
b. Deduce the half equations at the cathode and anode.
c. To ensure high standards of electroplated orchids, the copper coating must be at least 0.5 mm thick. Given that the total surface area of a typical orchid is 10 cm² and the operating current is 20 A, calculate the time required to electroplate an orchid. [Density of copper = 8.96 g cm⁻³]
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 15
Which components are used to make the standard hydrogen electrode?
A. H₂(g), H⁺(aq), Pt(s).
B. H₂(g), H⁺(aq), Ni(s).
C. H₂(g), HO⁻(aq), Pt(s).
D. H₂(g), HO⁻(aq), Ni(s).
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 16
z mol of copper is deposited from CuSO₄ (aq) by a current I in time t. What is the amount of silver, in mol, deposited by electrolysis from AgNO₃ (aq) by a current `frac{I}{2}` in time 2t?
A. `frac{z}{4}`
B. `frac{z}{2}`
C. z
D. 2z
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 17
a. Electrolysis can be used to obtain chlorine from molten sodium chloride. Write an equation for the reaction occurring at each electrode and describe the two different ways in which electricity is conducted when the cell is in operation.
b. In one experiment involving the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, 0.1 mol of chlorine was formed. Deduce, giving a reason, the amount of sodium formed at the same time.
c. In another experiment involving the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, the time of the electrolysis was halved and the current increased from 1 amp to 5 amp, compared to the experiment in (b). Deduce the amount of chlorine formed, showing your working.
d. If dilute aqueous sodium chloride is electrolyzed, a different product is obtained at each electrode. Identify the product formed at each electrode and write an equation showing its formation.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 18
a. The standard electrode potentials for three electrode systems are given below.
Ti³⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Ti²⁺(aq) E° = −0.37 V
Fe³⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Fe²⁺(aq) E° = +0.77 V
Ce⁴⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Ce³⁺(aq) E° = +1.45 V
i. Using the data above, deduce which species is the best reducing agent, giving a reason in terms of electrons for your answer.
ii. Write an equation, including state symbols, for the overall reaction with the greatest cell potential.
iii. State and explain the sign of ΔG° for the reaction in (a)(ii).
b. State the name of a solution that would produce only hydrogen and oxygen when electrolyzed using platinum electrodes.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 19
a. Molten sodium chloride can be electrolyzed using graphite electrodes.
i. Draw the essential components of this electrolytic cell and identify the products that form at each electrode.
ii. State the half-equations for the oxidation and reduction processes and deduce the overall cell reaction, including state symbols.
b. Explain why solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 20
Chromium(III) oxide, Cr₂O₃, can undergo different reactions to give other chromium containing species as shown in the diagram below:
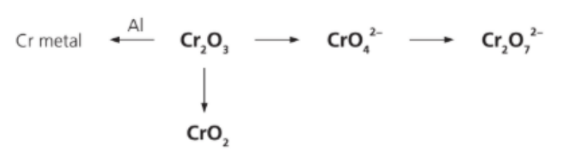
Which statement correctly describe these reactions?
A. The formation of Cr₂O₇²⁻ from CrO₄²⁻ is a redox reaction.
B. Aluminium is acting as an oxidizing agent.
C. CrO₃, CrO₄²⁻, Cr₂O₇²⁻ contains chromium in its highest oxidation state.
D. Cr₂O₃ reacts with CrO₃ in a disproportionation reaction to give CrO₂.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 21
Consider the following reactions which all occur in solution at room temperature:
Fe (s) + Cu²⁺ (aq) → Fe²⁺ (aq) + Cu (s)
Mg (s) + Zn²⁺ (aq) → Mg²⁺ (aq) + Zn (s)
Zn (s) + Fe²⁺ (aq) → Zn²⁺ (aq) + Fe (s)
Which is the correct combination of the strongest oxidizing agent and the strongest reducing agent?
| Strongest oxidizing agent | Strongest reducing agent | |
| A. | Zn (s) | Fe²⁺ (aq) |
| B. | Cu²⁺ (aq) | Mg (s) |
| C. | Mg (s) | Cu²⁺ (aq) |
| D. | Cu (s) | Mg²⁺ (aq) |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 22
Ethanedioic acid (oxalic acid),(COOH)₂, reacts with acidified potassium permanganate solution, KMnO4, according to the following equation:
5(COOH)₂(aq) + 2MnO₄⁻(aq) + 6H⁺(aq) → 10CO₂(g) + 2Mn²⁺(aq) + 8H₂O(l)
The reaction is a redox reaction.
a. Define oxidation in terms of electron transfer.
b. Calculate the change in oxidation numbers of carbon and manganese.
c. Identify the oxidizing and reducing agents.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 23
Chemical energy can be converted to electrical energy in the voltaic cell below.
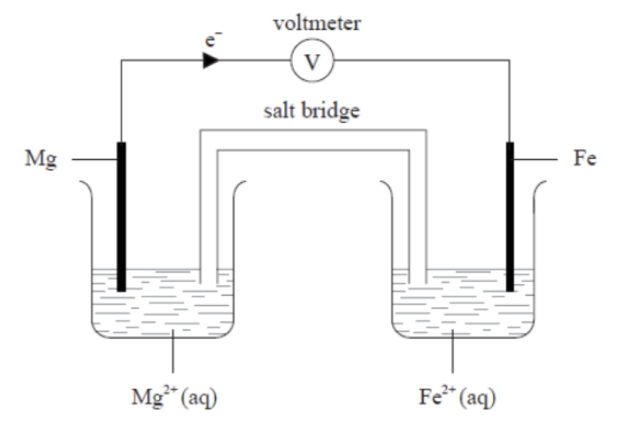
a. i. State the electron arrangement of a magnesium atom.
ii. State the half-equation which describes the change at the Mg electrode and deduce which metal is the positive electrode (cathode) of the cell.
b. Deduce the equation for the overall reaction occurring in the cell.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 24
Which is the species oxidized and the oxidizing agent in the reaction?
MnO₂(s) + 4HCl(aq) → MnCl₂(aq) + Cl₂(g) + 2H₂O(l)
| Species oxidized | Oxidizing agent | |
| A. | Cl⁻ | HCl |
| B. | MnO₂ | MnO₂ |
| C. | MnO₂ | HCl |
| D. | Cl⁻ | MnO₂ |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 25
Where does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell?
A. Positive electrode and anode.
B. Negative electrode and anode.
C. Positive electrode and cathode.
D. Negative electrode and cathode.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 26
Which describes the flow of electrons in a voltaic cell?
A. From the cathode (positive electrode) to the anode (negative electrode) through the external circuit.
B. From the anode (negative electrode) to the cathode (positive electrode) through the external circuit.
C. From the oxidizing agent to the reducing agent through the salt bridge.
D. From the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent through the salt bridge.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 27
Propan-2-ol can be used as a fuel in the fuel cell. At the anode propan-2-ol is oxidized to carbon dioxide. The electrons pass around the external circuit to the cathode. The protons formed from the oxidation move through the electrolyte to the cathode, where they react with oxygen to produce water.
a. Formulate half-equations for the reactions at the anode and cathode respectively.
b. Formulate the equation for the overall reaction.
c. The fuel cell has a cell potential (under standard conditions) of 1.56 V. By using suitable data from the data booklet suggest a value for the E° of the CO2/CH3CHOHCH3 electrode reaction.
d. Suggest a possible advantage of using the propan-2-ol fuel cell compared to a hydrogen fuel cell.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 28
Consider the following reaction:
3H2Se + 8HFeO4− + 6H2O → 8Fe(OH)3 + 3SeO42− + 2OH−
Which statement is correct?
A. HFeO4− is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
B. HFeO4− is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction.
C. H2Se is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction.
D. H2Se is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 29
Which statements are correct for a voltaic cell?
I. A spontaneous redox chemical reaction produces electrical energy.
II. Oxidation occurs at the cathode (negative electrode).
III. Electrons flow from anode (negative electrode) to cathode (positive electrode).
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 30
A voltaic cell is constructed from zinc and copper half-cells. Zinc is more reactive than copper.
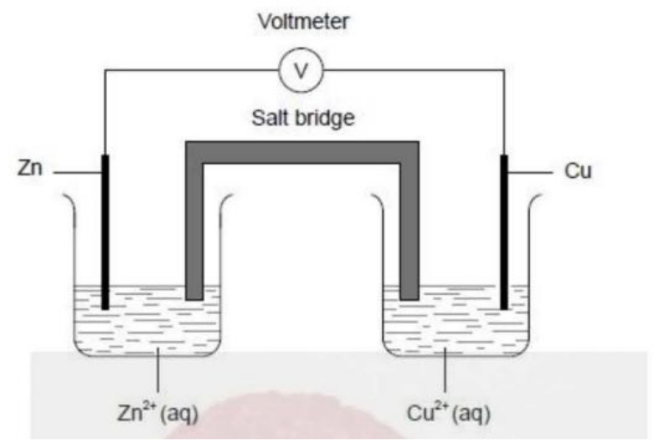
Which statement is correct when this cell produces electricity?
A. Electrons flow from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
B. The concentration of Cu²⁺ (aq) increases.
C. Electrons flow through the salt bridge.
D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half cell.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 31
The equations below represent reactions involved in the Winkler method for determining the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water:
2Mn(OH)2(s) + O2(aq) → 2MnO(OH)2(s)
MnO(OH)2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → Mn(SO4)2(s) + 3H2O(l)
Mn(SO4)2(s) + 2I−(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + I2(aq) + 2SO42−(aq)
2S2O32−(aq) + I2(aq) → S4O62−(aq) + 2I−(aq)
What is the amount, in mol, of thiosulfate ions, S2O32−(aq), needed to react with the iodine, I2(aq), formed by 1.00 mol of dissolved oxygen?
A. 2.00
B. 3.00
C. 4.00
D. 6.00
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 32
What are the products when molten sodium chloride is electrolyzed?
| Cathode | Anode | |
| A. | Hydrogen | Chlorine |
| B. | Sodium | Chloride |
| C. | Sodium | Chlorine |
| D. | Chlorine | Sodium |
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 33
A reaction takes place when a rechargeable battery is used:
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
Which statements are correct?
I. H+ is reduced.
II. The oxidation state of Pb metal changes from 0 to +2.
III. PbO2 is the oxidising agent.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 34
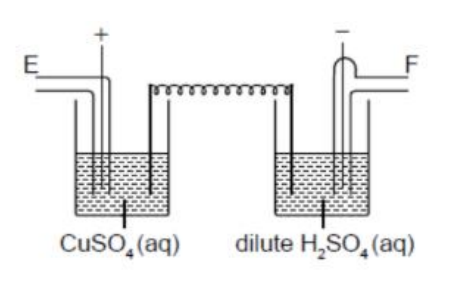
What are the relative volumes of gas given off at E and F during electrolysis of the two cells in series? Assume all electrodes are inert.
A. 1 : 1
B. 1 : 2
C. 2 : 1
D. 5 : 2
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 35
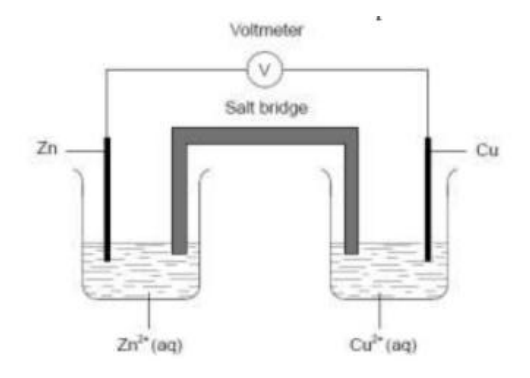
A voltaic cell is constructed from zinc and copper half-cells. Zinc is more reactive than copper. Which statement is correct when this cell produces electricity?
A. Electrons flow from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
B. The concentration of Cu²⁺(aq) increases.
C. Electrons flow through the salt bridge.
D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half cell.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Consider the following standard electrode potential values:
Fe³⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Fe²⁺(aq); E° = +0.77 V
Ni²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Ni(s); E° = −0.26 V
Fe²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Fe(s); E° = −0.45 V
Ca²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Ca(s); E° = −2.87 V
Answer: B. Fe(s) + 2Fe³⁺(s) → 3Fe²⁺(aq)
A spontaneous reaction occurs when
`""E_"cell"^∘=E_"reduction(cathode)"^∘-E_"reduction(anode)"^∘ > 0`
The more positive E∘ is the stronger the oxidizing agent. The more negative E∘ is, the stronger the reducing agent.
A. Incorrect:
Fe²⁺ + Ni(s) → Fe(s) + Ni²⁺
• Ni(s) → Ni²⁺ + 2e⁻ (oxidation, anode, E∘ = −0.26)
• Fe²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Fe(s) (reduction, cathode, E∘ = −0.45)
`""E_"cell"^o`= −0.45 − (−0.26) = −0.19 V
→ Not spontaneous
B. Correct:
Fe(s) + 2Fe³⁺ → 3Fe²⁺
• Fe(s) → Fe²⁺ + 2e⁻ (oxidation, E∘ = −0.45)
• Fe³⁺ + e⁻ → Fe²⁺ (reduction,E∘ = +0.77)
`""E_"cell"^o` = 0.77 − (−0.45) = +1.22 V
→ Spontaneous
C. Incorrect:
3Fe²⁺ → Fe(s) +2Fe³⁺
Reverse of option B → non-spontaneous (E∘ = −1.22 V)
D. Incorrect:
Ca²⁺ + Ni(s) → Ca(s) +Ni²⁺
• Ni(s) → Ni²⁺ + 2e⁻ (E∘ = −0.26)
• Ca²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Ca(s) (E∘ = −2.87)
`""E_"cell"^o` = −2.87 − (−0.26) = −2.61 V
→ Not spontaneous
Question 2
3-hydroxybutanoic acid is a metabolite which the body can use to provide energy when it is low on glucose.

a. Name the functional groups present in 3-hydroxybutanoic acid.
b. Draw the two stereoisomers of 3-hydroxybutanoic acid.
c. Draw the organic product formed when 3-hydroxybutanoic acid is left to react with an excess of a reducing agent and the mixture is quenched with acid.
d. i. When 3-hydroxybutanoic acid is reacted with potassium manganate(VII) (an oxidizing agent) an unstable compound with a degree of unsaturation of 2 is formed. Suggest the structure of this unstable compound.
ii. The unstable compound produced decomposes to form carbon dioxide and one other product with a degree of unsaturation of 1. Identify the product formed in this decomposition reaction.
Structure of 3-hydroxybutanoic acid
CH₃CH(OH)CH₂COOH
a. Functional groups present
• Hydroxyl (–OH) group (on C-3)
• Carboxylic acid (–COOH) group
b. Two stereoisomers
There is one chiral carbon (the carbon bearing the –OH group), so 3-hydroxybutanoic acid exists as two enantiomers (optical isomers):
• (R)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
• (S)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
c. Product from reaction with an excess reducing agent
Reduction converts both functional groups (–COOH → –CH₂OH and –OH remains → –CH₂OH):

→ Product: 1,3-butanediol (CH₃CH(OH)CH₂CH₂OH)
d. i. Reaction with KMnO₄ (oxidation)
• Oxidation of the secondary alcohol (–CH(OH)–) gives a carbonyl (C=O) group.
• The resulting compound has two double bonds (one C=O and one C=C if unstable) — degree of unsaturation = 2.
So the unstable compound is acetoacrylic acid:
CH₂ = C(COOH)–CO–OH
or more simply represented as:
CH₂ = C(COOH)–COOH
d. ii. Decomposition
This unstable compound decarboxylates (loses CO₂), forming a compound with one double bond (unsaturation = 1):
CH₂=CHCOOH
→ Product formed: Acrylic acid (propenoic acid, CH₂=CHCOOH)
Question 3
Which statement is correct for a voltaic but not for an electrolytic cell?
A. An electrolyte is required.
B. The anode is where oxidation occurs.
C. Ions move in the electrolyte.
D. Electrons flow from the negative. electrode to the positive electrode.
Answer: D. Electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode.
A. Incorrect: Both voltaic and electrolytic cells require electrolytes for ion conduction.
B. Incorrect: This is true for both types of cells — oxidation always happens at the anode (by definition).
C. Incorrect: Ion movement happens in both cells to maintain charge balance.
D. Correct: (For a voltaic cell only).
• In a voltaic cell, electrons flow spontaneously from the negative electrode (anode) to the positive electrode (cathode).
• In an electrolytic cell, the current is forced by an external power supply and the anode is positive — electrons flow into it instead.
Question 4
Which compound can be oxidized when heated with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate(VI)?
A. CH₃C(O)CH₂CH₃
B. CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃
C. (CH₃)₃COH
D. CH₃(CH₂)₂COOH
Answer: B. CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃
Acidified potassium dichromate(VI), K₂Cr₂O₇/H⁺ → is a strong oxidizing agent, oxidizing:
• Primary alcohols → aldehydes → carboxylic acids
• Secondary alcohols → ketones
• Tertiary alcohols → no reaction
• Ketones and carboxylic acids → generally not oxidized under normal conditions.
A. Incorrect: Ketones are not further oxidized by acidified dichromate under mild heating.
B. Correct: Secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones (butan-2-one).
C. Incorrect: Tertiary alcohols resist oxidation under these conditions (no hydrogen on the C–OH carbon).
D. Incorrect: Already in its fully oxidized form, cannot be further oxidized by dichromate(VI).
Question 5
Which of these functional groups will react with a reducing agent?
I. Alkoxy
II. Carboxyl
III. Carbonyl
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: C. II and III only.
I. Alkoxy (–OR)
This group is part of ethers (R–O–R) — they are quite stable and not easily reduced by normal reducing agents (e.g., LiAlH₄, NaBH₄).
⇒ Does not react with reducing agents.
II. Carboxyl (–COOH)
Carboxylic acids can be reduced (e.g., by LiAlH₄) to primary alcohols.
⇒ Reacts with reducing agents.
III. Carbonyl (C=O)
Carbonyl compounds (aldehydes, ketones) readily undergo reduction:
• Aldehydes → primary alcohols
• Ketones → secondary alcohols
⇒ Reacts with reducing agents.
Question 6
All non-cyclic structural isomers of alcohols with molecular formula C₄H₁₀O are reacted with hot acidified KMnO₄. How many will decolourize the purple KMnO₄?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer: B. 3
Step 1: List all non-cyclic structural isomers of alcohols with molecular formula C₄H₁₀O Possible alcohol isomers:
1. Butan-1-ol — CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂OH → primary alcohol
2. Butan-2-ol — CH₃CH(OH)CH₂CH₃ → secondary alcohol
3. 2-methylpropan-1-ol (isobutanol) — (CH₃)₂CHCH₂OH → primary alcohol
4. 2-methylpropan-2-ol (tert-butanol) — (CH₃)₃COH → tertiary alcohol → Total = 4 isomers
Step 2: Reactivity with hot acidified KMnO₄ (oxidation)
• Primary alcohols → oxidized to carboxylic acids
• Secondary alcohols → oxidized to ketones
• Tertiary alcohols → no reaction (resists oxidation)
Step 3: Which decolourise purple KMnO₄?
| Isomer | Type | Oxidized by KMnO₄? |
| Butan-1-ol | Primary | Yes |
| Butan-2-ol | Secondary | Yes |
| 2-methylpropan-1-ol | Primary | Yes |
| 2-methylpropan-2-ol | Tertiary | No |
Question 7
What is the oxidation half-equation in the redox reaction?
2S₂O₃²⁻(aq) + I₂(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2I⁻(aq)
A. I₂(aq) + 2e⁻ → 2I⁻(aq)
B. 2I⁻(aq) →. I₂(aq) + 2e⁻
C. 2S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2e⁻
D. S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2e⁻ → 2S₂O₃²⁻(aq)
Answer: C. 2S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2e⁻
Step 1: Identify oxidation and reduction
• I₂ → 2I⁻ : Reduction (gain of electrons).
• S₂O₃²⁻ → S₄O₆²⁻: Oxidation (loss of electrons).
Step 2: Write half-equations
Reduction (for iodine):
I₂ + 2e⁻ → 2I⁻
Oxidation (for thiosulfate):
2S₂O₃²⁻ → S₄O₆²⁻ + 2e⁻
Question 8
Which compounds are susceptible to oxidation with potassium manganate(VII)?
I. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂OH
II. (CH₃)₃CCH₂OH
III. CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: D. I, II and III.
Potassium manganate(VII), KMnO₄, is a strong oxidizing agent that oxidizes primary and secondary alcohols, but not tertiary alcohols.
Compound I: CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂OH – This is a primary alcohol (1-butanol). → Can be oxidized to butanal, and then to butanoic acid.
Compound II: (CH₃)₃CCH₂OH – The hydroxyl group is on a primary carbon (attached to one other carbon), so it is also a primary alcohol (neopentyl alcohol). → Can be oxidized, although it oxidizes more slowly due to steric hindrance. Compound III: CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃ – The hydroxyl group is attached to a secondary carbon (attached to two other carbons).
→ Can be oxidized to a ketone (2-butanone).
Question 9
Consider the following standard electrode potential values:
Cu⁺(aq) + e⁻ ⇌ Cu(s) E° = +0.52 V
MnO₄⁻(aq) + 8H⁺(aq) + 5e⁻ ⇌ Mn²⁺(aq) + 4H₂O(l) E° = +1.51 V
What is the cell potential for this reaction?
MnO₄⁻(aq) + 8H⁺(aq) + 5Cu(s) → Mn²⁺(aq) + 4H₂O(l) + 5Cu⁺(aq)
A. +2.03
B. +0.99
C. −0.99
D. −2.03
Answer: B. +0.99
• Cathode (reduction):
MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5e⁻ ⇌ Mn²⁺ + 4H₂O `""E_"red"^°` = +1.51 V
• Anode (oxidation):
Cu(s) ⇌ Cu⁺ + e⁻
The corresponding reduction potential for Cu+/Cu is +0.52 V.
Cell potential:
`""E_"cell"^∘=E_"cathode"^∘-E_"anode(asreduction")^∘`= 1.51 - 0.52 = +0.99`
Question 10
During a titrimetric analysis, 25.00 cm³ of an aqueous solution containing ethanol required 37.50 cm³ of 1.50 mol dm⁻³ of acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution for complete reaction. The density of ethanol is 0.790 g cm⁻³.
During the reaction, ethanol, CH₃CH₂OH, is oxidized to ethanoic acid, CH₃COOH, while dichromate(VI) ions, Cr₂O₇²⁻, react as shown in the following half-equation:
Cr₂O₇²⁻(aq) + 14H⁺(aq) + 6e⁻ → 2Cr³⁺(aq) + 7H₂O(l)
a. Explain, in terms of change in oxidation state, why dichromate(VI) ions undergo reduction.
b. Write the half-equation for the oxidation of ethanol, CH₃CH₂OH, to ethanoic acid, CH₃COOH.
c. Use the half-equations to construct an ionic equation for the above redox reaction.
d. Using the titration results and relevant data, calculate the volume of ethanol in 25.00 cm³ of the alcoholic solution.
e. Determine the concentration as a percentage by volume of the alcoholic solution.
a. Why dichromate(VI) is reduced (oxidation-state view)
In Cr₂O₇²⁻, chromium is +6, and it becomes +3 in Cr³⁺; the oxidation state decreases (it gains electrons), so dichromate(VI) is reduced.
b. Oxidation half-equation for ethanol → ethanoic acid (acidic solution)
CH₃CH₂OH + H₂O → CH₃COOH + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻
c. Overall ionic equation
Match electrons: 2×(dichromate half-equation) gives 12 e⁻; 3×(ethanol half-equation) gives 12 e⁻.
Add and simplify:
2Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 16H⁺ + 3CH₃CH₂OH → 4Cr³⁺+ 3CH₃COOH + 11H₂O
d. Volume of ethanol in the 25.00 cm³ sample
Moles of dichromate used:
`""n_(Cr_2O_7^2-)` = 1.50 moldm⁻³ × 0.03750dm³ = 0.05625 mol
Electron balance shows Cr₂O₇²⁻ : ethanol = 2 : 3.
So moles of ethanol:
nethanol = `frac{3}{2}`× 0.05625 = 0.084375 mol
Mass of ethanol:
m = n × M = 0.084375 × 46.07 ≈ 3.887 g
Volume of ethanol (density = 0.790 g cm⁻³):
V = `frac{m}{rho}=frac{3.887}{0.790}`≈ 4.92 cm³
e. Concentration as % (v/v)
%`frac{v}{v}=frac{4.92}{25.00}*100`≈ 19.7% (v/v)
Question 11
For which of the reactions below will the Gibbs energy change ΔG° be the most negative?
A. Cu(s) + 2Ag⁺(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) E° = +0.46 V
B. Co(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Cu(s) + Co²⁺(aq) E° = +0.62 V
C. Fe²⁺(aq) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Fe³⁺(aq) + Cu⁺(aq) E° = −0.61 V
D. H₂(g) + Cr²⁺(aq) → Cr(s) + 2H⁺(aq) E° = −0.74 V
Answer: B. Co(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Cu(s) + Co²⁺(aq) E° = +0.62 V
Reason:
ΔGo = −nF`""E_"cell"^o`
The most negative ΔGo occurs for the largest positive value of nEo.
Compute n (electrons transferred) and Eo:
A. Incorrect:
n = 2 (Cu⁰ → +2; 2×Ag⁺ 1e⁻ each).
nEo = 2(0.46) = 0.92
B. Correct:
n = 2 (Co⁰ → +2; Cu²⁺ → Cu).
nEo = 2(0.62) = 1.24 (largest) → most negative ΔGo.
C. Incorrect:
n = 1, Eo = −0.61 → nEo = −0.61 (overall ΔGo > 0, not spontaneous).
D. Incorrect:
n = 2, Eo = −0.74 → nEo = −1.48 (also ΔGo > 0).
Question 12
Using the standard electrode potentials given, calculate the standard cell potential when an I₂, I⁻ half-cell (E° = +0.54 V) is connected to a Cl₂/Cl⁻ half-cell (E° = +1.36 V).
A. +3.80 V
B. +1.90 V
C. +1.64 V
D. +0.82 V
Answer: D. +0.82 V
Step 1. Identify which half-cell is oxidized and which is reduced
The more positive Eo value means the species is a stronger oxidizing agent (more likely to be reduced).
• Cl₂/Cl⁻ has higher Eo= +1.36 V→ Cl₂ is reduced.
• I₂/ I⁻ will be oxidized (the reverse of its half-equation).
Step 2. Write half-equations
• Anode (oxidation):
2I₂ → I⁻ + 2e⁻
`""E_"oxidation"^o`= -0.54V
• Cathode (reduction):
Cl₂ + 2e⁻ → 2Cl⁻
`""E_"reduction"^o = +1.36`
Step 3. Calculate cell
`""E_"cell"^o=E_"cathode"^o-E_"anode (reduction)"^o`
`""E_"cell"^o`= 1.36 - 0.54 = +0.82 V
→ Cell potential = +0.82 V, spontaneous reaction.
Question 13
a. i. Draw a diagram for the voltaic cell formed by connecting the following standard half-cells:
Ni(s) | Ni²⁺(aq) || Mn²⁺(aq) | Mn(s)
ii. Describe the key features of the hydrogen half-cell.
b. i. Write an equation for the reaction in each half-cell, identifying the species which is oxidized and the oxidizing agent.
ii. State which electrode is the anode and state the direction of electron flow in the external circuit.
iii. For the overall cell, calculate its voltage and state the sign of ΔG.
a. i. Draw the cell diagram
The cell is:
Ni(s) | Ni²⁺(aq) || Mn²⁺(aq) | Mn(s)
Diagram description:
• Left-hand side (anode) → Ni(s) electrode dipping into Ni²⁺(aq)
• Right-hand side (cathode) → Mn(s) electrode dipping into Mn²⁺(aq)
• Salt bridge connects both solutions
• Voltmeter connected externally between the two electrodes
a. ii. Describe the key features of the hydrogen half-cell
The standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) has:
1. A platinum electrode coated with platinum black (inert, conducts electrons).
2. A solution containing 1.0 mol dm⁻³ H⁺ ions (usually from HCl).
3. Hydrogen gas at 1 atm bubbled over the electrode.
4. Temperature at 298 K (25 °C).
5. Assigned a standard potential of 0.00 V, used as the reference electrode.
b. i. Write half-equations and identify species
Given standard electrode potentials (approximate typical values):
Ni²⁺ + 2e− → Ni(s), Eo = −0.25 V
Mn²⁺ + 2e− → Mn(s), Eo = −1.18 V
The more positive Eo value means reduction occurs there (cathode). Hence:
• Ni²⁺/Ni is reduced (cathode reaction).
• Mn(s) is oxidized (anode reaction).
Half-equations:
At anode (oxidation):
Mn(s) → Mn²⁺(aq) + 2e−
At cathode (reduction):
Ni²⁺ (aq) + 2e− → Ni(s)
Overall equation:
Mn(s) + Ni²⁺(aq) →Mn²⁺(aq) + Ni(s)
• Oxidized species: Mn
• Oxidizing agent: Ni²⁺
b. ii. Which electrode is the anode and electron flow direction
• Anode: Mn electrode (oxidation occurs here).
• Cathode: Ni electrode (reduction occurs here).
• Electron flow: from Mn → Ni in the external circuit.
b. iii. Calculate cell voltage and sign of ΔG.
`""E_"cell"^o = E_"cathode"^o - E_"anode"^o`
`""E_"cell"^o`= (-0.25) - (-1.18) = +0.93V
`""E_"cell"^o` positive → reaction is spontaneous.
ΔG° = -nF`""E_"cell"^o` < 0
Question 14
In copper-plating, orchids are coated with a thin layer of graphite paste before placing them in a bath of aqueous copper(II) sulfate and electroplating with copper as the anode.
a. Suggest a reason why orchids are first coated with graphite.
b. Deduce the half equations at the cathode and anode.
c. To ensure high standards of electroplated orchids, the copper coating must be at least 0.5 mm thick. Given that the total surface area of a typical orchid is 10 cm² and the operating current is 20 A, calculate the time required to electroplate an orchid. [Density of copper = 8.96 g cm⁻³]
a. Graphite makes the orchid surface conductive and inert, so it can act as the cathode without reacting with the electrolyte.
b. Half-equations (Cu anode | CuSO₄(aq) | graphite-coated orchid cathode)
• Cathode (on the orchid):
Cu2+(aq) + 2e− → Cu(s)
• Anode (copper):
Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e−
c. Thickness required = 0.5 mm = 0.05 cm
Area = 10 cm²
Volume of Cu deposited:
V = A × thickness = 10 × 0.05 = 0.50 cm3
Mass of Cu:
m = pV = 8.96 × 0.50 = 4.48 g
Moles of Cu:
n =`frac{m}{M}`= `frac{4.48}{63.55}`≈ 0.0705 mol
Charge needed (z = 2 for Cu²⁺):
Q = nzF = 0.0705 × 2 × 96485 ≈ 1.37 × 104 C
Time at I = 20 A:
`t = frac{Q}{I}=frac{1.37*10^4}{20}`≈ 6.8 × 102 s ≈ 11.4 min
Question 15
Which components are used to make the standard hydrogen electrode?
A. H₂(g), H⁺(aq), Pt(s).
B. H₂(g), H⁺(aq), Ni(s).
C. H₂(g), HO⁻(aq), Pt(s).
D. H₂(g), HO⁻(aq), Ni(s).
Answer: A. H₂(g), H⁺(aq), Pt(s).
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is composed of:
• Hydrogen gas (H₂) at 1 atm pressure,
• 1.0 mol dm⁻³ H⁺ ions (usually from a strong acid like HCl)
• An inert platinum (Pt) electrode coated with platinum black to catalyze the redox reaction.
Half-equation:
2H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ↔ 2H₂(g)
Question 16
z mol of copper is deposited from CuSO₄ (aq) by a current I in time t. What is the amount of silver, in mol, deposited by electrolysis from AgNO₃ (aq) by a current `frac{I}{2}` in time 2t?
A. `frac{z}{4}`
B. `frac{z}{2}`
C. z
D. 2z
Answer: D. 2z
From Faraday’s Law:
`n = frac{It}{z_eF}`
where
n = moles of metal deposited,
I = current,
t = time,
ze = number of electrons per ion (valency),
F = Faraday constant.
Step 1: For copper
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu(s)
So, ze = 2.
`""n_"Cu"=frac{It}{2F}=z`
Step 3: For silver
Ag+ + e− → Ag(s)
So, ze = 1.
Now the conditions: Current =`frac{I}{2}`, time = 2t
`""n_"Ag"=frac{(frac{I}{2})*(2t)}{1*F}=frac{It}{F}`
Step 4: Express nAg in terms of z
From the copper case:
z = `frac{It}{2F}`⇒ `frac{It}{F}=2z`
Thus,
nAg = 2z
Question 17
a. Electrolysis can be used to obtain chlorine from molten sodium chloride. Write an equation for the reaction occurring at each electrode and describe the two different ways in which electricity is conducted when the cell is in operation.
b. In one experiment involving the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, 0.1 mol of chlorine was formed. Deduce, giving a reason, the amount of sodium formed at the same time.
c. In another experiment involving the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, the time of the electrolysis was halved and the current increased from 1 amp to 5 amp, compared to the experiment in (b). Deduce the amount of chlorine formed, showing your working.
d. If dilute aqueous sodium chloride is electrolyzed, a different product is obtained at each electrode. Identify the product formed at each electrode and write an equation showing its formation.
a. Electrolysis of molten sodium chloride
• At cathode (reduction):
Na+ + e− → Na(l)
• At anode (oxidation):
2Cl− → Cl2(g) + 2e−
Overall reaction:
2NaCl(l) → 2Na(l) + Cl2(g)
How electricity is conducted:
• In molten NaCl, conduction is by movement of ions (Na+ and Cl−).
• In the external circuit, conduction is by movement of electrons through the wires.
b. Given: 0.1 mol Cl2 is formed.
From the anode reaction:
2Cl− → Cl2 + 2e−
1 mol Cl2 corresponds to 2 mol e−.
→ 0.1 mol Cl2 corresponds to 0.2 mol e−.
At the cathode, each Na+ gains 1 e−t o form Na.
→ 0.2 mol e− forms 0.2 mol Na.
`=>` Amount of Na formed = 0.2 mol (For every 1 mol Cl2 formed, 2 mol Na are produced.)
c. If time is halved and current is increased from 1 A to 5 A, the charge (Q = It) changes by:
Q2 = I2t2 = 5 × `frac{t}{2}`= 2.5I1t
So the charge (and moles of electrons) increase by a factor of 2.5.
Hence, chlorine formed:
0.1 mol × 2.5 = 0.25 mol Cl2
d. Electrolysis of dilute aqueous NaCl (Brine)
Because water is present, H+ and OH− ions compete with Na+ and Cl−.
At cathode (reduction):
Hydrogen is produced (since water is reduced more easily than Na+):
2H2O(l) + 2e− → H2(g) + 2OH−(aq)
At anode (oxidation):
Chloride is oxidized (not OH− under these conditions):
2Cl− → Cl2(g) + 2e−
Products:
• Cathode: Hydrogen gas (H2)
• Anode: Chlorine gas (Cl2)
• Solution left behind: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Question 18
a. The standard electrode potentials for three electrode systems are given below.
Ti³⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Ti²⁺(aq) E° = −0.37 V
Fe³⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Fe²⁺(aq) E° = +0.77 V
Ce⁴⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Ce³⁺(aq) E° = +1.45 V
i. Using the data above, deduce which species is the best reducing agent, giving a reason in terms of electrons for your answer.
ii. Write an equation, including state symbols, for the overall reaction with the greatest cell potential.
iii. State and explain the sign of ΔG° for the reaction in (a)(ii).
b. State the name of a solution that would produce only hydrogen and oxygen when electrolyzed using platinum electrodes.
a. i. Best reducing agent: Ti²⁺(aq).
Reason: It donates electrons most readily (is most easily oxidized) because its couple has the most negative reduction potential:
Ti³⁺ + e⁻ → Ti²⁺, E° = –0.37 V.
ii. Pair the strongest oxidizing agent with the strongest reducing agent:
• Cathode (reduction, largest E°): Ce⁴⁺ + e⁻ → Ce³⁺ (E° = +1.45 V).
• Anode (oxidation): Ti²⁺ → Ti³⁺ + e⁻ (reverse of –0.37 V)
• Overall:
Ce⁴⁺(aq) + Ti²⁺(aq) → Ce³⁺(aq) + Ti³⁺(aq)
E°cell = 1.45 – (–0.37) = +1.82 V
iii. ΔG° = –nFE°
Here n = 1 and E°cell = +1.82 V → ΔG° < 0.
So the reaction is spontaneous and releases free energy.
b. A solution that gives only H₂ and O₂ with Pt electrodes: dilute sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄ (aq)).
Question 19
a. Molten sodium chloride can be electrolyzed using graphite electrodes.
i. Draw the essential components of this electrolytic cell and identify the products that form at each electrode.
ii. State the half-equations for the oxidation and reduction processes and deduce the overall cell reaction, including state symbols.
b. Explain why solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity.
a. i. Essential cell + products
• Diagram (describe): a container/crucible of molten NaCl(l) with two graphite electrodes dipped in. Connect the positive terminal of a DC supply to the anode, and the negative terminal to the cathode.
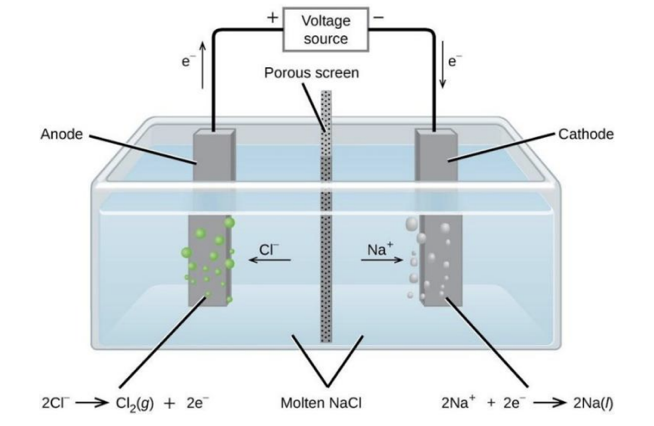
• Ions move: Na⁺ → cathode, Cl⁻ → anode.
• Product at positive electrode (anode): Cl₂(g).
• Product at negative electrode (cathode): Na(l) (sodium metal; molten at operating temperature).
a. ii. Half-equations and overall
• Cathode (reduction): Na⁺(l) + e⁻ → Na(l)
• Anode (oxidation): 2Cl⁻(l) → Cl₂(g) + 2e⁻
• Overall reaction:
2NaCl(l) → 2Na(l) + Cl₂(g)
b. Why solid NaCl doesn’t conduct
In the solid, ions are locked in a giant ionic lattice and cannot move, so there are no mobile charge carriers. (When molten or dissolved, the ions are free to move and it conducts.)
Question 20
Chromium(III) oxide, Cr₂O₃, can undergo different reactions to give other chromium containing species as shown in the diagram below:

Which statement correctly describe these reactions?
A. The formation of Cr₂O₇²⁻ from CrO₄²⁻ is a redox reaction.
B. Aluminium is acting as an oxidizing agent.
C. CrO₃, CrO₄²⁻, Cr₂O₇²⁻ contains chromium in its highest oxidation state.
D. Cr₂O₃ reacts with CrO₃ in a disproportionation reaction to give CrO₂.
Answer: C. CrO₃, CrO₄²⁻, Cr₂O₇²⁻ contains chromium in its highest oxidation state.
A. Incorrect:
• In acid: 2CrO₄²⁻ + 2H⁺ ⇌ Cr₂O₇²⁻ + H₂O.
• Cr stays +6 in both chromate and dichromate → acid–base/condensation equilibrium, not redox.
B. Incorrect:
• Thermite-type reduction: Cr₂O₃ + 2Al → 2Cr + Al₂O₃.
• Al is oxidized to Al³⁺, so it is the reducing agent, not oxidizing.
C. Correct:
In all three, chromium is +6, which is Cr’s maximum common oxidation state.
D. Incorrect:
Cr₂O₃ (Cr³⁺) + CrO₃ (Cr⁶⁺) → 3CrO₂ (Cr⁴⁺).
This is comproportionation (different oxidation states combine to an intermediate), not disproportionation.
Question 21
Consider the following reactions which all occur in solution at room temperature:
Fe (s) + Cu²⁺ (aq) → Fe²⁺ (aq) + Cu (s)
Mg (s) + Zn²⁺ (aq) → Mg²⁺ (aq) + Zn (s)
Zn (s) + Fe²⁺ (aq) → Zn²⁺ (aq) + Fe (s)
Which is the correct combination of the strongest oxidizing agent and the strongest reducing agent?
| Strongest oxidizing agent | Strongest reducing agent | |
| A. | Zn (s) | Fe²⁺ (aq) |
| B. | Cu²⁺ (aq) | Mg (s) |
| C. | Mg (s) | Cu²⁺ (aq) |
| D. | Cu (s) | Mg²⁺ (aq) |
Answer: B.
Given reactions:
• Fe(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Fe²⁺(aq) + Cu(s)
→ Fe is oxidized (reducing agent), Cu²⁺ is reduced (oxidizing agent).
• Mg(s) + Zn²⁺(aq) → Mg²⁺(aq) + Zn(s)
→ Mg is oxidized (reducing agent), Zn²⁺ is reduced (oxidizing agent).
• Zn(s) + Fe²⁺(aq) → Zn²⁺(aq) + Fe(s)
→ Zn is oxidized (reducing agent), Fe²⁺ is reduced (oxidizing agent).
Step 1: Determine relative reactivity
From the above:
• Mg can reduce Zn²⁺ → Mg is stronger reducing agent than Zn.
• Zn can reduce Fe²⁺ → Zn is stronger reducing agent than Fe.
• Fe can reduce Cu²⁺ → Fe is stronger reducing agent than Cu.
So the reducing power order (strongest → weakest): Mg > Zn > Fe > Cu The oxidizing power order (reverse, for the ions): Cu²⁺ > Fe²⁺ > Zn²⁺ > Mg²⁺
Step 2: Identify strongest agents
• Strongest oxidizing agent: the one that’s most easily reduced → Cu²⁺(aq)
• Strongest reducing agent: the one that’s most easily oxidized → Mg(s)
Question 22
Ethanedioic acid (oxalic acid),(COOH)₂, reacts with acidified potassium permanganate solution, KMnO4, according to the following equation:
5(COOH)₂(aq) + 2MnO₄⁻(aq) + 6H⁺(aq) → 10CO₂(g) + 2Mn²⁺(aq) + 8H₂O(l)
The reaction is a redox reaction.
a. Define oxidation in terms of electron transfer.
b. Calculate the change in oxidation numbers of carbon and manganese.
c. Identify the oxidizing and reducing agents.
a. Oxidation (in terms of electron transfer): loss of electrons.
b. Oxidation-number changes
• Carbon in ethanedioic (oxalic) acid, (COOH)₂: each carbon is +3 (carboxyl carbon).
In the product CO₂, carbon is +4.
→ Change per C: +3 → +4 (+1, i.e., oxidation).
With 10 carbons total (from 5(COOH)₂), total electrons lost = 10 e⁻.
• Manganese in MnO₄⁻: +7 → in Mn²⁺: +2.
→ Change per Mn: +7 → +2 (−5, i.e., reduction).
With 2 Mn, total electrons gained = 10 e⁻ (balances the carbon loss).
c. Agents
• Oxidizing agent: MnO₄⁻ (acidified KMnO₄); it is reduced to Mn²⁺.
• Reducing agent: (COOH)₂ (ethanedioic/oxalic acid); it is oxidized to CO₂.
Question 23
Chemical energy can be converted to electrical energy in the voltaic cell below.

a. i. State the electron arrangement of a magnesium atom.
ii. State the half-equation which describes the change at the Mg electrode and deduce which metal is the positive electrode (cathode) of the cell.
b. Deduce the equation for the overall reaction occurring in the cell.
a. i. Electron arrangement of magnesium atom
Magnesium has atomic number 12, so its electron arrangement is: 2, 8, 2 or in subshell notation: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s²
a. ii. Half-equation at the Mg electrode and identification of electrodes At the magnesium electrode, magnesium loses electrons (oxidation): Mg(s) → Mg²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻
• Since oxidation occurs at magnesium, the Mg electrode is the anode (negative electrode).
• The Fe electrode therefore is the cathode (positive electrode) because reduction occurs there.
At the iron electrode (cathode): Fe²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Fe(s)
b. Overall cell reaction
Combine the two half-equations:
Mg(s) + Fe²⁺(aq) → Mg²⁺(aq) + Fe(s)
Question 24
Which is the species oxidized and the oxidizing agent in the reaction?
MnO₂(s) + 4HCl(aq) → MnCl₂(aq) + Cl₂(g) + 2H₂O(l)
| Species oxidized | Oxidizing agent | |
| A. | Cl⁻ | HCl |
| B. | MnO₂ | MnO₂ |
| C. | MnO₂ | HCl |
| D. | Cl⁻ | MnO₂ |
Answer: D.
Step 1: Determine oxidation states
| Element | Reactant | Oxidation state | Product |
| Mn | In MnO₂ → +4 | In MnCl₂ → +2 | ↓ Reduction |
| Cl | In HCl → -1 | In Cl₂ → 0 | ↑ Oxidation |
Step 2: Identify species oxidized and oxidizing agent
• Species oxidized: Chloride ion (Cl⁻) because it goes from -1 → 0.
• Species reduced: Manganese in MnO₂ (from +4 → +2).
• Oxidizing agent: The substance that causes oxidation (is reduced itself).
→ MnO₂ is reduced, so MnO₂ is the oxidizing agent.
Question 25
Where does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell?
A. Positive electrode and anode.
B. Negative electrode and anode.
C. Positive electrode and cathode.
D. Negative electrode and cathode.
Answer: B. Negative electrode and anode.
For voltaic (galvanic) cells:
• Oxidation occurs at the anode.
• Reduction occurs at the cathode.
• In a voltaic cell, the anode is negative and the cathode is positive (because electrons flow spontaneously from anode → cathode).
Question 26
Which describes the flow of electrons in a voltaic cell?
A. From the cathode (positive electrode) to the anode (negative electrode) through the external circuit.
B. From the anode (negative electrode) to the cathode (positive electrode) through the external circuit.
C. From the oxidizing agent to the reducing agent through the salt bridge.
D. From the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent through the salt bridge.
Answer: B. From the anode (negative electrode) to the cathode (positive electrode) through the external circuit.
A. Incorrect: Wrong direction. Electrons move toward the cathode, not away from it.
B. Correct: This is exactly how electrons flow in a voltaic cell.
C. Incorrect: The salt bridge carries ions, not electrons.
D. Incorrect: The salt bridge allows ion movement, not electrons.
Question 27
Propan-2-ol can be used as a fuel in the fuel cell. At the anode propan-2-ol is oxidized to carbon dioxide. The electrons pass around the external circuit to the cathode. The protons formed from the oxidation move through the electrolyte to the cathode, where they react with oxygen to produce water.
a. Formulate half-equations for the reactions at the anode and cathode respectively.
b. Formulate the equation for the overall reaction.
c. The fuel cell has a cell potential (under standard conditions) of 1.56 V. By using suitable data from the data booklet suggest a value for the E° of the CO2/CH3CHOHCH3 electrode reaction.
d. Suggest a possible advantage of using the propan-2-ol fuel cell compared to a hydrogen fuel cell.
a. Half-equations
• At the anode (oxidation):
Propan-2-ol (CH3CHOHCH3) is oxidized to carbon dioxide. For simplicity, you can write the overall oxidation as:
CH3CHOHCH3 + 9H2O → 3CO2 + 24H+ + 24e−
This shows oxidation (loss of electrons).
• At the cathode (reduction):
Oxygen is reduced to water:
6O2 + 24H+ + 24e− → 12H2O
b. Overall cell reaction
Add both half-equations, canceling electrons and balancing water and protons:
CH3CHOHCH3 + 3O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
c. Cell potential
`""E_"cell"^°`= 1.56 V
and we know:
`E_(O_2"/"H_2O)^o`= +1.23V
Use the formula:
Ecell = Ecathode - Eanode
So:
1.56 = 1.23 - `""E_"anode"^o`
`""E_"anode"^o`= -0.33V
→ `""E_(CO_2"/"CH_3CHOHCH_3)^o`= -0.33 V
d. Advantage of using propan-2-ol fuel cell over hydrogen fuel cell
• Propan-2-ol is a liquid fuel, easier and safer to store and transport than hydrogen gas.
• It has a higher energy density, giving longer operation for the same volume of fuel.
• It can be produced from renewable biomass sources.
Question 28
Consider the following reaction:
3H2Se + 8HFeO4− + 6H2O → 8Fe(OH)3 + 3SeO42− + 2OH−
Which statement is correct?
A. HFeO4− is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
B. HFeO4− is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction.
C. H2Se is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction.
D. H2Se is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
Answer: B. HFeO₄⁻ is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction.
Step 1: Identify agents
• Oxidizing agent = gets reduced
→ HFeO₄⁻ (Fe⁶⁺ → Fe³⁺)
• Reducing agent = gets oxidized
→ H₂Se (Se²⁻ → Se⁶⁺)
Step 2: Evaluate each option
A. Incorrect:
HFeO₄⁻ is the oxidizing agent, but it undergoes reduction, not oxidation. An oxidizing agent causes oxidation in another species by being reduced itself.
B. Correct:
Fe in HFeO₄⁻ goes from +6 to +3, meaning it gains electrons (reduction). Therefore, HFeO₄⁻ acts as the oxidizing agent.
C. Incorrect:
H₂Se is oxidized, not reduced. Its Se atom goes from −2 → +6, losing electrons, so it cannot be the oxidizing agent. It’s actually the reducing agent.
D. Incorrect:
While H₂Se does undergo oxidation, that makes it the reducing agent, not the oxidizing agent. The oxidizing agent must gain electrons, not lose them.
Question 29
Which statements are correct for a voltaic cell?
I. A spontaneous redox chemical reaction produces electrical energy.
II. Oxidation occurs at the cathode (negative electrode).
III. Electrons flow from anode (negative electrode) to cathode (positive electrode).
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: B. I and III only.
• Statement I: A spontaneous redox chemical reaction produces electrical energy.
→ Correct.
That’s the definition of a voltaic (galvanic) cell – a spontaneous redox reaction converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
• Statement II: Oxidation occurs at the cathode (negative electrode). → Incorrect. In a voltaic cell, oxidation occurs at the anode, which is the negative electrode. The cathode (positive electrode) is where reduction happens.
• Statement III: Electrons flow from anode (negative electrode) to cathode (positive electrode). → Correct.
Electrons are released during oxidation at the anode and travel through the external circuit to the cathode.
Question 30
A voltaic cell is constructed from zinc and copper half-cells. Zinc is more reactive than copper.

Which statement is correct when this cell produces electricity?
A. Electrons flow from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
B. The concentration of Cu²⁺ (aq) increases.
C. Electrons flow through the salt bridge.
D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half cell.
Answer: D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
A zinc–copper voltaic cell
• Zinc is more reactive → oxidized → anode (negative electrode)
• Copper is less reactive → reduced → cathode (positive electrode) Half equations:
Anode: Zn(s) → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻
Cathode: Cu²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Cu(s)
Electrons move through the wire from Zn to Cu.
Now check each option
A. Incorrect: Electrons flow from zinc → copper, not the reverse.
B. Incorrect: Cu²⁺ ions are used up (reduced to Cu(s)), so concentration decreases.
C. Incorrect: Ions, not electrons, move through the salt bridge.
D. Correct: Anions (negative ions, e.g., NO₃⁻ or Cl⁻) move toward the anode (Zn half cell) to balance the positive charge of Zn²⁺ being formed.
Question 31
The equations below represent reactions involved in the Winkler method for determining the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water:
2Mn(OH)2(s) + O2(aq) → 2MnO(OH)2(s)
MnO(OH)2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → Mn(SO4)2(s) + 3H2O(l)
Mn(SO4)2(s) + 2I−(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + I2(aq) + 2SO42−(aq)
2S2O32−(aq) + I2(aq) → S4O62−(aq) + 2I−(aq)
What is the amount, in mol, of thiosulfate ions, S2O32−(aq), needed to react with the iodine, I2(aq), formed by 1.00 mol of dissolved oxygen?
A. 2.00
B. 3.00
C. 4.00
D. 6.00
Answer: C. 4.00
Step 1: Relationship between O2 and I2
From (1):
2Mn(OH)2(s) + O2(aq) → 2MnO(OH)2(s)
So 1 mol of O2 produces 2 mol of MnO(OH)2.
From (3):
Mn(SO4)2 + 2I− → Mn2+ + I2 + 2SO42−
Each 1 mol of Mn compound produces 1 mol of I2.
Hence, 1 mol of O2 → 2 mol of I2.
Step 2: Relationship between I2 and S₂O₃²⁻
From (4):
2S2O32− + I2 → S4O62− + 2I−
So 1 mol of I₂ reacts with 2 mol of S2O32−.
Step 3: Combine ratios
1 mol O2 ⇒ 2 mol I2 ⇒ 2 × 2 = 4 mol S2O32−
Question 32
What are the products when molten sodium chloride is electrolyzed?
| Cathode | Anode | |
| A. | Hydrogen | Chlorine |
| B. | Sodium | Chloride |
| C. | Sodium | Chlorine |
| D. | Chlorine | Sodium |
Answer: C.
Molten sodium chloride contains:
• Na⁺ (sodium ions)
• Cl⁻ (chloride ions)
Since it’s molten, there’s no water – only these ions.
Step 2: Reactions at each electrode
• At the cathode (negative electrode): Reduction occurs – Na⁺ gains electrons:
Na⁺ + e⁻ → Na(l)
→ Product: sodium metal
• At the anode (positive electrode): Oxidation occurs – Cl⁻ loses electrons: 2Cl⁻ → Cl2(g) + 2e⁻
→ Product: chlorine gas
Question 33
A reaction takes place when a rechargeable battery is used:
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
Which statements are correct?
I. H+ is reduced.
II. The oxidation state of Pb metal changes from 0 to +2.
III. PbO2 is the oxidising agent.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: C. II and III only.
I. H⁺ is reduced → Incorrect
H⁺ is not reduced — it remains part of the water molecules formed, but the real reduction occurs in PbO2 (Pb4+ → Pb2+)
II. The oxidation state of Pb metal changes from 0 to +2 → Correct Pb(s) is oxidized to Pb2+ in PbSO4, so oxidation state increases from 0 → +2.
III. PbO2 is the oxidizing agent → Correct
PbO2 contains Pb in +4 oxidation state; it accepts electrons and is reduced to Pb2+ – hence, it acts as the oxidizing agent.
Question 34
What are the relative volumes of gas given off at E and F during electrolysis of the two cells in series? Assume all electrodes are inert.

A. 1 : 1
B. 1 : 2
C. 2 : 1
D. 5 : 2
Answer: C. 2 : 1
Cell 1: CuSO₄(aq) (inert electrodes)
• Cathode (−): Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu(s) (copper deposited)
• Anode (+): 2H₂O → O₂(g) + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ (since electrodes are inert and sulfate ions are not oxidized)
→ Gas evolved = O₂ at electrode E (anode)
Cell 2: Dilute H₂SO₄(aq) (inert electrodes)
• Cathode (−): 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂(g)
• Anode (+): 2H₂O → O₂(g) + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻
But since it’s in series with the CuSO₄ cell, the same current (same number of electrons) passes through both.
At F (cathode), H₂ gas is produced.
→ Gas evolved = H₂ at electrode F (cathode)
From stoichiometry:
• O₂ formation → 4e⁻ per O₂
• H₂ formation → 2e⁻ per H₂
For the same current, electrons passing are equal in both cells.
`frac{V_(H_2)}{V_(O_2)}=frac{4}{2}=2:1`
Question 35
A voltaic cell is constructed from zinc and copper half-cells. Zinc is more reactive than copper. Which statement is correct when this cell produces electricity?

A. Electrons flow from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
B. The concentration of Cu²⁺(aq) increases.
C. Electrons flow through the salt bridge.
D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half cell.
Answer: D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
Cell facts (Zn–Cu voltaic cell):
• Zinc is more reactive → anode (−): Zn(s) → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ (oxidation).
• Copper is cathode (+): Cu²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Cu(s) (reduction).
• Electrons travel in the external wire from Zn → Cu.
• Salt bridge carries ions: anions → anode (Zn half-cell), cations → cathode (Cu half-cell).
• Concentrations: [Zn²⁺] increases, [Cu²⁺] decreases.
A. Incorrect: Electrons flow from Zn (anode) to Cu (cathode).
B. Incorrect: Cu²⁺ is consumed at the cathode (it’s reduced to Cu), so its concentration decreases.
C. Incorrect: The salt bridge conducts ions, not electrons.
D. Correct: Anions migrate toward the anode (Zn half-cell) to balance the build-up of Zn²⁺.
Question 1
Consider the following standard electrode potential values:
Fe³⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Fe²⁺(aq); E° = +0.77 V
Ni²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Ni(s); E° = −0.26 V
Fe²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Fe(s); E° = −0.45 V
Ca²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Ca(s); E° = −2.87 V
Question 2
3-hydroxybutanoic acid is a metabolite which the body can use to provide energy when it is low on glucose.

a. Name the functional groups present in 3-hydroxybutanoic acid.
b. Draw the two stereoisomers of 3-hydroxybutanoic acid.
c. Draw the organic product formed when 3-hydroxybutanoic acid is left to react with an excess of a reducing agent and the mixture is quenched with acid.
d. i. When 3-hydroxybutanoic acid is reacted with potassium manganate(VII) (an oxidizing agent) an unstable compound with a degree of unsaturation of 2 is formed. Suggest the structure of this unstable compound.
ii. The unstable compound produced decomposes to form carbon dioxide and one other product with a degree of unsaturation of 1. Identify the product formed in this decomposition reaction.
Question 3
Which statement is correct for a voltaic but not for an electrolytic cell?
A. An electrolyte is required.
B. The anode is where oxidation occurs.
C. Ions move in the electrolyte.
D. Electrons flow from the negative. electrode to the positive electrode.
Question 4
Which compound can be oxidized when heated with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate(VI)?
A. CH₃C(O)CH₂CH₃
B. CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃
C. (CH₃)₃COH
D. CH₃(CH₂)₂COOH
Question 5
Which of these functional groups will react with a reducing agent?
I. Alkoxy
II. Carboxyl
III. Carbonyl
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 6
All non-cyclic structural isomers of alcohols with molecular formula C₄H₁₀O are reacted with hot acidified KMnO₄. How many will decolourize the purple KMnO₄?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Question 7
What is the oxidation half-equation in the redox reaction?
2S₂O₃²⁻(aq) + I₂(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2I⁻(aq)
A. I₂(aq) + 2e⁻ → 2I⁻(aq)
B. 2I⁻(aq) →. I₂(aq) + 2e⁻
C. 2S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2e⁻
D. S₄O₆²⁻(aq) + 2e⁻ → 2S₂O₃²⁻(aq)
Question 8
Which compounds are susceptible to oxidation with potassium manganate(VII)?
I. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂OH
II. (CH₃)₃CCH₂OH
III. CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 9
Consider the following standard electrode potential values:
Cu⁺(aq) + e⁻ ⇌ Cu(s) E° = +0.52 V
MnO₄⁻(aq) + 8H⁺(aq) + 5e⁻ ⇌ Mn²⁺(aq) + 4H₂O(l) E° = +1.51 V
What is the cell potential for this reaction?
MnO₄⁻(aq) + 8H⁺(aq) + 5Cu(s) → Mn²⁺(aq) + 4H₂O(l) + 5Cu⁺(aq)
A. +2.03
B. +0.99
C. −0.99
D. −2.03
Question 10
During a titrimetric analysis, 25.00 cm³ of an aqueous solution containing ethanol required 37.50 cm³ of 1.50 mol dm⁻³ of acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution for complete reaction. The density of ethanol is 0.790 g cm⁻³.
During the reaction, ethanol, CH₃CH₂OH, is oxidized to ethanoic acid, CH₃COOH, while dichromate(VI) ions, Cr₂O₇²⁻, react as shown in the following half-equation:
Cr₂O₇²⁻(aq) + 14H⁺(aq) + 6e⁻ → 2Cr³⁺(aq) + 7H₂O(l)
a. Explain, in terms of change in oxidation state, why dichromate(VI) ions undergo reduction.
b. Write the half-equation for the oxidation of ethanol, CH₃CH₂OH, to ethanoic acid, CH₃COOH.
c. Use the half-equations to construct an ionic equation for the above redox reaction.
d. Using the titration results and relevant data, calculate the volume of ethanol in 25.00 cm³ of the alcoholic solution.
e. Determine the concentration as a percentage by volume of the alcoholic solution.
Question 11
For which of the reactions below will the Gibbs energy change ΔG° be the most negative?
A. Cu(s) + 2Ag⁺(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) E° = +0.46 V
B. Co(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Cu(s) + Co²⁺(aq) E° = +0.62 V
C. Fe²⁺(aq) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Fe³⁺(aq) + Cu⁺(aq) E° = −0.61 V
D. H₂(g) + Cr²⁺(aq) → Cr(s) + 2H⁺(aq) E° = −0.74 V
Question 12
Using the standard electrode potentials given, calculate the standard cell potential when an I₂, I⁻ half-cell (E° = +0.54 V) is connected to a Cl₂/Cl⁻ half-cell (E° = +1.36 V).
A. +3.80 V
B. +1.90 V
C. +1.64 V
D. +0.82 V
Question 13
a. i. Draw a diagram for the voltaic cell formed by connecting the following standard half-cells:
Ni(s) | Ni²⁺(aq) || Mn²⁺(aq) | Mn(s)
ii. Describe the key features of the hydrogen half-cell.
b. i. Write an equation for the reaction in each half-cell, identifying the species which is oxidized and the oxidizing agent.
ii. State which electrode is the anode and state the direction of electron flow in the external circuit.
iii. For the overall cell, calculate its voltage and state the sign of ΔG.
Question 14
In copper-plating, orchids are coated with a thin layer of graphite paste before placing them in a bath of aqueous copper(II) sulfate and electroplating with copper as the anode.
a. Suggest a reason why orchids are first coated with graphite.
b. Deduce the half equations at the cathode and anode.
c. To ensure high standards of electroplated orchids, the copper coating must be at least 0.5 mm thick. Given that the total surface area of a typical orchid is 10 cm² and the operating current is 20 A, calculate the time required to electroplate an orchid. [Density of copper = 8.96 g cm⁻³]
Question 15
Which components are used to make the standard hydrogen electrode?
A. H₂(g), H⁺(aq), Pt(s).
B. H₂(g), H⁺(aq), Ni(s).
C. H₂(g), HO⁻(aq), Pt(s).
D. H₂(g), HO⁻(aq), Ni(s).
Question 16
z mol of copper is deposited from CuSO₄ (aq) by a current I in time t. What is the amount of silver, in mol, deposited by electrolysis from AgNO₃ (aq) by a current `frac{I}{2}` in time 2t?
A. `frac{z}{4}`
B. `frac{z}{2}`
C. z
D. 2z
Question 17
a. Electrolysis can be used to obtain chlorine from molten sodium chloride. Write an equation for the reaction occurring at each electrode and describe the two different ways in which electricity is conducted when the cell is in operation.
b. In one experiment involving the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, 0.1 mol of chlorine was formed. Deduce, giving a reason, the amount of sodium formed at the same time.
c. In another experiment involving the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, the time of the electrolysis was halved and the current increased from 1 amp to 5 amp, compared to the experiment in (b). Deduce the amount of chlorine formed, showing your working.
d. If dilute aqueous sodium chloride is electrolyzed, a different product is obtained at each electrode. Identify the product formed at each electrode and write an equation showing its formation.
Question 18
a. The standard electrode potentials for three electrode systems are given below.
Ti³⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Ti²⁺(aq) E° = −0.37 V
Fe³⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Fe²⁺(aq) E° = +0.77 V
Ce⁴⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Ce³⁺(aq) E° = +1.45 V
i. Using the data above, deduce which species is the best reducing agent, giving a reason in terms of electrons for your answer.
ii. Write an equation, including state symbols, for the overall reaction with the greatest cell potential.
iii. State and explain the sign of ΔG° for the reaction in (a)(ii).
b. State the name of a solution that would produce only hydrogen and oxygen when electrolyzed using platinum electrodes.
Question 19
a. Molten sodium chloride can be electrolyzed using graphite electrodes.
i. Draw the essential components of this electrolytic cell and identify the products that form at each electrode.
ii. State the half-equations for the oxidation and reduction processes and deduce the overall cell reaction, including state symbols.
b. Explain why solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity.
Question 20
Chromium(III) oxide, Cr₂O₃, can undergo different reactions to give other chromium containing species as shown in the diagram below:

Which statement correctly describe these reactions?
A. The formation of Cr₂O₇²⁻ from CrO₄²⁻ is a redox reaction.
B. Aluminium is acting as an oxidizing agent.
C. CrO₃, CrO₄²⁻, Cr₂O₇²⁻ contains chromium in its highest oxidation state.
D. Cr₂O₃ reacts with CrO₃ in a disproportionation reaction to give CrO₂.
Question 21
Consider the following reactions which all occur in solution at room temperature:
Fe (s) + Cu²⁺ (aq) → Fe²⁺ (aq) + Cu (s)
Mg (s) + Zn²⁺ (aq) → Mg²⁺ (aq) + Zn (s)
Zn (s) + Fe²⁺ (aq) → Zn²⁺ (aq) + Fe (s)
Which is the correct combination of the strongest oxidizing agent and the strongest reducing agent?
| Strongest oxidizing agent | Strongest reducing agent | |
| A. | Zn (s) | Fe²⁺ (aq) |
| B. | Cu²⁺ (aq) | Mg (s) |
| C. | Mg (s) | Cu²⁺ (aq) |
| D. | Cu (s) | Mg²⁺ (aq) |
Question 22
Ethanedioic acid (oxalic acid),(COOH)₂, reacts with acidified potassium permanganate solution, KMnO4, according to the following equation:
5(COOH)₂(aq) + 2MnO₄⁻(aq) + 6H⁺(aq) → 10CO₂(g) + 2Mn²⁺(aq) + 8H₂O(l)
The reaction is a redox reaction.
a. Define oxidation in terms of electron transfer.
b. Calculate the change in oxidation numbers of carbon and manganese.
c. Identify the oxidizing and reducing agents.
Question 23
Chemical energy can be converted to electrical energy in the voltaic cell below.

a. i. State the electron arrangement of a magnesium atom.
ii. State the half-equation which describes the change at the Mg electrode and deduce which metal is the positive electrode (cathode) of the cell.
b. Deduce the equation for the overall reaction occurring in the cell.
Question 24
Which is the species oxidized and the oxidizing agent in the reaction?
MnO₂(s) + 4HCl(aq) → MnCl₂(aq) + Cl₂(g) + 2H₂O(l)
| Species oxidized | Oxidizing agent | |
| A. | Cl⁻ | HCl |
| B. | MnO₂ | MnO₂ |
| C. | MnO₂ | HCl |
| D. | Cl⁻ | MnO₂ |
Question 25
Where does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell?
A. Positive electrode and anode.
B. Negative electrode and anode.
C. Positive electrode and cathode.
D. Negative electrode and cathode.
Question 26
Which describes the flow of electrons in a voltaic cell?
A. From the cathode (positive electrode) to the anode (negative electrode) through the external circuit.
B. From the anode (negative electrode) to the cathode (positive electrode) through the external circuit.
C. From the oxidizing agent to the reducing agent through the salt bridge.
D. From the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent through the salt bridge.
Question 27
Propan-2-ol can be used as a fuel in the fuel cell. At the anode propan-2-ol is oxidized to carbon dioxide. The electrons pass around the external circuit to the cathode. The protons formed from the oxidation move through the electrolyte to the cathode, where they react with oxygen to produce water.
a. Formulate half-equations for the reactions at the anode and cathode respectively.
b. Formulate the equation for the overall reaction.
c. The fuel cell has a cell potential (under standard conditions) of 1.56 V. By using suitable data from the data booklet suggest a value for the E° of the CO2/CH3CHOHCH3 electrode reaction.
d. Suggest a possible advantage of using the propan-2-ol fuel cell compared to a hydrogen fuel cell.
Question 28
Consider the following reaction:
3H2Se + 8HFeO4− + 6H2O → 8Fe(OH)3 + 3SeO42− + 2OH−
Which statement is correct?
A. HFeO4− is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
B. HFeO4− is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction.
C. H2Se is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction.
D. H2Se is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
Question 29
Which statements are correct for a voltaic cell?
I. A spontaneous redox chemical reaction produces electrical energy.
II. Oxidation occurs at the cathode (negative electrode).
III. Electrons flow from anode (negative electrode) to cathode (positive electrode).
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 30
A voltaic cell is constructed from zinc and copper half-cells. Zinc is more reactive than copper.

Which statement is correct when this cell produces electricity?
A. Electrons flow from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
B. The concentration of Cu²⁺ (aq) increases.
C. Electrons flow through the salt bridge.
D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half cell.
Question 31
The equations below represent reactions involved in the Winkler method for determining the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water:
2Mn(OH)2(s) + O2(aq) → 2MnO(OH)2(s)
MnO(OH)2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → Mn(SO4)2(s) + 3H2O(l)
Mn(SO4)2(s) + 2I−(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + I2(aq) + 2SO42−(aq)
2S2O32−(aq) + I2(aq) → S4O62−(aq) + 2I−(aq)
What is the amount, in mol, of thiosulfate ions, S2O32−(aq), needed to react with the iodine, I2(aq), formed by 1.00 mol of dissolved oxygen?
A. 2.00
B. 3.00
C. 4.00
D. 6.00
Question 32
What are the products when molten sodium chloride is electrolyzed?
| Cathode | Anode | |
| A. | Hydrogen | Chlorine |
| B. | Sodium | Chloride |
| C. | Sodium | Chlorine |
| D. | Chlorine | Sodium |
Question 33
A reaction takes place when a rechargeable battery is used:
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
Which statements are correct?
I. H+ is reduced.
II. The oxidation state of Pb metal changes from 0 to +2.
III. PbO2 is the oxidising agent.
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 34
What are the relative volumes of gas given off at E and F during electrolysis of the two cells in series? Assume all electrodes are inert.

A. 1 : 1
B. 1 : 2
C. 2 : 1
D. 5 : 2
Question 35
A voltaic cell is constructed from zinc and copper half-cells. Zinc is more reactive than copper. Which statement is correct when this cell produces electricity?

A. Electrons flow from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
B. The concentration of Cu²⁺(aq) increases.
C. Electrons flow through the salt bridge.
D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half cell.