Question 1
Which is most likely to hydrolyse via a SN1 mechanism?
A. CH₃CHBrCH₂CH₃.
B. (CH₃)₃CBr.
C. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Br.
D. (CH₃)₂CHBr.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 2
The iron(III) ion forms the complex ion shown.

Which statements are correct?
I. The charge on the complex ion is 3⁺
II. The water molecules act as Lewis bases
III. The complex ion forms a coloured solution
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 3
Which statement about the reaction of a hydroxide ion with the organic reagent is correct?
A. 1-bromopentane predominately follows an SN1 mechanism.
B. 2-bromo-2-methyl butane predominately follows an SN2 mechanism.
C. Reaction with 1-bromopentane occurs at a slower rate than with 1-chloropentane.
D. Reaction with 1-bromopentane occurs at a slower rate than with 2-bromo-2-methyl butane.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 4
Describe an experiment to compare the rates of hydrolysis of 2 - chlorobutane, 2 - bromobutane and 2 -iodobutane. State and explain the trend in the rates of reaction.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 5
Alkenes react readily with the interhalogen compound, iodine monochloride, I–Cl to give a halogenoalkane containing both I and Cl. ICl reacts faster with alkenes than pure halogens.
a. Suggest why ICl reacts with alkenes faster than the pure halogens, Cl₂, Br₂ and I₂.
b. Name and draw the mechanism of reaction between propene and ICl to give the major product.
c. Draw the pair of enantiomers of the major product from the reaction between propene and ICl.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 6
When phenylamine, C₆H₅NH₂, is added to an aqueous solution of copper(II) ions the solution turns a deeper shade of blue due to the formation of a new complex ion nvolving phenylamine.
a. What name is given to the bond between the copper and phenylamine?
b. Define a Lewis acid and identify the Lewis acid in the complex ion.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 7
Substitution mechanisms depend on molecular structure and carbocation stability.
a. Compare the mechanisms of SN1 and SN2 reactions with reference to the number of steps involved.
b. For the reaction of (CH3)3CBr with OH⁻, identify the likely mechanism and explain your choice.
c. Outline the full mechanism for the reaction you chose, using curly arrows.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 8
Electrophilic substitution reactions in benzene proceed via a unique multi-step mechanism.
a. Identify the electrophile used in the nitration of benzene and write the overall reaction equation.
b. Describe the three-step mechanism for this electrophilic substitution reaction using curly arrows.
c. State the name of the organic product and its molecular formula.
Hard
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 9
Reactions between Lewis acids and bases involve coordinate bonding in many inorganic and organic systems.
a. Define the terms Lewis acid and Lewis base.
b. Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in the reaction:
BF₃ + NH₃ → F₃B·NH₃
c. Explain the nature of the bond formed in this reaction.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 10
A part of the mechanism for a reaction is shown.

Which statement is correct?
A. The hydroxide ion is acting as an electrophile.
B. The C–Cl bond will undergo heterolytic fission.
C. The leaving group is OH.
D. The product of the reaction is a secondary alcohol
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 11
What are the type of reaction and role of the nitronium ion, NO₂⁺, in the following reaction?
C₆H₆ + NO₂⁺ → C₆H₅NO₂ + H⁺
| Type of reaction | Role of NO₂⁺ | |
| A. | Substitution | Electrophile |
| B. | Addition | Electrophile |
| C. | Substitution | Nucleophile |
| D. | Addition | Nucleophile |
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 12
What is the molecular geometry of the transition state in an SN2 reaction?
A. Tetrahedral.
B. Planar.
C. Trigonal pyramidal.
D. Trigonal bipyramidal.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 13
Which of the following would increase the rate of a nucleophilic substitution reaction with a haloalkane?
A. Using a halogen with higher electronegativity.
B. Using a polar aprotic solvent.
C. Using a lower concentration of nucleophile.
D. Increasing the size of the alkyl group.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 14
A secondary haloalkane undergoes nucleophilic substitution in water. A racemic mixture of products is formed. Which mechanism occurred?
A. SN1.
B. SN2.
C. Electrophilic substitution.
D. Elimination.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 15
Which condition would favor an SN2 mechanism over an SN1?
A. Tertiary haloalkane and weak nucleophile.
B. Polar protic solvent and tertiary haloalkane.
C. Primary haloalkane and strong nucleophile.
D. Stable carbocation formation.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 16
a. State, giving a reason, if but-1-ene exhibits cis-trans isomerism.
b. State the type of reaction which occurs between but-1-ene and hydrogen fluoride at room temperature.
c. Explain the mechanism of the reaction between but-1-ene with hydrogen fluoride, using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs.
d. State, giving a reason, if the product of this reaction exhibits stereoisomerism.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 17
a. State the reagents used in the nitration of benzene.
b. State an equation for the formation of NO₂⁺.
c. Which role does NO₂⁺ play in nitration of benzene?
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 18
Which of the following correctly shows a lone pair donation in a nucleophilic substitution mechanism?
A. Arrow from halogen to carbon.
B. Arrow from nucleophile to halogen.
C. Arrow from lone pair on nucleophile to carbon atom.
D. Arrow from carbon to nucleophile.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 19
Which of these is not able to act as a nucleophile?
A. Ammonia molecule.
B. Water molecule.
C. Methane molecule.
D. Ethanol molecule.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 20
What are the species produced by heterolytic fission of bromine molecules?
A. 2Br•
B. Br⁺ + Br⁻
C. 2Br⁺
D. 2Br⁻
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 21
Study the reaction scheme below. What could compound X be?
Step 1. CH₃CH₂I → X
Step 2. X → CH₃COOH
A. CH₃CHO
B. CH₃OCH₃
C. H₂C=CHI
D. CH₃CH₂OH
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 22
Heterolytic fission of the hydrogen–chlorine bond occurs when hydrogen chloride molecules are dissolved in water.
a. Complete the equation and add curly arrows to show the fission process occurring.
H—Cl →
Hydrogen chloride in the gaseous phase will react with gaseous ethene to form X.
HCl + CH₂=CH₂ → X
b. i. State the type of reaction occurring and name X.
ii. Suggest a suitable nucleophile to turn X into ethanol.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 23
Halogenoalkanes can undergo substitution with different nucleophiles.
a. Write the equation for the reaction between CH₃Cl and CN⁻.
b. Identify the organic product.
c. State the role of CH₃Cl in this reaction.
d. Explain why CN⁻ is considered a strong nucleophile.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 24
What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene?
A. 1-chlorobutane
B. 1,2-dichlorobutane
C. 2,3-dichlorobutane
D. 2-chlorobutane
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 25
What is the mechanism of the reaction between alkenes and halogens in the absence of light?
A. Radical substitution.
B. Electrophilic substitution.
C. Electrophilic addition.
D. Nucleophilic substitution.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 26
Which of the following statements correctly describes an electron pair sharing reaction?
A. It involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
B. It leads to the formation of ionic bonds.
C. It results in the formation of covalent bonds through shared pairs of electrons.
D. It is only applicable to metallic elements.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 27
Which terms correctly describe the role an azide ion, N₃⁻, plays in the following reaction:
N₃⁻ + CH₃CH₂Br → CH₃CH₂N₃ + Br⁻
I. Nucleophile
II. Lewis base
III. Lewis acid
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. I only.
D. III only.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 28
What is the leaving group in the reaction:
CH₃CH₂Br + OH⁻ → CH₃CH₂OH + Br⁻
A. CH₃CH₂⁺.
B. OH⁻.
C. Br⁻.
D. CH₃CH₂OH.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 29
A student is investigating the reactivity of unsaturated hydrocarbons. They add bromine water to propene (CH₃CH=CH₂) in the absence of light and observe a color change.
a. Write the balanced equation for the reaction of propene with bromine.
b. Explain why this reaction proceeds via an electrophilic addition mechanism.
c. Predict the organic product and provide its IUPAC name.
d. Describe how this reaction is used to test for unsaturation in organic compounds.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 30
Which type of bond is formed when a Lewis acid reacts with a Lewis base?
A. Covalent.
B. Hydrogen.
C. Double.
D. Dipole–dipole.
Easy
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 31
The acidity of boric acid can be described by:
B(OH)₃(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ B(OH)₄⁻(aq) + H⁺(aq)
Which statement is correct?
A. Boric acid donates a pair of electrons to form a new bond.
B. Boric acid is a Brønsted–Lowry acid.
C. Boric acid is a Lewis acid.
D. Boric acid is a weak diprotic acid.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 32
2-bromopropane undergoes nucleophilic substitution with aqueous NaOH via the following mechanism.
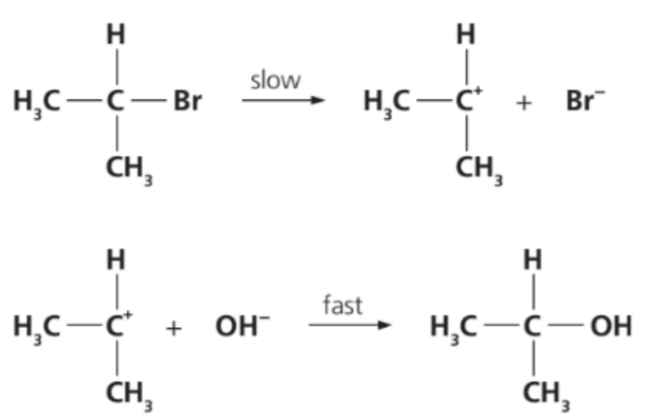
Which of the reaction pathway diagram fits the above mechanism?
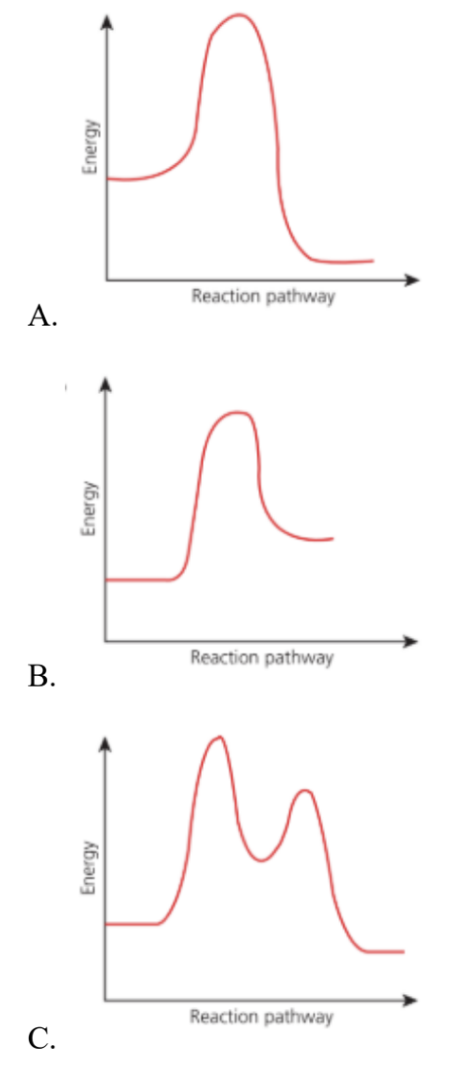
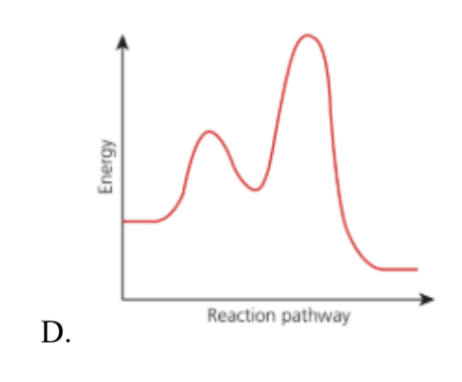
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 33
In which complex ion does iron have the oxidation state +2?
A. [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺
B. [Fe(NH₃)₄Cl₂]Cl
C. [FeCl₄]⁻
D. [Fe(CO)₄Cl₂]
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 34
Why does the reaction CH₃CH₂X + OH⁻ → CH₃CH₂OH + X⁻ occur faster when X = Br than when X = Cl?
A. The Br⁻ is a stronger nucleophile than Cl⁻.
B. The C–Br bond is weaker than the C–Cl bond.
C. The C–Cl bond is more polar than the C–Br bond.
D. The Br⁻ is less hydrated in solution than Cl⁻.
Medium
Mark as Complete
Mark Scheme
Question 1
Which is most likely to hydrolyse via a SN1 mechanism?
A. CH₃CHBrCH₂CH₃.
B. (CH₃)₃CBr.
C. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Br.
D. (CH₃)₂CHBr.
Answer: B. (CH₃)₃CBr.
SN1 goes via a carbocation; rate is fastest when that cation is most stable: Tertiary > Secondary > Primary
A. Incorrect: secondary bromide → less stable cation → less SN1-favored.
B. Correct: Tertiary carbocation → highly stabilized → favors SN1
C. Incorrect: primary bromide → very unstable cation → SN2 instead.
D. Incorrect: secondary bromide → not as good as tertiary for SN1.
Question 2
The iron(III) ion forms the complex ion shown.

Which statements are correct?
I. The charge on the complex ion is 3⁺
II. The water molecules act as Lewis bases
III. The complex ion forms a coloured solution
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Answer: D. I, II and III.
Statement I: Correct.
Each water molecule is neutral, and the iron is Fe³⁺. Therefore, the overall charge on the complex is 3+.
Total charge: + 3 + (6 × 0) = +3
Statement II: Correct.
A Lewis base donates a lone pair of electrons. Each water molecule donates a lone pair from its oxygen atom to form a coordinate bond with Fe³⁺. Thus, water acts as a Lewis base, and Fe³⁺ acts as a Lewis acid.
Statement III: Correct.
Fe³⁺ has partially filled 3d orbitals. In the complex, d–d electronic transitions occur when light is absorbed, producing a coloured solution (usually yellow or pale violet for [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺).
Question 3
Which statement about the reaction of a hydroxide ion with the organic reagent is correct?
A. 1-bromopentane predominately follows an SN1 mechanism.
B. 2-bromo-2-methyl butane predominately follows an SN2 mechanism.
C. Reaction with 1-bromopentane occurs at a slower rate than with 1-chloropentane.
D. Reaction with 1-bromopentane occurs at a slower rate than with 2-bromo-2-methyl butane.
Answer: D. Reaction with 1-bromopentane occurs at a slower rate than with 2- bromo-2-methyl butane.
A. Incorrect:
1-bromopentane is primary; primary halides react with OH⁻ mainly by SN2 (backside attack).SN1 is disfavored because primary carbocations are unstable.
B. Incorrect:
2-bromo-2-methylbutane is tertiary; steric hindrance blocks SN2. Tertiary halides react mainly by SN1 via a stable tertiary carbocation.
C. Incorrect:
Br⁻ is a better leaving group than Cl⁻ (weaker C–Br bond), so 1-bromopentane reacts faster, not slower.
D. Correct:
Tertiary halides (2-bromo-2-methylbutane) react faster via SN1 (easy carbocation formation) than primary halides (1-bromopentane) reacting by SN2; therefore, 1- bromopentane is slower.
Question 4
Describe an experiment to compare the rates of hydrolysis of 2 - chlorobutane, 2 - bromobutane and 2 -iodobutane. State and explain the trend in the rates of reaction.
• Experiment (compare hydrolysis rates)
1. Set up a 50 °C water bath. Put three test tubes in it to pre-warm.
2. To each tube add the same volumes and concentrations of ethanol–water (1:1) and aq. AgNO₃ (e.g., 1.0 cm³ ethanol, 1.0 cm³ H₂O, 1.0 cm³ 0.1 mol dm⁻³ AgNO₃). Ethanol helps dissolve the halogenoalkanes.
3. Add 0.5 cm³ of each halogenoalkane separately to the tubes: 2-chlorobutane, 2-bromobutane, 2-iodobutane. Start timing on mixing, keep tubes in the bath, swirl. 4. Measure the time to first persistent precipitate (turbidity): Ag⁺ reacts with the halide ion liberated by hydrolysis to give AgX(s).
o AgCl — white
o AgBr — cream
o AgI — yellow
5. Repeat/average. All conditions (T, volumes, solvent, concentrations) kept identical so time ∝ relative rate.
• Observations → order of rates
AgI forms almost immediately; AgBr forms after a short time; AgCl appears last (slowest).
• Rate trend: 2-iodobutane > 2-bromobutane > 2-chlorobutane
Explanation:
Hydrolysis involves breaking the C–X bond in/leading to the rate-determining step. C– I is the longest/weakest (lowest bond enthalpy) and I⁻ is the best leaving group (large, polarizable, stabilizes charge), so hydrolysis is fastest. C–Cl is strongest; Cl⁻ is the poorest leaving group, so it’s slowest.
Question 5
Alkenes react readily with the interhalogen compound, iodine monochloride, I–Cl to give a halogenoalkane containing both I and Cl. ICl reacts faster with alkenes than pure halogens.
a. Suggest why ICl reacts with alkenes faster than the pure halogens, Cl₂, Br₂ and I₂.
b. Name and draw the mechanism of reaction between propene and ICl to give the major product.
c. Draw the pair of enantiomers of the major product from the reaction between propene and ICl.
a. Why does ICl react faster than Cl₂, Br₂, I₂?
ICl is strongly polar (Iδ⁺–Clδ⁻). The iodine end is already electrophilic, so the alkene’s π bond can attack Iδ⁺ easily to form the first intermediate. This pre-polarity (and relatively weaker I–Cl vs C–Cl bond) makes electrophilic addition faster. b. Name and outline the mechanism with propene → major product Mechanism: Electrophilic addition via a halonium ion (iodonium).
• Step 1 (electrophile formation/attack):
Propene’s π electrons attack Iδ⁺ of ICl; Cl⁻ departs. A cyclic iodonium ion forms across the double bond.
• Step 2 (nucleophilic opening):
Cl⁻ attacks the more substituted carbon of the iodonium ring from the back (anti-attack), opening the ring.
• Regiochemistry & product:
Chloride ends up on the secondary carbon; iodine on the terminal carbon → 2-chloro-1-iodopropane (anti addition).
c. Pair of enantiomers of the major product
The product 2-chloro-1-iodopropane has a chiral center at C-2 (substituents: CH₃, H, Cl, CH₂I), so it is formed as a racemic pair: (R)- and (S)-2-chloro-1-iodopropane (mirror images).
Question 6
When phenylamine, C₆H₅NH₂, is added to an aqueous solution of copper(II) ions the solution turns a deeper shade of blue due to the formation of a new complex ion nvolving phenylamine.
a. What name is given to the bond between the copper and phenylamine?
b. Define a Lewis acid and identify the Lewis acid in the complex ion.
a. Coordinate covalent bond (also called a dative bond).
Explanation: The nitrogen atom in phenylamine donates a lone pair of electrons to the empty orbital of the Cu²⁺ ion, forming a coordinate bond.
b. Definition: A Lewis acid is an electron-pair acceptor.
Identification: The Lewis acid in the complex is the Cu²⁺ ion, because it accepts a lone pair of electrons from the nitrogen atom of phenylamine.
Question 7
Substitution mechanisms depend on molecular structure and carbocation stability.
a. Compare the mechanisms of SN1 and SN2 reactions with reference to the number of steps involved.
b. For the reaction of (CH3)3CBr with OH⁻, identify the likely mechanism and explain your choice.
c. Outline the full mechanism for the reaction you chose, using curly arrows.
a. Compare SN1 and SN2 (number of steps)
• SN1: Two-step mechanism.
1. Slow ionization: C–X bond breaks → carbocation + X⁻ (rate-determining).
2. Fast nucleophile attack on the planar carbocation.
• SN2: One-step mechanism.
Single concerted backside attack: nucleophile donates its lone pair to carbon as the C–X bond breaks (one transition state).
b. For (CH₃)₃CBr + OH⁻: likely mechanism & why
• Mechanism: SN1
• Reason: The substrate is tertiary (t-butyl). Tertiary carbocations are highly stabilized (inductive/hyperconjugation), which favors SN1. Also, severe steric hindrance blocks the backside approach needed for SN2.
c. Full SN1 mechanism with curly arrows (text description)
• Step 1 (slow, RDS – ionization):
(CH₃)₃C–Br → (CH₃)₃C⁺ + Br⁻
Curly arrow: from the C–Br bond to Br, showing heterolytic fission.
• Step 2 (fast – nucleophilic attack):
(CH₃)₃C⁺ + OH⁻ → (CH₃)₃COH
Curly arrow: from the lone pair on O of OH⁻ to the carbocation carbon. Overall product: tert-butanol, (CH₃)₃COH.
Rate law (consistent with SN1): rate = k [t-butyl bromide]
Question 8
Electrophilic substitution reactions in benzene proceed via a unique multi-step mechanism.
a. Identify the electrophile used in the nitration of benzene and write the overall reaction equation.
b. Describe the three-step mechanism for this electrophilic substitution reaction using curly arrows.
c. State the name of the organic product and its molecular formula.
a. Electrophile + overall equation
• Electrophile: Nitronium ion, NO₂⁺ (made in situ from conc. HNO₃/H₂SO₄).
HNO₃ + 2H₂SO₄ → NO₂⁺ + H₃O⁺ + 2HSO₄⁻
• Overall nitration:
C₆H₆ + HNO₃ —(H₂SO₄)→ C₆H₅NO₂ + H₂O
b. Three-step mechanism (curly-arrow description)
1. Electrophile generation: As above, NO₂⁺ is formed from HNO₃/H₂SO₄.
2. Electrophilic attack (σ-complex formation): A benzene π bond donates to NO₂⁺ (arrow from the ring to N), giving the arenium (σ) complex with loss of aromaticity and delocalized positive charge in the ring.
3. Deprotonation / rearomatization: A base (usually HSO₄⁻) removes the proton from the carbon bearing NO₂ (arrow from C–H bond to ring), restoring aromaticity and regenerating H₂SO₄. Product: nitrobenzene
c. Product name and formula
• Name: Nitrobenzene
• Molecular formula: C₆H₅NO₂
Question 9
Reactions between Lewis acids and bases involve coordinate bonding in many inorganic and organic systems.
a. Define the terms Lewis acid and Lewis base.
b. Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in the reaction:
BF₃ + NH₃ → F₃B·NH₃
c. Explain the nature of the bond formed in this reaction.
a. Definitions
• Lewis acid: electron-pair acceptor.
• Lewis base: electron-pair donor.
b. Identify acid/base in BF₃ + NH₃ → F₃B·NH₃
• Lewis acid: BF₃ (B is electron-deficient; vacant p orbital).
• Lewis base: NH₃ (lone pair on N).
c. Nature of the bond
A coordinate (dative) covalent bond forms from the lone pair on N in NH₃ to the empty orbital on B in BF₃ (often written F₃B ← NH₃); both bonding electrons come from the base.
Question 10
A part of the mechanism for a reaction is shown.

Which statement is correct?
A. The hydroxide ion is acting as an electrophile.
B. The C–Cl bond will undergo heterolytic fission.
C. The leaving group is OH.
D. The product of the reaction is a secondary alcohol
Answer: B. The C–Cl bond will undergo heterolytic fission.
A. Incorrect: OH⁻ donates an electron pair, so it is a nucleophile, not an electrophile.
B. Correct: The arrow shows both bonding electrons moving to Cl, forming Cl⁻ - this is heterolytic fission.
C. Incorrect: The leaving group here is Cl⁻, not OH⁻.
D. Incorrect: The carbon attacked is attached to one other carbon (CH₃CH₂Cl or CH₃CH₂–), so the product is a primary alcohol, not secondary.
Question 11
What are the type of reaction and role of the nitronium ion, NO₂⁺, in the following reaction?
C₆H₆ + NO₂⁺ → C₆H₅NO₂ + H⁺
| Type of reaction | Role of NO₂⁺ | |
| A. | Substitution | Electrophile |
| B. | Addition | Electrophile |
| C. | Substitution | Nucleophile |
| D. | Addition | Nucleophile |
Answer: A.
Reaction:
C₆H₆ + NO₂⁺ → C₆H₅NO₂ + H⁺
This is the nitration of benzene, which proceeds by an electrophilic substitution mechanism.
• Type of reaction:
It’s a substitution reaction because one hydrogen atom on the benzene ring is replaced by a nitro group (–NO₂), while the ring retains its aromaticity.
• Role of NO₂⁺ (nitronium ion):
NO₂⁺ is electron-deficient, so it acts as an electrophile – it seeks out and reacts with the electron-rich π-system of benzene.
Question 12
What is the molecular geometry of the transition state in an SN2 reaction?
A. Tetrahedral.
B. Planar.
C. Trigonal pyramidal.
D. Trigonal bipyramidal.
Answer: D. Trigonal bipyramidal.
In an SN2 (bimolecular nucleophilic substitution) reaction, the nucleophile attacks the carbon from the opposite side of the leaving group (backside attack). At the transition state, the carbon is partially bonded to both the incoming nucleophile and the leaving group, creating five groups around carbon:
• 3 existing substituents (around carbon)
• 1 incoming nucleophile (partial bond)
• 1 leaving group (partial bond)
This gives the carbon a five-coordinate transition state geometry, which is trigonal bipyramidal.
Question 13
Which of the following would increase the rate of a nucleophilic substitution reaction with a haloalkane?
A. Using a halogen with higher electronegativity.
B. Using a polar aprotic solvent.
C. Using a lower concentration of nucleophile.
D. Increasing the size of the alkyl group.
Answer: B. Using a polar aprotic solvent.
A. Incorrect:
A more electronegative halogen (e.g., Cl) forms a stronger C–X bond, which is harder to break. Reaction rate decreases because the leaving group ability worsens. (C–I < C– Br < C–Cl in strength, and I⁻ is the best leaving group.)
B. Correct:
Polar aprotic solvents (e.g., acetone, DMSO, DMF) do not solvate anions well, so nucleophiles remain free and strong. This increases the rate of SN2 nucleophilic substitution reactions because the nucleophile can attack the carbon more easily.
C. Incorrect:
In an SN2 mechanism, rate ∝ [haloalkane][nucleophile]. Lowering nucleophile concentration slows down the reaction.
D. Incorrect:
Larger alkyl groups cause steric hindrance, blocking the nucleophile’s approach. Rate of substitution decreases, especially for SN2 reactions.
Question 14
A secondary haloalkane undergoes nucleophilic substitution in water. A racemic mixture of products is formed. Which mechanism occurred?
A. SN1.
B. SN2.
C. Electrophilic substitution.
D. Elimination.
Answer: A. SN1.
A racemic mixture (50:50 of enantiomers) forms only when the reaction involves a planar carbocation intermediate, which allows attack from both sides of the plane – this is the hallmark of an SN1 mechanism.
Question 15
Which condition would favor an SN2 mechanism over an SN1?
A. Tertiary haloalkane and weak nucleophile.
B. Polar protic solvent and tertiary haloalkane.
C. Primary haloalkane and strong nucleophile.
D. Stable carbocation formation.
Answer: C. Primary haloalkane and strong nucleophile.
A. Incorrect: Tertiary carbons are too sterically hindered → SN2 cannot occur. Weak nucleophile also slows it down. Favors SN1.
B. Incorrect: Polar protic solvents (e.g., water, ethanol) stabilize carbocations → favor SN1, not SN2.
C. Correct: Low steric hindrance + strong nucleophile → ideal for SN2.
D. Incorrect: Carbocation stability matters for SN1, not SN2.
Question 16
a. State, giving a reason, if but-1-ene exhibits cis-trans isomerism.
b. State the type of reaction which occurs between but-1-ene and hydrogen fluoride at room temperature.
c. Explain the mechanism of the reaction between but-1-ene with hydrogen fluoride, using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs.
d. State, giving a reason, if the product of this reaction exhibits stereoisomerism.
a. Does but-1-ene show cis–trans isomerism?
No. In CH₂=CH–CH₂–CH₃ the left-hand C of the C=C has two identical substituents (H,H), so each C of the double bond does not bear two different groups.
b. Type of reaction with HF at room temp
Electrophilic addition (hydrohalogenation).
c. Mechanism (curly-arrow description)
The π bond of but-1-ene polarizes HF and attacks H⁺, forming the more stable secondary carbocation at C-2 (Markovnikov addition). Arrow from the C=C to H, and from the H– F bond to F giving F⁻. F⁻ then attacks the planar carbocation (arrow from F⁻ lone pair to C-2) to give 2-fluorobutane.
d. Does the product show stereoisomerism? Reason.
Yes (optical isomerism). 2-Fluorobutane has a chiral center at C-2 (attached to F, H, CH₃, and CH₂CH₃), and attack on the planar carbocation occurs from either face → a racemic mixture of enantiomers.
Question 17
a. State the reagents used in the nitration of benzene.
b. State an equation for the formation of NO₂⁺.
c. Which role does NO₂⁺ play in nitration of benzene?
a. Reagents used in the nitration of benzene
Concentrated nitric acid (HNO₃) and concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) Sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst and generates the electrophile.
b. Equation for the formation of NO₂⁺
HNO₃ + 2H₂SO₄→ NO₂⁺ + H₃O⁺ + `""2SO_4^-`
This reaction produces the nitronium ion (NO₂⁺), the active electrophile.
c. Role of NO₂⁺ in nitration of benzene
NO₂⁺ acts as an electrophile, attacking the electron-rich π-system of benzene to form nitrobenzene.
Question 18
Which of the following correctly shows a lone pair donation in a nucleophilic substitution mechanism?
A. Arrow from halogen to carbon.
B. Arrow from nucleophile to halogen.
C. Arrow from lone pair on nucleophile to carbon atom.
D. Arrow from carbon to nucleophile.
Answer: C. Arrow from lone pair on nucleophile to carbon atom.
A. Incorrect: Halogen takes electrons away from carbon, not donates.
B. Incorrect: Nucleophile attacks carbon, not halogen.
C. Correct: Shows electron pair donation from nucleophile to electrophilic carbon.
D. Incorrect: Reversed direction – arrows always show from donor to acceptor.
Question 19
Which of these is not able to act as a nucleophile?
A. Ammonia molecule.
B. Water molecule.
C. Methane molecule.
D. Ethanol molecule.
Answer: C. Methane molecule.
A nucleophile donates an electron pair to an electrophile. To act as a nucleophile, a molecule must have:
• A lone pair of electrons, or
• A π bond (source of electrons), and
• Reasonable electron density (not too low in polarity).
| Option | Structure / Key Features | Has Lone Pair? | Can donate e⁻ pair? | Acts as Nucleophile? | Explanation |
| A. Ammonia | Nitrogen has a lone pair | Yes | Yes | Yes | Ammonia is a good nucleophile; the N atom attacks electrophiles. |
| B. Water | Oxygen has two lone pairs | Yes | Yes | Yes | Water can act as a nucleophile, though weak; O donates electrons. |
| C. Methane | Carbon -hydrogen bonds only | No | No | No | Carbon has no lone pair or π bond; CH₄ is completely neutral and not polarizable → cannot donate electrons. |
| D. Ethanol | Oxygen has lone pairs | Yes | Yes | Yes | Oxygen donates electrons; ethanol is a weak but real nucleophile. |
Question 20
What are the species produced by heterolytic fission of bromine molecules?
A. 2Br•
B. Br⁺ + Br⁻
C. 2Br⁺
D. 2Br⁻
Answer: B. Br⁺ + Br⁻
• Heterolytic fission → ions formed (Br⁺, Br⁻).
• Homolytic fission → radicals formed (Br•, Br•).
Question 21
Study the reaction scheme below. What could compound X be?
Step 1. CH₃CH₂I → X
Step 2. X → CH₃COOH
A. CH₃CHO
B. CH₃OCH₃
C. H₂C=CHI
D. CH₃CH₂OH
Answer: D. CH₃CH₂OH.
A. Incorrect:
Ethanal would indeed oxidize to acetic acid, but getting ethanal directly from ethyl iodide in one step is not realistic. From CH₃CH₂I, you would first form ethanol (SN2 with OH⁻) and then oxidize to the aldehyde – already more than one step.
B. Incorrect:
You can’t make dimethyl ether from ethyl iodide in one step (Williamson ether synthesis from CH₃CH₂I would give methoxyethane CH₃OCH₂CH₃, not CH₃OCH₃). And even if you had CH₃OCH₃, simple oxidation doesn’t give acetic acid.
C. Incorrect:
Dehydrohalogenation of CH₃CH₂I gives ethene, not vinyl iodide. Moreover, oxidation of vinyl iodide would not straightforwardly yield acetic acid.
D. Correct:
Question 22
Heterolytic fission of the hydrogen–chlorine bond occurs when hydrogen chloride molecules are dissolved in water.
a. Complete the equation and add curly arrows to show the fission process occurring.
H—Cl →
Hydrogen chloride in the gaseous phase will react with gaseous ethene to form X.
HCl + CH₂=CH₂ → X
b. i. State the type of reaction occurring and name X.
ii. Suggest a suitable nucleophile to turn X into ethanol.
a. Heterolytic fission of H–Cl
When hydrogen chloride dissolves in water, heterolytic fission occurs – the bond breaks unequally, with both bonding electrons going to chlorine.
H–Cl →H⁺ +Cl⁻
Curly arrows: One arrow from the bond (between H and Cl) to the Cl atom – showing both bonding electrons moving to Cl.
b. i. Reaction of HCl with ethene
HCl +CH₂=CH₂ → CH₃CH₂Cl
• The H⁺ from HCl adds to one carbon of the double bond.
• The Cl⁻ attaches to the other carbon.
Type of reaction: Electrophilic addition (because H⁺ is an electrophile attacking the π bond).
Name of X: Chloroethane (CH₃CH₂Cl)
b. ii. Suitable nucleophile to turn X into ethanol
CH₃CH₂Cl + OH− →CH₃CH₂OH + Cl⁻
Suitable nucleophile: Hydroxide ion (OH⁻)
Question 23
Halogenoalkanes can undergo substitution with different nucleophiles.
a. Write the equation for the reaction between CH₃Cl and CN⁻.
b. Identify the organic product.
c. State the role of CH₃Cl in this reaction.
d. Explain why CN⁻ is considered a strong nucleophile.
a. Write the equation for the reaction between CH₃Cl and CN⁻
This is a nucleophilic substitution (SN2) reaction where cyanide ion replaces the halogen:
CH₃Cl + CN⁻ → CH₃CN + Cl⁻
b. Identify the organic product
The organic product is CH₃CN, which is called ethanenitrile (or methyl cyanide, acetonitrile).
c. State the role of CH₃Cl in this reaction
CH₃Cl acts as the substrate or electrophile. The carbon atom in CH₃Cl is δ⁺ (electron deficient) because of the electronegative chlorine, making it susceptible to attack by the nucleophile CN⁻.
d. Explain why CN⁻ is considered a strong nucleophile
CN⁻ carries a negative charge, giving it high electron density. The carbon atom in CN⁻ has a lone pair of electrons, which it can readily donate to an electrophilic carbon. This makes CN⁻ strongly attracted to positive centers, allowing it to attack quickly in substitution reactions.
Question 24
What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene?
A. 1-chlorobutane
B. 1,2-dichlorobutane
C. 2,3-dichlorobutane
D. 2-chlorobutane
Answer: D. 2-chlorobutane.
When an alkene reacts with HCl, the reaction is an electrophilic addition:
CH3CH = CHCH3 + HCl →?
• The π bond in the alkene attacks the H⁺ (electrophile).
• The Cl⁻ then attaches to the carbocation formed.
Step 1: Apply the mechanism
Because but-2-ene is symmetrical, adding H⁺ to either carbon of the double bond forms the same intermediate:
CH3CH+ − CH2CH3
or
CH3CH2 − CH+CH3
Both are equivalent → same product.
Step 2: Final product
The chlorine atom attaches to the carbocation carbon → product:
CH3CHClCH2CH3
That is 2-chlorobutane.
Question 25
What is the mechanism of the reaction between alkenes and halogens in the absence of light?
A. Radical substitution.
B. Electrophilic substitution.
C. Electrophilic addition.
D. Nucleophilic substitution.
Answer: C. Electrophilic addition.
Step 1: Reaction type
Alkenes contain a C=C double bond with high electron density (π bond). Halogen molecules (e.g., Br₂, Cl₂) can react without light — meaning no free radicals are formed.
When halogens react with alkenes:
• The electron-rich double bond polarizes the halogen molecule.
• One halogen atom becomes slightly δ⁺ (electrophile) and attacks the π bond.
• This leads to addition across the double bond — the π bond breaks and two new σ bonds form.
Step 2: Mechanism
This process is called electrophilic addition:
CH₂ = CH₂ + Br₂ → CH₂BrCH₂Br
Question 26
Which of the following statements correctly describes an electron pair sharing reaction?
A. It involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
B. It leads to the formation of ionic bonds.
C. It results in the formation of covalent bonds through shared pairs of electrons.
D. It is only applicable to metallic elements.
Answer: C. It results in the formation of covalent bonds through shared pairs of electrons.
A. Incorrect: That describes ionic bonding, not sharing.
B. Incorrect: Ionic bonds come from electron transfer, not sharing.
C. Correct: Covalent bonds are formed by sharing electron pairs between atoms.
D. Incorrect: Metals form metallic bonds, not covalent bonds.
Question 27
Which terms correctly describe the role an azide ion, N₃⁻, plays in the following reaction:
N₃⁻ + CH₃CH₂Br → CH₃CH₂N₃ + Br⁻
I. Nucleophile
II. Lewis base
III. Lewis acid
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. I only.
D. III only.
Answer: A. I and II only.
Reaction:
N₃⁻ + CH₃CH₂Br → CH₃CH₂N₃ + Br⁻ (an SN₂ substitution)
Role of N₃⁻: It donates a lone pair to the electrophilic carbon, forming a new C–N bond and displacing Br⁻. Donating an electron pair = nucleophile and Lewis base. It is not a Lewis acid (which accepts e⁻ pairs).
I. Nucleophile → Correct: N₃⁻ attacks the carbon and donates electrons.
II. Lewis base → Correct: By donating an electron pair, it is a Lewis base.
III. Lewis acid → Incorrect: It does not accept an electron pair; the electrophilic carbon in ethyl bromide is the Lewis acid.
Question 28
What is the leaving group in the reaction:
CH₃CH₂Br + OH⁻ → CH₃CH₂OH + Br⁻
A. CH₃CH₂⁺.
B. OH⁻.
C. Br⁻.
D. CH₃CH₂OH.
Answer: C. Br−.
• The hydroxide ion (OH-) attacks the carbon bonded to bromine (the electrophilic carbon).
• The bromine atom leaves, taking the bonding electron pair with it. This is a nucleophilic substitution (SN2) reaction.
A leaving group is the atom or group that detaches from the molecule, taking its bonding electrons. Here:
CH₃CH₂Br → CH₃CH₂⁺ + Br−
The group that leaves is Br−.
Question 29
A student is investigating the reactivity of unsaturated hydrocarbons. They add bromine water to propene (CH₃CH=CH₂) in the absence of light and observe a color change.
a. Write the balanced equation for the reaction of propene with bromine.
b. Explain why this reaction proceeds via an electrophilic addition mechanism.
c. Predict the organic product and provide its IUPAC name.
d. Describe how this reaction is used to test for unsaturation in organic compounds.
a. Balanced equation
CH₃CH=CH₂ + Br₂ → CH₃CHBrCH₂Br
b. Why electrophilic addition?
The C=C π bond is an electron-rich region that polarizes Br₂. One Br becomes δ⁺ (acts as the electrophile) and is added first, forming a bromonium ion intermediate; the Br⁻ then attacks, opening the ring. Net result: addition across the double bond, not substitution, and no light/radicals are required.
c. Organic product + IUPAC name
Product: CH₃CHBrCH₂Br, named 1,2-dibromopropane.
d. Test for unsaturation
Alkenes decolorize bromine water (orange/brown → colorless) rapidly in the dark due to this electrophilic addition. Saturated hydrocarbons do not decolorize it under these conditions.
Question 30
Which type of bond is formed when a Lewis acid reacts with a Lewis base?
A. Covalent.
B. Hydrogen.
C. Double.
D. Dipole–dipole.
Answer: A. Covalent.
• A Lewis acid = an electron pair acceptor
• A Lewis base = an electron pair donor
When a Lewis base donates a lone pair to a Lewis acid, a new bond is formed in which both electrons come from one atom (the base). This type of bond is called a coordinate covalent bond, which is a form of covalent bond.
Question 31
The acidity of boric acid can be described by:
B(OH)₃(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ B(OH)₄⁻(aq) + H⁺(aq)
Which statement is correct?
A. Boric acid donates a pair of electrons to form a new bond.
B. Boric acid is a Brønsted–Lowry acid.
C. Boric acid is a Lewis acid.
D. Boric acid is a weak diprotic acid.
Answer: C. Boric acid is a Lewis acid.
B(OH)₃ (boric acid) does not donate a proton (H⁺) directly. Instead, it reacts with water, accepting a lone pair of electrons from the oxygen atom in H₂O to form B(OH)₄⁻. In doing so, H₂O loses a proton (H⁺).
That means:
• B(OH)₃ acts as an electron pair acceptor → Lewis acid.
• H₂O acts as a Lewis base (electron pair donor).
A. Incorrect: Boric acid accepts, not donates, an electron pair.
B. Incorrect: It does not donate H⁺ directly; it causes water to release H⁺.
C. Correct: It accepts an electron pair from water.
D. Incorrect: It’s weak and monobasic, not diprotic.
Question 32
2-bromopropane undergoes nucleophilic substitution with aqueous NaOH via the following mechanism.

Which of the reaction pathway diagram fits the above mechanism?


The mechanism shown for 2-bromopropane + NaOH is an SN1 (unimolecular nucleophilic substitution) reaction.
1. Step 1 (slow): Formation of the carbocation after the C–Br bond breaks.
→ This is the rate-determining step and requires high activation energy.
2. Step 2 (fast): The OH⁻ nucleophile attacks the carbocation to form the product.
→ This step is fast and requires less activation energy.
| Diagram | Description | Fits SN1? |
| A. Incorrect | One peak → one-step reaction | SN2 type |
| B. Incorrect | One peak → single transition state | SN2 type |
| C. Correct | Two peaks, first higher than second | Correct for SN1 |
| D. Incorrect | Two peaks, but second higher | Opposite order |
Question 33
In which complex ion does iron have the oxidation state +2?
A. [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺
B. [Fe(NH₃)₄Cl₂]Cl
C. [FeCl₄]⁻
D. [Fe(CO)₄Cl₂]
Answer: D. [Fe(CO)₄Cl₂]
A. Incorrect: [Fe(H₂O)₆]3+
Each H₂O = 0
Total charge = +3
So oxidation state of Fe = +3, not +2.
B. Incorrect: [Fe(NH₃)₄Cl₂]Cl
Let Fe = x
Inside the bracket:
NH₃ = 0 (neutral), Cl = –1 × 2 = –2
So total charge inside = x – 2
Outside, one Cl⁻ gives total 0 charge for compound:
(x − 2) + (−1) = 0 ⇒ x = +3, not +2
C. Incorrect: [FeCl₄]−
Each Cl = –1 × 4 = –4
Total charge = –1
So: x − 4 = −1 ⇒ x = +3, not +2
D. Correct: [Fe(CO)₄Cl₂]
CO is neutral (0), Cl = –1 × 2 = –2
No overall charge given (neutral complex): x − 2 = 0 ⇒ x = +2
Question 34
Why does the reaction CH₃CH₂X + OH⁻ → CH₃CH₂OH + X⁻ occur faster when X = Br than when X = Cl?
A. The Br⁻ is a stronger nucleophile than Cl⁻.
B. The C–Br bond is weaker than the C–Cl bond.
C. The C–Cl bond is more polar than the C–Br bond.
D. The Br⁻ is less hydrated in solution than Cl⁻.
Answer: B. The C–Br bond is weaker than the C–Cl bond.
A. Incorrect:
The nucleophile in this reaction is OH⁻, not the halide ion. The halide (Br⁻ or Cl⁻) acts as the leaving group, not the attacking species. So, the strength of Br⁻ as a nucleophile is irrelevant here.
B. Correct:
The C–Br bond is longer and weaker (bond energy ≈ 276 kJ/mol) than the C–Cl bond (bond energy ≈ 338 kJ/mol). Because it is easier to break, Br⁻ leaves more readily, making the substitution reaction faster. This is the main reason the reaction with bromoethane is faster than with chloroethane.
C. Incorrect:
Although this is true, greater polarity doesn’t mean faster reaction here. Bond strength, not polarity, controls the rate — the weaker bond (C–Br) breaks more easily.
D. Incorrect:
While it’s true that Br⁻ is less hydrated (due to its larger size), hydration affects nucleophiles in solution, not leaving groups. Since the halide is the leaving group, this factor doesn’t control the reaction rate.
Question 1
Which is most likely to hydrolyse via a SN1 mechanism?
A. CH₃CHBrCH₂CH₃.
B. (CH₃)₃CBr.
C. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Br.
D. (CH₃)₂CHBr.
Question 2
The iron(III) ion forms the complex ion shown.

Which statements are correct?
I. The charge on the complex ion is 3⁺
II. The water molecules act as Lewis bases
III. The complex ion forms a coloured solution
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II and III.
Question 3
Which statement about the reaction of a hydroxide ion with the organic reagent is correct?
A. 1-bromopentane predominately follows an SN1 mechanism.
B. 2-bromo-2-methyl butane predominately follows an SN2 mechanism.
C. Reaction with 1-bromopentane occurs at a slower rate than with 1-chloropentane.
D. Reaction with 1-bromopentane occurs at a slower rate than with 2-bromo-2-methyl butane.
Question 4
Describe an experiment to compare the rates of hydrolysis of 2 - chlorobutane, 2 - bromobutane and 2 -iodobutane. State and explain the trend in the rates of reaction.
Question 5
Alkenes react readily with the interhalogen compound, iodine monochloride, I–Cl to give a halogenoalkane containing both I and Cl. ICl reacts faster with alkenes than pure halogens.
a. Suggest why ICl reacts with alkenes faster than the pure halogens, Cl₂, Br₂ and I₂.
b. Name and draw the mechanism of reaction between propene and ICl to give the major product.
c. Draw the pair of enantiomers of the major product from the reaction between propene and ICl.
Question 6
When phenylamine, C₆H₅NH₂, is added to an aqueous solution of copper(II) ions the solution turns a deeper shade of blue due to the formation of a new complex ion nvolving phenylamine.
a. What name is given to the bond between the copper and phenylamine?
b. Define a Lewis acid and identify the Lewis acid in the complex ion.
Question 7
Substitution mechanisms depend on molecular structure and carbocation stability.
a. Compare the mechanisms of SN1 and SN2 reactions with reference to the number of steps involved.
b. For the reaction of (CH3)3CBr with OH⁻, identify the likely mechanism and explain your choice.
c. Outline the full mechanism for the reaction you chose, using curly arrows.
Question 8
Electrophilic substitution reactions in benzene proceed via a unique multi-step mechanism.
a. Identify the electrophile used in the nitration of benzene and write the overall reaction equation.
b. Describe the three-step mechanism for this electrophilic substitution reaction using curly arrows.
c. State the name of the organic product and its molecular formula.
Question 9
Reactions between Lewis acids and bases involve coordinate bonding in many inorganic and organic systems.
a. Define the terms Lewis acid and Lewis base.
b. Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in the reaction:
BF₃ + NH₃ → F₃B·NH₃
c. Explain the nature of the bond formed in this reaction.
Question 10
A part of the mechanism for a reaction is shown.

Which statement is correct?
A. The hydroxide ion is acting as an electrophile.
B. The C–Cl bond will undergo heterolytic fission.
C. The leaving group is OH.
D. The product of the reaction is a secondary alcohol
Question 11
What are the type of reaction and role of the nitronium ion, NO₂⁺, in the following reaction?
C₆H₆ + NO₂⁺ → C₆H₅NO₂ + H⁺
| Type of reaction | Role of NO₂⁺ | |
| A. | Substitution | Electrophile |
| B. | Addition | Electrophile |
| C. | Substitution | Nucleophile |
| D. | Addition | Nucleophile |
Question 12
What is the molecular geometry of the transition state in an SN2 reaction?
A. Tetrahedral.
B. Planar.
C. Trigonal pyramidal.
D. Trigonal bipyramidal.
Question 13
Which of the following would increase the rate of a nucleophilic substitution reaction with a haloalkane?
A. Using a halogen with higher electronegativity.
B. Using a polar aprotic solvent.
C. Using a lower concentration of nucleophile.
D. Increasing the size of the alkyl group.
Question 14
A secondary haloalkane undergoes nucleophilic substitution in water. A racemic mixture of products is formed. Which mechanism occurred?
A. SN1.
B. SN2.
C. Electrophilic substitution.
D. Elimination.
Question 15
Which condition would favor an SN2 mechanism over an SN1?
A. Tertiary haloalkane and weak nucleophile.
B. Polar protic solvent and tertiary haloalkane.
C. Primary haloalkane and strong nucleophile.
D. Stable carbocation formation.
Question 16
a. State, giving a reason, if but-1-ene exhibits cis-trans isomerism.
b. State the type of reaction which occurs between but-1-ene and hydrogen fluoride at room temperature.
c. Explain the mechanism of the reaction between but-1-ene with hydrogen fluoride, using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs.
d. State, giving a reason, if the product of this reaction exhibits stereoisomerism.
Question 17
a. State the reagents used in the nitration of benzene.
b. State an equation for the formation of NO₂⁺.
c. Which role does NO₂⁺ play in nitration of benzene?
Question 18
Which of the following correctly shows a lone pair donation in a nucleophilic substitution mechanism?
A. Arrow from halogen to carbon.
B. Arrow from nucleophile to halogen.
C. Arrow from lone pair on nucleophile to carbon atom.
D. Arrow from carbon to nucleophile.
Question 19
Which of these is not able to act as a nucleophile?
A. Ammonia molecule.
B. Water molecule.
C. Methane molecule.
D. Ethanol molecule.
Question 20
What are the species produced by heterolytic fission of bromine molecules?
A. 2Br•
B. Br⁺ + Br⁻
C. 2Br⁺
D. 2Br⁻
Question 21
Study the reaction scheme below. What could compound X be?
Step 1. CH₃CH₂I → X
Step 2. X → CH₃COOH
A. CH₃CHO
B. CH₃OCH₃
C. H₂C=CHI
D. CH₃CH₂OH
Question 22
Heterolytic fission of the hydrogen–chlorine bond occurs when hydrogen chloride molecules are dissolved in water.
a. Complete the equation and add curly arrows to show the fission process occurring.
H—Cl →
Hydrogen chloride in the gaseous phase will react with gaseous ethene to form X.
HCl + CH₂=CH₂ → X
b. i. State the type of reaction occurring and name X.
ii. Suggest a suitable nucleophile to turn X into ethanol.
Question 23
Halogenoalkanes can undergo substitution with different nucleophiles.
a. Write the equation for the reaction between CH₃Cl and CN⁻.
b. Identify the organic product.
c. State the role of CH₃Cl in this reaction.
d. Explain why CN⁻ is considered a strong nucleophile.
Question 24
What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene?
A. 1-chlorobutane
B. 1,2-dichlorobutane
C. 2,3-dichlorobutane
D. 2-chlorobutane
Question 25
What is the mechanism of the reaction between alkenes and halogens in the absence of light?
A. Radical substitution.
B. Electrophilic substitution.
C. Electrophilic addition.
D. Nucleophilic substitution.
Question 26
Which of the following statements correctly describes an electron pair sharing reaction?
A. It involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
B. It leads to the formation of ionic bonds.
C. It results in the formation of covalent bonds through shared pairs of electrons.
D. It is only applicable to metallic elements.
Question 27
Which terms correctly describe the role an azide ion, N₃⁻, plays in the following reaction:
N₃⁻ + CH₃CH₂Br → CH₃CH₂N₃ + Br⁻
I. Nucleophile
II. Lewis base
III. Lewis acid
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. I only.
D. III only.
Question 28
What is the leaving group in the reaction:
CH₃CH₂Br + OH⁻ → CH₃CH₂OH + Br⁻
A. CH₃CH₂⁺.
B. OH⁻.
C. Br⁻.
D. CH₃CH₂OH.
Question 29
A student is investigating the reactivity of unsaturated hydrocarbons. They add bromine water to propene (CH₃CH=CH₂) in the absence of light and observe a color change.
a. Write the balanced equation for the reaction of propene with bromine.
b. Explain why this reaction proceeds via an electrophilic addition mechanism.
c. Predict the organic product and provide its IUPAC name.
d. Describe how this reaction is used to test for unsaturation in organic compounds.
Question 30
Which type of bond is formed when a Lewis acid reacts with a Lewis base?
A. Covalent.
B. Hydrogen.
C. Double.
D. Dipole–dipole.
Question 31
The acidity of boric acid can be described by:
B(OH)₃(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ B(OH)₄⁻(aq) + H⁺(aq)
Which statement is correct?
A. Boric acid donates a pair of electrons to form a new bond.
B. Boric acid is a Brønsted–Lowry acid.
C. Boric acid is a Lewis acid.
D. Boric acid is a weak diprotic acid.
Question 32
2-bromopropane undergoes nucleophilic substitution with aqueous NaOH via the following mechanism.

Which of the reaction pathway diagram fits the above mechanism?


Question 33
In which complex ion does iron have the oxidation state +2?
A. [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺
B. [Fe(NH₃)₄Cl₂]Cl
C. [FeCl₄]⁻
D. [Fe(CO)₄Cl₂]
Question 34
Why does the reaction CH₃CH₂X + OH⁻ → CH₃CH₂OH + X⁻ occur faster when X = Br than when X = Cl?
A. The Br⁻ is a stronger nucleophile than Cl⁻.
B. The C–Br bond is weaker than the C–Cl bond.
C. The C–Cl bond is more polar than the C–Br bond.
D. The Br⁻ is less hydrated in solution than Cl⁻.